Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.Laswell'S Model of Communication: Mwamisi Dorcus Ndanu C01/0360/2019
Uploaded by
MutuaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.Laswell'S Model of Communication: Mwamisi Dorcus Ndanu C01/0360/2019
Uploaded by
MutuaCopyright:
Available Formats
MWAMISI DORCUS NDANU
C01/0360/2019
1.LaSwell's model of communication
His main aim was to analyse mass communication and the model is used for interpersonal or
group communication to disseminate a message to various groups in various situations. This
model describes who is saying something,what the message says,the channel used to convey
the message,who the message is aimed at and what effect the message has.
Components of this model
1.The communicator
Also the sender, who formulates and spreads the message. The sender can also be an
intermediary.
2. The content of the message
This is the message the sender spreads.
3. The medium used to convey and spread the message.
It consists of several communication tools,mass media and social media.
4. The receiver
The target individual or group.
5. The effect
This is the result the message lead to.
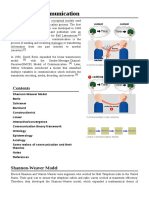
2.Shannon and Weaver model of communication
It's a mathematical theory of communication that urges that human communication can be
broken down into 6 key concepts:
1.Sender
The originator of the mmessage.
2.Encoder
Transmitter which converts the message into signals like waves or binary data through cables or
satellites.
3.Decoder
Reception place of the signal converting them into message.
4.Channel
The media through which the message is conveyed
5.Receiver
Destination of the message from the sender. They give feedback to the sender.
6.Noise
During transmission, the message can be distracted by physical noise like horn sounds,crowd
or thunder. Noise is the factor affecting the communication process.
3.Schramm's model of communication
Views communication as a process that takes place between a sender and a receiver, there's
also a message and a medium. This model can be used to determine the working of
communication between two people when they are exchanging information,ideas and attitudes.
It's circular rather than linear. Involves;
1.Encoder- sender of the message.
2.Decoder-receiber of the message.
3.Interpreter-person trying to understand/ analyse the message.
There's no separate sender and receiver, it's the same person.
4.Westley and MacLean model of communication
This model is seen in two contexts; interpersonal and mass communication. The difference
between the two contexts is the feedback. In interpersonal, the feedback is direct and fast while
in the mass communication it's indirect and slow. Communication begins when a person
responds selectively to their physical environment.
Components of this model
1.Source(A)- person creating and sending a message.
2.Environment(X)-physical state in which the communication process is studied.
3.Sensory experience (X1)-first thing the source sees that gives them an idea to write a
message.
4.Object of orientation (X1,X2)-what the source is exposed to,both social and cultural contexts.
5.Coding of interpretation(X')-decoding(message interpreted by the receiver.)
6.Receiver(B)-receives message from the source and interprets it.
7.Object of orientation receiver(X,b)-beliefs and the view pointsof the receiver which are based
on their past and objects of orientation.
8.Feedback(F)-once message is received, the receiver sends a message back to the source.
9.Gatekeepers(C)-person who ensures the message is filtered and tailored to the wishes of the
public and media companies.
5.Barlo and Lesikar model of communication
It focuses on encoding and decoding which happens before the sender sends the message and
before the receiver receives the message. He described the factors affecting the individual
components in communication making the communication more efficient. These are:
1.Sender(S)-the source of message who sends it to the receiver.
2.Message(M)-the substance being sent by the sender to the receiver in form of a
voice,audio,text or video.
3.Channel(C)-medium used to send the message like phone, internet.
4.Receiver(R)-person who gets the message in process.
You might also like
- Barc220920dus25 7164Document3 pagesBarc220920dus25 7164reza younesy75% (12)
- Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument13 pagesNature and Elements of CommunicationPhilip Jayson L. Lestojas100% (12)
- Models of Oral CommunicationDocument7 pagesModels of Oral CommunicationAiza Casas DagalaNo ratings yet
- Form No NTC 1-09 APPLICATION FOR PERMIT TO PURCHA - 230411 - 151417Document2 pagesForm No NTC 1-09 APPLICATION FOR PERMIT TO PURCHA - 230411 - 151417Jon CabalesNo ratings yet
- 22M528 Sealed ApplicationDocument37 pages22M528 Sealed ApplicationTodd FeurerNo ratings yet
- OCEC - Online Exam - Instruction - CandidateDocument4 pagesOCEC - Online Exam - Instruction - Candidate307 Seri .Rika100% (1)
- Triza Cherotich C01/0527/2019 Communication Skills Assignment Models of CommunicationDocument11 pagesTriza Cherotich C01/0527/2019 Communication Skills Assignment Models of CommunicationElijahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Nature of Language and CommunicationDocument9 pagesLesson 1: Nature of Language and CommunicationJehada AbdukadilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Nature of Language and CommunicationDocument9 pagesLesson 1: Nature of Language and CommunicationJehada AbdukadilNo ratings yet
- Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument5 pagesNature and Elements of Communicationsamantha beredoNo ratings yet
- Communication SkillDocument2 pagesCommunication SkillJenny AnneNo ratings yet
- Nature of CommunicationDocument4 pagesNature of CommunicationWazawski ScottNo ratings yet
- cc5 Unit 1 Suggestive NotesDocument7 pagescc5 Unit 1 Suggestive Notessuhel palNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Nature and Process of Communication Lesson 1 Communication Define ExplainedDocument6 pagesUnit 1 The Nature and Process of Communication Lesson 1 Communication Define ExplainedAirene Aala100% (2)
- Cos 100 Topic One NotesDocument10 pagesCos 100 Topic One NotesAPONDI SIMON ODONGONo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication - NotesDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Communication - NotesRamaduguKiranbabu100% (1)
- Oral Communication Week 1Document4 pagesOral Communication Week 1Mhagz MaggieNo ratings yet
- D2 Models of CommunicationDocument32 pagesD2 Models of CommunicationNeko CommsNo ratings yet
- Elements of CommunicationDocument2 pagesElements of Communicationlekz re100% (2)
- Prelim Lesson 1Document82 pagesPrelim Lesson 1jerainmallari12No ratings yet
- Concepts of Mass Communication Lecture 1Document4 pagesConcepts of Mass Communication Lecture 1temmyNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication LectureDocument3 pagesOral Communication LectureAmanda Leigh ResuelloNo ratings yet
- Purcom CompilationDocument91 pagesPurcom CompilationKaye bagasinNo ratings yet
- Model? Who Propounded It and When?Document15 pagesModel? Who Propounded It and When?V ANo ratings yet
- Cont 2 Lesson 3 4Document10 pagesCont 2 Lesson 3 4Raymar BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Hand Outs in OralDocument5 pagesHand Outs in OralArien kaye VallarNo ratings yet
- Health CommunicationDocument79 pagesHealth Communicationdesalegn nega waleNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper: What Do We Share? What Do We Impart? Why Do We Participate?Document21 pagesLesson Proper: What Do We Share? What Do We Impart? Why Do We Participate?BeaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two The Communication Process 2.1. Elements of CommunicationDocument7 pagesChapter Two The Communication Process 2.1. Elements of CommunicationwubeNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument13 pagesModels of CommunicationleonwaypNo ratings yet
- Nature and Process of CommunicationDocument5 pagesNature and Process of CommunicationBSN2G- SABLA-ON LORRAINE ANNENo ratings yet
- Definition Elements and Models of CommunicationDocument23 pagesDefinition Elements and Models of CommunicationMorbid FreelanceNo ratings yet
- 2 Communication ModelsDocument36 pages2 Communication ModelsKent DosejoNo ratings yet
- Proceess of BC& RWDocument10 pagesProceess of BC& RWAli ShahzadNo ratings yet
- CABALLERO, KRIZAH MARIE C. BSA 1A - Module 1 Assessment GECCOMDocument1 pageCABALLERO, KRIZAH MARIE C. BSA 1A - Module 1 Assessment GECCOMKrizahMarieCaballeroNo ratings yet
- CABALLERO, KRIZAH MARIE C. BSA 1A - Module 1 Assessment GECCOMDocument1 pageCABALLERO, KRIZAH MARIE C. BSA 1A - Module 1 Assessment GECCOMKrizahMarieCaballeroNo ratings yet
- Models of Communication - WikipediaDocument15 pagesModels of Communication - WikipediaCourage ChigerweNo ratings yet
- 2 Models of CommunicationDocument6 pages2 Models of Communicationgagan shahiNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelsDocument5 pagesCommunication Modelsmèj · ̊ ༘No ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument3 pagesModels of Communicationapi-417452748No ratings yet
- Models of Communication: Communication Major Dimensions SchemeDocument10 pagesModels of Communication: Communication Major Dimensions SchemeGladys NyoniNo ratings yet
- Media Information and LiteracyDocument38 pagesMedia Information and Literacyvankirbylucero123No ratings yet
- EFCOMDocument2 pagesEFCOMMa. Kimberlyn LaruaNo ratings yet
- The Functions Nature and Process of Communication PART 2Document25 pagesThe Functions Nature and Process of Communication PART 2tresvallesyhannieNo ratings yet
- Shannon and Weaver Model of CommunicationDocument2 pagesShannon and Weaver Model of CommunicationHasz RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Teacher: Dr. Ayesha Riaz Mam Humera Hina Mr. Faisal Ihsan EDU-504 - 3 (3-0)Document16 pagesTeacher: Dr. Ayesha Riaz Mam Humera Hina Mr. Faisal Ihsan EDU-504 - 3 (3-0)Nabeel TahirNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument7 pagesPurposive CommunicationHannah Pauleen G. LabasaNo ratings yet
- Communication Models PDFDocument6 pagesCommunication Models PDFSaurabh M. SaleNo ratings yet
- Communication Studies GuideDocument16 pagesCommunication Studies GuideAkiem JarrettNo ratings yet
- ORAL COMMUNICATION1112 Q1 LAS 3week 3 1 1Document17 pagesORAL COMMUNICATION1112 Q1 LAS 3week 3 1 1Wesley TampusNo ratings yet
- ECT 211 NOTES Communication ModelsDocument8 pagesECT 211 NOTES Communication Modelsaroridouglas880No ratings yet
- Communication TheoryDocument5 pagesCommunication TheoryJulie Ann GernaNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument20 pagesModels of CommunicationKAREN75% (4)
- Definition of Communication and PerceptionDocument12 pagesDefinition of Communication and PerceptionAhmed Elgazzar100% (1)
- Purposive CommunicationDocument13 pagesPurposive CommunicationKate Rose SantosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass CommunicationDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Mass CommunicationRimshaNo ratings yet
- Pur-Com PrelimsDocument8 pagesPur-Com PrelimsidyllictomuraNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument13 pagesOral CommunicationEJ ARREZANo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument8 pagesPurposive Communication ReviewerLuis Norbert SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Effective CommunicationDocument11 pagesEffective Communicationapi-373872186% (7)
- Academia de San Lorenzo Dema-Ala Inc.: Tialo, Sto. Cristo, City of San Jose Del Monte, BulacanDocument2 pagesAcademia de San Lorenzo Dema-Ala Inc.: Tialo, Sto. Cristo, City of San Jose Del Monte, BulacanMary Grace CastellonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Effective Communication Principles Processes and Ethics Part 2 Hand OutDocument15 pagesLesson 2 Effective Communication Principles Processes and Ethics Part 2 Hand OutMarky SantosNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - BC - FC - Oct 11, 2022Document22 pagesSession 3 - BC - FC - Oct 11, 2022ManjulaNo ratings yet
- Spam Detection PaperDocument3 pagesSpam Detection PaperMohammed Abdul RazzakNo ratings yet
- Noting and DraftingDocument12 pagesNoting and DraftingLalitha VbNo ratings yet
- DLSU (ACCCOB3 MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING 17E BY GARRISON) MHE Connect Via IBC Student Registration Payment InstructionDocument22 pagesDLSU (ACCCOB3 MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING 17E BY GARRISON) MHE Connect Via IBC Student Registration Payment InstructionNevan NovaNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 Assignment For ECE374: Posted: 02/20/15 Due: 02/27/15Document7 pagesHomework 2 Assignment For ECE374: Posted: 02/20/15 Due: 02/27/15Jp XtyraelNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Parts of A Business LetterDocument22 pagesWeek 6 Parts of A Business LetterMc HernanNo ratings yet
- ''Outlook QuestionsDocument7 pages''Outlook QuestionsRitesh KatalkarNo ratings yet
- Android Forensics With Belkasoft Training FAQDocument2 pagesAndroid Forensics With Belkasoft Training FAQVEDASTUS VICENTNo ratings yet
- Facebook ResponsesDocument6 pagesFacebook ResponsesFuzael AminNo ratings yet
- Creating A Case Via MyHRDocument14 pagesCreating A Case Via MyHRKarla Patricia Lopez LopezNo ratings yet
- Robowars: Important Notes and GuidelinesDocument5 pagesRobowars: Important Notes and GuidelinesAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Application As FiledDocument7 pagesApplication As FiledWei TingNo ratings yet
- Getting Started in English 255 & Tips For SuccessDocument5 pagesGetting Started in English 255 & Tips For SuccessKenton LyndsNo ratings yet
- ANC CloudDocument23 pagesANC Cloudhildanonkululeko107No ratings yet
- New Yammer End User GuideDocument24 pagesNew Yammer End User GuideDarwin JimenezNo ratings yet
- Todos Los Formatos Spanish Ab InitioDocument9 pagesTodos Los Formatos Spanish Ab InitioIshita KapadiaNo ratings yet
- 7 Steps: To Creating The Best Employee NewslettersDocument10 pages7 Steps: To Creating The Best Employee NewslettersGrace VersoniNo ratings yet
- Karnataka State Nursing Council: Nrts (Nurses Registration and Tracking SystemDocument6 pagesKarnataka State Nursing Council: Nrts (Nurses Registration and Tracking Systemhoqueanarul10hNo ratings yet
- TRACES - New E-Seal Enrollment Guide NewDocument16 pagesTRACES - New E-Seal Enrollment Guide NewchelarucarmenNo ratings yet
- Math CorrigerDocument1 pageMath CorrigerLeïla PNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023 AMC 8 Teacher's Manual (Updated Jan. 2023)Document10 pages2022-2023 AMC 8 Teacher's Manual (Updated Jan. 2023)daramolaabraham16No ratings yet
- User Manual: Model:B1248UDocument7 pagesUser Manual: Model:B1248Uwanto78No ratings yet
- Csc8710 Software Design and ModellingDocument6 pagesCsc8710 Software Design and ModellingBoniface KigoNo ratings yet
- Front Desk AM ChecklistDocument3 pagesFront Desk AM ChecklistAlyssaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Spanish January 2019 P2Document14 pagesCSEC Spanish January 2019 P2Doneike RhodenNo ratings yet
- Cisco ESA IronportDocument1,219 pagesCisco ESA Ironportsalu nasirNo ratings yet
- Gmail: FW: FWD: Transaction Alert For Your ICICI Bank Credit CardDocument1 pageGmail: FW: FWD: Transaction Alert For Your ICICI Bank Credit CardibicengNo ratings yet