Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LFT
Uploaded by
Fatema Al-KananiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LFT
Uploaded by
Fatema Al-KananiCopyright:
Available Formats
فاطمه جاسم محمد
1-Which of the following is not the likely cause of fatty liver?
a) Obesity
b) Starvation
c) Pregnancy
d) Diabetes mellitus
2- in alcoholic patient Which of the following is the nonfunctional plasma enzymes
increased ?
a) Alkaline phosphatase
b) Acid Phosphatase
c) Lactate dehydrogenase
d) Gamma-glutamyltransferase
3- Criggler Najjar syndrome is a genetic disorder associated with unconjugated
hyperbilirubinemia because deficient enzyme ?
a) Heme oxygenase
b) Biliverdin reductase
c) Bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyl synthase
d) Bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyl transferase
4- All of the following statement is true concerning urobilinogen except:
a) Produced by oxidative action of intestinal bacteria.
b) Undergoes significant enterohepatic circulation.
c) Urinary levels increased in biliary obstruction.
d) Fecal levels decreased in biliary obstruction.
5- Which of the following enzyme is deficient caused Galactosemia?
a) Galactokinase
b) Galactose 1- phosphate uridyl transferase
c) UDP-4- Epimerase
d) Galactose dehydrogenase
6- The biochemical investigation of the blood specimen showed Bilirubin- 4.9 mg/dl,
ALT- 155 IU/L, AST- 206 IU/L, Albumin- 26 mg/dL. What is the likely biochemical
diagnosis?
a) Hemolytic Jaundice
b) Acute hepatic disease
c) Chronic hepatic disease
d) Obstructive liver disease
7-the most common cause(s) of chronic liver disease
a) Alcohol abuse
b)genetic
c)virus
8-Which of the following marker is used for the differential diagnosis of obstructive
jaundice?
a) Lactate dehydrogenase
b) Creatine Kinase
c) Carbonic anhydrase
d) 5’- Nucleotidase
9-Criggler’s Najjar Syndrome II occurs due to
a) Excessive production of bilirubin
b) The absence of the conjugating enzyme
c) Partial deficiency of a conjugating enzyme
d) Overexpression of conjugating enzymes
10-Gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver because of the presence of
a) Phosphofructokinase
b) Pyruvate carboxylase
c) Glucose 6 phosphatase
d) Glucokinase
11-conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia results from
a. Gilbert’s
b. Physiological jaundice
c. Excess production of bilirubin
d. Decreased hepatic uptake
e. Cholestasis
12-In hepatitis B
a. Acute infection causes sub-clinical disease in 65% cases
b. The majority of cases of persistent infection result in cirrhosis
c. HBsAg appears soon after overt disease
d. Infection does not play a role in the development of HCC
e. Anti HBs appears soon after HBsAg
13-With regard to jaundice
a. Conjugated bilirubin causes kernicterus in adults
b. Unconjugated bilirubin does not colour the sclera
c. Unconjugated bilirubin is tightly bound to albumin
d. Unconjugated bilirubin produces bilirubin in urine
e. Conjugated bilirubin is tightly bound to albumin
14-Which of the following enzyme is a sensitive marker of alcoholic liver disease?
a) Alanine transaminase
b) Aspartate transaminase
c) Alkaline phosphatase
d) Gamma-Glutamyltransferase
15-Which of the following marker is used for the differential diagnosis of obstructive
jaundice?
a) Lactate dehydrogenase
b) Creatine Kinase
c) Carbonic anhydrase
d) 5’- Nucleotidase
16-Crigler's Najjar Syndrome II occurs due to
a) Excessive production of bilirubin
b) Complete Absence of a conjugating enzyme
c) Partial deficiency of the conjugating enzyme
d) Overexpression of conjugating enzymes
17-In viral hepatitis
a. The majority of cases of acute hepatitis B infection result in a carrier state, without
clinical evidence of disease
b. Anti HBs appears in the first week of infection
c. Anti HCV IgG does not confer immunity to Hep C
d. The major cause of death from Hep B is hepatocellular carcinoma
e. Hep A has an outer surface envelope of protein, lipid and carbohydrate
18- Glycogen storage disease known as von Gerck's disease. Due to the enzyme
missing from the followinga) glucokinase
b) glucose-6- phosphatase
c) phosphoglucomutase
d) phosphoglucoisomerase
19- What deficiency causes Korsakoff –Wernicke disease
a) high-calorie intake from carbohydrate
b) high intake of energy from alcohol
c) high intake of fat for energy
d) high intake of protein for energy
20- Identify the pentose phosphate pathway intermediate that oxidizes and generates
co-enzyme NADPH
a) fructose 6 phosphate
b) ribose-5-phosphate
c) glucose -6 phosphate
d) glucose -1 phosphate
Answers
1- b, 2-d, 3-d, 4-b, 5-b, 6-c, 7-a, 8- d, 9-c, 10- c
11- e, 12-a, 13-c, 14-b, 15-d, 16-c, 17-c, 18-b, 19-c, 20-c
You might also like
- Liver Function and Metabolism - MCQDocument6 pagesLiver Function and Metabolism - MCQNuhu SibaNo ratings yet
- MCQ ChoDocument31 pagesMCQ Choامجد حسين جواد كاظمNo ratings yet
- اختبار البايوكميستري دفعة 38 ترم رابع 231105 234035Document17 pagesاختبار البايوكميستري دفعة 38 ترم رابع 231105 234035Mohammed AyoubNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochemisclinical RevisionDocument21 pagesClinical Biochemisclinical Revisiondrafq20000% (1)
- بايو بيبر 1 د.جميلة السمهريDocument8 pagesبايو بيبر 1 د.جميلة السمهريOzgan SüleymanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates-Lipids 1Document6 pagesCarbohydrates-Lipids 1Michal VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Biochemistry MCQs Carbohydrates MetabolismDocument17 pages6 - Biochemistry MCQs Carbohydrates Metabolismwanna learn100% (2)
- CC RecallDocument7 pagesCC RecallDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Enhancement Course For Clerks Biochem Examination Part 1Document3 pagesEnhancement Course For Clerks Biochem Examination Part 1Kevin AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Bio T&D 17th March 2024Document8 pagesBio T&D 17th March 2024saketNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument8 pagesMCQVichhaiJacksonNo ratings yet
- Biological ChemistryDocument28 pagesBiological ChemistryArsilan Aziz LoneNo ratings yet
- Liver FunctionsDocument19 pagesLiver FunctionsPrabhakar Kumar100% (1)
- Biochemistry McqsDocument32 pagesBiochemistry McqsPriya VNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics MCQs-Inborn Errors of Metabolism 1Document9 pagesPediatrics MCQs-Inborn Errors of Metabolism 1Omar Ahmed0% (1)
- Biochemistry Student PDFDocument21 pagesBiochemistry Student PDFDar AaqibNo ratings yet
- PHS4300 Kennedy Sample MCQs 1Document4 pagesPHS4300 Kennedy Sample MCQs 1iDNENo ratings yet
- MCQDocument21 pagesMCQIvyljnNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Chemistry and MetabolismDocument16 pagesCarbohydrates Chemistry and Metabolismkarli geethanjaliNo ratings yet
- CCDocument9 pagesCCFritzie BlancheNo ratings yet
- Bio-Chemistry MCQ - No AnswerDocument8 pagesBio-Chemistry MCQ - No AnswerVichhaiJackson100% (1)
- Chapter 24 L19 Endocrine Function of PancreasDocument12 pagesChapter 24 L19 Endocrine Function of Pancreasmostafa33puvmNo ratings yet
- Take Care - BioDocument9 pagesTake Care - Biofyou56939No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism - MCQ On Glycolysis & GluconeogenesisDocument13 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism - MCQ On Glycolysis & Gluconeogenesisolayemi mariamNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry PDFDocument13 pagesBiochemistry PDFMnop PqrsNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Quiz No3Document5 pagesBiochemistry Quiz No3Akbar SadiqNo ratings yet
- En-Metabolism LipidicDocument25 pagesEn-Metabolism LipidicCristina THCSNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire On Clinical Chemistry For Students1 1Document9 pagesQuestionnaire On Clinical Chemistry For Students1 1Inah Mae Coleen CapuyanNo ratings yet
- High Yield MCQs - Dr. Nikita NanwaniDocument10 pagesHigh Yield MCQs - Dr. Nikita NanwaniDeeksha BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Copy1-Multiple Choice Question 2022Document11 pagesCopy1-Multiple Choice Question 2022JAINo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism MCQs (Cholesterol, Triglycerides, and Other Lipids) - 1639455481990Document8 pagesLipid Metabolism MCQs (Cholesterol, Triglycerides, and Other Lipids) - 1639455481990Lola MuhozaNo ratings yet
- DnlodDocument43 pagesDnlod312887No ratings yet
- 28-03-2020 Assignment 10 Lipids Metabolism Dr. TahaDocument2 pages28-03-2020 Assignment 10 Lipids Metabolism Dr. TahaTaha Akhtar KhanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism SamplexDocument13 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism SamplexCherie ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Glucose Quiz 1 @ukrok1Document4 pagesGlucose Quiz 1 @ukrok1Omran BashirNo ratings yet
- Metab AsdfgghhjhkjlDocument99 pagesMetab AsdfgghhjhkjlSend FileNo ratings yet
- Biochem PreproffDocument6 pagesBiochem PreproffaroobaNo ratings yet
- Q.P. Code: 526055Document3 pagesQ.P. Code: 526055hxifakhanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Mcqs for 2nd Year Mbbs Www Edu Apnafort Com TRẮC NGHIỆM HAYDocument69 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Mcqs for 2nd Year Mbbs Www Edu Apnafort Com TRẮC NGHIỆM HAYTrần Tiến Đạt0% (1)
- Module 3-Test 2 ONLINEDocument13 pagesModule 3-Test 2 ONLINEur.yared21No ratings yet
- July 2013Document32 pagesJuly 2013EmadSamirNo ratings yet
- IJRPR5933Document8 pagesIJRPR5933rifa iNo ratings yet
- MCG in Bariatric Surgery Prof - Safauldeen 2022Document5 pagesMCG in Bariatric Surgery Prof - Safauldeen 2022common gmailNo ratings yet
- Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesExam QuestionsAlyssa Mariae CodornizNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry OriginalDocument26 pagesBiochemistry OriginalShimmering Moon100% (1)
- TestDocument23 pagesTestParth sarthi Sen guptaNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 - Pharmacognosy - 4th Semester Question BankDocument3 pagesUnit 01 - Pharmacognosy - 4th Semester Question Bankgaurav saxenaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 1Document32 pagesBiochemistry 1zaydeeeeNo ratings yet
- 207 Sample Questions PDFDocument4 pages207 Sample Questions PDFsinan sinanNo ratings yet
- GIT MUST 501 TERM MCQ 21Document22 pagesGIT MUST 501 TERM MCQ 21catcat669111No ratings yet
- Lipids Review QuestionsDocument10 pagesLipids Review QuestionsDavid TamayoNo ratings yet
- Physio Pretest WordDocument143 pagesPhysio Pretest WordJanie-Vi Gorospe67% (3)
- BiochemcomquizDocument43 pagesBiochemcomquizaikaNo ratings yet
- Krok1 EngDocument27 pagesKrok1 Engdeekshit dcNo ratings yet
- Republic of The PhilippinesdwwwwDocument13 pagesRepublic of The PhilippinesdwwwwGo IdeasNo ratings yet
- List of MCQS EndocrineDocument40 pagesList of MCQS Endocrinehirsi200518No ratings yet
- Enzymes. Coenzymes. Bioenergetics. Citric Acid Cycle of Krebs. Tissue RespirationDocument27 pagesEnzymes. Coenzymes. Bioenergetics. Citric Acid Cycle of Krebs. Tissue RespirationHart ElettNo ratings yet
- Set 2 Engleza 2013 Sem IIDocument4 pagesSet 2 Engleza 2013 Sem IIdimaronNo ratings yet
- Bio - Chemistry T& D PaperDocument12 pagesBio - Chemistry T& D PaperPNo ratings yet
- International Textbook of Diabetes MellitusFrom EverandInternational Textbook of Diabetes MellitusR. A. DeFronzoNo ratings yet
- Cell-Mediated ImmunityDocument15 pagesCell-Mediated ImmunityFatema Al-KananiNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 دكتور مؤيدDocument27 pagesPresentation1 دكتور مؤيدFatema Al-KananiNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin and TazobactamندىDocument6 pagesPiperacillin and TazobactamندىFatema Al-KananiNo ratings yet
- Hormone: Mechanism & Action: DR Khaled Saleh AlgaririDocument35 pagesHormone: Mechanism & Action: DR Khaled Saleh AlgaririFatema Al-KananiNo ratings yet
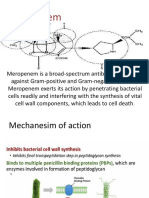
- meropenem ندىDocument5 pagesmeropenem ندىFatema Al-KananiNo ratings yet
- mcq renalفاطمه جاسم محمدDocument4 pagesmcq renalفاطمه جاسم محمدFatema Al-KananiNo ratings yet
- Inhalers Used in Asthma and COPD PDFDocument1 pageInhalers Used in Asthma and COPD PDFconNo ratings yet
- Congenital Anomalies of KidneDocument7 pagesCongenital Anomalies of KidneSanthosh.S.U100% (2)
- Slipped Disc Minicase CompleteDocument17 pagesSlipped Disc Minicase CompleteGerold ChuaNo ratings yet
- 6.2 Diabetes MellitusDocument53 pages6.2 Diabetes MellitusMohammad AlrefaiNo ratings yet
- Macrocytic AnemiaDocument48 pagesMacrocytic AnemiaMONo ratings yet
- Chicken Pox InfographicsDocument1 pageChicken Pox InfographicsBIANCA PILNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument68 pagesDrugs Acting On The Autonomic Nervous SystemjisooNo ratings yet
- Artikel Ilmiah (PKL) MiaDocument10 pagesArtikel Ilmiah (PKL) MiaKrismarita HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Phoenix, Arizona: Principles To Guide Zoning For Community Residences For People With DisabilitiesDocument44 pagesPhoenix, Arizona: Principles To Guide Zoning For Community Residences For People With Disabilitiesdan-304518No ratings yet
- Dundon 2010Document9 pagesDundon 2010Ana-Maria ChiricNo ratings yet
- Activity1 P.E.Document3 pagesActivity1 P.E.jungcolemerjerihNo ratings yet
- V Vastu For Plot - A 2 Z VastuDocument7 pagesV Vastu For Plot - A 2 Z Vastuearth oneNo ratings yet
- Immune Mediated Myopathies.5Document22 pagesImmune Mediated Myopathies.5wahby khatir100% (1)
- Case Studies - Tetralogy of FallotDocument16 pagesCase Studies - Tetralogy of FallotKunwar Sidharth SaurabhNo ratings yet
- IAEA Planning National Radiotherapy Services - A Practical Tool PDFDocument100 pagesIAEA Planning National Radiotherapy Services - A Practical Tool PDFTomás Alexander Alvis MenachoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PharmacologyDocument77 pagesCardiovascular PharmacologyDhruva PatelNo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial Trauma A Clinical GuideDocument468 pagesMaxillofacial Trauma A Clinical GuideDr.Sudarsan SenNo ratings yet
- B Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 2 (Week 3)Document17 pagesB Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 2 (Week 3)Daisy Soriano PrestozaNo ratings yet
- Spars Pandemic Scenario PDFDocument89 pagesSpars Pandemic Scenario PDFLinda Maya100% (6)
- The Heart Activity 4 PDFDocument4 pagesThe Heart Activity 4 PDFJ Joseph TaylorNo ratings yet
- 8 Pseudocyst of Pinna and Its Treatment With Surgical Deroofing - An Experience at Tertiary Hospitals 2013Document13 pages8 Pseudocyst of Pinna and Its Treatment With Surgical Deroofing - An Experience at Tertiary Hospitals 2013solikin ikinNo ratings yet
- MSF Medical Protocol For Sexual Violence Care - 2020 - FINAL - 30 06 20Document47 pagesMSF Medical Protocol For Sexual Violence Care - 2020 - FINAL - 30 06 20Dulce Paola Herrera100% (3)
- Defense Medical Epidemiology Database Report - Jan 26, 2022Document41 pagesDefense Medical Epidemiology Database Report - Jan 26, 2022adan_infowars100% (2)
- Do-6 ReadingDocument7 pagesDo-6 ReadingNazar KuzivNo ratings yet
- Problem StatementDocument18 pagesProblem StatementvmrekhateNo ratings yet
- Medical Records, Insurance, and ContractsDocument24 pagesMedical Records, Insurance, and ContractsBernard Kwaku OkaiNo ratings yet
- Clinicians Treatment Manual. Family Focused TreatmentDocument147 pagesClinicians Treatment Manual. Family Focused Treatmentsoeli pNo ratings yet
- Can You Recall The Typhoons That Hit The Different Regions ofDocument15 pagesCan You Recall The Typhoons That Hit The Different Regions ofRaj MiraflorNo ratings yet
- Whizzology 1N (Document19 pagesWhizzology 1N (GMSDisco100% (3)
- Grade 9 Science Biology 1 DLPDocument13 pagesGrade 9 Science Biology 1 DLPManongdo AllanNo ratings yet