Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Endeavour
Uploaded by
WEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAIOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Endeavour
Uploaded by
WEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAICopyright:
Available Formats
Science
endeavour
Wednesday, 25 March 2020 8:39 PM
Science
• Science is the study of natural things around us
• There are various branches of Science: chemistry( regarding
chemistry), physics ( regarding the nature of matter), biology ( about
living things) and life sciences(includes the study of genes)
Gathering scientific knowledge by scientific method
• It is the way go about finding out the things by
—systematic collections of observation using sense of sight,touch,smell
taste and hearing ; taking measurements.
—applying systematic thinking to make inferences from experimental
evidence.
—recording information accurately and analysing the results
—drawing possible conclusions based on results.
Essential scientific inquiry skills to have
— asking questions
—good planning and execution of investigation
—evaluating the experimental results
—communicating the conclusions
Laboratory safety rules
Teacher will go through with pupils a comprehensive list of rules but some
of the basic rules often overlooked by pupil are:
• Always wear goggles before handling chemicals or doing heating of
chemicals.
• Point the mouth of the test tube away from yourself or people
around you.
• Leftover chemicals should not be poured back into their bottles ,
dispose them.
• Do not eat food or drink the water from tap in the laboratory .
• Report all breakages ,spillages and accident immediately to
teacher .
• Read instructions carefully before doing the experiment but do ask
your teacher if still in doubt
Important symbols of danger
• Toxic (poisonous ) substance — substance that is poisonous
• Flammable substances — substance that catches fire easily
• Corrosive substance — substance that itches and burn skin
• Radioactive substance — substance that gives off harmful radiation
• Irritable substance — substance that may cause irritation to the eyes , noses and throats
Laboratory apparatus
• Common laboratory apparatus and their outline/section diagrams (do not draw 3-dimensional
diagram - use single clear lines).
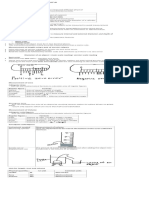
The Bunsen burner
A)Parts of a Bunsen burner and their functions
Parts Functions
Barrel To raise the flame to a suitable height for burning to take place
Collar To control the amount of air entering the barrel
Air-hole To allow air to enter the barrel
Jet To allow the gas to rush into the barrel
Base To support the Bunsen burner
Gas tap To control the amount of gas entering the barrel
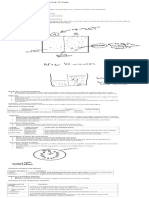
Differences between Luminous and Non-luminous flame:
Luminous flame Non-luminous flame
Orange flame , not very hot Blue flame , very hot
Produces soot No soot is produced
Unsteady flame Steady flame
Not suitable for heating Suitable for heating
C) A strike back occurs when there is too little gas and too much air, and the gas burns at the jet of
on top of the barrel of the burner . It cause the burner to becomes very hot and dangerous
You might also like
- Integrated Science 1ADocument3 pagesIntegrated Science 1AJanet LawNo ratings yet
- Expt24 PDFDocument3 pagesExpt24 PDFOrlando VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document20 pagesChap 1Nor Rafidah Che YusofNo ratings yet
- Module 2 OrgchemDocument7 pagesModule 2 OrgchemJHUNNTY LOZANONo ratings yet
- Manual For Basic Practical ChemisryDocument82 pagesManual For Basic Practical Chemisrykiya01No ratings yet
- Science Laboratory Notes Science Tingkatan 1 Power Point Bab 1 General RulesDocument15 pagesScience Laboratory Notes Science Tingkatan 1 Power Point Bab 1 General RulesEzra Loganathan MuniandiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Common Laboratory OperationsDocument10 pagesExperiment 1 - Common Laboratory OperationsrairasheneNo ratings yet
- SSI 3013: Information and Communication Technology in ScienceDocument8 pagesSSI 3013: Information and Communication Technology in SciencehannahNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Science Chapter 1.2 & 1.3Document50 pagesForm 1 Science Chapter 1.2 & 1.3WalkingFish100% (1)
- Science Unit 1 NotesDocument6 pagesScience Unit 1 NoteschangharleychangNo ratings yet
- Lighting A Bunsen Burner - Experimental Skill and InvestigationDocument9 pagesLighting A Bunsen Burner - Experimental Skill and InvestigationDannahNo ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument7 pagesChem ReviewerJane EbascoNo ratings yet
- Lighting A Bunsen Burner - Experimental Skill and InvestigationDocument9 pagesLighting A Bunsen Burner - Experimental Skill and InvestigationKath kathNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Rules and SafetyDocument9 pagesLaboratory Rules and SafetyJerome MosadaNo ratings yet
- Che Presentation 109Document8 pagesChe Presentation 109Ragib MahatabNo ratings yet
- An A' Level Project On ObesityDocument16 pagesAn A' Level Project On ObesitySharizah Bte Md AminNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 Experiment 1 (Common Laboratory Techniques and Operations) 0Document16 pagesWEEK 2 Experiment 1 (Common Laboratory Techniques and Operations) 0Niki KevinNo ratings yet
- Lab OrientationDocument26 pagesLab OrientationdarchgurlNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Safety and GlasswareDocument7 pagesLaboratory Safety and Glasswareفهد سعيد ال مطره الغامديNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lesson 1Document26 pagesChemistry Lesson 1Vincent Gener TanoNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Science Chapter 1 2 1 3Document50 pagesForm 1 Science Chapter 1 2 1 3jayweinx0% (1)
- Intr0duction To ScienceDocument7 pagesIntr0duction To ScienceNaseeb AliNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 - Lab - Purify A Mixture - Percent Comp PDFDocument2 pagesMod 2 - Lab - Purify A Mixture - Percent Comp PDFconnieNo ratings yet
- Power Point Fire Prevention and Suppression TechniquesDocument23 pagesPower Point Fire Prevention and Suppression TechniquesLaarni Delideli EscalaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 - Basic Lab Apparatus and TechniquesDocument33 pagesExercise 2 - Basic Lab Apparatus and TechniquesFatima KateNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Laboratory FormatDocument15 pagesChemistry Laboratory FormatAbesamis RanmaNo ratings yet
- Lab. Instruments & Scientific EnquiryDocument15 pagesLab. Instruments & Scientific EnquiryChalise SupremeNo ratings yet
- TB Science F1 Chapter 1Document136 pagesTB Science F1 Chapter 1Salmee SallehNo ratings yet
- Resource 20230426185811 Doc-20230426-Wa0043.Document5 pagesResource 20230426185811 Doc-20230426-Wa0043.ATHARVA SINGH BAGHELNo ratings yet
- F1 Chapter 1 KSSMDocument226 pagesF1 Chapter 1 KSSMnorhmsNo ratings yet
- Bunsen Burner Basics: Publication No. 10512Document4 pagesBunsen Burner Basics: Publication No. 10512ericbattyNo ratings yet
- High Temperature Experiments in Chemistry and Materials ScienceFrom EverandHigh Temperature Experiments in Chemistry and Materials ScienceNo ratings yet
- TB Science f1 Chapter 1Document141 pagesTB Science f1 Chapter 1CHAN SIOK WEI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction of ScienceDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction of SciencenixleonNo ratings yet
- Stove-Tec Wood Charcoal Stove User ManualDocument7 pagesStove-Tec Wood Charcoal Stove User ManualBill FranklinNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document3 pagesLab 6mariyambashir22No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Laboratory Class OrientationDocument54 pagesBiomolecules Laboratory Class OrientationUnlucky WitchNo ratings yet
- ASSIST - Reflux and Distillation - 2018-04-12Document6 pagesASSIST - Reflux and Distillation - 2018-04-12kamsi akudinobiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1.1Document68 pagesLaboratory 1.1jmarafolsjoreNo ratings yet
- SafetyDocument5 pagesSafetyPande AdnyanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Scientific Investigation What Is Science?Document18 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Scientific Investigation What Is Science?Madyha AzmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SciDocument37 pagesChapter 1 ScimaxxNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem PrelimsDocument26 pagesGen Chem PrelimsANDREA LOUISE ELCANONo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument48 pagesINTRODUCTIONJed Nicole AngonNo ratings yet
- BIO 105L - CHAPTER 6 - Melting Point DeteminationDocument4 pagesBIO 105L - CHAPTER 6 - Melting Point DeteminationFranchiezca AoananNo ratings yet
- (ECHELAB) Familiarization With Chemistry Apparatus and Basic Laboratory OperationsDocument3 pages(ECHELAB) Familiarization With Chemistry Apparatus and Basic Laboratory OperationsG02 - BALACANAO JHERICE A.No ratings yet
- 1.2 Your Science LaboratoryDocument18 pages1.2 Your Science LaboratoryCHAI SZE JIA MoeNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Modul 2022 1Document47 pagesBasic Chemistry Modul 2022 1Ohh ChimmyNo ratings yet
- Experiment (1: Etermination of Elting Oints PurposeDocument4 pagesExperiment (1: Etermination of Elting Oints PurposeabasoudaNo ratings yet
- The Infrared Grill Master: Recipes and Techniques for Perfectly Seared, Deliciously Smokey BBQ Every TimeFrom EverandThe Infrared Grill Master: Recipes and Techniques for Perfectly Seared, Deliciously Smokey BBQ Every TimeNo ratings yet
- Burner and Hotplates Safety062911 PDFDocument5 pagesBurner and Hotplates Safety062911 PDFŠĭlệncěIšmyPŕIdệNo ratings yet
- Доклад 2Document8 pagesДоклад 2Рая НиколчеваNo ratings yet
- SCI 104 Lecture 1 Laboratory Safety and MeasurementsDocument35 pagesSCI 104 Lecture 1 Laboratory Safety and MeasurementsYanaNo ratings yet
- BSCM 234 T2 Lesson 7Document53 pagesBSCM 234 T2 Lesson 7Mike AnnisNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual 2Document47 pagesLaboratory Manual 2Omwoma SolomonNo ratings yet
- Final Saftey Measures in LabDocument78 pagesFinal Saftey Measures in LabImran KhizarNo ratings yet
- English For Chemistry 1Document12 pagesEnglish For Chemistry 1Zulham AliNo ratings yet
- Activity # 3: Task by Group!!Document6 pagesActivity # 3: Task by Group!!krekre sungahidNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: The Real Self (Part 1) Lesson 1: Is That Really Me?: Confidential (For Internal Circulati On Only)Document1 pageUnit 1: The Real Self (Part 1) Lesson 1: Is That Really Me?: Confidential (For Internal Circulati On Only)WEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- Length, Area and VolumeDocument1 pageLength, Area and VolumeWEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- 口试 (0ral 50 Marks (五十分) ) (10 Min preparation)Document1 page口试 (0ral 50 Marks (五十分) ) (10 Min preparation)WEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- Ray Model of LightDocument1 pageRay Model of LightWEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- Transport System in Living ThingsDocument1 pageTransport System in Living ThingsWEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- 1C2 - 2020 WEI SHANGLI at STANLEY NGAI - Checkpoint 14.1 and 14.2Document1 page1C2 - 2020 WEI SHANGLI at STANLEY NGAI - Checkpoint 14.1 and 14.2WEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- Effect of Heat: Solution: The Ball Expands When HeatedDocument1 pageEffect of Heat: Solution: The Ball Expands When HeatedWEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- Transmission of HeatDocument1 pageTransmission of HeatWEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- Transfer of Sound Energy Through VibrationDocument1 pageTransfer of Sound Energy Through VibrationWEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- Density of Transport NetworksDocument1 pageDensity of Transport NetworksWEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- Unit 1: The Real Self (Part 1) Lesson 1: Is That Really Me?: Confidential (For Internal Circulati On Only)Document1 pageUnit 1: The Real Self (Part 1) Lesson 1: Is That Really Me?: Confidential (For Internal Circulati On Only)WEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- Supa TomlinDocument33 pagesSupa TomlinDiya JosephNo ratings yet
- Resultados SaludDignaDocument2 pagesResultados SaludDignaAdriana RamosNo ratings yet
- Study Notebook: Learning Delivery Modalities Course For TeachersDocument45 pagesStudy Notebook: Learning Delivery Modalities Course For TeachersAr Anne UgotNo ratings yet
- Maternity and Women Health Care 10th Edition Lowdermilk Test BankDocument13 pagesMaternity and Women Health Care 10th Edition Lowdermilk Test Banklilyadelaides4zo100% (31)
- The Different Types of InsomniaDocument5 pagesThe Different Types of InsomniaDavid WillNo ratings yet
- Case Study CholecystitisDocument27 pagesCase Study Cholecystitisyhanne98% (225)
- Body-Weakness-Ncp X Drug StudyDocument3 pagesBody-Weakness-Ncp X Drug Studyhayascent hilarioNo ratings yet
- Random Blood Sugar Test AssignmentDocument1 pageRandom Blood Sugar Test AssignmentmadamcloudnineNo ratings yet
- Research Objective ResultDocument2 pagesResearch Objective ResultTriciaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Scale Projects Are Defined As Those Construction Projects That Are Intended For PurelyDocument12 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Scale Projects Are Defined As Those Construction Projects That Are Intended For PurelyBobby Olavides SebastianNo ratings yet
- Crab LouseDocument4 pagesCrab Louseenzo abrahamNo ratings yet
- Higher FunctionDocument181 pagesHigher FunctionMeilisa OngNo ratings yet
- 1 CQU Guide To Reflective WritingDocument2 pages1 CQU Guide To Reflective WritingFokso FutekoNo ratings yet
- SALAM Specialist Hospital Kuala Terengganu: Code Blue 299Document1 pageSALAM Specialist Hospital Kuala Terengganu: Code Blue 299IT Dept. SALAM SPECIALIST HOSPITAL KUALA TERENGGANUNo ratings yet
- SiapDocument7 pagesSiapRizky FatahNo ratings yet
- Concept of HealthDocument20 pagesConcept of HealthMOZAIDNo ratings yet
- Mental HealthDocument58 pagesMental HealthKshitij MauryaNo ratings yet
- Agri Fos 400 MSDSDocument3 pagesAgri Fos 400 MSDSDaniela VargasNo ratings yet
- Sri Mulyani PDFDocument7 pagesSri Mulyani PDFHasna RofifahNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat ExpiredDocument2 pagesDaftar Obat Expiredmira elviantiNo ratings yet
- Neurology 1.03 Approach To Cerebral Function - Dr. MartinezDocument7 pagesNeurology 1.03 Approach To Cerebral Function - Dr. MartinezDeomicah SolanoNo ratings yet
- Anila 8611Document18 pagesAnila 8611Anila zafarNo ratings yet
- Count To Ten Allowing YourselfDocument1 pageCount To Ten Allowing YourselfwisgeorgekwokNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Notes On MT130 Module 1 and 2Document18 pagesSupplementary Notes On MT130 Module 1 and 2Junaid AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Health Risk AssessmentDocument45 pagesHealth Risk AssessmentAboghassanNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 CasesDocument7 pagesLec 2 CasesJoudaziz2003No ratings yet
- FNCP HyperacidityDocument2 pagesFNCP HyperacidityJeriel DelavinNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 15Document1 pageTHBHDK 15RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care - TraditionalDocument38 pagesNursing Care - Traditionalchishimba louisNo ratings yet
- Women - Community Empowerment Project ProposalDocument8 pagesWomen - Community Empowerment Project Proposalnusra_t75% (4)