Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adjuncts Conjuncts and Disjuncts
Uploaded by
نسمة املOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adjuncts Conjuncts and Disjuncts
Uploaded by
نسمة املCopyright:
Available Formats
adjuncts, conjuncts and disjuncts
Different types of adverbials: adjuncts, conjuncts and
disjuncts
We use adverbial words, phrases and clauses in different ways. These uses fall into
three categories of adverbials.
Adjuncts are an integral part of the sentence, which provide the reader with information
which is additional to that contained in the subject, verb, object or complement. They
convey information about:
where (place and direction): in the park, over the hill, next to sofa, at a 90°
angle, into the forest, towards the sea
when (time, duration, frequency): at midnight, on Tuesday, for 3 minutes, during
the Jurassic period, while they are spawning, until you reach the station, often, never,
regularly, daily, rarely, continually, occasionally
how (manner, means and instrument): in silence, angrily, with a smile, as
carefully as you can, with great skill, cautiously, by train, by means of a trick, with the
lawnmower, with a pencil
why (reason, purpose): because of the rain, since he left, due to her
carelessness, for ease
The above types of adjuncts are those we most commonly use in primary education;
however, the list is not exhaustive and there are others types. For example, adjuncts
can also:
intensify (definitely, certainly, indeed, really, surely, of course, completely,
entirely, fully)
focus (just, only, purely, simply)
modify adjectives and other adverbs, to provide degrees of intensity (click here
for more information)
contrast (however careful, though unsure)
Conjuncts are those adverbial words, phrases and clauses which have a cohesive
function, connecting different sections of a text. We generally use them at or near the
beginning of a sentence, so that they provide a link to the previous sentence or
paragraph. They help the text to flow by giving continuity to earlier information for the
reader.
As with adjuncts, there are different ways of using conjuncts:
addition – also, furthermore, moreover, in addition, what is more
opposition – however, nevertheless, on the other hand
reinforcing – besides, anyway, after all
explaining – for example, in other words, that is to say
listing – first(ly), first of all, next, finally
indicating result – therefore, consequently, as a result
indicating time – just then, meanwhile, later, in the meantime
Disjuncts are adverbial words, phrases and clauses which enable the speaker or writer
to express beliefs or opinions about what they are communicating. They signal the
attitude of the speaker/writer. For example, obviously, unfortunately, personally, of
course, in my opinion, which is certain, although this is clearly incorrect.
You might also like
- Kinds of Nouns Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesKinds of Nouns Exercise PDFAngel Adriazola RománNo ratings yet
- Structure: Features and OrganizationDocument56 pagesStructure: Features and OrganizationJulieSanchezErsandoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Discourse AnalysisDocument5 pagesQuiz 2 Discourse AnalysisFia ekaNo ratings yet
- Gr. 8 SentencesDocument54 pagesGr. 8 SentencesCamille De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- GerundDocument13 pagesGerundKristian Aji NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Degree of Comparison in English Grammar With Examples PDFDocument3 pagesDegree of Comparison in English Grammar With Examples PDFhemisphereph2981No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Communicative EnglishDocument3 pagesLesson Plan For Communicative EnglishnuruludetNo ratings yet
- Slang and ColloquialismDocument25 pagesSlang and ColloquialismGenelyn TalladNo ratings yet
- DeterminerDocument8 pagesDeterminerpreethamNo ratings yet
- Trương Thùy Khánh Vân - 63NNA5: Compound SentencesDocument8 pagesTrương Thùy Khánh Vân - 63NNA5: Compound SentencesVân Trương Thùy KhánhNo ratings yet
- Hugging The Jukebox TasksDocument3 pagesHugging The Jukebox TasksSafa KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Adjuncts, Disjuncts, ConjunctsDocument13 pagesUnit 3. Adjuncts, Disjuncts, ConjunctsLinh NinhNo ratings yet
- Clause AnalysisDocument35 pagesClause AnalysisJayapal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Issues Worksheet 2018Document3 pagesEnvironmental Issues Worksheet 2018Paola QuindeNo ratings yet
- Context CluesDocument12 pagesContext CluesAlessandra Julianne Raye Medel100% (1)
- Adjectives Mini LessonDocument3 pagesAdjectives Mini Lessonapi-242423412100% (1)
- Adjuncts, Disjuncts and Conjuncts: I. Common Features of Adverbials A. Expression (Or Realization)Document7 pagesAdjuncts, Disjuncts and Conjuncts: I. Common Features of Adverbials A. Expression (Or Realization)Linh NinhNo ratings yet
- Phrases, Clauses, Finite and Non-Finite VerbsDocument3 pagesPhrases, Clauses, Finite and Non-Finite VerbsSanthosh SNo ratings yet
- Noun - PronounDocument19 pagesNoun - PronounAlula FarzanaNo ratings yet
- LappDocument14 pagesLappapi-301715107No ratings yet
- Class Summary ReportDocument4 pagesClass Summary Reportjonalyn tamayo100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Assignment Poem and StoryDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Assignment Poem and StoryRosman DrahmanNo ratings yet
- Sheet Part of SpeechDocument10 pagesSheet Part of SpeechMarchy MarchNo ratings yet
- Phrases and ClausesDocument11 pagesPhrases and ClausesChepie Creencia33% (3)
- Final Print Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesFinal Print Lesson PlanAl Reymond GonzagaNo ratings yet
- MCS GCUF NotesDocument17 pagesMCS GCUF NotesMuhammad MussawarNo ratings yet
- PREPOSITION TypesDocument13 pagesPREPOSITION TypesRonesa OmarNo ratings yet
- Scoring GuideDocument2 pagesScoring Guideapi-290638407No ratings yet
- Misplaced and Dangling ModifiersDocument13 pagesMisplaced and Dangling Modifiersapi-308785195No ratings yet
- Stress and IntonationsDocument4 pagesStress and IntonationsRuku GovalNo ratings yet
- Tree Diagram MorphosyntaxDocument6 pagesTree Diagram MorphosyntaxAlifa TrisdayantiNo ratings yet
- Position of AdjectivesDocument2 pagesPosition of AdjectivesAngyang He100% (1)
- Use Sentence, Clauses and Phrases Appropriately andDocument29 pagesUse Sentence, Clauses and Phrases Appropriately andGeraldine F. SagarioNo ratings yet
- 9 Modifier 1 Haun (Autosaved)Document55 pages9 Modifier 1 Haun (Autosaved)Harunur RashidNo ratings yet
- Tie 030 Unit 9 - Subordinators and Transitions of Comparison and Contrast - HoDocument5 pagesTie 030 Unit 9 - Subordinators and Transitions of Comparison and Contrast - Hoapi-209731670100% (2)
- English Assessment TestsDocument11 pagesEnglish Assessment TestsVasile SilionNo ratings yet
- Paraphrase, Summary, PrecisDocument16 pagesParaphrase, Summary, PrecisXiao NaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 English Grammar - Unit 4-PronounsDocument14 pagesGrade 7 English Grammar - Unit 4-PronounsDaniel KunkelNo ratings yet
- Advance Reading ComprehensionDocument16 pagesAdvance Reading ComprehensionYeoh Lay TeenNo ratings yet
- Logical ConnectorsDocument20 pagesLogical ConnectorsSi Madeline100% (1)
- Modal Adverb Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesModal Adverb Lesson Planapi-587326479100% (1)
- Conversation Passive Causative With Puppets - Video: StudentDocument4 pagesConversation Passive Causative With Puppets - Video: StudentSOLEDAD IAN FUENTES QUISBERTNo ratings yet
- ParallelismDocument7 pagesParallelismmariaNo ratings yet
- Chamber Theater: (3 Year - 4 Year)Document2 pagesChamber Theater: (3 Year - 4 Year)Ronix OngNo ratings yet
- 6 English - 1 Functions of NounsDocument9 pages6 English - 1 Functions of NounsRochelle Acala Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Use The Past and Past Perfect Tenses Correctly in Varied ContextsDocument6 pagesUse The Past and Past Perfect Tenses Correctly in Varied ContextsG4 - TURCO, SHERVIE HEART E.No ratings yet
- ENG DraftDocument7 pagesENG DraftJustine Maria Ira AmenNo ratings yet
- Chipko MovementDocument18 pagesChipko MovementNichole MaudeNo ratings yet
- Cases of Pronoun DLPDocument19 pagesCases of Pronoun DLPJennylyn Corrales TomasNo ratings yet
- VII Dad and The Cat and The Tree - PoemDocument1 pageVII Dad and The Cat and The Tree - PoemRupali DeepNo ratings yet
- Unicorn in The GardenDocument4 pagesUnicorn in The GardenSujatha MenonNo ratings yet
- Ela Lesson Plan-Sentence Structure Run On SentencesDocument3 pagesEla Lesson Plan-Sentence Structure Run On Sentencesapi-475816581No ratings yet
- Lp-Because I Could Not Stop For DeathDocument3 pagesLp-Because I Could Not Stop For DeathMarco KalaloNo ratings yet
- English DeterminersDocument12 pagesEnglish Determinerswaqarali78692No ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument17 pagesReported SpeechalwiNo ratings yet
- Derivational Suffix ListDocument6 pagesDerivational Suffix ListBrent LeeNo ratings yet
- 12 Verb TensesDocument36 pages12 Verb Tensesモーラーリー いたちNo ratings yet
- English For Cultural Literacy 7: UNIT I: Expressing Attitudes MeaningfullyDocument36 pagesEnglish For Cultural Literacy 7: UNIT I: Expressing Attitudes MeaningfullyTrisha AliparoNo ratings yet
- Subject Terminology For English Lang and LitDocument3 pagesSubject Terminology For English Lang and Litapi-200352820No ratings yet
- English ReviewerDocument4 pagesEnglish ReviewerCasey Eunice CataluñaNo ratings yet
- Countable and Uncountable Nouns Unit 6 ةـدودـعملـا ـرـيغـو ةـدودـعملـا ءامسلاـاDocument6 pagesCountable and Uncountable Nouns Unit 6 ةـدودـعملـا ـرـيغـو ةـدودـعملـا ءامسلاـانسمة املNo ratings yet
- Choose The Correct AdjectiveDocument1 pageChoose The Correct AdjectiveLiliaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Quiz المضاع التامDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect Quiz المضاع التامنسمة املNo ratings yet
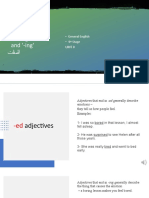
- Adjectives ending in '-ed' and '-ing' تاـفصلــا: - General English - 4 Stage Unit 8Document6 pagesAdjectives ending in '-ed' and '-ing' تاـفصلــا: - General English - 4 Stage Unit 8نسمة املNo ratings yet
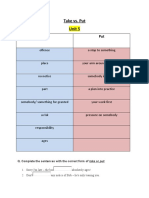
- Take vs. PutDocument2 pagesTake vs. Putنسمة املNo ratings yet
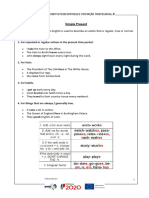
- Present Perfect TenseDocument7 pagesPresent Perfect Tenseنسمة املNo ratings yet
- Roles of The ObjectDocument1 pageRoles of The Objectنسمة املNo ratings yet
- Ex 183Document1 pageEx 183نسمة املNo ratings yet
- Negation: Definition, Rules & ExamplesDocument3 pagesNegation: Definition, Rules & Examplesنسمة املNo ratings yet
- Pronunciation Problems 1Document14 pagesPronunciation Problems 1Yavuz TunciNo ratings yet
- Rules of Numbers in ArabicDocument2 pagesRules of Numbers in Arabicapi-19715112No ratings yet
- Thesis Writing TagalogDocument8 pagesThesis Writing TagalogDustin Pytko100% (2)
- Xys QMXX 8 SDocument1 pageXys QMXX 8 SALLEAH ALBITNo ratings yet
- Present Simple+Present ContinuousDocument7 pagesPresent Simple+Present ContinuousBarbara MatadinhoNo ratings yet
- Error AnalysisDocument5 pagesError AnalysisNajah BwalyaNo ratings yet
- Allied School H.M Campus Qadirabad: Test English Class 9Document2 pagesAllied School H.M Campus Qadirabad: Test English Class 9Sami UllahNo ratings yet
- Ok. We Can Go Another TimeDocument46 pagesOk. We Can Go Another TimeMohamed MousaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document9 pagesUnit 3Estefani ZambranoNo ratings yet
- I Think I'Ll Travel To LimaDocument2 pagesI Think I'Ll Travel To LimaLois FernandoNo ratings yet
- An Outline of The History of LinguisticsDocument5 pagesAn Outline of The History of LinguisticsKoSaRNo ratings yet
- WEEK 10 - Unit 3 - Wild LifeDocument6 pagesWEEK 10 - Unit 3 - Wild LifeAnas RamliNo ratings yet
- De Luyen HSG - KeyDocument6 pagesDe Luyen HSG - KeyThanh LamNo ratings yet
- My English LabDocument93 pagesMy English LabANA85% (40)
- LESSON PLAN Expressions of Ability Bahasa Inggris Kelas 8Document11 pagesLESSON PLAN Expressions of Ability Bahasa Inggris Kelas 8Isna Wildi AlaydaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper in English Language TeachingDocument7 pagesResearch Paper in English Language Teachinghgrmzbikf100% (1)
- Grade 9 DLL ENGLISH 9 Q1 Week 2Document3 pagesGrade 9 DLL ENGLISH 9 Q1 Week 2Love ApallaNo ratings yet
- English Guide. Students Sucre MiguelDocument5 pagesEnglish Guide. Students Sucre MiguelHenry David MayaNo ratings yet
- English 7 q1m4 Using Past and Past Perfect Tenses in Varied ContextsDocument19 pagesEnglish 7 q1m4 Using Past and Past Perfect Tenses in Varied ContextsacirnusosNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Examination in English Grade 9Document4 pagesFirst Quarter Examination in English Grade 9Juniel DapatNo ratings yet
- Yerevan State University: Faculty of European Languages and Communication English Philology ChairDocument17 pagesYerevan State University: Faculty of European Languages and Communication English Philology ChairLusine ArustamyanNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 7 - Q1 - Mod6Document24 pagesENGLISH 7 - Q1 - Mod6Ariane del Rosario100% (1)
- Latihan Simple Present Tense For Yr 6Document2 pagesLatihan Simple Present Tense For Yr 6Mohd Uzaini Mat JusohNo ratings yet
- Coll V Textbook Lesson 1Document22 pagesColl V Textbook Lesson 1Shaurya Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Contrastive Analysis of The English and Pashto AdjectiveDocument12 pagesContrastive Analysis of The English and Pashto Adjectivemuhammad faheemNo ratings yet
- Bahasa InggrisDocument41 pagesBahasa InggrisAntika WahyusNo ratings yet
- GCSE English Poetry - AQA Anthology Moon On The Tides (Character and Voice Poems Analysed)Document15 pagesGCSE English Poetry - AQA Anthology Moon On The Tides (Character and Voice Poems Analysed)Attiya75% (4)
- Media Language: The Way in Which A Text Is Constructed To Create Meaning For A Reader or Viewer of The TextDocument23 pagesMedia Language: The Way in Which A Text Is Constructed To Create Meaning For A Reader or Viewer of The TextNur-aine Londa HajijulNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice SMP 2Document2 pagesPassive Voice SMP 2Ami AzizahNo ratings yet
- 43 All India Conference of Dravidian LinguistsDocument6 pages43 All India Conference of Dravidian LinguistsV N BHATTATHIRINo ratings yet
- Writing Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsFrom EverandWriting Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsNo ratings yet
- The Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageFrom EverandThe Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (916)
- 1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundFrom Everand1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- Body Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.From EverandBody Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- Stonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonFrom EverandStonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSurrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Summary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Learn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (15)
- How Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideFrom EverandHow Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideNo ratings yet
- Wordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageFrom EverandWordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (427)
- Spanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesFrom EverandSpanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Learn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- Idioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsFrom EverandIdioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- The History of English: The Biography of a LanguageFrom EverandThe History of English: The Biography of a LanguageRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Learn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (151)
- Everything You'll Ever Need: You Can Find Within YourselfFrom EverandEverything You'll Ever Need: You Can Find Within YourselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (41)
- Learn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (136)
- Essential French in 2 hours with Paul Noble: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandEssential French in 2 hours with Paul Noble: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (39)
- Do You Talk Funny?: 7 Comedy Habits to Become a Better (and Funnier) Public SpeakerFrom EverandDo You Talk Funny?: 7 Comedy Habits to Become a Better (and Funnier) Public SpeakerRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (20)
- Living the Artist's Way: An Intuitive Path to Greater CreativityFrom EverandLiving the Artist's Way: An Intuitive Path to Greater CreativityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)