Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Find the Thévenin Equivalent Circuit for a Given Circuit
Uploaded by
Antonio MaldonadoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Find the Thévenin Equivalent Circuit for a Given Circuit
Uploaded by
Antonio MaldonadoCopyright:
Available Formats
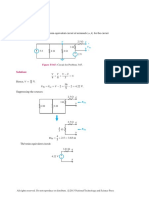
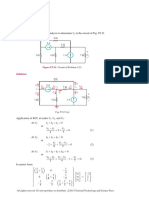
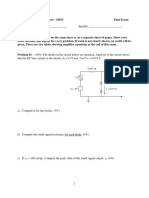
Problem 3.
71 Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit at terminals (a, b) of the circuit
in Fig. P3.71.
5Ω
Ix 10 Ω V2 20 Ω V3 2Ω a
V1 +
+
_ 19 V 4Ω 2Ix 8Ω Voc
b _
Figure P3.71: Circuit for Problems 3.71 and 3.72.
Solution:
V1 = 19 V
V2 −V1 V2 V2 −V3
+ + =0
10 4 20
V3 −V2 V3 V3 −V1
+ + − 2Ix = 0
20 8 5
V1 −V2
Ix =
10
Simultaneous solution of the above equations yields:
V2 = 6.94 V, V3 = 17.49 V.
VTh = Voc = V3 = 17.49 V.
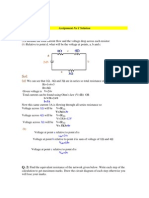
To find RTh , we calculate Isc :
V1 = 19 V
V2 −V1 V2 V2 −V3
+ − =0
10 4 20
V3 −V2 V3 V3 V3 −V1
+ + + − 2Ix = 0
20 8 2 5
V1 −V2
Ix =
10
5Ω
Ix 10 Ω V2 20 Ω V3 2Ω
V1 a
+ Isc
_ 19 V 4Ω 2Ix 8Ω
b
Solution is: V2 = 5.71 V, V3 = 7.71 V.
V3 7.71
Isc = = = 3.86 A.
2 2
Voc 17.49
RTh = = = 4.53 Ω.
Isc 3.86
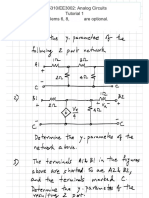
Hence, the Thévenin circuit is
All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. 2013
c National Technology and Science Press
4.53 Ω
a
+
17.49 V _
b
All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. 2013
c National Technology and Science Press
You might also like
- HW07 Sol PDFDocument8 pagesHW07 Sol PDFFatih OzerNo ratings yet
- SSLC Maths Question Bank Solution All Chapters PDFDocument70 pagesSSLC Maths Question Bank Solution All Chapters PDFChamarthiNagamani50% (2)
- Grade 9 Math Second Quarter ExamDocument6 pagesGrade 9 Math Second Quarter ExamJohn Lee TeodoroNo ratings yet
- GENERAL-EDUCATION MATH 100-Items 2017Document303 pagesGENERAL-EDUCATION MATH 100-Items 2017Peterson R Manuel100% (1)
- HW05 SolDocument10 pagesHW05 SolMuhammed FahdNo ratings yet
- Prob3 74s PDFDocument2 pagesProb3 74s PDFRAPETI SAI KUMAR (N160490)No ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering: Electrical and Electronic Engineering DepartmentDocument11 pagesFaculty of Engineering: Electrical and Electronic Engineering DepartmentAyman Ihab Saad AwadNo ratings yet
- EE31594 Quiz 1 Sep 28, 2019Document10 pagesEE31594 Quiz 1 Sep 28, 2019Hyunsog ChoiNo ratings yet
- EENG223 Final Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesEENG223 Final Solutions PDFRamoona LatifNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering E E E D: E 223 Circuit Theory I I 221 - Electrical Circuits Midterm Exam Spring 2009-10Document6 pagesFaculty of Engineering E E E D: E 223 Circuit Theory I I 221 - Electrical Circuits Midterm Exam Spring 2009-10JOSE LUIS LEON RUBIANONo ratings yet
- Answer Key PDFDocument58 pagesAnswer Key PDFRuth Abegail de VeraNo ratings yet
- Use Source Transformation To Find I in The Circuit of Fig. 4.100Document16 pagesUse Source Transformation To Find I in The Circuit of Fig. 4.100Syam SundarNo ratings yet
- Prob3 7s PDFDocument1 pageProb3 7s PDFclaireNo ratings yet
- Find Vx using nodal analysisDocument2 pagesFind Vx using nodal analysisFelipe TordecillaNo ratings yet
- Network Test SolutionDocument16 pagesNetwork Test Solutionlalita kumariNo ratings yet
- Mid 2020 SDocument11 pagesMid 2020 Samedpv56No ratings yet
- Analog SolutionDocument15 pagesAnalog SolutionajjjindoreNo ratings yet
- Mesh and Nodal Analysis Experiment ResultsDocument9 pagesMesh and Nodal Analysis Experiment ResultsRick AlvientoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - SolutionDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 - SolutionSalil ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- ECE 209, Lec B2 Homework 6: April 2, 2021Document4 pagesECE 209, Lec B2 Homework 6: April 2, 2021Stone RricNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Homework ProblemsDocument21 pagesSolutions of Homework ProblemsHusni MustafaNo ratings yet
- Quiz-3 ADocument5 pagesQuiz-3 AmonalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits For Engineers (EC1000) : Lecture-4 Network TheoremsDocument11 pagesElectrical Circuits For Engineers (EC1000) : Lecture-4 Network TheoremsnithishNo ratings yet
- ENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems Midterm ExaminationDocument9 pagesENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems Midterm ExaminationTaha EtemNo ratings yet
- ESE-2017: Prelims Exam: E & T EngineeringDocument9 pagesESE-2017: Prelims Exam: E & T EngineeringamithbaluNo ratings yet
- EEE Exams: Emman Joshua B. Busto June 8, 2017Document5 pagesEEE Exams: Emman Joshua B. Busto June 8, 2017reneSantosIVNo ratings yet
- P04 Com para Tors SolDocument8 pagesP04 Com para Tors SolAsza ShahizaNo ratings yet
- Physics of Electronic Devices Problem 1 Diode Application & BJT Prob 1Document17 pagesPhysics of Electronic Devices Problem 1 Diode Application & BJT Prob 1Luật Lê QuangNo ratings yet
- # 1 (7 Problems)Document8 pages# 1 (7 Problems)wl0o0dyNo ratings yet
- Node and Supernode Final 2Document10 pagesNode and Supernode Final 2Ellen Kay CacatianNo ratings yet
- 101 Milestone Problems On Electronics CommunicationDocument31 pages101 Milestone Problems On Electronics CommunicationAmandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document8 pagesTutorial 5Muhammad FauziNo ratings yet
- 04-MB-4 Version Anglaise - Mai 2014Document4 pages04-MB-4 Version Anglaise - Mai 2014LuisAranaNo ratings yet
- EECE210_Quiz2_Sp11_SolutionDocument10 pagesEECE210_Quiz2_Sp11_Solutiondani khNo ratings yet
- ENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems Midterm ExaminationDocument9 pagesENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems Midterm ExaminationTaha EtemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 SolutionsDocument118 pagesChapter 03 Solutions조상영No ratings yet
- Experiment Title: Bias Point Detail Analysis of DC Circuit With Dependent Sources Using Pspice SchematicsDocument4 pagesExperiment Title: Bias Point Detail Analysis of DC Circuit With Dependent Sources Using Pspice SchematicsAshraful IslamNo ratings yet
- sm10 7 8Document2 pagessm10 7 8nicehsy0804No ratings yet
- vo vo i: 10Ω io 5io 10ΩDocument1 pagevo vo i: 10Ω io 5io 10Ωgain xing GuoNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering: Electrical and Electronic Engineering DepartmentDocument5 pagesFaculty of Engineering: Electrical and Electronic Engineering DepartmentAyman Ihab Saad AwadNo ratings yet
- Demonstration: Superposition TheoremDocument13 pagesDemonstration: Superposition TheoremridaNo ratings yet
- Eca-Ese Questions (Dsy Students) Max. Marks 60 Duration 1.30 HRDocument4 pagesEca-Ese Questions (Dsy Students) Max. Marks 60 Duration 1.30 HRPrasadNo ratings yet
- EENG223/INFE221 Final Exam Circuit Theory I/Electric CircuitsDocument7 pagesEENG223/INFE221 Final Exam Circuit Theory I/Electric Circuitskwakwa4No ratings yet
- EE101 Assignment Waveforms, Circuits (40chDocument3 pagesEE101 Assignment Waveforms, Circuits (40chBikash SahNo ratings yet
- Final - EE330 - Dorr - Spring 2020Document8 pagesFinal - EE330 - Dorr - Spring 2020Bruce SmithNo ratings yet
- Network ProblemsDocument12 pagesNetwork ProblemssriramNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis II & Network Synthesis: Lecture One: RevisionDocument47 pagesCircuit Analysis II & Network Synthesis: Lecture One: RevisionSalmaanCadeXaajiNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2008Document28 pagesCircuit Theory Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2008Muhammad Umair100% (3)
- Thevenin Theorem 2Document18 pagesThevenin Theorem 2monkeydluffyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document6 pagesTutorial 1soham1994No ratings yet
- HD74LV573A: Octal D-Type Transparent Latches With 3-State OutputsDocument16 pagesHD74LV573A: Octal D-Type Transparent Latches With 3-State OutputsSergeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document20 pagesChapter 2badrilaminNo ratings yet
- CSE209 Lab4Document4 pagesCSE209 Lab4Tasnim Saima RaitaNo ratings yet
- Chap3 HW2 SolutionDocument6 pagesChap3 HW2 SolutionAbdi ZerihunNo ratings yet
- 2.tutorial 2Document4 pages2.tutorial 2Harsh SameerNo ratings yet
- Nodal Analysis: Format ApproachDocument4 pagesNodal Analysis: Format ApproachA.K.M.TOUHIDUR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Solution Assignment 5Document8 pagesSolution Assignment 5Ahmed JamalNo ratings yet
- Final SKEE1013 20172018 - 2Document5 pagesFinal SKEE1013 20172018 - 2Dua IslamNo ratings yet
- ECE-221 Fundamentals of Circuits Lab 2Document4 pagesECE-221 Fundamentals of Circuits Lab 2tash7827No ratings yet
- Institute of Technology Kharagpur End-Semester Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesInstitute of Technology Kharagpur End-Semester Exam QuestionsSanket KumarNo ratings yet
- Quiz I SolutionDocument5 pagesQuiz I SolutionSerge DemirdjianNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Circuitos Electrónicos 2 Laboratorio de Simulación 1Document1 pageCircuitos Electrónicos 2 Laboratorio de Simulación 1Antonio MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Average Quiz Score: Aaaaaaaaaaaa 2 1.00 2 50.00% Total: 0 0.00 2 0%Document2 pagesAverage Quiz Score: Aaaaaaaaaaaa 2 1.00 2 50.00% Total: 0 0.00 2 0%Antonio MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- SQLDocument5 pagesSQLHenry Marcial Arevalo FloresNo ratings yet
- Current Use of Linux in Spacecraft Ight Software: IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine October 2017Document25 pagesCurrent Use of Linux in Spacecraft Ight Software: IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine October 2017Antonio MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Arcade Game Lesson by SlidesgoDocument45 pagesArcade Game Lesson by SlidesgoAntonio MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Algebra Lineal LIC EneMay2017.Antonio - Maldonado.tarea 3Document2 pagesAlgebra Lineal LIC EneMay2017.Antonio - Maldonado.tarea 3Antonio MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- 9th Maths Ch. 2 - Zubair MukhtarDocument2 pages9th Maths Ch. 2 - Zubair MukhtarMissh Kaini MaharNo ratings yet
- Prime NumbersDocument27 pagesPrime NumbersAASFI Private SchoolNo ratings yet
- A Finite Element Formulation For Nonlinear Incompressible Elastic and Inelastic AnalysisDocument53 pagesA Finite Element Formulation For Nonlinear Incompressible Elastic and Inelastic Analysisguanicad712827No ratings yet
- 9 Ideal Truss: Force MethodDocument8 pages9 Ideal Truss: Force MethodAiman RashidNo ratings yet
- Classical Dynamics: Example Sheet 3 SolvedDocument3 pagesClassical Dynamics: Example Sheet 3 SolvedShweta SridharNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Examples for Interpolation and Curve FittingDocument25 pagesMATLAB Examples for Interpolation and Curve FittingQuốc SơnNo ratings yet
- Math ModDocument4 pagesMath ModKarysse Arielle Noel JalaoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U: Mathematics 9794/01Document4 pagesCambridge Pre-U: Mathematics 9794/01Rushil MohabeerNo ratings yet
- Methods For Chemical: Engineers With MAUAB ApplicationsDocument1 pageMethods For Chemical: Engineers With MAUAB Applicationskara_25No ratings yet
- Mathematics in Africa: World History of MathematicsDocument6 pagesMathematics in Africa: World History of MathematicsJacob ObboNo ratings yet
- Math-9-LAW #4-Q1-4Document8 pagesMath-9-LAW #4-Q1-4Keira cassandra delacruzNo ratings yet
- Paper Dynamic Fuzzy ControlDocument8 pagesPaper Dynamic Fuzzy ControlEwarAlexNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression ExplainedDocument110 pagesSimple Linear Regression ExplainedAhmed ElsayedNo ratings yet
- SPM Perlis Addmath P2 2010 AnsDocument3 pagesSPM Perlis Addmath P2 2010 AnsHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- 1 Advanced Algebra WorksheetDocument2 pages1 Advanced Algebra WorksheetJoy DacuanNo ratings yet
- Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat: Erik Sweet, K. Vajravelu, Robert A. Van Gorder, I. PopDocument8 pagesCommun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat: Erik Sweet, K. Vajravelu, Robert A. Van Gorder, I. PopSrinivas JangiliNo ratings yet
- BRX 120 Unit 2Document2 pagesBRX 120 Unit 2Khai HuynhNo ratings yet
- Exponential and Logarithmic EquationsDocument11 pagesExponential and Logarithmic Equationshazel_enaNo ratings yet
- Exam Question OnlineTest2110 BQT1614Document9 pagesExam Question OnlineTest2110 BQT1614Syamala 29No ratings yet
- 07 Week 09 - The Steady Magnetic FieldDocument24 pages07 Week 09 - The Steady Magnetic FieldJunaidy VandeanganNo ratings yet
- Taylor SeriesDocument3 pagesTaylor SeriesiamheretohelpNo ratings yet
- Probability: Random ExperimentDocument15 pagesProbability: Random ExperimentabdulbasitNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument17 pagesUntitled DocumentMatthew FlynnNo ratings yet
- QMDocument6 pagesQMiyd70712No ratings yet
- Non-Positional Number System: Data RepresentationDocument13 pagesNon-Positional Number System: Data Representationlixus mwangiNo ratings yet
- PatternDocument3 pagesPatternVinyl OquiñoNo ratings yet
- Elkies N.D. Lectures On Analytic Number Theory (Math259, Harvard, 1998) (100s) - MTDocument100 pagesElkies N.D. Lectures On Analytic Number Theory (Math259, Harvard, 1998) (100s) - MTBerndt EbnerNo ratings yet