Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Force and Motion
Force and Motion
Uploaded by
ISABELITACopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Force and Motion
Force and Motion
Uploaded by
ISABELITACopyright:
Available Formats
FORCE and MOTION Law of Universal Gravitation
Force - Isaac Newton saw an apple fall on the
ground and concluded that gravity
- Can cause an object to start moving,
affects all things on earth and the whole
speed up, slow down, change direction
universe
or stop
- Proposed Idea: Sun exerts a force on
- Can be represented by an arrow
Earth and its moon, as well as on the
o Length shows the strength of
other planets in the Solar System.
the force
- Every object in the universe attracts
- F= mass x acceleration
every object with a gravitational force.
Newton – standard unit of force based on Intl o Gravitational force STRONGER
System of Units (SI) 1kg-m/s when object is MASSIVE or has
more mass.
Isaac Newton – scientist who explained how o Gravitational force WEAKER
force and motion are related. when object is FARTHER from
Forces in same direction combine each other
o Earth’s gravitational force on
Forces in opposite direction cancel our body pulls us toward the
Balanced Forces center of the Earth, so we
always fall toward the ground.
– forces that are equal and in opposite
directions Factors Affecting Gravity
- No change in motion - Depends on mass of the objects and
Examples: distance between them
- Less mass less gravitational force
- book resting on a table (gravity - Smaller distance greater
pushing it downward, table pushing it upward) gravitational force
- tug of war , balanced if both teams - Mass of earth < mass of Jupiter
exert equal force o less gravity on earth compared
to on Jupiter
Unbalanced Forces
Mass – amount of matter that an object
- One force exerted is greater than the contains
other
- Always cause a change in motion - stays the same no matter where the
- When two unbalanced forces are measurement is taken
exerted in opposite directions, the - unit of mass Kilogram
combined force is the difference - mass is the same when you are on the
between the two forces moon or on Earth
- When two balanced forces are exerted
in the same direction, the combined
force is the sum of the two forces.
Gravity – force of one object pulling on another
object
Weight – force with which an object is attracted parked on a steep surface, shoes of
toward another object ballet dancers (pointe)
- weigh more on Earth than on Moon Rolling friction – produced when an object rolls
because Earth exerts more gravitational over a surface
force than moon
- Force needed to overcome rolling
CONTACT FORCE – force that requires 2 objects friction is much less compared to the
to touch force needed to overcome sliding
friction
Friction – one kind of contact force
- Rolling friction increases when driving
- results when two objects rub against on a soft, muddy surface more
each other energy is required to plow the mud and
- makes it harder for one surface to move clear the path
past another
Fluid – substance that is capable of flowing
- amount of friction depends on Texture,
easily and changes its shape when acted upon
Shape, Speed , weight and whether
by a force
surface is wet or dry
- acts in the direction opposite the Fluid Friction – when an object moves through a
object’s motion liquid or gas
4 Types of Friction - When resistance is present to an
object’s motion through a liquid or gas
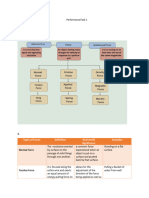
Static Friction – force that prevents an object at
- Happens when an object falls through
rest from sliding In response to the force
the air Air Resistance
exerted on it
o Parachutes increase fluid
- There can only be static friction , if force friction, slowing down the fall
is applied on an object to move it of a skydiver
- Force exerted and static friction form a - Much less than static or sliding friction
pair of BALANCED forces, thus o Reason why fluids are used to
preventing the object to move lessen friction
- May be overcome by stronger force o Fluids lubricants (oil and
o If pushed by stronger force and grease)
object moves, Static friction is - Movement of ship depends on wind
converted to Sliding Friction and resistance of water current
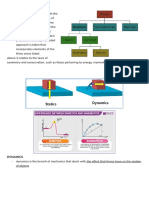
Sliding Friction – when resistive force opposes =================
the sliding of two solid surfaces over each other
Location – place where you are right now
- Depends on weight and type of surface
Galileo Galilei – first scientist who
it slides on
suggested that once an object moves, there
o Heavier object exerts more
is no force required to keep that object
pressure on surface greater
moving. Isaac Newton formulated the 3
sliding friction
Laws of Motion.
- Examples: apply hand brake or put a
heavy stone behind the tire of a car
Motion – change in position relative to a Second Law of Motion (Acceleration)
frame of reference
- Describes how acceleration, mass and
o Affected by force force are related
- Force = mass x acceleration
First Law of Motion (Inertia)
- For a given force, the greater the mass
- An object at rest will remain at rest and of an object, the smaller change in
an object in motion will remain in motion.
uniform motion in the same direction o Same force will cause an object
unless a net force acts on it with a small mass to accelerate
more than an object with a
Inertia – object’s tendency to remain in its state large mass
of motion - The greater the force applied, the
- Amount of inertia in a body has greater change in motion for a given
depends on its mass. mass.
o Greater mass, greater inertia o A large force can cause an
- Matter has inertia object to accelerate more than
a small force can.
Speed – ratio between distance and time
Third Law of Motion (Action and Reaction)
- S= D/T
- Distance travelled by a moving object - When an object exerts a force on a
per unit time second object, the second object exerts
a force on the first object as well
Distance- length between any two points - For every action, there is an equal but
Time – period during which a certain distance is opposite reaction
covered o Forces are the same in strength
but opposite in direction
Velocity – includes speed and direction - Law of Action and Reaction
- It is impossible to have one force
- Speed of an object and the direction
without an equal force opposing it
toward which it is moving
o Forces come in pairs
- Change in velocity occurs in 2 ways
o Change in speed - Examples: bump cars,
o Change in direction
- V= D with direction/ time
Acceleration – rate of change of velocity per
unit time
- Can be change in direction, speed or
both
- Any object that is changing in speed or
direction is accelerating
- Can also be a decrease in speed
Deceleration
- A=(V2- V1)/ t = distance/ t2 , m/s2
You might also like
- Coursepack Phys 2130Document214 pagesCoursepack Phys 2130andrewaoun7687No ratings yet
- Readme Corespondence AnalysisDocument3 pagesReadme Corespondence AnalysisISABELITANo ratings yet
- Physics ModuleDocument32 pagesPhysics ModuleDENOMINATOR0% (1)
- 9 ForceandlawsofmotionDocument16 pages9 ForceandlawsofmotionMeme Mayandis100% (1)
- Physics-Notes 02Document7 pagesPhysics-Notes 02JanusNo ratings yet
- 1stQA ScienceDocument3 pages1stQA ScienceAriana Kayree DavidNo ratings yet
- Science - Pointers To Review - 3QDocument33 pagesScience - Pointers To Review - 3QCathee LeañoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Reviewer 2nd MonthlyDocument2 pagesSCIENCE Reviewer 2nd MonthlyRaizza Mae NovelaNo ratings yet
- Term Definition or Information Examples/Diagrams: Newton's Laws of Motion Notes 2014-2015Document4 pagesTerm Definition or Information Examples/Diagrams: Newton's Laws of Motion Notes 2014-2015Raj Komol100% (1)
- Physics 1 - Fundamental Physics (Forces)Document6 pagesPhysics 1 - Fundamental Physics (Forces)Claire FabellarNo ratings yet
- Module in Science 6 3rd QuarterDocument7 pagesModule in Science 6 3rd QuarterLaurence MacasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4. Week 4. Phy1105Document4 pagesLecture 4. Week 4. Phy1105Farzana AlamNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 - Q4 Science LessonDocument13 pagesGrade 4 - Q4 Science LessonHF ManigbasNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Summary Notes)Document7 pagesUnit-1 (Summary Notes)chellykuukiNo ratings yet
- Physics Nmat ReviewerDocument7 pagesPhysics Nmat ReviewerLeanna DaneNo ratings yet
- Module 1 and 2 Notes - Grade 8Document6 pagesModule 1 and 2 Notes - Grade 8Jenny JuanitezNo ratings yet
- P1 Chapter 1Document1 pageP1 Chapter 1Rehan ShahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 MotionDocument4 pagesLecture 2 MotionAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- ST00602 Lec2 Forces and MotionDocument115 pagesST00602 Lec2 Forces and MotionImran AminNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument39 pagesPHYSICSF E R N A NNo ratings yet
- What Is Force and MotionDocument2 pagesWhat Is Force and MotionJJ SurioNo ratings yet
- Force and Friction UstDocument24 pagesForce and Friction UstConrado Dominic Ordinario Ruiz100% (1)
- ForcesDocument21 pagesForcesLovejoy TiñaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 3 LectureDocument2 pagesModule 1 3 LectureaileenNo ratings yet
- What Is PhysicsDocument5 pagesWhat Is PhysicswatermelonNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws - Lesson 2 - Force and Its RepresentationDocument19 pagesNewton's Laws - Lesson 2 - Force and Its RepresentationMartin BaalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-Different Types of ForcesDocument56 pagesLesson 1-Different Types of Forcesclyde domingoNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 6 CDCDocument3 pagesScience Grade 6 CDCVlad VizcondeNo ratings yet
- FORCESDocument11 pagesFORCESJennieNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newtons LawsDocument17 pagesForces and Newtons LawsChun MaruNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. Motion and Forces 2023 To 2024 VersionDocument37 pagesUnit 2. Motion and Forces 2023 To 2024 VersionMr. CNo ratings yet
- FORCESDocument46 pagesFORCESLiericka May SupasNo ratings yet
- Forces - Notes From SLSDocument2 pagesForces - Notes From SLSVanessa OngNo ratings yet
- Gravity Friction and Pressure DLDocument7 pagesGravity Friction and Pressure DLpaulNo ratings yet
- Law of MotionDocument76 pagesLaw of MotionLove With Books 2470% (1)
- Group3 PhysicsDocument26 pagesGroup3 PhysicsCarl Eric Amora Velasco IINo ratings yet
- Of Motion and Describe The Motion of All ObjectsDocument4 pagesOf Motion and Describe The Motion of All ObjectsAnn AtienzaNo ratings yet
- P Forces Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesP Forces Knowledge Organiserc.sproatNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter PhysicsDocument4 pages3rd Quarter PhysicsEricka BobadillaNo ratings yet
- Asm1 8776Document4 pagesAsm1 8776vishwajitmisal0No ratings yet
- PHYSICS HANDOUT Newtons LawDocument6 pagesPHYSICS HANDOUT Newtons LawAlexander DolinNo ratings yet
- Force Causes Change in Motion By: Avigael MarayaDocument18 pagesForce Causes Change in Motion By: Avigael MarayaHazel LiporadaNo ratings yet
- M16 ForceDocument60 pagesM16 ForceGiselle GiganteNo ratings yet
- General Physics: Newton Law of MotionDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics: Newton Law of MotionJewel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- PT#1 - ScienceDocument3 pagesPT#1 - ScienceCearaVie MadronioNo ratings yet
- Science - Forces1123333Document17 pagesScience - Forces1123333Saarah KhanNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Modules - Q3 - Sir AljonDocument14 pagesScience 6 - Modules - Q3 - Sir AljonNojla SenoirbNo ratings yet
- 7 Force and FrictionDocument14 pages7 Force and Frictionapi-314464220No ratings yet
- Free-Body Diagrams PDFDocument33 pagesFree-Body Diagrams PDFRITUPARNA BISWASNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 GravitationDocument27 pagesChapter - 3 GravitationSwayam Subhankar dasNo ratings yet
- What Is A Force? 2. How Is The Car Able To Move and Stop? 3. What Is Keeping It On The Ground?Document11 pagesWhat Is A Force? 2. How Is The Car Able To Move and Stop? 3. What Is Keeping It On The Ground?Cinara RahimovaNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument16 pagesForceLIZETTE GARCIANo ratings yet
- 3 Gaya, Usaha, Dan EnergiDocument29 pages3 Gaya, Usaha, Dan EnergiResa AlamsyahNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1Document2 pagesGeneral Physics 1Aifah HernandezNo ratings yet
- DYNAMICSDocument6 pagesDYNAMICSFatima NadeemNo ratings yet
- Contact Versus Action-at-a-Distance ForcesDocument5 pagesContact Versus Action-at-a-Distance ForcesAna Marie RentonNo ratings yet
- Forces Card Sort AnswersDocument4 pagesForces Card Sort AnswersGabriel PoonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document74 pagesChapter 3Thalagawali RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Sample Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 11 (7e)Document1 pageSample Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 11 (7e)Lovie AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Physics VIVA PPT Group 5Document11 pagesPhysics VIVA PPT Group 5NIHARIKA JHANo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 General Physics 2 SLM EditedDocument7 pagesLesson 1 General Physics 2 SLM EditedDIANNE PLANANo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Chapter 10 GravitationDocument6 pagesClass 9 Science Chapter 10 GravitationUNBOXING GURUJINo ratings yet
- 96 The Effects of GravityDocument7 pages96 The Effects of GravityGabe SkorczNo ratings yet
- PE Reaction PaperDocument1 pagePE Reaction PaperISABELITANo ratings yet
- Populations and CommunitiesDocument4 pagesPopulations and CommunitiesISABELITANo ratings yet
- Examples Colloids: SubstanceDocument4 pagesExamples Colloids: SubstanceISABELITANo ratings yet
- The Legend of Kapeng BarakoDocument1 pageThe Legend of Kapeng BarakoISABELITANo ratings yet
- Math Awareness Week Competition: 2007 Examination For 3rd-4th GradesDocument1 pageMath Awareness Week Competition: 2007 Examination For 3rd-4th GradesISABELITANo ratings yet
- How Is The Church, The Sheepfold of Christ?Document3 pagesHow Is The Church, The Sheepfold of Christ?ISABELITANo ratings yet
- Primary Division New PRACTICE SET #2: Abca Ab BC CA AbcaDocument6 pagesPrimary Division New PRACTICE SET #2: Abca Ab BC CA AbcaISABELITANo ratings yet
- Stomer Savin Credit Atm Cacdspecial CH Personal Home Equitinstlmnt L Invest Fun Joe Mary John Paul George Cust12 Cust13 - . - . .Document6 pagesStomer Savin Credit Atm Cacdspecial CH Personal Home Equitinstlmnt L Invest Fun Joe Mary John Paul George Cust12 Cust13 - . - . .ISABELITANo ratings yet
- Penalty Point Will Be Deducted For Incorrect Answers.) : ST THDocument4 pagesPenalty Point Will Be Deducted For Incorrect Answers.) : ST THISABELITA100% (1)
- Math Awareness Month CompetitionDocument2 pagesMath Awareness Month CompetitionISABELITANo ratings yet
- Math Awareness Month CompetitionDocument1 pageMath Awareness Month CompetitionISABELITANo ratings yet
- 2005 Aitmo IndividualDocument4 pages2005 Aitmo IndividualISABELITANo ratings yet
- COMPILED 3RD PERIODICAL TEST (Mam Inkay Peralta)Document94 pagesCOMPILED 3RD PERIODICAL TEST (Mam Inkay Peralta)Jaizy BartoloNo ratings yet
- 2005 Aitmo TeamDocument2 pages2005 Aitmo TeamISABELITANo ratings yet
- Science 5 QTR 1Document4 pagesScience 5 QTR 1ISABELITANo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Lesson Plan Week 5Document7 pagesGrade 11 Lesson Plan Week 5Nouman ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Pure Mathematics and MechanicsDocument8 pagesQuestion Paper Pure Mathematics and MechanicsSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Gravity - Definition, Physics, & Facts - BritannicaDocument1 pageGravity - Definition, Physics, & Facts - Britannicaxxxbilly1986xxxNo ratings yet
- The Aristotelian and Galilean Conceptions of Vertical, Horizontal and Projectile MotionsDocument3 pagesThe Aristotelian and Galilean Conceptions of Vertical, Horizontal and Projectile MotionsRia Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Motionmountain Volume1 PDFDocument601 pagesMotionmountain Volume1 PDFAngelNo ratings yet
- AIATS Schedule For RM (XII Passed) 2020-21Document2 pagesAIATS Schedule For RM (XII Passed) 2020-21FarhanNo ratings yet
- College Physics 1st Edition Freedman Solutions ManualDocument34 pagesCollege Physics 1st Edition Freedman Solutions Manuallorijonescjqkbxwnom100% (30)
- 1.relativity 1 2 Spring 22-23Document31 pages1.relativity 1 2 Spring 22-23arthey FriendNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Cambridge International As and A Level Physics Workbook With CD Rom Cambridge International Examinations 2Nd Edition David Sang PDFDocument54 pagesFull Chapter Cambridge International As and A Level Physics Workbook With CD Rom Cambridge International Examinations 2Nd Edition David Sang PDFmichelle.schwartz743100% (1)
- Scientific+Revolution+Thinkers+DBQ+Part+2 (1) COMPLETEDDocument4 pagesScientific+Revolution+Thinkers+DBQ+Part+2 (1) COMPLETEDVerosicallaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 CURRICULUM MAP MODIFIEDDocument43 pagesGrade 8 CURRICULUM MAP MODIFIEDALONANo ratings yet
- GG Stokes 1845 PDFDocument55 pagesGG Stokes 1845 PDFAnkit soniNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Physics (30S) : A Course For Independent StudyDocument50 pagesGrade 11 Physics (30S) : A Course For Independent StudylynNo ratings yet
- Physics Module Forces & MotionDocument87 pagesPhysics Module Forces & Motionnickphysics4927100% (1)
- Constraint PDFDocument12 pagesConstraint PDFNeelesh BenaraNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Rectilinear Motion and Free FallingDocument10 pagesModule 7 Rectilinear Motion and Free FallingJay LopezNo ratings yet
- Coast Guard Navik DB SyllabusDocument1 pageCoast Guard Navik DB SyllabusDhruv SinghNo ratings yet
- ENS 130 ENVIRONMENTAL PHYSICS - Revised - No AnswersDocument84 pagesENS 130 ENVIRONMENTAL PHYSICS - Revised - No AnswersDynah WairimuNo ratings yet
- Principles of Traditional Animation - John LasseterDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Traditional Animation - John LasseterJansen DavidNo ratings yet
- Summer Experiment 5 (Physics For Eng) .UpdatedDocument6 pagesSummer Experiment 5 (Physics For Eng) .Updatedjhayve stephen mark patrimonioNo ratings yet
- 1 CMS 2017-18Document22 pages1 CMS 2017-18anislinek15No ratings yet
- CAPE PHYSICS UNIT 1 LessonDocument21 pagesCAPE PHYSICS UNIT 1 LessonA.BensonNo ratings yet
- Mock Board Examination in Geas ADocument9 pagesMock Board Examination in Geas AmonNo ratings yet
- Problem 6Document42 pagesProblem 6ahmedNo ratings yet
- Wk1-2 Module 1Document61 pagesWk1-2 Module 1JonathanNo ratings yet
- UT & TE Planner - AY 2023-24 - Phase-01Document1 pageUT & TE Planner - AY 2023-24 - Phase-01Atharv KumarNo ratings yet