Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assessment Task 1.2 Tabular Presentation
Uploaded by
heyheyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment Task 1.2 Tabular Presentation
Uploaded by
heyheyCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment Task 1.
2 Tabular Presentation (60 Points)
Name: Catherine Acutim
Course and Year: BSA-2A
Directions: Create a tabular presentation on the following: Use the given tabular presentation given
below.
a. Philosophies of the Quality Gurus (1) Edward Deming (2) Joseph M. Juran and (3) Philip Crosby
b. The Frameworks for Quality and Performance Excellence
(1) Malcolm Baldrige Award
(2) ISO 9000
(3) Six Sigma
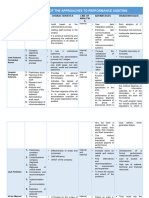
A. Philosophies of Quality Gurus
Quality Gurus Philosophies Philosophical Definition and
Implication to Quality
Management
(1) Edward Deming
a) System of Profound a) System of Profound
Knowledge Knowledge - Without
b) Chain Reaction for the profound
Quality Improvement knowledge,
c) The 14 Points of management action can
Management cause ruination. The
system of Profound
Knowledge is made up
of four interrelated
parts: (1) theory of
systems, which is a
series of functions or
activities within an
organization that work
together for the aim of
the organization, (2)
theory of variation
which managers must be
able to recognize a
stable system and
understand the concepts
of special and common
causes of variation, (3)
theory of knowledge
that addresses the way
in which knowledge is
advanced, and (4) theory
of psychology which is
important since
management needs to
have knowledge of
people and how they
interact, of their needs,
and of their working and
learning styles.
b) Chain of Reaction – by
improving quality, cost
decrease and
productivity improves.
As a result, there is a
greater potential for an
increased market share.
To address the first box
in the chain reaction
(improve quality),
management must
adopt the 14 principles
of management and
understand the
statistical approach to
process improvement.
To appreciate fully the
meaning of improving
quality in Deming's chain
reaction, an
understanding of the
concept of variation is
required. It presen5s
that higher quality leads
to higher productivity
which in turn leads to
long term competitive
strength.
c) 14 Points of
Management - these
points present tactical
practices that
management should
adhered upon. These
points provide yhr basis
for initiating and
sustaining an
organizational
transformation that
focuses on customer
satisfaction through
quality. These
obligations are
management's
responsibility and they
cannot be delegated. To
adopt the 14 points,
management needs to
put aside short term
thinking for the long-
term good of the
company so that they
can be in business
tomorrow.
(2) Joseph M. Juran a) The Juran Quality a) Juran’s Quality Trilogy –
Trilogy provides a systematic
b) Pursuit of Quality in approach to carrying out
two levels Juran's methodology for
c) Quality Definition managing quality.
Essential to
implementation,
however, is active
leadership, starting at
the top.
(1)Quality planning –
Begins with identifying
customers, both
external and internal,
determining their needs,
and developing product
features that respond to
customer needs.
(2)Quality Control –
Involves determining
what to control,
establishing units of
measurement so that
data may be objectively
evaluated, establishing
standards of
performance, measuring
actual performance and
the standard, and taking
action on the difference.
(3)Quality Improvement
– Is best achieved by
identifying specific
projects for
improvement, getting
the right people
involved, diagnosing
causes of poor
performance,
developing remedies for
the causes, proving that
the remedies will be
effective, and providing
control to hold
improvements.
b) Pursuit of quality on
two levels:
(1) the mission of the
firm as whole is to
achieve high
product quality, and
(2) the mission of
each individual
department in the
firm is to achieve
high production
quality. Like
Deming, Juran
advocates a never-
ending spiral of
activities that
includes market
research, product
development,
design, planning for
manufacture,
purchasing,
production process
control, and
inspection and
testing, followed by
customer feedback.
Because of the
interdependence of
these functions, the
need for competent
company-wide
quality management
is great. Senior
management must
play an active and
enthusiastic
leadership role in
the quality
management
process.
c) Quality Definition - he
defines quality as
fitness for use .
Categories of Quality
Quality of Design –
Focuses on market
research, product
concept, and design
specifications.
Quality of
conformance –
Includes
technology,
manpower, and
management.
Availability –
Focuses on
reliability,
maintainability, and
logistical support.
Field Service –
Quality comprises
promptness,
competence, and
integrity.
(3) Philip Crosby The Absolute Quality Absolutes of Quality
Management Management Perspectives
Quality means
conformance to
requirements not
elegance.
There is no such thing as
quality problem.
There is no such thing as
the economics of
quality: it is always
cheaper to do the job
right the first time.
The only performance
measurement is the cost
of quality.
The only performance
standard is zero defects.
These absolutes help
management focus on
quality improvement and,
more importantly, help
them make the shift from
what Crosby calls
conventional wisdom to the
idea that quality and cost
are not in competition with
each other.
B. Frameworks for Total Quality Management and Performance Excellence
Quality Frameworks Definition/Purpose Scope and Limitations
(1)Malcolm Baldrige Award Malcolm Baldrige National Consists hierarchical set of
Quality Award categories and areas:
- Has been one of Categories (leadership;
the most strategy; customers;
powerful measurement; analysis
catalysts of Total and knowledge
Quality in U.S.A management;
and throughout Workforce; Operations;
the world. Result)
- Establishes a
Baldrige focuses on
framework for
performance excellence for the
understanding
entire organization in an overall
and integrating management framework,
principles of identifying and tracking
performance important organizational
excellence. results.
- Was highly
regarded by
world leader,
having played a
major role in
carrying out the
administration’s
trade policy,
resolving
technology and
transfer
differences with
China and India.
Purposes of the Award
Help stimulate American
Companies to improve
quality and productivity
for the pride of
recognition while
obtaining a competitive
edge through increased
profits.
Recognize the
achievements of those
companies that improve
the quality of their
goods and services that
provide an example to
others. Establish
guidelines and criteria
that can be used by
business, industrial,
governmental, and other
enterprises in evaluating
their own quality
improvement efforts.
Provide specific
guidance for other
American enterprises
were able to change
their cultures and
achieve eminence.
(2) ISO 9000 ISO 9000 is defined as a set of They are not specific to any one
international standards on industry and can be applied to
quality management and quality organizations of any size.
assurance developed to help
ISO certifications exist in many
companies effectively document
areas of industry, from energy
the quality system elements
management and social
needed to maintain an efficient
responsibility to medical devices
quality system.
and energy management. ISO
ISO certification certifies that a standards are in place to ensure
management system, consistency. Each certification
manufacturing process, service, has separate standards and
or documentation procedure has criteria and is classified
all the requirements for numerically.
standardization and quality
Individualsndividuals cannot
assurance. ISO (International
become ISO certified. Only
Organization for
businesses and organizations
Standardization) is an
can. It’s also worth noting that
independent, non-
ISO doesn’t provide the
governmental, international
certification. Instead,
organization that develops
certification is made possible
standards to ensure the quality,
through third party
safety, and efficiency of
organizations.
products, services, and systems.
ISO 9000 can help a company
satisfy its customers, meet
regulatory requirements, and
achieve continual improvement.
It should be considered to be a
first step or the base level of a
quality system.
ISO 9000 is a series, or family, of
quality management standards,
while ISO 9001 is a standard
within the family. The ISO 9000
family of standards also contains
an individual standard named
ISO 9000. This standard lays out
the fundamentals and
vocabulary for quality
management systems (QMS).
(3) Six Sigma Six Sigma is a method that Scope of Six Sigma
provides organizations tools to
With the organization the Six
improve the capability of their
Sigma contributes to the
business processes. This increase
organizations competitive
in performance and decrease in
advantage and changing the
process variation helps lead to
culture within the organization
defect reduction and
from “reactive problem solving
improvement in profits,
to proactive problem
employee morale, and quality of
orevention”. Six Sigma also
products or services. It is an
benefits the organization in all
approach in measuring product
its sectors. Such as
and service quality. It is the
manufacturing, financial, health
realization of many fundamental
care, engineering and
concepts of “total quality
construction, research and
management” notably, the
development sector.
integration of human and
process elements of Limitations of Six Sigma
improvement. Six Sigma
concentrates on measuring One of the challenges of the
product quality and driving fact-driven process of
process improvement and cost identifying a problem and
savings throughout the working toward a solution is
organization. that it tends to leave out a key
component: humans—and
more importantly, how humans
impact and work through
different obstacles. Sometimes
it is often beneficial to give
employees a chance to tackle
issues head-on before investing
in a complete operational
overhaul.
The one-size-fits-all approach to
Six Sigma can also be somewhat
limiting at times, especially
within organizations or
disciplines that rely on
creativity. Employees who crave
the freedom to toss caution
(and sometimes process) to the
wind in an effort to innovate
may find the Six Sigma process
stifling.
Six Sigma also does not
technically allow for the
introduction of new tools or
methods, even when they could
be beneficial. Since Six Sigma
generally requires total
dedication across all teams, it’s
difficult to use or experiment
with other process
methodologies for other areas
of the organization.
You might also like
- Holistic Management: Managing What Matters for Company SuccessFrom EverandHolistic Management: Managing What Matters for Company SuccessNo ratings yet
- MCS Program Learning OutlinesDocument14 pagesMCS Program Learning OutlinesRyan X RoseNo ratings yet
- DocScanner 07-Jan-2022 2.29 PMDocument11 pagesDocScanner 07-Jan-2022 2.29 PMKGBNo ratings yet
- Planning Organization LeadingDocument2 pagesPlanning Organization LeadingHazim RasidNo ratings yet
- PERFORMANCE MANAGMENT(1)Document2 pagesPERFORMANCE MANAGMENT(1)Muhammed SwalihNo ratings yet
- MGT AssignmentDocument55 pagesMGT Assignmentshahiduddinshaikh786No ratings yet
- Audit Comparative TableDocument5 pagesAudit Comparative TableScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Management TheoryDocument1 pageManagement TheoryNoor AminNo ratings yet
- ORGMAN - Reviewer (CH 1 - 5)Document5 pagesORGMAN - Reviewer (CH 1 - 5)Gustav SanchezNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1: The Project Management and Information Technology ContextDocument3 pagesLESSON 1: The Project Management and Information Technology ContextGeorgie AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- OMLG4Lesson1 2Document23 pagesOMLG4Lesson1 2Khassie B. GrandeNo ratings yet
- Od Chapter OneDocument8 pagesOd Chapter OnePia Izella Meulio MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Process: Understanding StrategyDocument2 pagesStrategic Management Process: Understanding StrategyJ. KNo ratings yet
- ISO 20000 Checklist: Questions for Initial Audit of Service Management SystemDocument14 pagesISO 20000 Checklist: Questions for Initial Audit of Service Management SystemARRY WIDODONo ratings yet
- Information Systems: Quantitative MethodsDocument2 pagesInformation Systems: Quantitative MethodsAnagha M NairNo ratings yet
- Nota Epsa PSLDocument14 pagesNota Epsa PSLSu Kanthi Seeniwasan100% (1)
- DLM - Lecture 1.spring 2023Document26 pagesDLM - Lecture 1.spring 2023Nada HSNNo ratings yet
- The Competency Framework 1697547786Document13 pagesThe Competency Framework 1697547786montaserangirNo ratings yet
- MBA MANAGEMENT FUNDAMENTALSDocument21 pagesMBA MANAGEMENT FUNDAMENTALSChirag PatilNo ratings yet
- MAN418 - Management and Organizational Dynamics With RubericDocument7 pagesMAN418 - Management and Organizational Dynamics With RubericHafiz Amanullah FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Managers & Managing: Efficiency, Effectiveness, Tasks & SkillsDocument2 pagesManagers & Managing: Efficiency, Effectiveness, Tasks & SkillsDiva Tertia AlmiraNo ratings yet
- COORDINATING MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS AND THEORIESDocument4 pagesCOORDINATING MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS AND THEORIESEmmanuel Villeja LaysonNo ratings yet
- Corporate GovernanceDocument1 pageCorporate GovernanceJessa RomNo ratings yet
- The Internal Alignment ChallengeDocument15 pagesThe Internal Alignment ChallengeMaria DiezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 OrganizingDocument22 pagesChapter 4 OrganizingTweenie RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument6 pagesFinals ReviewerDharnel Jude EpeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document14 pagesChapter 11Willma PaladaNo ratings yet
- Study Manual ForDocument80 pagesStudy Manual ForctroselyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Organizing and StaffingDocument65 pagesChapter 3 - Organizing and StaffingManvendra Pratap Singh Bisht80% (5)
- ISO 21001:2018 Educational Organization Management System: Depok, 23 January 2020Document77 pagesISO 21001:2018 Educational Organization Management System: Depok, 23 January 2020Hemant Dusane100% (1)
- MANAGEMENT MCQSDocument57 pagesMANAGEMENT MCQSgaikwadvedant182No ratings yet
- Orgweek1 5wpicDocument7 pagesOrgweek1 5wpicjasmineotapNo ratings yet
- CAF-4-Spring-2019 AnswerDocument6 pagesCAF-4-Spring-2019 AnswerWaqas AhmadNo ratings yet
- OrgMan 12 NotesDocument18 pagesOrgMan 12 NotesDenine Dela Rosa OrdinalNo ratings yet
- Visser-A Conceptual Framework For Maintenance ManagementDocument9 pagesVisser-A Conceptual Framework For Maintenance ManagementnuwanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Management PDFDocument99 pagesLaboratory Management PDFPam Fajardo100% (5)
- MAPR Notes PDFDocument8 pagesMAPR Notes PDFgigihdNo ratings yet
- Making Mega Health Care DecisionsDocument9 pagesMaking Mega Health Care DecisionsDipesh BajajNo ratings yet
- Manage functions & theoriesDocument3 pagesManage functions & theoriesErika Joille PatayonNo ratings yet
- Internal Control Questionnaire Control EnvironmentDocument2 pagesInternal Control Questionnaire Control EnvironmentMitch Tokong MinglanaNo ratings yet
- Management Chapter 1Document13 pagesManagement Chapter 1Pankaj SangaleNo ratings yet
- Accountability Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesAccountability Cheat Sheet: by ViaAnaze_hNo ratings yet
- Aud1206 Operations Auditing Finals ReviewerDocument3 pagesAud1206 Operations Auditing Finals ReviewerJazmine Arianne DalayNo ratings yet
- Department of Commerce, Mar Thoma College of Science & Technology, AyurDocument7 pagesDepartment of Commerce, Mar Thoma College of Science & Technology, AyurNaveen Jacob JohnNo ratings yet
- Governance Model Defined PDFDocument6 pagesGovernance Model Defined PDFWilmar CárdenasNo ratings yet
- COSO Quiz ReviewDocument24 pagesCOSO Quiz ReviewNicah AcojonNo ratings yet
- EA ToolDocument53 pagesEA ToolJojit BalodNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Business Notes (Introduction)Document2 pagesFundamentals of Business Notes (Introduction)collegestudent20000% (1)
- Sumeru CaseDocument3 pagesSumeru CaseAPARNA BARAHATENo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - PMDocument17 pagesUnit 2 - PMDIVYANo ratings yet
- Principle - Practices of Management - 3Document15 pagesPrinciple - Practices of Management - 3Dev RanjanNo ratings yet
- Anderson On Board Evaluation - Chartered Secretary (Aug 2010)Document2 pagesAnderson On Board Evaluation - Chartered Secretary (Aug 2010)David W. AndersonNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Four Main Functions of ManagementDocument2 pagesIntroduction to the Four Main Functions of ManagementSamantha Villabas IbeNo ratings yet
- A Transition Model For Agile Process Leadership ArtefactDocument9 pagesA Transition Model For Agile Process Leadership ArtefactDwane PaulsonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management Planning and OgranizationDocument2 pagesNursing Management Planning and OgranizationAndee SalegonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Type: Summative: End of CO: in LMSDocument17 pagesAssessment Type: Summative: End of CO: in LMSaniketNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Modern Management Concepts and Skills 12 e 12th Edition 0132622610Document13 pagesSolution Manual For Modern Management Concepts and Skills 12 e 12th Edition 0132622610PhilipWoodpsen100% (36)
- Ethiopian Institutes of Architecture, Building Construction and City Development (Eiabc)Document37 pagesEthiopian Institutes of Architecture, Building Construction and City Development (Eiabc)malik macNo ratings yet
- Building Better Policies: The Nuts and Bolts of Monitoring and Evaluation SystemsFrom EverandBuilding Better Policies: The Nuts and Bolts of Monitoring and Evaluation SystemsNo ratings yet
- Aesthetic 2Document8 pagesAesthetic 2heyheyNo ratings yet
- MC OS PPT StyleDocument6 pagesMC OS PPT StyleheyheyNo ratings yet
- Taxation of Partnership and PartnersDocument8 pagesTaxation of Partnership and PartnersheyheyNo ratings yet
- Estates and TrustsDocument6 pagesEstates and TrustsheyheyNo ratings yet
- FM Master Manufacturing Budgets April-June 2021Document8 pagesFM Master Manufacturing Budgets April-June 2021heyheyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AIS James HallDocument45 pagesChapter 7 AIS James HallheyheyNo ratings yet
- Presentation Flemming Ruud 2019 enDocument30 pagesPresentation Flemming Ruud 2019 enheyheyNo ratings yet
- Emerging Technologies For Business ProcessesDocument19 pagesEmerging Technologies For Business ProcessesheyheyNo ratings yet
- Ibnu Sina (With MorphDocument13 pagesIbnu Sina (With MorphheyheyNo ratings yet
- COL Finance Sample Exam PDFDocument32 pagesCOL Finance Sample Exam PDFHammad KhakwaniNo ratings yet
- Paper ResearchDocument8 pagesPaper ResearchheyheyNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Planning Handout R1Document24 pagesLong-Term Planning Handout R1sh1q2hNo ratings yet
- Activity 1.6.2Document1 pageActivity 1.6.2Stephen JohnNo ratings yet
- Risk and Capital Management Report As at 30 June 2015Document179 pagesRisk and Capital Management Report As at 30 June 2015heyheyNo ratings yet
- Asisgn. 1 Mod 2 - NCA HELD FOR SALE & DISCONTINUED OPNS.Document5 pagesAsisgn. 1 Mod 2 - NCA HELD FOR SALE & DISCONTINUED OPNS.Kristine Vertucio0% (1)
- Aesthetic Theme 2Document6 pagesAesthetic Theme 2Siti MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Video Presentation TemplateDocument3 pagesVideo Presentation TemplateSiti MaisarahNo ratings yet
- ACCTG A Final ExamDocument2 pagesACCTG A Final ExamheyheyNo ratings yet
- Presentation on Blackpink by Kim JendeukDocument6 pagesPresentation on Blackpink by Kim JendeukheyheyNo ratings yet
- How Is How When When Is When?: Google Search Google Search I'm Feeling Lucky I'm Feeling LuckyDocument3 pagesHow Is How When When Is When?: Google Search Google Search I'm Feeling Lucky I'm Feeling LuckyWushuuu PabatangNo ratings yet
- Youtube TemplateDocument5 pagesYoutube TemplateheyheyNo ratings yet
- Twice Twitter PPT TemplateDocument6 pagesTwice Twitter PPT Templateheyhey100% (1)
- Youtube TemplateDocument5 pagesYoutube TemplateheyheyNo ratings yet
- Ready For Presentation?: SubjectDocument5 pagesReady For Presentation?: SubjectHarfiansyah ArofNo ratings yet
- Explaining The Philosophical Approaches For Continuous ImprovementDocument48 pagesExplaining The Philosophical Approaches For Continuous ImprovementheyheyNo ratings yet
- CVP Multiple Product DiscussionDocument5 pagesCVP Multiple Product DiscussionheyheyNo ratings yet
- The Title and Subtitles: Everything Written HereDocument8 pagesThe Title and Subtitles: Everything Written HereheyheyNo ratings yet
- Foreign Currency Deposit Act RA 6426Document1 pageForeign Currency Deposit Act RA 6426heyheyNo ratings yet
- For 9.220, Term 1, 2002/03 02 - Lecture13.ppt Instructor VersionDocument18 pagesFor 9.220, Term 1, 2002/03 02 - Lecture13.ppt Instructor VersionheyheyNo ratings yet
- Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions For 9957W Automatic Balancing ValveDocument2 pagesInstallation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions For 9957W Automatic Balancing ValveManuel Molina CamposNo ratings yet
- Kuruk Etra:: Dharma-K Etra Śalya-ParvaDocument1 pageKuruk Etra:: Dharma-K Etra Śalya-ParvaRavinder Khullar100% (1)
- How To Make Lampblack - AllDocument6 pagesHow To Make Lampblack - AllclaudjiuNo ratings yet
- Revised Bsy Elementary Siatonwest 2 and Pio-Macahig - 2014-15 As of June 6 2014Document31 pagesRevised Bsy Elementary Siatonwest 2 and Pio-Macahig - 2014-15 As of June 6 2014api-273918959No ratings yet
- 1z0 447 DemoDocument5 pages1z0 447 Demojosegitijose24No ratings yet
- Template PharmaconDocument4 pagesTemplate PharmaconDanang RaharjoNo ratings yet
- Use of Passive VoiceDocument13 pagesUse of Passive VoiceLuciana DicieroNo ratings yet
- Review Relative Clauses, Articles, and ConditionalsDocument10 pagesReview Relative Clauses, Articles, and ConditionalsNgoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Second Travel of Rizal: Week 8 Unit 3Document22 pagesSecond Travel of Rizal: Week 8 Unit 3John Russell GasangNo ratings yet
- DesignMind Data WarehouseDocument31 pagesDesignMind Data WarehouseMark GinnebaughNo ratings yet
- Environmental, Health and Safety Guidelines For Textiles ManufacturingDocument20 pagesEnvironmental, Health and Safety Guidelines For Textiles ManufacturingHitesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Transcricao How To Be Happy (Before Success) - by Earl NightingaleDocument62 pagesTranscricao How To Be Happy (Before Success) - by Earl NightingalepauloalaraNo ratings yet
- Cultural Understanding Impacts Consumer BehaviorDocument10 pagesCultural Understanding Impacts Consumer BehaviorNguyễn Hữu Thảo NguyênNo ratings yet
- ECMT1020 - Week 06 WorkshopDocument4 pagesECMT1020 - Week 06 Workshopperthwashington.j9t23No ratings yet
- Las 4.4 - Hope 4 - Mountaineering (Hiking, Trekking, Camping, Orienteering)Document5 pagesLas 4.4 - Hope 4 - Mountaineering (Hiking, Trekking, Camping, Orienteering)Maricel EsperatNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Farrukh QAMAR - Assessment 2 Student Practical Demonstration of Tasks AURAMA006 V2Document19 pagesMuhammad Farrukh QAMAR - Assessment 2 Student Practical Demonstration of Tasks AURAMA006 V2Rana Muhammad Ashfaq Khan0% (1)
- O & M Manual TemplateDocument11 pagesO & M Manual Templatesooriya_82No ratings yet
- Otr Product CatalogDocument116 pagesOtr Product CatalogIwan KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Materials that absorb and decayDocument2 pagesMaterials that absorb and decayDominic NoblezaNo ratings yet
- 7Document19 pages7Maria G. BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering Economy: Title of The LessonDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Engineering Economy: Title of The LessonsdanharoldNo ratings yet
- Murder Conviction UpheldDocument9 pagesMurder Conviction UpheldBobNo ratings yet
- Is The Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Index An Adequate Framework To Measure The Progress of The 2030 Agenda?Document9 pagesIs The Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Index An Adequate Framework To Measure The Progress of The 2030 Agenda?hadi_friendNo ratings yet
- Employee Leave Management System: FUDMA Journal of Sciences July 2020Document7 pagesEmployee Leave Management System: FUDMA Journal of Sciences July 2020MOHAMMED ASHICKNo ratings yet
- Biotensegrity and Myofascial Chains A Global Approach To An Integrated Kinetic ChainDocument8 pagesBiotensegrity and Myofascial Chains A Global Approach To An Integrated Kinetic ChainMohamed ElMeligieNo ratings yet
- HW3 - Chapter 9-2Document3 pagesHW3 - Chapter 9-2Zachary MedeirosNo ratings yet
- EN3: Introduction To Engineering and Statics: 3. Resultant of Systems of ForcesDocument6 pagesEN3: Introduction To Engineering and Statics: 3. Resultant of Systems of ForceskarthikaNo ratings yet
- m5 Mage The AscensionDocument20 pagesm5 Mage The AscensionQuentin Agnes0% (1)
- Review of Dr. Mark Cheng's "Prehab-Rehab 101" SeriesDocument6 pagesReview of Dr. Mark Cheng's "Prehab-Rehab 101" SeriesWilliam TortorielloNo ratings yet