Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PID Short Questions
Uploaded by
66umer66Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PID Short Questions
Uploaded by
66umer66Copyright:
Available Formats
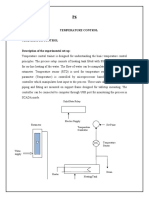
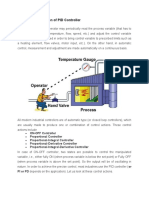
1.What is a ‘controller’? Where are its application areas?
A controller is an instrument used for controlling a process variable
(measurement). Its continuously monitors the error signal and gives a corrective
output to the final control element.
2.Explain the following terms in a controller?
Measurement variable: It is the demand variable measured and controlled.
Desired Variable: it is the demand signal (setpoint) to which the process
variable is controlled.
Deviation: it is the error signal caused by the difference between the
measurement and the demand signal.
Output: It is the corrective signal from the controller to the final control element.
3.Explain what is ‘direct action’ and ‘reverse action’ on a controller?
Direct action : In a direct acting controller, the output increases when the
process measurement (variable) increases.
Reverse action : In a reverse action controller, the output decreases when the
process measurement (variable) increases.
4.What is a gap controller?
A controller whose output changes from ;minimum to maximum (on-off) and
vice-versa when the error signal (deviation) exceeds the set gap depending on
the controller action.
5.What is a ‘proportional band’? Explain with an example?
It is the range in percentage for which the controller output changes
proportionally from minimum to maximum and vice-versa when the
measurement deviates from the setpoint.
For example: A controller set at 50% proportional band
The controller output changes from minimum to maximum and vice-versa when
the measurement exceeds 25% either side of the setpoint depending on the
controller action.
6.What is a ‘gain’? Write the relation (formula) between a gain and
proportional band?
A controller ‘gain’ is inversely proportional to its proportional band.
. g=(1/p)*100
. g=gain
. P = proportional band
7.What is a ‘reset action’? Explain with an example?
Reset action in a controller is the integration of the proportional action by the
set period. The reset action repeats the proportional action’s output per the
reset time set, until the error signal becomes zero or the output gets saturated.
For example :if the reset action is set for 30 sec.
For a 0.5 volt correction output ;by the proportional action will be repeated by
the reset action every 30 secs., until the error signal becomes zero or the output
gets saturated.
8.What is a ‘batch’ facility on a controller?
Whenever a deviation persists for a long time the controller output saturates at
the maximum of minimum output (-2.5 VDC or + 12.5 VDC/0 kPa or 140 kPa)
depending on the controller action. In a normal controller when the process
reverts to normal the output takes its time to come into control range.
In a batch controller the output reverts to the control limit (0VDC OR 10.00V DC
20 kPa or 100 kPa) as soon as the deviation enters the batch limits
9.What will be the output (increases or decreases) of a direct action
controller when the process goes above the setpoint?
In a direct acting controller, the controller output increases when the process
(measurement) goes above the setpoint)
10.What will be the output of a reverse acting controller when the process
changes from 50% to 75% where the proportional band is set at 50%,
setpoint is set at 50%?
The controller output will be zero.
11.What is a ‘bump-less transfer’ in a controller’s auto/manual change
over?
‘Bump-less transfer’ is to eliminate the change in the controller’s output when
the controller is changed from auto to manual control and vice-versa.
12.Explain how to change a controller from auto to manual and vise-
versa?
Pneumatic controllers : While taking the controller from auto to manual, the
manual output is to be balanced to the auto output and then transfer the auto-
manual switch to manual. While changing the controller from manual to auto,
the controller setpoint is matched to the manual output and then auto-manual
switch is transferred.
Electronic controllers : Auto to manual control may be transferred directly as
the electronic circuit keeps the auto and manual output matched. But while
changing the controller from manual to auto, the controller setpoint is to match
to the process variable and then auto-manual switch is transferred.
13.What type of controller (P, PI, PID) is preferred on the following process
control loops?
Pressure: If the load change is minimum, then a proportional controller is
suitable. If a frequent load change is expected then a Proportional + Integral
controller is preferred.
Level : Normally a proportional controller is preferred.
Flow: Proportional + Integral controller is preferred
Temperature: Proportional + Integral + Derivative controller is preferred
14.what are the advantages and disadvantages of BANG BANG
Controller?
Advantages:
1. Simple/cheap to implement
2. Hugely better performance than open loop
3. Needs only primitive actuators
Disadvantages:
1. Performance (higher drag)
2. Increase of tension on the plant i.e. suddenly turning plant off and on
reduces the over all plant life
15.why we use BANG BANG controller even knowing all defects?
Because its response time is cheap simple and batter as compared to other
controller
You might also like
- PID Controllers: Final Control ElementDocument3 pagesPID Controllers: Final Control ElementJêmš NavikNo ratings yet
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsFrom EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Automatic Controllers & Control ModesDocument74 pagesAutomatic Controllers & Control ModesVishal IyerNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Ic1352 - Process Control-2 MarksDocument21 pagesIc1352 - Process Control-2 MarksKaushal Kishor100% (1)
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Engineering Questions & AnswersDocument10 pagesInstrumentation Engineering Questions & AnswerscontgautamNo ratings yet
- Reporter: John Alvin B. SerenioDocument25 pagesReporter: John Alvin B. SerenioPrincess CutabNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Overview Professor GopalankrishnaDocument23 pagesControl Systems Overview Professor GopalankrishnaJameNo ratings yet
- Building Management System - BMS 1Document31 pagesBuilding Management System - BMS 1jaffna100% (1)
- Pid EeeeDocument28 pagesPid Eeeecyprian obotaNo ratings yet
- Close Loop Control Sys IntroDocument7 pagesClose Loop Control Sys IntroDwi Mulyanti DwimulyantishopNo ratings yet
- Exp - P6 - Temperature ControlDocument10 pagesExp - P6 - Temperature ControlSiddesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Introduction to DDC Systems Architecture & ComponentsDocument22 pagesIntroduction to DDC Systems Architecture & ComponentsBala SrivasNo ratings yet
- Controller Principles 2020 NotesDocument17 pagesController Principles 2020 NotesJoseph ChalilNo ratings yet
- Control DynamicDocument10 pagesControl Dynamicكرار نعيم100% (1)
- W7ADocument15 pagesW7AShujah RashidNo ratings yet
- Working or Operation of PID ControllerDocument7 pagesWorking or Operation of PID Controllerjohn glenn magnoNo ratings yet
- CH 05 (Process Controllers)Document35 pagesCH 05 (Process Controllers)32anikkumarpaulNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Process Control J5800Document49 pagesCH 4 - Process Control J5800mohd_mizanNo ratings yet
- Control System PPKDocument8 pagesControl System PPKP Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Pid Control TheoryDocument8 pagesPid Control TheorySonu SinghNo ratings yet
- Bms For HvacDocument63 pagesBms For HvacWasantha Jayarathna100% (1)
- Automatic control principles and algorithmsDocument35 pagesAutomatic control principles and algorithmssharmadeveshNo ratings yet
- PID controller basics for industrial processesDocument5 pagesPID controller basics for industrial processesVignesh RajanNo ratings yet
- P, I, D, PI, PD, and PID ControlDocument14 pagesP, I, D, PI, PD, and PID ControlArnav KothiyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document22 pagesChapter 1Anonymous AFFiZnNo ratings yet
- Control SystemsDocument18 pagesControl Systemsgayatri jaltareNo ratings yet
- 000 Digital Control LecturesDocument67 pages000 Digital Control LecturesPX PRNo ratings yet
- Ce Mod1Document22 pagesCe Mod1AYUSH CHANDRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document17 pagesChapter 9Sagar PawarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Direct Digital Control Systems: Purpose of This GuideDocument82 pagesIntroduction To Direct Digital Control Systems: Purpose of This GuidekdpmansiNo ratings yet
- Process Control Concepts: Understanding Feedback Loops, Variables, and TerminologyDocument39 pagesProcess Control Concepts: Understanding Feedback Loops, Variables, and Terminologykaezzar10100% (1)
- Unit 3Document11 pagesUnit 3mayuraher9511No ratings yet
- Exp - P8 - Multiprocess TrainerDocument19 pagesExp - P8 - Multiprocess TrainerSiddesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Lec-26,27&28Document29 pagesLec-26,27&28Aditya ThakreNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1: Now Manually Move The AVS-1 Bar To Control The Flow Through The Valve in To The ContainerDocument16 pagesExperiment No.1: Now Manually Move The AVS-1 Bar To Control The Flow Through The Valve in To The ContainerfahadfiazNo ratings yet
- PID - Scanner 2000Document12 pagesPID - Scanner 2000hectorivantovarjaimesNo ratings yet
- Regulation and Control Course OverviewDocument15 pagesRegulation and Control Course Overviewyeabsira gashawNo ratings yet
- Tarea2 Investigacion-Mcca-190090Document13 pagesTarea2 Investigacion-Mcca-190090Christian MendezNo ratings yet
- What Is PID-Tutorial Overview: Proportional Band Integral DerivativeDocument5 pagesWhat Is PID-Tutorial Overview: Proportional Band Integral Derivativethenu.chandru1042No ratings yet
- Control StrategyDocument44 pagesControl StrategyAyunie FazlinNo ratings yet
- Automation & Controls Processes ExplainedDocument17 pagesAutomation & Controls Processes ExplainedMalaka UdayangaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Control Systems CourseDocument11 pagesIntroduction to Control Systems CourseYidersal MarewNo ratings yet
- Pid Controller Tuning: S.no Name of The ChapterDocument35 pagesPid Controller Tuning: S.no Name of The ChapterAmit TripathiNo ratings yet
- Process - Control SimulatorDocument7 pagesProcess - Control SimulatorSakshi RajputNo ratings yet
- Air-conditioning Control EssentialsDocument92 pagesAir-conditioning Control EssentialsSunil Varma VeeravalliNo ratings yet
- Acfrogdgl836ldvbuspou Eyl6uhjugculhmtzdojwbgtlkkup E7yn7z3wkk04xjugsulhx0ouzu9rws3smog3t9o06r7-Cs1zavkubqcfvimg43ogdym21jddxoevtgcy ZznougjhwjcxkhnDocument40 pagesAcfrogdgl836ldvbuspou Eyl6uhjugculhmtzdojwbgtlkkup E7yn7z3wkk04xjugsulhx0ouzu9rws3smog3t9o06r7-Cs1zavkubqcfvimg43ogdym21jddxoevtgcy ZznougjhwjcxkhnMOHAMED THARIKNo ratings yet
- CPB 30004 - CHAPTER 1 - INTRO Sept 2014Document52 pagesCPB 30004 - CHAPTER 1 - INTRO Sept 2014Ashwin MNo ratings yet
- Things To Think About Ch.13 (Process Control A)Document21 pagesThings To Think About Ch.13 (Process Control A)Salsa NisaNo ratings yet
- PID Control and Instrumentation FundamentalsDocument3 pagesPID Control and Instrumentation FundamentalsZeny NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Control System NotesDocument179 pagesControl System NotesChandrashekarNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Positioner PresentationDocument43 pagesInstrumentation Positioner PresentationSangram Patnaik100% (1)
- Deaerator Level ControlDocument6 pagesDeaerator Level ControlAli BariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PID ControlDocument6 pagesIntroduction To PID ControlIonescu ViorelNo ratings yet
- Name: Roll: Year: Department: Subject: Subject CodeDocument11 pagesName: Roll: Year: Department: Subject: Subject CodeMayukh BiswasNo ratings yet
- Open Loop Control System Trainer: Hitech Instruction ManualDocument4 pagesOpen Loop Control System Trainer: Hitech Instruction ManualnileshsawNo ratings yet
- Che821 - Lecture NineDocument36 pagesChe821 - Lecture Nineprof.kess.unibenNo ratings yet
- Model Predictive Control (MPC): An advanced process control techniqueDocument4 pagesModel Predictive Control (MPC): An advanced process control technique66umer66No ratings yet
- Adaptive ControllersDocument9 pagesAdaptive Controllers66umer66No ratings yet
- Testing Results Ground Element Micom P443 220kV CircuitDocument6 pagesTesting Results Ground Element Micom P443 220kV Circuit66umer66No ratings yet
- Neural-Network QuestionsDocument3 pagesNeural-Network Questions66umer660% (1)
- NILM Using FHMM & CODocument15 pagesNILM Using FHMM & CO66umer66No ratings yet
- Bill For Services Rendered by TSG NTDC, Lahore: Invoice No.Document3 pagesBill For Services Rendered by TSG NTDC, Lahore: Invoice No.66umer66No ratings yet
- 220kv Bund RD-SKP IV D 60 Distance Relay Testing ResultsDocument18 pages220kv Bund RD-SKP IV D 60 Distance Relay Testing Results66umer66No ratings yet
- Testing Results D 60 220Kv Bund RD - KSK Ii Zone Iii Phase and Earth Elements Test ResultsDocument5 pagesTesting Results D 60 220Kv Bund RD - KSK Ii Zone Iii Phase and Earth Elements Test Results66umer66No ratings yet
- Testing Results 220KV Bund Road - KSK Ii Phase and Ground Elements PDFDocument10 pagesTesting Results 220KV Bund Road - KSK Ii Phase and Ground Elements PDF66umer66No ratings yet
- Testing Results 220kv Bund RD-KSK II D-60 Distance Relay Phase and Earth ElementsDocument19 pagesTesting Results 220kv Bund RD-KSK II D-60 Distance Relay Phase and Earth Elements66umer66No ratings yet
- Testing Results 220Kv Bund RD-KSK Ii D-60 Distance Relay Phase and Earth ElementsDocument19 pagesTesting Results 220Kv Bund RD-KSK Ii D-60 Distance Relay Phase and Earth Elements66umer66No ratings yet
- Testing Results Siemens 7sa5131 220kv Bund Road - SKP 1 CCTDocument12 pagesTesting Results Siemens 7sa5131 220kv Bund Road - SKP 1 CCT66umer66No ratings yet
- Testing Results For Phase Element of D-60 220Kv KSK-SKT CCT: Wednesday, May 24, 2017 2:23 PMDocument7 pagesTesting Results For Phase Element of D-60 220Kv KSK-SKT CCT: Wednesday, May 24, 2017 2:23 PM66umer66No ratings yet
- Testing Results 220kv Bund Road - KSK II Phase and Ground ElementsDocument10 pagesTesting Results 220kv Bund Road - KSK II Phase and Ground Elements66umer66No ratings yet
- 220kv Bund Road-Skp IIDocument7 pages220kv Bund Road-Skp II66umer66No ratings yet
- Testing Results of 220kv Bund RD - KSK I Phase To Phase and Phase To Earth ElementsDocument11 pagesTesting Results of 220kv Bund RD - KSK I Phase To Phase and Phase To Earth Elements66umer66No ratings yet
- Testing Results Micromho 220Kv Bund RD - KSK Ii Phase and Current ElementsDocument18 pagesTesting Results Micromho 220Kv Bund RD - KSK Ii Phase and Current Elements66umer66No ratings yet
- Unfiled Notes Apr 2017 Pages 1-4Document4 pagesUnfiled Notes Apr 2017 Pages 1-466umer66No ratings yet
- Introduction To Distributed Generation PDFDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Distributed Generation PDF66umer66No ratings yet
- DG in SG Pros & Cons For Efficicient Electricity Distribution Within The GridDocument3 pagesDG in SG Pros & Cons For Efficicient Electricity Distribution Within The Grid66umer66No ratings yet
- Digital Filter Design TechniquesDocument24 pagesDigital Filter Design Techniquesmeseret sisayNo ratings yet
- Modulos y Servos FanucDocument14 pagesModulos y Servos FanucIrving LopezNo ratings yet
- NEXUS 1262 Modbus MapDocument406 pagesNEXUS 1262 Modbus MapThomas PendergrassNo ratings yet
- ECE.488 Multi-Various Analog ControlsDocument3 pagesECE.488 Multi-Various Analog ControlsphoebezzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Design of Optimal ControllersDocument64 pagesChapter 3 Design of Optimal ControllersTsedenia TamiruNo ratings yet
- PID and Open vs Closed Loop SystemsDocument2 pagesPID and Open vs Closed Loop SystemsGabriel GabuyaNo ratings yet
- Control StrategyDocument44 pagesControl StrategyAyunie FazlinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ME 446: Automatic Controls 446 - 1Document4 pagesIntroduction To ME 446: Automatic Controls 446 - 1Francisco HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Z Wave Technical Basics SmallDocument125 pagesZ Wave Technical Basics SmallFaqrie AziziNo ratings yet
- Suresh Resume - I & C EngineerDocument3 pagesSuresh Resume - I & C EngineerKartheek RamishettiNo ratings yet
- INI3601 ContentDocument3 pagesINI3601 ContentSiphamandla CokaNo ratings yet
- Nraq.E183931 - Programmable ControllersDocument4 pagesNraq.E183931 - Programmable ControllersDenislav PashovNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Control EngineeringDocument10 pagesInstrumentation and Control EngineeringArvin Loui BasconNo ratings yet
- How To Analyze A Cascade Control Loop Instrumentation Tools PDFDocument7 pagesHow To Analyze A Cascade Control Loop Instrumentation Tools PDFCarlos Manuel Salazar GarciaNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument23 pagesSeminar ReportSwapnil Behera100% (1)
- DR Husari Control NotesDocument149 pagesDR Husari Control NotesFiras QasemNo ratings yet
- Simulasi Pengendalian Level Steam DrumDocument15 pagesSimulasi Pengendalian Level Steam DrumSatria dinusaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Pros and Cons of Rockwell'S Plantpax Versus Deltav? Is Plantpax Actually A DCS?Document4 pagesWhat Are The Pros and Cons of Rockwell'S Plantpax Versus Deltav? Is Plantpax Actually A DCS?AlanNo ratings yet
- 4Dflz 10.08Document14 pages4Dflz 10.08zokiNo ratings yet
- ME 464 Exam Paper Final-VettedDocument5 pagesME 464 Exam Paper Final-VettedSaad RasheedNo ratings yet
- PLC PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERDocument44 pagesPLC PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERBùi Văn XêNo ratings yet
- Root LocusDocument4 pagesRoot LocusAyie ZulkhairieNo ratings yet
- EC3351 Control System Internal AssessmentDocument1 pageEC3351 Control System Internal AssessmentARUNKUMAR CHELLAPPANo ratings yet
- LAB No. 10 Analysis of Linear Control System Using Root Loci TechniqueDocument7 pagesLAB No. 10 Analysis of Linear Control System Using Root Loci TechniqueSanjar BeyNo ratings yet
- P&Id SymbolsDocument18 pagesP&Id SymbolsGeorge_Wabag_2014No ratings yet
- Module 3Document104 pagesModule 3mutencoNo ratings yet
- Material Clase 10 PDFDocument6 pagesMaterial Clase 10 PDFStefany CorreaNo ratings yet
- Janyu - Industrial Automation DivisionDocument24 pagesJanyu - Industrial Automation DivisionN RaoNo ratings yet
- Fayoum University Automatic Control ReportDocument4 pagesFayoum University Automatic Control ReportahmedelebyaryNo ratings yet
- Course Code and Title:: EEE 402: Control SystemsDocument9 pagesCourse Code and Title:: EEE 402: Control SystemsMd. Abu ShayemNo ratings yet
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (542)
- Off-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemFrom EverandOff-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemNo ratings yet
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionFrom Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialFrom EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Upcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)From EverandUpcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionFrom EverandPractical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Ramblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowFrom EverandRamblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowNo ratings yet
- Lithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsFrom EverandLithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026From EverandThe Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonFrom EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesFrom EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesFrom EverandThe Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationFrom EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinFrom EverandThe Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- High Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsFrom EverandHigh Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (331)
- Understanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveFrom EverandUnderstanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (16)