Professional Documents
Culture Documents
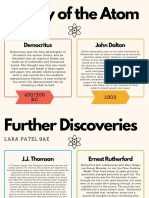
Isaac Newton Theorized J.J. Thomson Determined The Charge Rutherford Found That
Uploaded by
Camille Careng0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views3 pagesOriginal Title
TIMELINE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views3 pagesIsaac Newton Theorized J.J. Thomson Determined The Charge Rutherford Found That
Uploaded by
Camille CarengCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
400 B.
C 1704 1803 1906 1911
Isaac Newton theorized J.J. Thomson determined the charge
a mechanical universe to mass ratio of electrons Rutherford found that
with small, solid masses the atom is mostly empty
in motion space, with nearly all of its
mass concentrated in a
John Dalton proposed that elements tiny central nucleus. The
consisted of atoms that were nucleus is positively
identical and had the same mass and charged and surrounded
that compounds were atoms from at a great distance by the
different elements combined negatively charged
together. electrons.
Democritus’ atomic
theory posited that all
matter is made up
small indestructible
units he called atoms.
1913 1932 1817 1864 1869
John Newlands put forward his
James law of octaves in 1864 in which he
Chadwick discovered arranged all the elements known
neutrons, particles whose at the time into a table in order of
mass was close to that of a relative atomic mass. When he did Dmitri
proton. this, he found that each element Mendeleev created the
was similar to the element eight periodic table.
places further on. For example,
starting at Li, Be is the second
Niels Bohr proposed element, B is the third and Na is
an atomic structure the eighth element.
theory that stated the
outer orbit of an atom
could hold more Johann Dobereiner organized elements
electrons than the in groups called triads and proposed the
inner orbit. “Law of Octaves” for organizing the
elements
1913
Henry Moseley was an outstandingly skilled experimental physicist. In 1913 he used self-built equipment to prove that every element’s identity is uniquely
determined by the number of protons it has. His discovery revealed the true basis of the periodic table and enabled Moseley to predict confidently the
existence of four new chemical elements, all of which were found.
You might also like
- LB1D3 20220824 Inorganic ChemistryDocument2 pagesLB1D3 20220824 Inorganic ChemistryPhoebe BironNo ratings yet
- "The Development of Atomic Theory": "Nothing Exists Except Atoms and Empty Space: Everything Else Is Opinion."Document2 pages"The Development of Atomic Theory": "Nothing Exists Except Atoms and Empty Space: Everything Else Is Opinion."Caryl SantosNo ratings yet
- Inorg HandoutDocument9 pagesInorg HandoutAlyssa BardillonNo ratings yet
- Atom History NotesDocument1 pageAtom History NotesAlven Rey100% (1)
- The Ideas About Atom and Atomic ModelDocument2 pagesThe Ideas About Atom and Atomic ModelJea Lyca GuiñetaNo ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesAtomic TheoryRodelio ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Democritus The Curies (Marie and Peirre)Document1 pageDemocritus The Curies (Marie and Peirre)Freya SolaniaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Atoms, Ions and MoleculesDocument14 pagesLESSON 2 Atoms, Ions and MoleculesscientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory Timeline: Date Discoverer DiscoveryDocument5 pagesAtomic Theory Timeline: Date Discoverer DiscoveryImel Grace FlordelizNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure PDFDocument49 pagesAtomic Structure PDFAshishNo ratings yet
- Structure of An Atom and The Periodic TableDocument2 pagesStructure of An Atom and The Periodic TableErika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- History of The AtomDocument17 pagesHistory of The Atomali100% (1)
- Physical Science: Prepared By: Ms. Shaira G. SalardaDocument41 pagesPhysical Science: Prepared By: Ms. Shaira G. SalardaShaira SalardaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of New ElementsDocument24 pagesSynthesis of New ElementsMichael FernandoNo ratings yet
- Atoms From The Eyes of PhilosophersDocument9 pagesAtoms From The Eyes of Philosophersgina moraNo ratings yet
- BabyDocument6 pagesBabyAnnie SampatuNo ratings yet
- Baladad Richelle 11 ABM-B Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesBaladad Richelle 11 ABM-B Physical ScienceIvy Jane R AlarconNo ratings yet
- Timeline Atomic TheoryDocument1 pageTimeline Atomic Theoryantonio.damicoNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science-LessonsDocument38 pagesPhysical-Science-LessonsJansen MunioNo ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesAtomic TheoryTriumfo, DianeNo ratings yet
- Antoine Lavoiser: DemocritusDocument2 pagesAntoine Lavoiser: DemocritusMicaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document9 pagesLesson 2Mary Ann Elacion AballaNo ratings yet
- ChristianDocument21 pagesChristianAdrian John ManalotoNo ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument1 pageAtomic TheoryFunny BwoNo ratings yet
- Assignment /quiz 1:: 1 - Dalton Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesAssignment /quiz 1:: 1 - Dalton Atomic TheoryRuffa Mae PortugalNo ratings yet
- History of The Atom TimelineDocument2 pagesHistory of The Atom Timelinetasnim.islam0803No ratings yet
- NotesDocument3 pagesNotesClarice TorresNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 ESL History of Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesActivity 2 ESL History of Atomic StructureAshmi KNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure of MatterDocument35 pagesAtomic Structure of MatterJhon Vincent C. PerezNo ratings yet
- Atoms:: Development of The Atomic TheoryDocument18 pagesAtoms:: Development of The Atomic TheoryJamie BaczewskiNo ratings yet
- 12s080201batomsdevelopment of The Atomic Theory1 171015140731Document21 pages12s080201batomsdevelopment of The Atomic Theory1 171015140731Cristeah AlemaniaNo ratings yet
- Early Description of MatterDocument24 pagesEarly Description of MatterAllea JeanNo ratings yet
- Atomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Document16 pagesAtomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Nilimoy Choudhury100% (1)
- Gen Chem Second PreDocument15 pagesGen Chem Second PreShayne Herrera IINo ratings yet
- Not IndivisibleDocument4 pagesNot IndivisibleChristine De San Jose0% (1)
- AtomsDocument26 pagesAtomsJhul Mhel SonioNo ratings yet
- Ramil DrugsDocument3 pagesRamil DrugsAileen Labastida BarcenasNo ratings yet
- History of The Atom TimelineDocument6 pagesHistory of The Atom Timelineur momNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument2 pagesReviewerMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- The AtomDocument1 pageThe AtomAadit SirohiyaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory TimelineDocument1 pageAtomic Theory TimelinePia LomboyNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory TimelineDocument1 pageAtomic Theory TimelineDanilo Macahis100% (1)
- Evolution of Atomic TheoryDocument3 pagesEvolution of Atomic TheoryPaolo Lorenzo LoraNo ratings yet
- Timeline: Advancement of ChemistryDocument5 pagesTimeline: Advancement of ChemistryCHRISTIAN CARL CABAJARNo ratings yet
- Timeline of The Development of The AtomDocument6 pagesTimeline of The Development of The AtomacerNo ratings yet
- Model Development of The AtomDocument2 pagesModel Development of The AtomFrazer ShineNo ratings yet
- Atoms:: Development of The Atomic TheoryDocument23 pagesAtoms:: Development of The Atomic TheoryAndy SwiftNo ratings yet
- Project Standard 8Document6 pagesProject Standard 8Saqib MandhaiNo ratings yet
- Development of Atomic TheoryDocument1 pageDevelopment of Atomic TheoryLaw RenceNo ratings yet
- Atom Time LineDocument1 pageAtom Time Lineapi-222503660No ratings yet
- How The Ideas of The Atom, Along With The Idea of The Elements EvolvedDocument50 pagesHow The Ideas of The Atom, Along With The Idea of The Elements EvolvedChosen ExeNo ratings yet
- Development of AtomDocument7 pagesDevelopment of AtomMichelley Ann MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument91 pagesAtomic StructureUmmu juraijNo ratings yet
- ATOMS: Development of The Atomic Theory DemocritusDocument3 pagesATOMS: Development of The Atomic Theory DemocritusEros ErosNo ratings yet
- Atomic ResearchDocument2 pagesAtomic ResearchRebecca SunNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of The AtomDocument23 pagesHistorical Development of The AtomAdrian John Manaloto100% (1)
- Nr. Phys Chapter OneDocument23 pagesNr. Phys Chapter Oneabdii100% (1)
- AtomDocument50 pagesAtomRomina Mae FernandezNo ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument5 pagesAtomic TheoryasharaqueenNo ratings yet
- Comparative Skeletal Anatomy of Domestic SpeciesDocument17 pagesComparative Skeletal Anatomy of Domestic SpeciesCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- Lec Outline 8 Vet Histo SKELETAL AND SMOOTH MUSCLESownDocument11 pagesLec Outline 8 Vet Histo SKELETAL AND SMOOTH MUSCLESownCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- Broiler Breeder ProductionDocument7 pagesBroiler Breeder ProductionCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- College of Human Kinetics Lesson 3: Types of Aerobics I: Cagayan State UniversityDocument4 pagesCollege of Human Kinetics Lesson 3: Types of Aerobics I: Cagayan State UniversityCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- College of Human Kinetics: Cagayan State UniversityDocument4 pagesCollege of Human Kinetics: Cagayan State UniversityCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 Horse Judging Performance (Group Output) : CriteriaDocument4 pagesActivity No. 1 Horse Judging Performance (Group Output) : CriteriaCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- College of Human Kinetics: Cagayan State UniversityDocument4 pagesCollege of Human Kinetics: Cagayan State UniversityCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Origin and Development of Volleyball: Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesLesson 1: Origin and Development of Volleyball: Learning ObjectivesCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Understanding The Aerobics Exercise: College of Human KineticsDocument7 pagesLesson 1: Understanding The Aerobics Exercise: College of Human KineticsCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- P.E. 13 VolleyballDocument33 pagesP.E. 13 VolleyballCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- Safari - 17 Oct 2019 at 7:58 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 17 Oct 2019 at 7:58 PMCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam in Art AppreciationDocument1 pageMidterm Exam in Art AppreciationCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- Butuan or Limasawa?: Beautiful Island, 2006) - The Tradition, Unlike The OtherDocument1 pageButuan or Limasawa?: Beautiful Island, 2006) - The Tradition, Unlike The OtherCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- Safari - 15 Oct 2019 at 2:40 AMDocument1 pageSafari - 15 Oct 2019 at 2:40 AMCamille CarengNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry l2.0Document5 pagesOrganic Chemistry l2.0Camille CarengNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument15 pagesPeriodic TableTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- 9th Science One MarkDocument28 pages9th Science One MarkVathi N. KhalleelulahNo ratings yet
- Imaginarium - Class 10 - January - 2019 PDFDocument55 pagesImaginarium - Class 10 - January - 2019 PDFIwje JsjsNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH 5 Periodic Classification of Elements - Class 10th Science Study RankersDocument7 pagesNotes of CH 5 Periodic Classification of Elements - Class 10th Science Study RankerssamyNo ratings yet
- Newlands Law of OctavesDocument5 pagesNewlands Law of OctavesPaarth Saxena X-B RNNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements Revision NotesDocument19 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements Revision Notesfulltime entertainmentNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and PeriodicityDocument9 pagesPeriodic Table and PeriodicityApeksha MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY BOOK 2 ObjDocument44 pagesCHEMISTRY BOOK 2 ObjHaris AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Science Project WorkDocument16 pagesScience Project WorkSushikant Chaturvedi79% (42)
- ScienceDocument259 pagesScienceAbhishek KumbalurNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MCQs 2nd Year. TESTDocument48 pagesChemistry MCQs 2nd Year. TESTPremier AcademyNo ratings yet
- History of Periodic TableDocument24 pagesHistory of Periodic TableMaca RenaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table NCERT Highlighted PDF White (3) - ExtractedDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table NCERT Highlighted PDF White (3) - Extractedangelinaprateeka02No ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument11 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsVivek Earnest NathNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument165 pagesPeriodic Tablesarizal100% (2)
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument2 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument14 pagesPeriodic TableJefferson Gaucho AyikaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Questions For Class 10 Science Periodic Classification of Elements With AnswersDocument30 pagesMCQ Questions For Class 10 Science Periodic Classification of Elements With AnswersAymen WaelNo ratings yet
- Elementary OrderDocument156 pagesElementary OrderRaghu NandanNo ratings yet
- History of The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument25 pagesHistory of The Periodic Table of ElementsPao Deleon100% (2)
- 1 3 2 5 2Document37 pages1 3 2 5 2Himanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table: The Study of ElementsDocument26 pagesThe Periodic Table: The Study of Elementsbiromin100% (1)
- Tel/Fax No.: (047) 811-1683 The Historical Development of The Periodic TableDocument8 pagesTel/Fax No.: (047) 811-1683 The Historical Development of The Periodic TableCarl PaduaNo ratings yet
- PPDocument4 pagesPPrameshNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument38 pagesPeriodic Table of ElementsLia Marlia100% (2)
- History of The Periodic TableDocument25 pagesHistory of The Periodic TableLeah Jane MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10th Science PDFDocument14 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements Class 10th Science PDFPranjul Singh100% (1)
- General Chemistry (Pesonalities and Their Contributions)Document3 pagesGeneral Chemistry (Pesonalities and Their Contributions)Dean Mark AnacioNo ratings yet
- History of Periodic TableDocument94 pagesHistory of Periodic TableMUHAMMAD SYAFI BIN ABDUL MALIK / UPMNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument30 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesKRISH RAWAT100% (1)