0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views10 pagesBench Working and Fitting Shop: (1) Holding Device
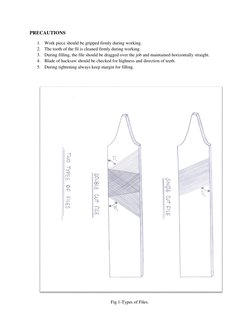
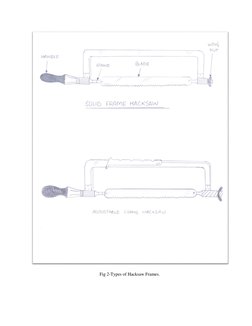
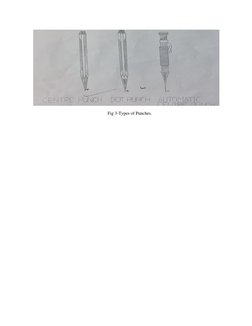
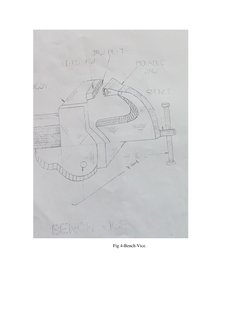
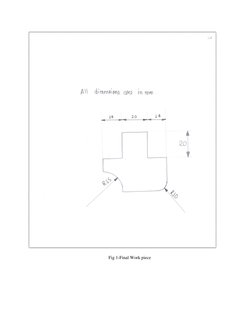
The document provides information about tools and processes used in a bench working and fitting shop. It describes various types of holding devices like vices, measuring tools like calipers and micrometers, marking tools like scribes and punches, cutting tools like chisels and hacksaws, and finishing tools like files and scrapers. It also gives examples of practical exercises performed in the shop, such as making a square piece of mild steel and creating a fitting based on a provided sketch. The key tools and materials used include hacksaws, files, mild steel, vices, calipers and hammers.
Uploaded by
Aashish KushwahaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views10 pagesBench Working and Fitting Shop: (1) Holding Device
The document provides information about tools and processes used in a bench working and fitting shop. It describes various types of holding devices like vices, measuring tools like calipers and micrometers, marking tools like scribes and punches, cutting tools like chisels and hacksaws, and finishing tools like files and scrapers. It also gives examples of practical exercises performed in the shop, such as making a square piece of mild steel and creating a fitting based on a provided sketch. The key tools and materials used include hacksaws, files, mild steel, vices, calipers and hammers.
Uploaded by
Aashish KushwahaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd