Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wong - NCP Pneumonia Redo
Uploaded by
Lecery Sophia Wong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views5 pagesOriginal Title
Wong_ncp Pneumonia Redo
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views5 pagesWong - NCP Pneumonia Redo
Uploaded by
Lecery Sophia WongCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
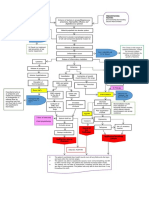
Assessment of Explanation of Goals Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Nursing Dx. the Problem and
Objectives
SUBJECTIVE Ineffective airway GOAL: DIAGNOSTIC: Breath sounds are Outcome criteria for
DATA: clearance is defined >Patient will have a >Auscultate breath normally clear or LTO:
“Nagkaroon siya ng as the inability to patent airway sounds q 2 hours, have scattered fine FM
ubo tapos lagnat na clear secretions or clearance. noting for rate, crackles at bases, > The patient
pawala-wala, obstructions from depth, sounds or which can be manifested clear
nasundan ng the respiratory tract LTO: any respiratory cleared through breath sounds over
pagtatae nung to maintain a clear After 2 weeks of distress (tachypnea, deep breathing. The all lung fields and
pinainom ko ng airway. nursing stridor, crackles or presence of coarse vital signs are back
paracetamol” As Retained interventions, the wheezes) crackles during late within the normal
verbalized by the secretions create a patient will have inspiration indicates ranges.
mother. vicious cycle of lung clear breath sounds fluid in the airway;
damage in a patient over all the lung wheezing indicates PM
that is unable to fields and improved an airway >Patient
OBJECTIVE clear them. When vital signs, obstruction. Thus, manifested
DATA: an irritant is specifically the this is done in order decrease crackle
>RR 40cpm inhaled, the lung respiratory rate. to monitor if there sound upon
>Irregular, shallow, defense are any presence of auscultation and
breathes through mechanisms are set STO: crackles/crackling vital signs are
mouth in motion. An Within 24 hours of >Monitor vital sounds. partially improved.
>Uses accessory inflammatory nursing signs, specifically
muscle for response occurs, in intervention, the pulse oximetry > To obtain UM
breathing which biochemical patient will be able reading and baseline data for >Crackles/Crackling
>Unable to breathe reactions take place to: respiratory rate future comparison sound is heard upon
in supine position (including release of Manifest less as well as to assess auscultation and did
>Auscultation water into the signs of any signs and not decreased in
reveals bilateral area), producing respiratory symptoms of sound; the vital
Crackles on lower excess mucus to distress such as respiratory distress. signs did not
lobes with catch and eliminate dyspnea and If there are any improve.
decreased breath the irritant or tachypnea secretions in the Outcome criteria for
sounds at posterior bacteria from the Manifest an RR airway, the
area lungs. When the of normal THERAPEUTIC: respiratory rate will STO:
mucus cannot be range, 16- >Administer increase. FM
NURSING mobilized and 20cpm from 40 Salbutamol through > The patient was
DIAGNOSIS: removed, secretions cpm, with nebulization as able to expectorate
Ineffective airway are retained. normal depth prescribed by the >Salbutamol, a sputum, have
clearance related to Plugging off of the and rhythm. physician. beta2 adrenergic normal breathing
retained secretion airways may lead to agonist, causes and RR is within
at lower lung fields atelectasis, Follow and bronchodilation and normal range. The
as evidence by pneumonia and a exhibit simple > Elevate head of vasodilation thereby patient also
difficulty breathing ventilation- deep breathing bed to 45 degrees, aiding in keeping achieved increased
perfusion mismatch. exercises or change patient’s the airway clear water intake.
Inflammation and position every 2
infections cause Increase water hours >To relax smooth PM
damage to the intake of up to respiratory >Minimal secretions
airways with 1-2 (250 mL) musculature, expectorated,
changes to its cups per hour reduce airway breathing and RR
lining. This injury is edema and mobilize are improved. The
the beginning of a secretion. patient was not
cycle in which consistent in
airways slowly lose > Also, a way of drinking 1-2 cups
their ability to clear postural drainage per hour.
out mucus. Thus, > Ensure increased where secretions
the presence of intake of warm are accumulated for
secretions on the water of up to 1-2 better expectoration UM
lower lung fields of (250 mL) cups per >The patient was
the patient. hour not able to
Retained expectorate,
secretion in the >Demonstrate > To prevent breathing and RR
airway tract can proper way of dehydration. does not show any
impair the covering mouth sign of
ventilation of the when coughing and improvements. The
patient leading to the use of mask as patient was only
ineffective airway PPE able to drink less
clearance. As a than 1 cup
result to ineffective >To help mobilize throughout the
airway clearance, secretions and for shift.
the patient had the patient to
manifestations of expectorate larger
dyspnea and amount of sputum.
tachypnea.
Breathing comes > Hydration can
naturally and help prevent the
effortlessly to accumulation of
everyone, but there viscous secretions
are some who are and improve
incapable of >Encourage rest, secretion clearance.
keeping their limit activities to Increased water
airways clear. When level of respiratory intake also helps
there is an tolerance. flush out toxins
obstruction in the from the body.
airway, coughing
takes place which it
is the main >It can supply
mechanism for more oxygen thus
clearing it. Increase lessening the effort
in the production of of the patient when
secretions in breathing and so
conditions such as the use of
pneumonia can accessory muscles.
repress these > For infection
mechanisms. control
Pneumonia is
essentially when
fluid or pus gets >Educate patient to >It helps in
trapped in the cough out phlegm reducing fatigue
alveoli of the lungs. or secretions from the energy
instead of expended in
swallowing them coughing and
generally from
being ill
>Educate mother/
caregiver on >Phlegm consists
different airway of the bacteria
clearance causing Pneumonia.
techniques, such as By expectorating
postural drainage the phlegm,
and chest
physiotherapy >For infection
control
>Educate on proper
disposal of >Various
secretions therapies/modalities
may be required to
acquire and
>Reinforce proper maintain adequate
hand hygiene on airways and
the patient and improve respiratory
caregivers functions. This is
taught to the
mother since the
child still needs
assistance
REFERENCE LIST:
Doenges, M, et al. (2017). Nurses Pocket Guide Diagnosis. Prioritized Interventions and Rationales. 14 th edition
Ackley, B. J., Ladwig, G. B., Msn, R. N., Makic, M. B. F., Martinez-Kratz, M., & Zanotti, M. (2019). Nursing Diagnosis Handbook E-
Book: An Evidence-Based Guide to Planning Care. Mosby
Pillitteri, A. (2014). Maternal & child health nursing: Care of the childbearing & childrearing family .
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Case Study ONLINEDocument2 pagesCase Study ONLINELecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Wong Worksheet PediaDocument3 pagesWong Worksheet PediaLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Wong - NCP Pneumonia RedoDocument5 pagesWong - NCP Pneumonia RedoLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Wong CusDocument1 pageWong CusLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Wong - NCP Pneumonia RedoDocument5 pagesWong - NCP Pneumonia RedoLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- The Ten Commandments and Other Biblical PassagesDocument2 pagesThe Ten Commandments and Other Biblical PassagesLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Isbar Galanza PediaDocument1 pageIsbar Galanza PediaLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Pediatric CAP Diagnostic and Treatment ChallengesDocument2 pagesPediatric CAP Diagnostic and Treatment ChallengesLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- LSCW - Hand Out - Postpartum ComplicationsDocument2 pagesLSCW - Hand Out - Postpartum ComplicationsLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- WONG Concept MapDocument1 pageWONG Concept MapLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- WONG, LECERY C. Significance of Studying LiDocument1 pageWONG, LECERY C. Significance of Studying LiLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Promissory NoteDocument1 pagePromissory NoteLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- WONG, LECERY C. Significance of Studying LiDocument1 pageWONG, LECERY C. Significance of Studying LiLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Wong - Activity Checklist Pediatric WardDocument2 pagesWong - Activity Checklist Pediatric WardLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Post Partum Journal (Drnur)Document4 pagesPost Partum Journal (Drnur)Lecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- That May Used in Neurological Ward: Miguelito M. GultianoDocument32 pagesThat May Used in Neurological Ward: Miguelito M. GultianoLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- 10 Reasons To Read The BibleDocument3 pages10 Reasons To Read The BibleLauren CarlosIINo ratings yet
- Wong, L.C. - Philippine Health SituationDocument1 pageWong, L.C. - Philippine Health SituationLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- College Nursing Learning Contract GuideDocument2 pagesCollege Nursing Learning Contract GuideLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Etiologic Agent: Tuberculosis Is A Disease Caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Although TB IsDocument3 pagesEtiologic Agent: Tuberculosis Is A Disease Caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Although TB IsLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Pediatric CAP Diagnostic and Treatment ChallengesDocument2 pagesPediatric CAP Diagnostic and Treatment ChallengesLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Wong, Lecery Sophia C. Obward BSN 2-I1 Iii. Drug Study 1. Naproxen SodiumDocument3 pagesWong, Lecery Sophia C. Obward BSN 2-I1 Iii. Drug Study 1. Naproxen SodiumLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Wong, L.C - Perioperative NursingDocument5 pagesWong, L.C - Perioperative NursingLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Wongl C - Act2-Respiratory-DisordersDocument2 pagesWongl C - Act2-Respiratory-DisordersLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- WONG BrochureCovid 19Document2 pagesWONG BrochureCovid 19Lecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Wong, Lecery Sophia C. Obward BSN 2-I1 Iii. Drug Study 1. Naproxen SodiumDocument3 pagesWong, Lecery Sophia C. Obward BSN 2-I1 Iii. Drug Study 1. Naproxen SodiumLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Pediatric CAP Diagnostic and Treatment ChallengesDocument2 pagesPediatric CAP Diagnostic and Treatment ChallengesLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- WONG BrochureCovid 19Document2 pagesWONG BrochureCovid 19Lecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- WONG TeachingCarePlanCOVID 19Document3 pagesWONG TeachingCarePlanCOVID 19Lecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- A4.Fundamentals - 25item With RationaleDocument4 pagesA4.Fundamentals - 25item With RationaleBlardy Falking You Benchod BlardyNo ratings yet
- Cu 10 (Ncma111)Document2 pagesCu 10 (Ncma111)Arjay VerdejoNo ratings yet
- Thorax, Skin, Hair, Nails ObjectivesDocument3 pagesThorax, Skin, Hair, Nails Objectivesctramel001100% (1)
- Lung Sounds 1Document1 pageLung Sounds 1Kyle LatayanNo ratings yet
- Physical Examinations Respiratory System: InspectionDocument5 pagesPhysical Examinations Respiratory System: InspectionAzizan HannyNo ratings yet
- Chest ExaminationDocument5 pagesChest Examinationalin malekNo ratings yet
- Thoracic and Lung Assessment: College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Maasin City, Southern LeyteDocument4 pagesThoracic and Lung Assessment: College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Maasin City, Southern LeytePrincess Diana Jean ModesteNo ratings yet
- The Breath Sounds: Intensity (Or Loudness)Document6 pagesThe Breath Sounds: Intensity (Or Loudness)Santhosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Thorax and Lungs 2014Document9 pagesAssessment of The Thorax and Lungs 2014alphabennydelta4468No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Nursing Health Assessment The Foundation of Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Patricia M DillonDocument20 pagesTest Bank For Nursing Health Assessment The Foundation of Clinical Practice 3rd Edition Patricia M DillonGinaBranchsxtkw100% (25)
- Physical Examination in Respiratory SystemDocument58 pagesPhysical Examination in Respiratory SystemMarian0% (1)
- Health and Physical Assessment in Nursing 3rd Edition DAmico Test Bank DownloadDocument27 pagesHealth and Physical Assessment in Nursing 3rd Edition DAmico Test Bank DownloadSharon Reper100% (24)
- Respiratory Sounds: by Oluwaseun OlaiyaDocument16 pagesRespiratory Sounds: by Oluwaseun OlaiyaOlaiya OluwaseunNo ratings yet
- Advanced Assessment Chest Assessment and Auscultation: Base Hospital GroupDocument41 pagesAdvanced Assessment Chest Assessment and Auscultation: Base Hospital GroupdeebertoNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 - MidDocument266 pagesNCM 101 - MidJustine Vens G. Agustin100% (1)
- Respiratory Exam GuideDocument18 pagesRespiratory Exam GuideIbi Yulia Setyani100% (1)
- HA Lec Overall 16 23Document8 pagesHA Lec Overall 16 23Sofia Denise JoseNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Respiratory SystemDocument35 pagesExamination of The Respiratory SystemRashhmi Karthodi100% (1)
- Auscultation of Lung Sounds and MurmursDocument8 pagesAuscultation of Lung Sounds and MurmursKarl RobleNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Exam GuideDocument8 pagesRespiratory System Exam GuideBhanu PrakashNo ratings yet
- NRLTL QuizletDocument6 pagesNRLTL QuizletReniella HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Assessment: ObjectivesDocument19 pagesRespiratory System: Assessment: ObjectivesNURSES- NOOK & CORNERNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Assessment Interview and Exam GuideDocument13 pagesRespiratory Assessment Interview and Exam GuideChristine LeeNo ratings yet
- Lung Sounds 5Document1 pageLung Sounds 5Kyle LatayanNo ratings yet
- Breath Sounds: ConsiderationsDocument10 pagesBreath Sounds: ConsiderationsKarl RobleNo ratings yet
- Lung Sounds: Inasa Nabila 1810211113Document10 pagesLung Sounds: Inasa Nabila 1810211113Inasa NabilaNo ratings yet
- MVS Pulmonary AuscultationDocument8 pagesMVS Pulmonary Auscultationvashini9151No ratings yet
- Respiratory System (Physical Examination)Document30 pagesRespiratory System (Physical Examination)Noor Ahmad AhadiNo ratings yet
- 07 - Lung Sounds - LearnerDocument2 pages07 - Lung Sounds - LearnerRafaelNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Respiratory Disease A Case Study Approach To Patient Care 3rd Edition WilkinsDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Respiratory Disease A Case Study Approach To Patient Care 3rd Edition Wilkinsdelphianimpugnerolk3gNo ratings yet