Professional Documents
Culture Documents
First Law Thermodynamic: U - U Q - W Is Increased
Uploaded by
Gnabry0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views3 pagesThis document discusses the first law of thermodynamics and key concepts including heat (Q), work (W), and internal energy (U). It provides examples to demonstrate how to use the first law of thermodynamics equations.
The first law states that the change in internal energy of a system (ΔU) is equal to the heat (Q) added to the system minus the work (W) done by the system. It also defines that heat transferred into a system (Qin) is positive and heat leaving is negative (Qout), while work done on a system (Win) is negative and work done by a system (Wout) is positive.
Several examples are provided to demonstrate calculating changes
Original Description:
Original Title
Note First LAw (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the first law of thermodynamics and key concepts including heat (Q), work (W), and internal energy (U). It provides examples to demonstrate how to use the first law of thermodynamics equations.
The first law states that the change in internal energy of a system (ΔU) is equal to the heat (Q) added to the system minus the work (W) done by the system. It also defines that heat transferred into a system (Qin) is positive and heat leaving is negative (Qout), while work done on a system (Win) is negative and work done by a system (Wout) is positive.
Several examples are provided to demonstrate calculating changes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views3 pagesFirst Law Thermodynamic: U - U Q - W Is Increased
Uploaded by
GnabryThis document discusses the first law of thermodynamics and key concepts including heat (Q), work (W), and internal energy (U). It provides examples to demonstrate how to use the first law of thermodynamics equations.
The first law states that the change in internal energy of a system (ΔU) is equal to the heat (Q) added to the system minus the work (W) done by the system. It also defines that heat transferred into a system (Qin) is positive and heat leaving is negative (Qout), while work done on a system (Win) is negative and work done by a system (Wout) is positive.
Several examples are provided to demonstrate calculating changes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
First Law Thermodynamic
1. Q
2. W
3. U
4. Q=W
5. U2-U1= Q – W
6. ∑U = ∑Q – ∑W
7. U2-U1 = +ve the internal energy is increased
8. U2-U1 = -ve the internal energy is decreased
Heat
1. Symbol: Q Unit: KiloJoule, KJ
2. (Qin) = +ve.
3. (Qout) = -ve.
4. ∑Q =∑ Qin +∑ Qout
5. SYSTEM
I. Q1 = - 0.06kJ
II. Q2 = - 0.012kJ
III. Q3 = + 0.79 kJ
IV. Q4 = +0.12 kJ
V. Q5 = -0.51 kJ
Solution :
∑Q = 0.12 +0.79 – 0.51 –0.06 – 0.012 = 0.328kJ
Work
1. Symbol: W Unit: KiloJoule, KJ
2. (Win) = -ve.
3. (Wout) = +ve.
4. ∑W =∑ Win +∑ Wout
5. SYSTEM
I. W1 = 0.06kJ
II. W2 = 0.012kJ
III. W3 = - 0.79 kJ
IV. W4 = -0.12 kJ
V. W5 = 0.51 kJ
Solution :
∑Q = -0.12 -0.79 + 0.51 +0.06 + 0.012 = - 0.328 kJ
+Q -Q
SYSTEM
-W +W
1. Q=W complete cycle
2. U2-U1= Q – W
3. ∑U = ∑Q – ∑W
4. U2-U1 = ∑Q – ∑W
Example 2.1 Solution :
Qin=+10kJ Wout=?
SYSTEM
Win=-2kJ Qout=-3kJ
The figure above shows a certain process,
which undergoes a complete cycle of operations.
Determine the value of work output for complete
cycle.
Example 2.2 Solution:
A system is allowed to do work amounting to 500kNm
while heat transfer energy amounting 800kJ is
transferred into it. Find the change of internal energy
and state whether it is increase or decrease.
Example 2.3 Solution:
In a compression stroke for gas engine, work done by
the piston on the gas is 70kJ/kg. The amount of heat
that were transferred out is 42kJ/kg. Calculate the
difference of internal energy.
Example 2.4 Solution :
During a complete cycle operation, a system is
subjected to the following:
Heat transfer is 800kJ supplied and 150kJ rejected
Work done by the system is 200kJ
Calculate the work transferred from surrounding
to the system.
You might also like
- Topic: Problems On Fundamentals of Thermodynamics &first Law of Thermodynamics Sub - Title: ThermodynamicsDocument12 pagesTopic: Problems On Fundamentals of Thermodynamics &first Law of Thermodynamics Sub - Title: Thermodynamicsbharathkumar0310No ratings yet
- Problems 2Document4 pagesProblems 2Shane PatulotNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document12 pagesCH 04hirenpatel_universalNo ratings yet
- Soal Dan Pembahasan Termodinamika Teknik PDFDocument32 pagesSoal Dan Pembahasan Termodinamika Teknik PDFTri WidayatnoNo ratings yet
- Me6301 QBDocument46 pagesMe6301 QBNaveen Dhanuraj100% (1)
- Unit 3 TNSDocument12 pagesUnit 3 TNSravitejabvNo ratings yet
- HMWK 3 Solutions PDFDocument7 pagesHMWK 3 Solutions PDFGUTIERREZ ALVARADO MAGNO ENRIQUENo ratings yet
- Note Chapter14 19 20Document48 pagesNote Chapter14 19 20Nursyafiqa IdwaniNo ratings yet
- Processes of Ideal GasesDocument20 pagesProcesses of Ideal Gasesemmarie llantinoNo ratings yet
- Tugas Termodinamika Kelompok 1Document8 pagesTugas Termodinamika Kelompok 1Jasmine AprilNo ratings yet
- 2-2 First Law of Thermodynamics - Session 2Document17 pages2-2 First Law of Thermodynamics - Session 2Baddam Jayasurya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Topic:: ThermodynamicsDocument26 pagesTopic:: ThermodynamicsMarco PlaysNo ratings yet
- CHE 325 (3 Units) : Dr. F. B. ElehinafeDocument28 pagesCHE 325 (3 Units) : Dr. F. B. ElehinafeGlory UsoroNo ratings yet
- Chap4firstlawthermodynamics 130703012634 Phpapp02 141209125348 Conversion Gate02Document61 pagesChap4firstlawthermodynamics 130703012634 Phpapp02 141209125348 Conversion Gate02Abdelkader Faklani DouNo ratings yet
- Topic: Thermodynamic Process & Problems. Sub. Title ThermodynamicsDocument28 pagesTopic: Thermodynamic Process & Problems. Sub. Title Thermodynamicsbharathkumar0310No ratings yet
- ch02 PDFDocument56 pagesch02 PDFJacky DeejaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document7 pagesLecture 4Moeen Ul IslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SolutionsDocument56 pagesChapter 2 SolutionsMarcus young100% (2)
- Recitation 5 PDFDocument15 pagesRecitation 5 PDFOnur ÖZÇELİKNo ratings yet
- 2-1 First Law of Thermodynamics - Session 1Document38 pages2-1 First Law of Thermodynamics - Session 1Baddam Jayasurya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Spring 2021-22 PDFDocument9 pagesLecture 4 - Spring 2021-22 PDFDipto PaulNo ratings yet
- Recitation 4 PDFDocument16 pagesRecitation 4 PDFOnur ÖZÇELİKNo ratings yet
- Me 231 Topic 2Document26 pagesMe 231 Topic 2Raymond PeraltaNo ratings yet
- HC Verma Solutions Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument22 pagesHC Verma Solutions Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 Laws of ThermodynamicsHorus GamingNo ratings yet
- Chap7-Closed System SKKC2133 1617-1Document30 pagesChap7-Closed System SKKC2133 1617-1Chai Hong LohNo ratings yet
- First Law of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics: Physics Bsed - Science IiDocument3 pagesFirst Law of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics: Physics Bsed - Science IiJenny ColiatNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Thermodynamics (NOC21-ME73) Assignment-4Document8 pagesConcepts of Thermodynamics (NOC21-ME73) Assignment-4Saurabh ManralNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics SolutionDocument15 pagesThermodynamics SolutionSureshbabu0% (1)
- Mae 320 HW 04 SolDocument7 pagesMae 320 HW 04 SolEvan DurstNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document55 pagesCH 03정민교No ratings yet
- LN15 1718 PDFDocument46 pagesLN15 1718 PDFelty TanNo ratings yet
- LN15 1718 PDFDocument46 pagesLN15 1718 PDFelty TanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial3 s16Document5 pagesTutorial3 s16smart100% (1)
- Unit 13: The First Law of Thermodynamics, Thermodynamic Processes, Thermodynamic Process For An Ideal GasDocument25 pagesUnit 13: The First Law of Thermodynamics, Thermodynamic Processes, Thermodynamic Process For An Ideal Gassarah29415631No ratings yet
- Chapter Three First Law of Thermodynamics: Fig. 3-1 Cyclic ProcessDocument9 pagesChapter Three First Law of Thermodynamics: Fig. 3-1 Cyclic ProcessEnenamahNo ratings yet
- 3.0 First Law of Thermodynamics and Its ProcessDocument11 pages3.0 First Law of Thermodynamics and Its ProcessGnabryNo ratings yet
- AE 231 Thermodynamics Recitation 7 Recitation 7: Instructor: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Sinan EyiDocument10 pagesAE 231 Thermodynamics Recitation 7 Recitation 7: Instructor: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Sinan EyiOnur ÖZÇELİKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Energy Balance For Closed and Open Systems - AzizulDocument102 pagesChapter 7 - Energy Balance For Closed and Open Systems - Azizulmuhammad izzulNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 SolutionDocument31 pagesAssignment 2 SolutionSirish Chand Putla0% (1)
- CH 5 Hard ProblemsDocument6 pagesCH 5 Hard ProblemsShazia AhmedNo ratings yet
- As3 9Document7 pagesAs3 9Vivek VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20Document73 pagesChapter 20maryamhomayoonfalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 SolnDocument2 pagesTutorial 3 Solnkaeshav manivannanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - ThermodynamicsDocument73 pagesChapter 20 - Thermodynamicswiggly18No ratings yet
- Answer Quiz-4 PDFDocument1 pageAnswer Quiz-4 PDFOnur ÖZÇELİKNo ratings yet
- Heat and Internal EnergyDocument2 pagesHeat and Internal EnergyRosalyn Angcay QuintinitaNo ratings yet
- First Law of Thermodynamics in Four Thermodynamic ProcessesDocument6 pagesFirst Law of Thermodynamics in Four Thermodynamic ProcessesMD Al Fahad NirobNo ratings yet
- Aula 6Document57 pagesAula 6JehuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document8 pagesLecture 4Refai SayyadNo ratings yet
- Porblem Set 2 (Chapter 8)Document3 pagesPorblem Set 2 (Chapter 8)khozin ltmptNo ratings yet
- P Bar P Bar T C K K T C K V L M: Exercise 1: Let's Study A Quantity of AirDocument5 pagesP Bar P Bar T C K K T C K V L M: Exercise 1: Let's Study A Quantity of AirHoàng Long Nguyễn BùiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document37 pagesChapter 8yobingewatcher06No ratings yet
- 1 Law of Thermodynamics Worksheet: Show Your WorkDocument4 pages1 Law of Thermodynamics Worksheet: Show Your WorkAngelica Calamba CalicaNo ratings yet
- Unit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesUnit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsRengganis Putri ParmudyaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2: Phase Change: Name Class Matrix No. Lecturer'S NameDocument18 pagesLab Report 2: Phase Change: Name Class Matrix No. Lecturer'S NameGnabryNo ratings yet
- Labsheet Principle of Conservation of EnergyDocument4 pagesLabsheet Principle of Conservation of EnergyGnabryNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1: Zeroth Law: Name Class Matrix No Lecturer'S NameDocument16 pagesLab Report 1: Zeroth Law: Name Class Matrix No Lecturer'S NameGnabryNo ratings yet
- Labsheet Linear MotionDocument6 pagesLabsheet Linear MotionGnabryNo ratings yet
- Labsheet Linear MotionDocument6 pagesLabsheet Linear MotionGnabryNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Experiment Outcome: Experiment: EL2-1S Title: Physical Characteristic of Fluid Duration: 2 Hours: 1 0F 5Document7 pages1.0 Experiment Outcome: Experiment: EL2-1S Title: Physical Characteristic of Fluid Duration: 2 Hours: 1 0F 5GnabryNo ratings yet
- Case Study DBM Maths - 3Document11 pagesCase Study DBM Maths - 3Gnabry100% (2)
- Chapter 1 (1-2)Document27 pagesChapter 1 (1-2)GnabryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (1-3)Document19 pagesChapter 1 (1-3)GnabryNo ratings yet
- Rumusan Bab2Document1 pageRumusan Bab2GnabryNo ratings yet
- Practical Task 3Document1 pagePractical Task 3GnabryNo ratings yet
- Case Study DBM Maths - 3Document11 pagesCase Study DBM Maths - 3GnabryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (1-1)Document42 pagesChapter 1 (1-1)GnabryNo ratings yet
- Jj20063 - Thermodynamics End of Chapter 1: Name: Matrix No.: ClassDocument1 pageJj20063 - Thermodynamics End of Chapter 1: Name: Matrix No.: ClassGnabryNo ratings yet
- 3.0 First Law of Thermodynamics and Its ProcessDocument11 pages3.0 First Law of Thermodynamics and Its ProcessGnabryNo ratings yet
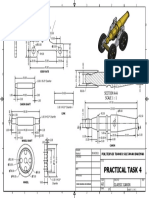
- Practical Task 4: Section A-A Scale 1: 1Document1 pagePractical Task 4: Section A-A Scale 1: 1GnabryNo ratings yet
- SOM 2-1 (Students Note)Document17 pagesSOM 2-1 (Students Note)GnabryNo ratings yet
- Note Ideal Gas TutorialDocument5 pagesNote Ideal Gas TutorialGnabryNo ratings yet
- A Cast-Iron Machine Part Is Acted at Cantilever Beam As Shown inDocument2 pagesA Cast-Iron Machine Part Is Acted at Cantilever Beam As Shown inGnabryNo ratings yet
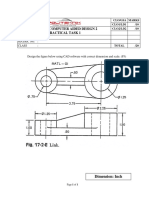
- Djj30122 - Computer Aided Design 2 Practical Task 1: Name: Matric No.: ClassDocument1 pageDjj30122 - Computer Aided Design 2 Practical Task 1: Name: Matric No.: ClassGnabryNo ratings yet
- Teacher Education and Social ChangeDocument5 pagesTeacher Education and Social ChangeGnabryNo ratings yet
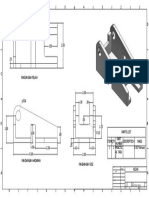
- Practical Task 2Document1 pagePractical Task 2GnabryNo ratings yet
- Experiment: E3 Title: The Study of Phase Change Duration: 2 Hours: 1 0F 5Document5 pagesExperiment: E3 Title: The Study of Phase Change Duration: 2 Hours: 1 0F 5GnabryNo ratings yet