Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology: Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors
Uploaded by
John Pearl FernandezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pathophysiology: Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors
Uploaded by
John Pearl FernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
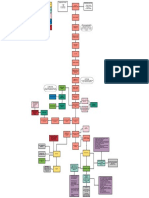
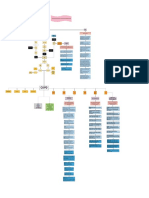
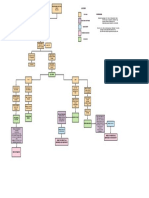
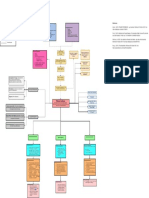
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
PREDISPOSING FACTORS PRECIPITATING FACTORS
AGE VEHICULAR ACCIDENT, ALCOHOLISM AND OCCUPATION (PLUMBER)
Direct, high energy force
(Vehicular accident) Legend:
Predisposing and Precipitating
Factors
Open bone fracture
Mechanism of Action
Signs and Symptoms
Fractures with varying degrees of
commination
Diagnostics and Laboratory Tests
GUSTILO-ANDERSON Admitting Diagnosis
CLASSIFICATION
Medical Management
Nursing Diagnosis
Type II Type IIIB
Wound – 1 to 10 cm Extensive contamination
Possible contamination
Extensive commination
Moderate commination
Extensive periosteal stripping
Open II complete, displaced, M3rd Open IIIB complete. Displaced
Femur, and Right middle Tibia Fibula Right
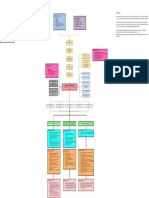
COMPLICATIONS
Immobilized leg causing decrease
Displaced fracture
in action Bleeding in the injury site Soft tissue damage
Presence of abrasions on right arm
Breakage in the skin X-ray
Limited range of motion due to Blood loss
fractures and 13 kg skeletal Abrasion on both upper extremities
traction on right leg Pain at the fracture site
Decreased fluid volume Hypo perfusion of the kidney
Slight muscle weakness on both Intense inflammatory reaction Pain scale: 8/10
legs. Decreased electrolytes Decreased production of
Erythropoietin
Ranitidine
Tramadol
Muscle grade strength 1/5 on R IV THERAPY RBC: 3.30x10
lower ext. HCT: 0.33
HGB: 10.6 g/dl Maintenance of immobilization to
#1 PLR 1L @30 gtts/min
MCH: 25.40 Acute pain Increase risk for micro bacteria facilitate bone healing
#2 PNSS 1L @30 gtts/min MCHC: 31.3 entry
Impaired physical mobility Sodium: 133.0 mmol/L
#3 D5LR 1L + Amino Acid + Sorbitol
@30 gtts/min Skeletal Traction
Kidneys are unable to filter creatinine Infection
and can cause damage
Neutrophils: 59.50%
Lymphocytes: 2.50
Creatinine: 1.44 mg/dl Monocytes: 9.50
SGOT: 48.14 Eosinophil: 3.80
SGPT: 46.96 Basophils: 0.20
Nephrotoxic drug
Cefuroxime
You might also like
- ABSITE Killer PlusDocument16 pagesABSITE Killer PlusMark Soliman100% (1)
- ARDS Concept Map - BunayogDocument2 pagesARDS Concept Map - BunayogJacela Annsyle BunayogNo ratings yet
- TAHBSO Concept MapDocument1 pageTAHBSO Concept MapSherika Mariz Moreno GuarinNo ratings yet
- With Rationale 013 Irrigating A Colostomy Students Copy 1Document5 pagesWith Rationale 013 Irrigating A Colostomy Students Copy 1John Pearl Fernandez100% (1)
- Ethical and Legal Issues in Perioperative NursingDocument3 pagesEthical and Legal Issues in Perioperative NursingJohn Pearl Fernandez100% (2)
- John Medina - Brain Rules PDFDocument11 pagesJohn Medina - Brain Rules PDFDiego Cunha100% (2)
- Medication Passport: Clinical Site Student Please Complete Student Please Complete Context Please Date and SignDocument3 pagesMedication Passport: Clinical Site Student Please Complete Student Please Complete Context Please Date and SignGiselle GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Mindanao Sanitarium & Hospital College: Brgy San Miguel, Iligan City 9200Document5 pagesMindanao Sanitarium & Hospital College: Brgy San Miguel, Iligan City 9200Kabang MoaNo ratings yet
- MDMS (Govt) SeatMatrix 2023 2024Document4 pagesMDMS (Govt) SeatMatrix 2023 2024Zora DNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Male Concept MapDocument1 pageBreast Cancer Male Concept MapJed ArominNo ratings yet
- Ilovepathology - Com (1) UrinDocument2 pagesIlovepathology - Com (1) UrinNori VeilaNo ratings yet
- GTK DrugsDocument5 pagesGTK DrugsAngela OngNo ratings yet
- Copd FinalDocument1 pageCopd FinalCourtney KateNo ratings yet
- Expert Advice For Today's Ob/Gyn: ObstetricsDocument66 pagesExpert Advice For Today's Ob/Gyn: Obstetricsjavierv44No ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument1 pageSpina BifidaKevinNo ratings yet
- Pengantar (Fix)Document21 pagesPengantar (Fix)ubayyumrNo ratings yet
- Mindanao Sanitarium & Hospital College: Brgy San Miguel, Iligan City 9200Document9 pagesMindanao Sanitarium & Hospital College: Brgy San Miguel, Iligan City 9200Kabang MoaNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Perspective. Mark Plus - FINALDocument9 pagesHealthcare Perspective. Mark Plus - FINALenggar ayusaraswatiNo ratings yet
- Parashospitaltriff PDFDocument96 pagesParashospitaltriff PDFBajane wala baba बजाने वाला बाबाNo ratings yet
- Format For Case Analysis Through Concept Mapping: I. Introduction and ObjectivesDocument2 pagesFormat For Case Analysis Through Concept Mapping: I. Introduction and ObjectivesMariel GamaloNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Format: Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors (Contributing) (Triggering)Document2 pagesPathophysiology Format: Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors (Contributing) (Triggering)AyaBasilioNo ratings yet
- Vol3 No 7 ATLS PDFDocument10 pagesVol3 No 7 ATLS PDFlinaNo ratings yet
- 69 - Principles of Cancer TreatmentDocument1 page69 - Principles of Cancer TreatmentRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial Trauma in The Emergency Department: Pearls and Pitfalls in Airway ManagementDocument13 pagesMaxillofacial Trauma in The Emergency Department: Pearls and Pitfalls in Airway ManagementWahyuNo ratings yet
- Crown LengtheningDocument11 pagesCrown LengtheningVictoria ChenNo ratings yet
- Final CasesDocument5 pagesFinal CasesKabang MoaNo ratings yet
- Borang Pemeriksaan-Mammografi 1Document2 pagesBorang Pemeriksaan-Mammografi 1hsentosaoshNo ratings yet
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease and Other Genetic PolyneuropathiesDocument18 pagesCharcot-Marie-Tooth Disease and Other Genetic PolyneuropathiesSalih ÇayırNo ratings yet
- (Select Companies Highlighted) : Tallahassee Jacksonville PensacolaDocument1 page(Select Companies Highlighted) : Tallahassee Jacksonville PensacolaCocoNo ratings yet
- Rle Requirements Wardspcl Area NCP DSDocument3 pagesRle Requirements Wardspcl Area NCP DSAzhly AntenorNo ratings yet
- Safety Pathway - Hospital - EnglishDocument1 pageSafety Pathway - Hospital - Englishamir monirNo ratings yet
- Concept Map FiguresDocument1 pageConcept Map FiguresBoy MadNo ratings yet
- CARINA Final CasesDocument5 pagesCARINA Final CasesmhynaNo ratings yet
- Lap. Promkes September Amondo 2017Document28 pagesLap. Promkes September Amondo 2017Hendrik SuparwanNo ratings yet
- Effects of Peer-Led Interventions For Patients With Cancer: A Meta-AnalysisDocument23 pagesEffects of Peer-Led Interventions For Patients With Cancer: A Meta-AnalysisMuthya GhitaNo ratings yet
- OT Brochure PDFDocument7 pagesOT Brochure PDFAngel HerreraNo ratings yet
- List of Philhealth Accredited Level 3 Hospital As of October 31, 2019Document35 pagesList of Philhealth Accredited Level 3 Hospital As of October 31, 2019Lex CatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanNecy Tessa C. AcostaNo ratings yet
- 2006casedifficultyassessmentformb Edited2010Document2 pages2006casedifficultyassessmentformb Edited2010AndreiMunteanuNo ratings yet
- Generic Concept MapDocument1 pageGeneric Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Effects of Dexamethasone in Traumatic Brain Injury.106Document7 pagesEffects of Dexamethasone in Traumatic Brain Injury.106claudio RivasNo ratings yet
- The Bethesda System For Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology 2nd EditionDocument5 pagesThe Bethesda System For Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology 2nd Editiondina adhaNo ratings yet
- 244drug Study FORM - DocsDocument3 pages244drug Study FORM - DocsJoseph Joshua OtazaNo ratings yet
- Phlebothrombosis: Azole, I. (2021) - PHLEBOTHROMBOSIS. - PPT Download. Retrieved 25 October 2021, FromDocument1 pagePhlebothrombosis: Azole, I. (2021) - PHLEBOTHROMBOSIS. - PPT Download. Retrieved 25 October 2021, FromSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- My PRC VSMMCDocument5 pagesMy PRC VSMMCapi-3733712No ratings yet
- Hannover Polytrauma Score.4Document2 pagesHannover Polytrauma Score.4Helmi IsmunandarNo ratings yet
- Venous Thrombosis: Complications of Deep Vein Thrombosis. Saint Luke's Health System. (N.D.) - Retrieved OctoberDocument1 pageVenous Thrombosis: Complications of Deep Vein Thrombosis. Saint Luke's Health System. (N.D.) - Retrieved OctoberSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Silver SulfadiazineDocument1 pageDrug Study Silver SulfadiazineMaica Lectana100% (1)
- 65 - Approach To Patients With CancerDocument1 page65 - Approach To Patients With CancerRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Orthopaedics PDFDocument70 pagesPaediatric Orthopaedics PDFBestman OjiginiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 HFMEADocument1 pageWorksheet 2 HFMEAnurNo ratings yet
- Jay MINORDocument1 pageJay MINORJay Aled ZurcNo ratings yet
- RosaDocument8 pagesRosaThaís SimionatoNo ratings yet
- Item Response Theory and Computerized Adaptive.3Document5 pagesItem Response Theory and Computerized Adaptive.3danebrosNo ratings yet
- Interaction Theories of NursingDocument1 pageInteraction Theories of NursingJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Percutaneous Needle Tenotomy - TotalCareDocument3 pagesPercutaneous Needle Tenotomy - TotalCareDaniel Alejandro Vargas PérezNo ratings yet
- Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Title 38 Physician and Dentist Pay Ranges For Use at Indian Health Service (Includes Base Pay)Document1 pageDepartment of Veterans Affairs (VA) Title 38 Physician and Dentist Pay Ranges For Use at Indian Health Service (Includes Base Pay)tieNo ratings yet
- Barlow Durand (2015) - CH2. An Integrative Approach To PsychopatologyDocument38 pagesBarlow Durand (2015) - CH2. An Integrative Approach To Psychopatologymaria joseNo ratings yet
- Osteosarcoma of The Jaw Primary Versus Secondary.62Document4 pagesOsteosarcoma of The Jaw Primary Versus Secondary.62sandip ghoseNo ratings yet
- Role of Lipids in The Regulation of InflammationDocument23 pagesRole of Lipids in The Regulation of InflammationFrancisco MirettiNo ratings yet
- Urogenital System Embryology (ANA204) OFRDocument8 pagesUrogenital System Embryology (ANA204) OFROloruntomi AdesinaNo ratings yet
- (According To Priority) (Cues & Evidences/ Objective & Subjective) (Objectives-Long Term & Short Term)Document1 page(According To Priority) (Cues & Evidences/ Objective & Subjective) (Objectives-Long Term & Short Term)opxNo ratings yet
- Goreng PisangDocument2 pagesGoreng PisangAbdul SamadNo ratings yet
- Assessment 7Document1 pageAssessment 7John Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Source Criticism Skills Reference Sheet: Skill Name Guiding QuestionsDocument1 pageSource Criticism Skills Reference Sheet: Skill Name Guiding QuestionsJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Assessment 4 A. List 9 Environmental Protection Laws and Briefly Describe EachDocument3 pagesAssessment 4 A. List 9 Environmental Protection Laws and Briefly Describe EachJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Assessment 3Document1 pageAssessment 3John Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Fernandez, John PearlDocument2 pagesFernandez, John PearlJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Assessment 5Document3 pagesAssessment 5John Pearl Fernandez100% (1)
- Communication SBAR ToolDocument1 pageCommunication SBAR ToolJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology: Nursing Health Assessment IDocument2 pagesMSU-Iligan Institute of Technology: Nursing Health Assessment IJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination and Review of Systems: Patient's Name / Room No. - 1Document2 pagesPhysical Examination and Review of Systems: Patient's Name / Room No. - 1John Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Changing A Bowel Diversion Ostomy WITH ANSWERDocument9 pagesChanging A Bowel Diversion Ostomy WITH ANSWERJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Theory and The Rise of Globalization Studies: John Pearl Fernandez - Contemporary Arts (Notes)Document11 pagesTheory and The Rise of Globalization Studies: John Pearl Fernandez - Contemporary Arts (Notes)John Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- ) Administering Nasogastric Tube or Orogastric Tube FeedingDocument6 pages) Administering Nasogastric Tube or Orogastric Tube FeedingJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Transnational Corporation (TNC) - The Central: Economic Globalization: CorporationsDocument8 pagesTransnational Corporation (TNC) - The Central: Economic Globalization: CorporationsJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Con Research Agenda: MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingDocument1 pageCon Research Agenda: MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument14 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Raw Presentation: Nicky C. Yungco, Msc. Assistant Professor Iv, Dept. of Mathematics and Statistics Msu-IitDocument19 pagesRaw Presentation: Nicky C. Yungco, Msc. Assistant Professor Iv, Dept. of Mathematics and Statistics Msu-IitJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: - SectionDocument2 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: - SectionJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- What Reflexes Should Be Present in A NewbornDocument3 pagesWhat Reflexes Should Be Present in A NewbornJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- General InstructionDocument1 pageGeneral InstructionJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Identified Problem: Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Identified Problem: Nursing DiagnosisJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Cystic Hygroma - Symptoms - Diagnosis - Treatment of Cystic Hygroma - NY Times Health InformationDocument3 pagesCystic Hygroma - Symptoms - Diagnosis - Treatment of Cystic Hygroma - NY Times Health InformationRenno AdiNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument342 pagesPDFZae M HakimNo ratings yet
- Examination of ElbowDocument18 pagesExamination of Elbowharmohit singhNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank Health Assessment For Nursing Practice 6th Edition Wilson PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank Health Assessment For Nursing Practice 6th Edition Wilson PDF Full Chapterbeatermany.imubd2100% (19)
- Lesotho Retention StrategyDocument67 pagesLesotho Retention Strategymustafa100% (2)
- Presc Audit ReportDocument85 pagesPresc Audit ReportAnuj KaushalNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 1 First Aid 2021-101-230Document130 pagesUSMLE Step 1 First Aid 2021-101-230mariana yllanesNo ratings yet
- Analytical Case Study of Bmiof Mildly Symptomatic Covid-19 Patients With Reference To MizajDocument7 pagesAnalytical Case Study of Bmiof Mildly Symptomatic Covid-19 Patients With Reference To MizajyusufNo ratings yet
- Yasir Waheed CV For HECDocument4 pagesYasir Waheed CV For HECمحمد بلال سرورNo ratings yet
- Child Labor in The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesChild Labor in The PhilippinesMark Gerald Lagamia0% (1)
- You Get To Know "Why" in Everything You Do, You'll Know More Than You Knew. 2Document16 pagesYou Get To Know "Why" in Everything You Do, You'll Know More Than You Knew. 2ChaoticMikiNo ratings yet
- Applied Bryology BryotechnologyDocument12 pagesApplied Bryology Bryotechnology-No ratings yet
- Child Abuse and Juvenile DelinquencyDocument42 pagesChild Abuse and Juvenile DelinquencyArmarni Seany Desmangles100% (2)
- Essie Hoiball and T.C. Fry - I Live On Fruit (1981)Document40 pagesEssie Hoiball and T.C. Fry - I Live On Fruit (1981)Charles100% (11)
- 2018 2019 Daily Lesson Log AutosavedDocument322 pages2018 2019 Daily Lesson Log AutosavedAinah 16No ratings yet
- Case Study Presentation-Mindy Duran-FinalDocument30 pagesCase Study Presentation-Mindy Duran-Finalapi-278622211No ratings yet
- Illich 1982Document5 pagesIllich 1982CsscamposNo ratings yet
- Cor Pulmonale PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesCor Pulmonale PATHOPHYSIOLOGYChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- DNA and ChromosomeDocument15 pagesDNA and ChromosomeYudha OkpriandaNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) : Case Investigation FormDocument2 pagesCoronavirus Disease (COVID-19) : Case Investigation FormJudeLaxNo ratings yet
- Situs Inversus JClinSci - 2018 - 15 - 3 - 168 - 244747Document4 pagesSitus Inversus JClinSci - 2018 - 15 - 3 - 168 - 244747Anonymous 9QxPDpNo ratings yet
- Bazaar DrugsDocument104 pagesBazaar DrugsKartik Vashishta100% (1)
- Sps. Flores v. Sps. PinedaDocument7 pagesSps. Flores v. Sps. PinedaRachel CayangaoNo ratings yet
- OME Video DurationsDocument7 pagesOME Video DurationsLucas RiosNo ratings yet
- USMLE 1 Hematology BookDocument368 pagesUSMLE 1 Hematology BookPRINCENo ratings yet
- Ultimate Guide To Surviving in The WildDocument175 pagesUltimate Guide To Surviving in The WildSal Ot100% (1)
- Scid 5 CVDocument26 pagesScid 5 CVZubair Mahmood KamalNo ratings yet
- Mediclaim Policy - Buy Group Health Insurance Online - Future GeneraliDocument39 pagesMediclaim Policy - Buy Group Health Insurance Online - Future GeneraliRizwan KhanNo ratings yet