Professional Documents
Culture Documents
XRIO Converter Manual AREVA P443 P445 ENU TU2.22 V1.000
Uploaded by
Sakthi MuruganCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
XRIO Converter Manual AREVA P443 P445 ENU TU2.22 V1.000
Uploaded by
Sakthi MuruganCopyright:
Available Formats
OMICRON PTL AREVA P443 P445 XRIO Converter User Manual
OMICRON PTL
XRIO Converter
AREVA MiCOMho P443 and P445
User Manual
V1.000
© OMICRON electronics GmbH 1/13
OMICRON PTL AREVA P443 P445 XRIO Converter User Manual
Contents
1 General Information ..................................................................................................................................3
2 Quick Start Information ............................................................................................................................3
3 Using the Converter..................................................................................................................................4
4 Required Software Version ......................................................................................................................4
5 Functional Range ......................................................................................................................................4
6 Not Supported Functions .........................................................................................................................5
7 OMICRON Test Strategy ...........................................................................................................................5
8 Converter Structure ..................................................................................................................................6
8.1 AREVA P443 P445 Section .................................................................................................................6
8.1.1 Relay Parameter Section Block......................................................................................................6
8.1.2 Additional Information.....................................................................................................................6
8.1.3 Template Controller (Advanced view) ............................................................................................7
8.1.4 RIOPlus (Advanced view)...............................................................................................................8
8.1.4.1 NamePlate...............................................................................................................................8
8.1.4.2 ProtectedObject ......................................................................................................................8
8.1.4.3 PowerSystemParameters .......................................................................................................8
8.1.4.4 DistanceProtection ..................................................................................................................8
8.1.4.5 SwitchOnToFaultFunction.......................................................................................................9
8.1.4.6 OvercurrentProtection (Main CT) ............................................................................................9
8.2 RIO .....................................................................................................................................................10
8.2.1 Distance........................................................................................................................................10
8.2.2 Phase Overcurrent .......................................................................................................................10
8.2.3 Earth Fault ....................................................................................................................................10
8.3 Activating the RIO functions ...............................................................................................................11
8.4 Specific Features................................................................................................................................11
8.4.1 Not-Supported Parameters...........................................................................................................11
8.4.2 Loop Impedances for phase to ground distance zones ...............................................................11
8.4.3 Mho dynamic expansion...............................................................................................................12
8.4.4 Quadrilateral phase resistive reaches ..........................................................................................12
8.4.5 Phase Overcurrent Forward/Reverse testing ...............................................................................12
8.4.6 Earth Fault Forward/Reverse testing............................................................................................12
8.4.7 Handling the Binary String Value .................................................................................................12
© OMICRON electronics GmbH 2/13
OMICRON PTL AREVA P443 P445 XRIO Converter User Manual
1 General Information
The AREVA P443 P445 XRIO converter is designed for testing AREVA MiCOMho P44y (P443 and P445)
distance protection relays by using the OMICRON Test Universe 2.22 software. The converter provides all
necessary data for testing the distance, phase overcurrent and earth fault overcurrent protection functions
of the MiCOMho P44y relays.
Note: The abbreviation P44y is always used for P443 or P445 relays. It is never used for P441, P442 or
P444 relays, as they differ too much from the above named.
The converter was tested with the following relay:
• AREVA MiCOMho P443
• Catalog number: P443217A4B0200G
Note: This converter was tested with the relay described above. It will also work with AREVA P445
distance protection relays. However, be aware that the P445 relays have less functionality than the P443
relays (e.g. only Mho characteristic for Distance phase zones). In this case, set the additional parameters
accordingly. See the relay documentation for more information.
2 Quick Start Information
To work with the AREVA P44y XRIO converter:
1. Start a new OMICRON Control Center (OCC) document or open an existing OCC document.
2. Insert a new test object or open the existing test object.
3. On the File menu, click Import.
4. Browse to the "AREVA P443 P445 ENU TU2.22 Vx.xxx.xrio" file.
5. Click Open.
6. Enter all necessary settings in the Relay Parameter Section.
7. Click OK.
Figure 1: Opening and importing the AREVA P44y XRIO converter
© OMICRON electronics GmbH 3/13
OMICRON PTL AREVA P443 P445 XRIO Converter User Manual
3 Using the Converter
The AREVA P44y XRIO converter can be used as a stand-alone converter or in association with a relay
specific test template, for example with the OMICRON Distance Protection template for the AREVA P44y
relay.
In any way the converter is used, follow the quick start instructions and create your test by using
LinkToXRIO or start using the relay specific test template (for more information, see the test template
documentation).
4 Required Software Version
To use this converter, you must have a valid license for the OMICRON Test Universe 2.22 software or
later.
5 Functional Range
The AREVA P44y XRIO converter implements the following functions:
• 21P/21G Distance protection (Mho and Quad)
• 50/27 Switch on to Fault
• 50/51/67 Phase overcurrent
• 50N/51N/67N Earth/ground overcurrent
Figure 2: Functional range of the AREVA P44y XRIO converter
© OMICRON electronics GmbH 4/13
OMICRON PTL AREVA P443 P445 XRIO Converter User Manual
Some of the functions listed above use the RIO interface of the Test Universe software. Consequently, the
test modules are configured automatically without using LinkToXRIO.
The following functions are using the RIO interface:
• 21P/21G Distance protection (Mho and Quad)
• 50/51/67 Phase overcurrent
• 50N/51N/67N Earth/ground overcurrent
For testing the other functions, you must use LinkToXRIO.
6 Not Supported Functions
The following functions are currently not supported:
• Setting the group change options
• Directional Earth Fault (DEF) unit protection
• Delta directional comparison
• 85 Communication-aided schemes
• 67/46 Negative Sequence overcurrent
• 46BC Broken conductor
• 59N Residual voltage protection
• 49 Thermal overload
• 68 Power Swing Blocking
• 78 Out of Step Tripping
• 27/59 Voltage protection
• 50BF CB Fail
• Current and Voltage transformer Supervision (CTS / VTS)
• 79 Autoreclose
• 25 Check synchronism
Although these functions are not supported, their setting values are available in the Relay Parameter
Section.
7 OMICRON Test Strategy
The OMICRON test strategy is described in the OMICRON Protection Test Template (PTT) Distance
Protection documentation. For detailed information, see the PTT Distance Protection documentation for
the AREVA P443 and P445.
© OMICRON electronics GmbH 5/13
OMICRON PTL AREVA P443 P445 XRIO Converter User Manual
8 Converter Structure
The converter is divided into two sections: the AREVA P443 P445 section and the RIO section. Both
sections consist of several function blocks.
8.1 AREVA P443 P445 Section
The Relay Parameter Section includes parameters which can be changed by the user. All relay
parameters are included in this section and can be set to the actual relay values.
8.1.1 Relay Parameter Section Block
Setting parameters are included in this block. The parameters are grouped and named as in the AREVA
MiCOM S1 Studio Version 3.0.0 software. Each parameter in this block can be identified by its Parameter
Name or Foreign ID, which is identical to the parameter Name and Address (C.R), respectively, in the
MiCOM S1 Studio software.
Figure 3: Setting the parameters in the Relay Parameter Section
8.1.2 Additional Information
This block has been added for relay specific parameters such as tolerances which cannot be set by the
user, because they are constant values. All values set in this block can be found in the chapter "Technical
Data" of the relay's documentation. Typically, these blocks do not have to be changed (except the
General and Circuit Breaker Information blocks), as they are already set to the values given in the user
manual of the relay.
© OMICRON electronics GmbH 6/13
OMICRON PTL AREVA P443 P445 XRIO Converter User Manual
Figure 4: Setting general information
The parameters contained in the General Information block are linked to the device part of the RIO
section and are available in the test report.
8.1.3 Template Controller (Advanced view)
The Template Controller block contains special values which are needed for some tests, especially for
tests by using LinkToXRIO. These are mainly calculated values which cannot be calculated by using
LinkToXRIO and therefore have to be stored in this section. Other values needed for customer designed
tests can be stored in this block.
© OMICRON electronics GmbH 7/13
OMICRON PTL AREVA P443 P445 XRIO Converter User Manual
8.1.4 RIOPlus (Advanced view)
The RIOplus block contains the interface, which provides the link between the XRIO converter and all test
modules which have no access to RIO functions. All tests using basic test modules like Ramping or State
Sequencer have to be linked to the parameters in the RIOplus section of the converter.
8.1.4.1 NamePlate
The NamePlate block contains all necessary information to identify the protection device to be tested. This
block contains the relay vendor, serial number, model, the relay location and a description.
8.1.4.2 ProtectedObject
The Protected Object block contains the positive sequence line impedance value.
8.1.4.3 PowerSystemParameters
The number of phases, phase rotation and the nominal frequency are stored in this block.
8.1.4.4 DistanceProtection
This block contains all data necessary to test the Phase and Ground Distance protection function and the
Load Blinder function of the relay. The nominal values and CT/VT settings used by this protection function
can be found here. All distance and load blinder zones are modeled as sub blocks of the
DistanceProtection\ImpedanceZoneElements block. Each zone sub block stores information about the
reactive and resistive zone reach, the grounding factor, the trip time and characteristic shape of the
modeled distance zone. The following distance protection and load blinder zones are modeled in the
DistanceProtection block:
• MhoPhaseZone1: Zone 1 (Mho) of the Phase Distance protection function
• MhoPhaseZone2: Zone 2 (Mho) of the Phase Distance protection function
• MhoPhaseZone3: Zone 3 (Mho) of the Phase Distance protection function
• MhoPhaseZoneP: Zone P (Mho) of the Phase Distance protection function
• MhoPhaseZone4: Zone 4 (Mho) of the Phase Distance protection function
• MhoPhaseZone1X: Zone 1 Extended (Mho) of the Phase Distance protection function
• MhoGroundZone1: Zone 1 (Mho) of the Ground Distance protection function
• MhoGroundZone2: Zone 2 (Mho) of the Ground Distance protection function
• MhoGroundZone3: Zone 3 (Mho) of the Ground Distance protection function
• MhoGroundZoneP: Zone P (Mho) of the Ground Distance protection function
• MhoGroundZone4: Zone 4 (Mho) of the Ground Distance protection function
• MhoGroundZone1X: Zone 1 Extended (Mho) of the Ground Distance protection function
• QuadPhaseZone1: Zone 1 (Quad) of the Phase Distance protection function
• QuadPhaseZone2: Zone 2 (Quad) of the Phase Distance protection function
• QuadPhaseZone3: Zone 3 (Quad) of the Phase Distance protection function
• QuadPhaseZoneP: Zone P (Quad) of the Phase Distance protection function
• QuadPhaseZone4: Zone 4 (Quad) of the Phase Distance protection function
• QuadPhaseZone1X: Zone 1 Extended (Quad) of the Phase Distance protection function
• QuadGroundZone1: Zone 1 (Quad) of the Ground Distance protection function
• QuadGroundZone2: Zone 2 (Quad) of the Ground Distance protection function
• QuadGroundZone3: Zone 3 (Quad) of the Ground Distance protection function
• QuadGroundZoneP: Zone P (Quad) of the Ground Distance protection function
• QuadGroundZone4: Zone 4 (Quad) of the Ground Distance protection function
• QuadGroundZone1X: Zone 1 Extended (Quad) of the Ground Distance protection function
© OMICRON electronics GmbH 8/13
OMICRON PTL AREVA P443 P445 XRIO Converter User Manual
• LoadBlinderFwd: Positive sector of the Load Blinder function
• LoadBlinderRev: Negative sector of the Load Blinder function
The directional element supervising the distance protection function of the P44y relay is modeled as sub
block of the DistanceProtection\DirectionalElements block.
The minimum current sensitivities for the tripping zones are stored in the sub blocks of the
DistanceProtection\StartingElements block.
8.1.4.5 SwitchOnToFaultFunction
This block contains all necessary data to test the switch on to fault protection function. The nominal values
and the CT/VT settings used by this protection function can be found here. The main setting parameters
of the switch on to fault are:
• SOTF Delay
• TOC Reset Delay
These main setting parameters are stored in the SwitchOnToFaultElement1 of the
SwitchOnToFaultElements block, as pre-fault states under the TestCondition block.
8.1.4.6 OvercurrentProtection (Main CT)
This block contains all necessary data to test the overcurrent protection functions (phase overcurrent and
Earth-Fault). These functions are based on the evaluation of the phase currents (Main CT). The nominal
values and CT/VT settings, used by these protection functions, can be found here. All overcurrent stages
are modeled as sub blocks of the OvercurrentElements block. Each function sub block stores information
about the supervised current, pickup value, pickup-drop off ratio, operating time, operating/reset curve
types and directional element of the modeled protection function. The modeled functions in this block are:
• 50/51/67 Phase overcurrent stages
• 50N/51N/67N Earth/ground overcurrent stages
© OMICRON electronics GmbH 9/13
OMICRON PTL AREVA P443 P445 XRIO Converter User Manual
8.2 RIO
The RIO section of the converter contains all specialized RIO functions which are needed to use the more
specialized test modules (like Advanced Distance or Overcurrent) provided by the OMICRON Test
Universe software.
Warning: Do not change any values in this section. The values have been set using the relay settings of
the Relay Parameter Section.
Note: Do not activate the former test object view in the advanced mode of the XRIO test object. Changing
parameters in this view may disable formulas in the RIO section.
8.2.1 Distance
This RIO function provides all necessary values for testing the Phase Distance, Ground Distance and
Load Blinder functions with the Advanced Distance test module.
8.2.2 Phase Overcurrent
This RIO function provides all necessary values for testing the phase overcurrent protection function with
the Test Universe Overcurrent test module.
The following RIO functions for testing this protection functions are available:
• Phase Overcurrent Forward direction
• Phase Overcurrent Reverse direction
The AREVA P44y XRIO converter constructs a resulting characteristic curve for each direction of the
phase overcurrent elements. This means that directional and non-directional stages are compared for
forward and reverse direction. The three smaller stages (of each forward and reverse direction) are
combined and the resulting characteristic curve is shown in the correspondent RIO overcurrent function
block. Non-directional stages will be considered for both forward and reverse directions.
8.2.3 Earth Fault
This RIO function provides all necessary values for testing the earth/ground overcurrent protection
function with the Test Universe Overcurrent test module.
The following RIO functions for testing this protection functions are available:
• Earth Fault Forward direction
• Earth Fault Reverse direction
The AREVA P44y XRIO converter constructs a resulting characteristic curve for each direction of the
earth fault elements. This means that directional and non-directional stages are compared for forward and
reverse direction. The three smaller stages (of each forward and reverse direction) are combined and the
resulting characteristic curve is shown in the correspondent RIO overcurrent function block. Non-
directional stages will be considered for both forward and reverse directions.
© OMICRON electronics GmbH 10/13
OMICRON PTL AREVA P443 P445 XRIO Converter User Manual
8.3 Activating the RIO functions
The RIO functions have to be set to active manually in each Overcurrent test module if the converter is
used in the stand-alone mode. Activate the corresponding RIO function you intend to use in the local test
object as shown bellow.
Figure 5: Activating a RIO function
8.4 Specific Features
This section deals with special requirements of some of the converter functions. Functions not listed here
have no known limitations to their functionalities.
8.4.1 Not-Supported Parameters
The setting parameter "Load Blinder V<" (31.D6) for the Load Blinder function is not taken in
consideration. For test shots with testing voltages smaller than this parameter, the load blind function is
bypassed. For this reason, try to avoid selection of test shots inside the Load Blinder zone that have
voltage values smaller than this setting.
The converter doesn't support Mutual coupling compensation between two parallel lines. The replica
impedance is not adjusted due to the mutual compensation factor kZm (settings 30.07; 30.08; 30.09 and
30.0A).
8.4.2 Loop Impedances for phase to ground distance zones
The Mho and Quad characteristics for phase to ground faults are modeled as loop impedances. This
means, the residual compensation modifies the replica impedance for each zone. Therefore their shape
and size shown in the impedance plane may differ from what can be expected from the setting values. It is
modeled in this way for two reasons:
a) The grounding factor for Mho zones is calculated by the RIO Distance function differently than the
relay;
b) The possibility to set different grounding factors for each zone (Quad or Mho).
© OMICRON electronics GmbH 11/13
OMICRON PTL AREVA P443 P445 XRIO Converter User Manual
Because of that, the internal calculation by the RIO Distance function is deactivated and the loop
impedances are used instead. Phase to phase zones are not covered by this specialty.
8.4.3 Mho dynamic expansion
The Mho characteristic modeled in the XRIO-converter is only valid for the Test Model selected as
"Constant test current" (ITest). If constant source impedance is set in the test settings of an Advanced
Distance test module, the Mho characteristic is different from the shown characteristic of the impedance
test plane. This happens due to the test voltage and test current dependency of the Mho characteristic
dynamic expansion in the P44y relays.
8.4.4 Quadrilateral phase resistive reaches
As mentioned in the P44y relay documentation, the phase resistive reach setting defines the fault arc
resistance that can be detected for a phase-phase fault. For such a fault, half of the fault resistance
appears in the positive sequence network, and half in the negative sequence network. Since the test
module shows the impedance characteristics in positive sequence terms, the right-hand intercept for
phase to phase faults will be found at half the setting applied (=Rph/2). Phase to ground zones are not
covered by this specialty, since they are shown as loop impedances as explained above.
8.4.5 Phase Overcurrent Forward/Reverse testing
For a successful test with the P44y converter, only one of the phase overcurrent stages in each direction
can have an IDMT characteristic which must have the smallest pickup value. The others must have a
definite time (DT) characteristic.
8.4.6 Earth Fault Forward/Reverse testing
For a successful test with the P44y converter, only one of the earth fault stages in each direction can
have an IDMT characteristic which must have the smallest pickup value. The others must have a definite
time (DT) characteristic.
8.4.7 Handling the Binary String Value
Some setting parameters of the relay can be entered in the MiCOM S1 Studio software using a pop-up
window with multiple selection options. The selection is represented in the parameter as a string of
binaries.
Figure 6: Binary String parameter in MiCOM S1 Studio
© OMICRON electronics GmbH 12/13
OMICRON PTL AREVA P443 P445 XRIO Converter User Manual
In the converter, the user must enter these values with the corresponding binary code as a string of zeros
and ones. Pay attention to the number of required bits of each setting value.
Figure 7: Binary String parameter in Converter
© OMICRON electronics GmbH 13/13
You might also like
- T3000 User Guide PDFDocument126 pagesT3000 User Guide PDFThanapaet Rittirut100% (2)
- Manual G36 O2 Analyzer - V.2.04 July 2017Document46 pagesManual G36 O2 Analyzer - V.2.04 July 2017Isidoros100% (3)
- The Technology of Instrument Transformers: Current and Voltage Measurement and Insulation SystemsFrom EverandThe Technology of Instrument Transformers: Current and Voltage Measurement and Insulation SystemsNo ratings yet
- f0253805 Vacutap VM enDocument10 pagesf0253805 Vacutap VM enhardian syaputraNo ratings yet
- 1MRB520006-BEN en XS92b Computer-Based 3-Phase Test SetDocument14 pages1MRB520006-BEN en XS92b Computer-Based 3-Phase Test SetFredrikNo ratings yet
- Catalogue - 40.5kV T Type OVCB PDFDocument20 pagesCatalogue - 40.5kV T Type OVCB PDFGanesh Duraisamy0% (1)
- DHS0001 HVA60 Service Manual b2 EN Rev01 - Physical Inspection Rev04Document12 pagesDHS0001 HVA60 Service Manual b2 EN Rev01 - Physical Inspection Rev04César ToquicaNo ratings yet
- Areva p132 p139 612 Xrio Converter Manual Enu Tu2.30 v1.000Document8 pagesAreva p132 p139 612 Xrio Converter Manual Enu Tu2.30 v1.000Robert MihayoNo ratings yet
- Turbine StartupDocument16 pagesTurbine StartupSakthi Murugan100% (1)
- Testing Procedure For Transmission System Protection Schemes For Vol IIDocument346 pagesTesting Procedure For Transmission System Protection Schemes For Vol IISakthi Murugan100% (1)
- PowerCommand Control ANSI Protective Functions Application Manual A058E477 - I1 - 201711Document58 pagesPowerCommand Control ANSI Protective Functions Application Manual A058E477 - I1 - 201711John67% (3)
- 07 TT 03 Using-DfrDocument5 pages07 TT 03 Using-Dfrcarlos vidalNo ratings yet
- COMPANO 100 User Manual ENUDocument172 pagesCOMPANO 100 User Manual ENUstartservice.cpsNo ratings yet
- NANJING REL ManualDocument470 pagesNANJING REL Manualajeez86No ratings yet
- ADR219 CMDocument133 pagesADR219 CMRajiv ChandranNo ratings yet
- 7SA522 CatalogueDocument53 pages7SA522 Cataloguetayson2002No ratings yet
- Service Manual R8605B Type M301, M302 System Analysis and Measurement CentreDocument268 pagesService Manual R8605B Type M301, M302 System Analysis and Measurement Centredave chaudhury100% (1)
- R6121e Mopn 0102Document14 pagesR6121e Mopn 0102zain shafiqNo ratings yet
- Transformer REFDocument4 pagesTransformer REFs_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- JVS Manual JRP 011Document12 pagesJVS Manual JRP 011Tamilventhan_sNo ratings yet
- ABB Relay REPAIRSDocument11 pagesABB Relay REPAIRSdarsu NaikNo ratings yet
- Referral Guide20 Jan 13Document16 pagesReferral Guide20 Jan 13Rambabu NagallaNo ratings yet
- P633 - Test - Tools Farhad Rev 01Document4 pagesP633 - Test - Tools Farhad Rev 01Mosa Elnaid ElnaidNo ratings yet
- Type P8n, PQ8n, PN8n: Auxiliary RelayDocument7 pagesType P8n, PQ8n, PN8n: Auxiliary RelayDinesh ThevanNo ratings yet
- Micom - 211 Motor Protection Relay Used For 275kwDocument8 pagesMicom - 211 Motor Protection Relay Used For 275kwShrikant KajaleNo ratings yet
- Inadvertent Energization Generator Protection IEEEDocument1 pageInadvertent Energization Generator Protection IEEEFirmanJohannesMaruliTuaSimanullangNo ratings yet
- Technical Overview of the MiCOM Px4x Protection Relay RangeDocument148 pagesTechnical Overview of the MiCOM Px4x Protection Relay RangeRichard Callo CNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Classical Ancillary Equipment CatalogueDocument94 pagesAuxiliary Classical Ancillary Equipment CatalogueĐinh ĐạtNo ratings yet
- CTA Remote Excel File LoaderDocument58 pagesCTA Remote Excel File LoaderAkbar SyawaludinNo ratings yet
- 7RW600 AnsiDocument216 pages7RW600 AnsiGaurang Patel100% (1)
- P94x Micom RelaysDocument398 pagesP94x Micom RelaysLasantha GunatillakeNo ratings yet
- Earth Fault RelayDocument1 pageEarth Fault RelayAliu AlaoNo ratings yet
- ONLOAD 2007 enDocument46 pagesONLOAD 2007 enpokojang100% (1)
- Restricted Earth-Fault Protection in REF 542plus: Application and Setting GuideDocument20 pagesRestricted Earth-Fault Protection in REF 542plus: Application and Setting GuideSandeep PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual for Fully Automatic Capacitance and Loss Factor Measuring Bridges Type 2816 and 2818Document151 pagesOperation Manual for Fully Automatic Capacitance and Loss Factor Measuring Bridges Type 2816 and 2818mikrurkNo ratings yet
- 7SG14 Duobias M Catalogue Sheet PDFDocument20 pages7SG14 Duobias M Catalogue Sheet PDFanuj100% (1)
- Floating Neutral Impact in Power DistributionDocument9 pagesFloating Neutral Impact in Power DistributionSugeng SumarnoNo ratings yet
- ProtectionDocument157 pagesProtectionsivaepeNo ratings yet
- ETS-50-00 Outdoor AIS AC Substation Common Conditions and Technical RequirementsDocument8 pagesETS-50-00 Outdoor AIS AC Substation Common Conditions and Technical Requirementsraghavendran raghuNo ratings yet
- Short CKT IECDocument9 pagesShort CKT IECSagun KatuwalNo ratings yet
- R8563C Kitz 204Document64 pagesR8563C Kitz 204Rinda_Rayna100% (1)
- Ground Fault LocationDocument8 pagesGround Fault Locationzbyszko201234No ratings yet
- Stub Bus PDFDocument1 pageStub Bus PDFpgcilNo ratings yet
- P438 EN M R-b5-A 311 661 PDFDocument1,192 pagesP438 EN M R-b5-A 311 661 PDFAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- MHOA04 MHOB04 MHOC04 SalesenDocument16 pagesMHOA04 MHOB04 MHOC04 Salesendreamsky702243No ratings yet
- SPAJ 115c ManualDocument56 pagesSPAJ 115c ManualPatel AshokNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker Technical SpecificationsDocument24 pagesCircuit Breaker Technical SpecificationssanjayNo ratings yet
- Megawin Switchgear: Numerical Over Current ProtectionDocument4 pagesMegawin Switchgear: Numerical Over Current ProtectionRock hackNo ratings yet
- PCS S Series PCS-9611S Feeder Relay Y: FunctionsDocument3 pagesPCS S Series PCS-9611S Feeder Relay Y: FunctionsAdityanugrahaNo ratings yet
- Bus Switching Scheme PDFDocument6 pagesBus Switching Scheme PDFJAYKUMAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Differential Bus ProtectionDocument14 pagesDifferential Bus ProtectionRodriguez Villalobos NelsonNo ratings yet
- C264 BrochureDocument8 pagesC264 Brochurechaima haddoudiNo ratings yet
- SopDocument45 pagesSopDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- P632 EN M R-32-D 311 652 Volume 2Document444 pagesP632 EN M R-32-D 311 652 Volume 2Đặng Phước ĐứcNo ratings yet
- p345 Technical ManualDocument1 pagep345 Technical ManualabhayambujNo ratings yet
- EcodialAdvanceCalculation HelpDocument33 pagesEcodialAdvanceCalculation HelpChàng NgốcNo ratings yet
- Alstom - Digital Integrated Generator Protection RelayDocument24 pagesAlstom - Digital Integrated Generator Protection RelayNinh Quoc TrungNo ratings yet
- REM610 Ref Manual IECDocument160 pagesREM610 Ref Manual IECfiatraj1No ratings yet
- 182.testing With MZTU-34 Relay-GenPro PDFDocument7 pages182.testing With MZTU-34 Relay-GenPro PDFAnonymous nPR5nm8XMNo ratings yet
- PCS-902 - Setting List - EN - GE1500035 - Reppie Waste To Energy Project 132kV Line - SUBQ00442749 - R1.04Document27 pagesPCS-902 - Setting List - EN - GE1500035 - Reppie Waste To Energy Project 132kV Line - SUBQ00442749 - R1.04teferayirga100% (1)
- XRIO Converter Manual AREVA P441 P442 P444 E33 ENU TU2.20 V1.000Document9 pagesXRIO Converter Manual AREVA P441 P442 P444 E33 ENU TU2.20 V1.000karthikNo ratings yet
- Application of VFD in Power PlantDocument62 pagesApplication of VFD in Power PlantSakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- OPM-07 Rev.000, Resubmitted On 20.03.13 - NIGRIEDocument113 pagesOPM-07 Rev.000, Resubmitted On 20.03.13 - NIGRIESakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- KSS On Generator Cooling SystemDocument38 pagesKSS On Generator Cooling SystemSakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- FUEL FIRING SYSTEM Presentation by UMADocument59 pagesFUEL FIRING SYSTEM Presentation by UMASakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Nikunj Sir FinalDocument32 pagesNikunj Sir FinalSakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Turbine Vol 1Document863 pagesTurbine Vol 1Sakthi Murugan100% (1)
- OPM-06 Rev.000 Clean Up SystemDocument84 pagesOPM-06 Rev.000 Clean Up SystemSakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Ride Details Fare Details: Ved PrakashDocument3 pagesRide Details Fare Details: Ved PrakashSakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- MHI-Steam Turbine-Construction of Turbine Proper and Main ValvesDocument104 pagesMHI-Steam Turbine-Construction of Turbine Proper and Main ValvesSakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- XRIO Converter Manual Siemens 7SD610 V4.6 TU2.22 ENU V1.000Document9 pagesXRIO Converter Manual Siemens 7SD610 V4.6 TU2.22 ENU V1.000Sakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Efficiency calculation of 3000KW/4P/11KV motorDocument47 pagesEfficiency calculation of 3000KW/4P/11KV motorSakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- OPM-01 Rev.000, 2nd Submission (09.09.13) - NIGRIEDocument186 pagesOPM-01 Rev.000, 2nd Submission (09.09.13) - NIGRIESakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Helpful CalculatorsDocument26 pagesHelpful CalculatorsarcelitasNo ratings yet
- OPM-03 Rev.000, 3rd Submission (01.08.13) - NIGRIEDocument256 pagesOPM-03 Rev.000, 3rd Submission (01.08.13) - NIGRIESakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Power CalculationDocument2 pagesPower Calculationnaran19794735No ratings yet
- UK Tutorial HouseInstallationDocument27 pagesUK Tutorial HouseInstallationRaffi DemirdjianNo ratings yet
- XRIO Converter Manual 7SJ6x V4.6 ENU TU2.11 v1.001Document9 pagesXRIO Converter Manual 7SJ6x V4.6 ENU TU2.11 v1.001Sakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
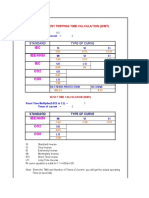
- IEC Iee/Ansi IEC CO2 CO8: Over Current Tripping Time Calculation (Idmt)Document2 pagesIEC Iee/Ansi IEC CO2 CO8: Over Current Tripping Time Calculation (Idmt)Sakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- XRIO Converter Manual 7UT51x V3.0 ENU TU2.2 V1.000Document9 pagesXRIO Converter Manual 7UT51x V3.0 ENU TU2.2 V1.000Sakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Siemens 7SD610 V4.6 XRIO Converter Manual ENU TU2.30 V1.100Document9 pagesSiemens 7SD610 V4.6 XRIO Converter Manual ENU TU2.30 V1.100Sakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- XRIO Converter Manual 7SA522 V4.6 ENU TU2.11 v1.100Document12 pagesXRIO Converter Manual 7SA522 V4.6 ENU TU2.11 v1.100Sakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- UK Tutorial HouseInstallationDocument27 pagesUK Tutorial HouseInstallationRaffi DemirdjianNo ratings yet
- UK Tutorial MotorControl PDFDocument27 pagesUK Tutorial MotorControl PDFDefinal ChaniagoNo ratings yet
- Protection SystemDocument153 pagesProtection SystemArinder Singh100% (1)
- Siemens 7SJ4x Feeder PTT User Manual ENUDocument5 pagesSiemens 7SJ4x Feeder PTT User Manual ENUSakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Directional Earth Fault BasicsDocument7 pagesDirectional Earth Fault BasicsNillutpal BoruahNo ratings yet
- Bus Bar Hand Book-2Document55 pagesBus Bar Hand Book-2Sakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Source-Agnostic Time-Domain Distance RelayDocument10 pagesSource-Agnostic Time-Domain Distance Relaycalon presidenNo ratings yet
- MCCB Catalog Ca08100005eDocument525 pagesMCCB Catalog Ca08100005evairam_eee01No ratings yet
- Intellisys SSR 10-450 (APDD 422C)Document107 pagesIntellisys SSR 10-450 (APDD 422C)Miguel NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Calculation of KVARDocument15 pagesCalculation of KVARAnshul Jain100% (1)
- Protect Ringmaster systems with the VIP 300 relayDocument19 pagesProtect Ringmaster systems with the VIP 300 relaymuhamed MuneerNo ratings yet
- Hydranm2 Gea 12934a HRDocument2 pagesHydranm2 Gea 12934a HRMarcus SiaNo ratings yet
- Switchgear Specification For High Voltage Switchgears CT PT BreakerDocument26 pagesSwitchgear Specification For High Voltage Switchgears CT PT BreakerSumit TyagiNo ratings yet
- Inverter Diagnostics - 7100 - 0243444 - 0001 - A0Document14 pagesInverter Diagnostics - 7100 - 0243444 - 0001 - A0Hadriyudin BaharudinNo ratings yet
- Molded Case Circuit Breakers Section 6: Buylog CatalogDocument106 pagesMolded Case Circuit Breakers Section 6: Buylog CatalogShahadad PNNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER KEYDocument12 pagesELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER KEYSURYA PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Iec 60071 1 2019Document15 pagesIec 60071 1 2019Luan SantosNo ratings yet
- BB&LBBDocument33 pagesBB&LBBMelkin NPNo ratings yet
- Earthing Calculation GuideDocument12 pagesEarthing Calculation GuideJackie JonesNo ratings yet
- Sdg13lax 8e1 Manual v2Document71 pagesSdg13lax 8e1 Manual v2JGT TNo ratings yet
- Utility Grounding: Application GuideDocument7 pagesUtility Grounding: Application Guidesosorel10No ratings yet
- Power System Protection (Differential)Document10 pagesPower System Protection (Differential)Aisamuddin SubaniNo ratings yet
- Geely Emgrand X7 2013 WiringDiagrams 240113 194347Document231 pagesGeely Emgrand X7 2013 WiringDiagrams 240113 194347sakrkoko4No ratings yet
- IC-P0070, Ambient Air Temperature Sensor ADocument3 pagesIC-P0070, Ambient Air Temperature Sensor ABùi Xuân ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Manual Idm 8001 CCRDocument96 pagesManual Idm 8001 CCRRabie BakiraNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1 (PSP) RP-17-EE-404Document3 pagesAssignment No 1 (PSP) RP-17-EE-404hamzaNo ratings yet
- CA08100005E Vol04 Ibook PDFDocument797 pagesCA08100005E Vol04 Ibook PDFFelipe FrancoNo ratings yet
- HV Protection Relays Setting Calculation Rev 4 PDFDocument58 pagesHV Protection Relays Setting Calculation Rev 4 PDFMohideen SikanderNo ratings yet
- Addressable Loop Modules: Introduction FC410MIMDocument8 pagesAddressable Loop Modules: Introduction FC410MIMLORIUNEANo ratings yet
- Cutting Press Catalog-Year 2017Document10 pagesCutting Press Catalog-Year 2017Dennis RamirezNo ratings yet
- 1 Motor Protection Single SessionDocument27 pages1 Motor Protection Single Sessionmubarakkirko100% (1)
- SIMOCODE-DP Motor Protection and Control DevicesDocument16 pagesSIMOCODE-DP Motor Protection and Control DeviceschochoroyNo ratings yet
- BS en 45545-5Document18 pagesBS en 45545-5rohita kumar dahNo ratings yet