Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oct.19-23 - Skeletal - Appendicular - Laboratory
Uploaded by
kristineOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oct.19-23 - Skeletal - Appendicular - Laboratory
Uploaded by
kristineCopyright:
Available Formats
ANATOMY - Laboratory
Skeletal System - Appendicular
Dr. Ernesto R. Tagorda Jr. MD, FPSGS,FPCS
Week 7 | October 23, 2020
OUTLINE
A. UPPER EXTRREMITIES
B. LOWER EXTREMITIES
C. PECTORAL GIRDLE
D. PELVIC GIRDLE
Legends
Atlas To Remember
🕮 ☞
A. UPPER EXTREMITIES : arm, forearm, hand 🕮
Feature / location function
Humerus: longest and largest bone of the upper limb.
Articulates proximally with the scapula and distally at the elbow with ulna and radius.
* Proximal end rounded head Articulates with glenoid cavity of scapula
to form glenohumeral joint
*body (shaft ) proximal end – roughly
cylindrical
Prepared by: Subida, Takchangen; Yap Page 1 of 13
ANATOMY | Skeletal System - Appendicular (Dr. Tagorda) | Week 7 | AY 2020-2021(1st Semester)
distal – flattened and broad
*capitulum Round knob Articulates with the head of the
radius
*trochlea medial to capitulum Articulates with the ulna
spool shaped surface
* Coronoid fossa crown shaped receives the coronoid process of the
anterior depression ulna when the forearm is flexed
* radial fossa Anterior depression above the articulates with the head of the radius
capitulum when the forearm is flexed (bent).
* medial epicondyle and lateral rough projections on either side Attachment of tendons of most muscles
epicondyle of the distal end of the humerus of the forearm
*olecranon fossa Large posterior depression Receives olecranon of the ulna when
the forearm is extended
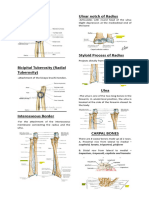
Ulna – longer than the radius (mnemonic – pu : pinky is on the ulna side)
*olecranon Proximal end Forms the prominence of the elbow
*coronoid process Anterior projection Articulates with the trochlea of the humerus
*trochlear notch Large curve between
olecranon and coronoid
process
*radial notch Depression inferior and lateral Articulates with the head of the radius
to the trochlear notch
*ulnar tuberosity Inferior to the coronoid biceps brachii muscle attaches
Prepared by: Subida, Takchangen; Yap Page 2 of 13
ANATOMY | Skeletal System - Appendicular (Dr. Tagorda) | Week 7 | AY 2020-2021(1st Semester)
process
*styloid process Posterior side of the ulna’s attachment for theulnar collateral ligament
distal end to the wrist
Radius – smaller bone (thumb side ) ; proximal end – narrow ; distal - wide
*proximal end Narrow articulates with the capitulum of the
Disc –shape head humerus and the radial notch of the
ulna
*radial tuberosity Attachment for the tendons of the biceps
brachii muscle
*styloid process attachment for the brachioradialis muscle
and for attachment of the radial
collateral ligament to the wrist.
**The ulna and radius articulate with the humerus at the elbow joint**
Carpus (wrist)
scaphoid Boat like Proximal : articulates with
lunate Moon shaped the distal ends of the ulna
Prepared by: Subida, Takchangen; Yap Page 3 of 13
ANATOMY | Skeletal System - Appendicular (Dr. Tagorda) | Week 7 | AY 2020-2021(1st Semester)
pisiform Pea shaped and radius to form the wrist
joint
trapezium four-sided figure with no two distal
sides parallel
trapezoid four-sided figure with two
sides parallel
capitate Head shaped, largest carpal
bone, rounded projection
hamate hooked
B. LOWER EXTREMITIES : thigh, leg, foot 🕮
Femur - longest, heaviest, and strongest bone in the body.
* proximal end Round head - contains a articulates with the
Prepared by: Subida, Takchangen; Yap Page 4 of 13
ANATOMY | Skeletal System - Appendicular (Dr. Tagorda) | Week 7 | AY 2020-2021(1st Semester)
small centered acetabulum of the hip bone
depression(pit) called the
fovea capitis
*distal end articulates with the tibia and
patella.
* greater trochanter It is a landmark commonly attachment for the tendons
used to locate the site for of some of the thigh and
intramuscular injections into buttock muscles.
the lateral surface of the
thigh.
*lesser trochanter inferior and medial to the
greater trochanter.
Prepared by: Subida, Takchangen; Yap Page 5 of 13
ANATOMY | Skeletal System - Appendicular (Dr. Tagorda) | Week 7 | AY 2020-2021(1st Semester)
Tibia - articulates at its proximal end with the femur and fibula, and at its distal end with the fibula and
Prepared by: Subida, Takchangen; Yap Page 6 of 13
ANATOMY | Skeletal System - Appendicular (Dr. Tagorda) | Week 7 | AY 2020-2021(1st Semester)
the talus bone of the ankle
* tibial tuberosity Anterior surface attachment for the patellar ligament
Fibula – smaller (does not articulate with the femur, but it does help stabilize the ankle joint)
* head (proximal end) articulates with the inferior surface of the
lateral condyle of the tibia below the
level of the knee joint to form the
proximal tibiofibular joint.
*distal end more arrow head-shaped
lateral malleolus - projection articulates with the talus of the ankle.
tarsus(ankle) - proximal region of the foot and consists of seven tarsal bones
● Talus : most superior tarsal bone, is the only bone of the foot that articulates with the fibula and tibia
● Calcaneus: is the largest and strongest tarsal bone.
● The anterior tarsal bones are the navicular(like a little boat), threecuneiform bones(wedge-shaped)
called the third (lateral),second (intermediate),and first (medial) cuneiforms,and thecuboid(cube-
shaped
metatarsus - the intermediate region of the foot, consists of five metatarsal bones numbered I to V (or 1–5)
from the medial to lateral position
phalanges -distal component of the foot. The toes are numbered I to V (or 1–5) beginning with the great toe,
from medial to lateral.
Prepared by: Subida, Takchangen; Yap Page 7 of 13
ANATOMY | Skeletal System - Appendicular (Dr. Tagorda) | Week 7 | AY 2020-2021(1st Semester)
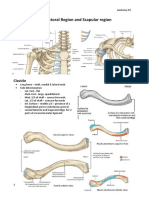
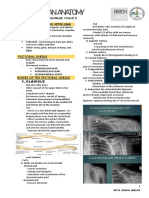
C. PECTORAL GIRDLE 🕮
Pectoral girdle
clavicle s-shaped Sternal head (rounded) -
articulates with the
manubrium of the sternum at
the sternoclavicular joint
Acromial end (broad, flat)-
articulates with the acromion
of the scapula to form the
acromioclavicular joint
scapula articulates with the clavicle at
the acromioclavicular joint.
The glenoid cavity of the
scapula articulates with the
head of the humerus to form
the glenohumeral (shoulder)
joint.
Prepared by: Subida, Takchangen; Yap Page 8 of 13
ANATOMY | Skeletal System - Appendicular (Dr. Tagorda) | Week 7 | AY 2020-2021(1st Semester)
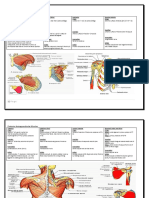
D. PELVIC GIRDLE 🕮
Prepared by: Subida, Takchangen; Yap Page 9 of 13
ANATOMY | Skeletal System - Appendicular (Dr. Tagorda) | Week 7 | AY 2020-2021(1st Semester)
Prepared by: Subida, Takchangen; Yap Page 10 of
13
ANATOMY | Skeletal System - Appendicular (Dr. Tagorda) | Week 7 | AY 2020-2021(1st Semester)
Prepared by: Subida, Takchangen; Yap Page 11 of
13
ANATOMY | Skeletal System - Appendicular (Dr. Tagorda) | Week 7 | AY 2020-2021(1st Semester)
Prepared by: Subida, Takchangen; Yap Page 12 of
13
ANATOMY | Skeletal System - Appendicular (Dr. Tagorda) | Week 7 | AY 2020-2021(1st Semester)
Pelvic girdle
*bony pelvis strong and stable support for the vertebral
column and pelvic and lower abdominal
organs
Hip bone
The ilium largest of the three body - helps form the acetabulum
components of the hip bone
* superior ala(wing) and an
inferior body
ischium inferior, posterior portion of
the hip bone
* superior body and an inferior
ramus
The pubis anterior and inferior part of the Flexibility – baby delivery
hip bone
REFERENCES
1. Gerard Tortora and Bryan Derrickson. Principles of anatomy and physiology. 12 edition. Printed in the United States of
America. Copyright © 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
2. Peter Abrahams, Jonathan Spratt, Marios Loukas and Albert Van Schoor. Clinical Atlas of Human Anatomy. 7th edition.
Copyright © 2013, Elsevier Limited.
Prepared by: Subida, Takchangen; Yap Page 13 of
13
You might also like
- Kinesiology Flashcards, 3E - Lippert, Lynn S., Minor, Mary Alice DuesterhauseDocument219 pagesKinesiology Flashcards, 3E - Lippert, Lynn S., Minor, Mary Alice DuesterhauseMatiasJ100% (25)
- Muscle Origin Insertion Nerve Action Comment ShoulderDocument10 pagesMuscle Origin Insertion Nerve Action Comment ShoulderAdam IrsyaddyraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Upper LimbDocument9 pagesAnatomy - Upper LimbjainilNo ratings yet
- Muscle, Origin, InsertionDocument9 pagesMuscle, Origin, Insertionshananana1616No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesMuscular SystemKylaNicole SierrasNo ratings yet
- Osteology Osteology Is The Study of Bones That Are Considered The Framework of The BodyDocument40 pagesOsteology Osteology Is The Study of Bones That Are Considered The Framework of The BodybingchillingNo ratings yet
- Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper ExtremityDocument12 pagesMuscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper ExtremityKaren ManlapazNo ratings yet
- The Girdles Sternum and Paired AppendagesDocument9 pagesThe Girdles Sternum and Paired AppendagesAmberValentineNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesSkeletal SystemmelendezramesesjosephNo ratings yet
- Asset - 8288 - Anatomy of The Canine Forelimb PDFDocument35 pagesAsset - 8288 - Anatomy of The Canine Forelimb PDFBianca ElenaNo ratings yet
- Final IbcDocument26 pagesFinal IbcAngeliitha Tqm Ramos GarciaNo ratings yet
- Oia Keisha PDFDocument7 pagesOia Keisha PDFJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Origins and InsertionsDocument12 pagesOrigins and InsertionsFrancesca vitaleNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy of The Forearm: A CAL Package Designed By-Pratik SinhaDocument24 pagesGross Anatomy of The Forearm: A CAL Package Designed By-Pratik Sinhaapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Muscles of RabbitDocument19 pagesMuscles of RabbitshanleymojaresNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Lesson 4Document40 pagesSkeletal System Lesson 4Ella Nika FangonNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Upper Limb Muscles of The Back Superficial Back Proximal Distal Action InnervationDocument7 pagesMuscles of The Upper Limb Muscles of The Back Superficial Back Proximal Distal Action InnervationKris GulleyNo ratings yet
- Arm and ForearmDocument4 pagesArm and ForearmANIS MUNIRAH BINTI MOHD ARSHAD -No ratings yet
- SCAPULA /shoulder Blade/: Biceps Brachii MuscleDocument5 pagesSCAPULA /shoulder Blade/: Biceps Brachii MuscleFor AstroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 03 - Pectoral and Scapular Region (Pre Med 101)Document10 pagesAnatomy 03 - Pectoral and Scapular Region (Pre Med 101)Navoda Dulshan PereraNo ratings yet
- A&P - Muscle WorksheetDocument4 pagesA&P - Muscle WorksheetJerry GNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Upper Limb (Oct 25, 2022)Document48 pagesBones of The Upper Limb (Oct 25, 2022)huzaifa arshadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Knee Joint Lateral RetinaculumDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The Knee Joint Lateral RetinaculumHenrique TapumNo ratings yet
- Ao UcsDocument6 pagesAo Ucsdennis ferreraNo ratings yet
- Wrist and Hand TransesDocument5 pagesWrist and Hand TranseskatrizmaervillagantolNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal Systemstar fireNo ratings yet
- Muscle OIAN - HandDocument3 pagesMuscle OIAN - Handanais MitchellNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall To Upper Limb: Muscle Origin Insertion Action Nerve SupplyDocument13 pagesThoracic Wall To Upper Limb: Muscle Origin Insertion Action Nerve SupplyShandria AlbertoNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument9 pagesAnatomyfarahjurdi8No ratings yet
- Narins 2002Document10 pagesNarins 2002Manta RayNo ratings yet
- 0.5x ANATOMY LOWER LIMBSDocument24 pages0.5x ANATOMY LOWER LIMBSArijeet77No ratings yet
- Lesson 11: Skeletal Muscle Lesson ObjectivesDocument6 pagesLesson 11: Skeletal Muscle Lesson ObjectivesRichee LunnayNo ratings yet
- BIO 1133 Exercise 7 (Skeletal System of The Frog)Document7 pagesBIO 1133 Exercise 7 (Skeletal System of The Frog)Tonet LapeNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Shoulder and ArmDocument3 pagesMuscles of Shoulder and ArmAhadNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Tulang Extremitas SuperiorDocument30 pagesAnatomi Tulang Extremitas SuperiorZUHRUF YARISUNA KHOLID FIRDAUSNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb TransDocument18 pagesUpper Limb Transashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomy-MSKDocument86 pages1 Anatomy-MSKashim tiwariNo ratings yet
- Rad Ana Midterm Upper ExtremityDocument3 pagesRad Ana Midterm Upper ExtremityAlvin Karl ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Upper Limb 27Document300 pagesAnatomy of Upper Limb 27Abdisa AdemNo ratings yet
- Lower Anatomy PT 2120Document29 pagesLower Anatomy PT 2120mahmoudmyoussef2001No ratings yet
- Muscle Origin Insertion Action: Thin Sheet Half of The Jaw Thin Sheet Tip of Jaw From HyoidDocument3 pagesMuscle Origin Insertion Action: Thin Sheet Half of The Jaw Thin Sheet Tip of Jaw From HyoidRejaelSenoroNo ratings yet
- Muscle Innervation Chart IIDocument7 pagesMuscle Innervation Chart IIkimsue9448No ratings yet
- UE Muscles OINADocument3 pagesUE Muscles OINAUshuaia Chely FilomenoNo ratings yet
- Trunk Range of MotionDocument6 pagesTrunk Range of MotionacNo ratings yet
- Wrist and Hand NotesDocument3 pagesWrist and Hand Notesdreianne90No ratings yet
- Ngo, Ricky Justin N. 3bio7 Cat MusculatureDocument13 pagesNgo, Ricky Justin N. 3bio7 Cat MusculatureRicky Justin NgoNo ratings yet
- Rodilla MSKDocument8 pagesRodilla MSKaliciaNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb by DR - JalalDocument55 pagesUpper Limb by DR - JalalAbedelaal MohamedNo ratings yet
- Elbow Complex (Kinesiology)Document2 pagesElbow Complex (Kinesiology)Kimmybee Garcia50% (2)
- M1 Anatomy Tutorial - Bones, Joints and Proximal Muscles of The Upper Limb (David)Document8 pagesM1 Anatomy Tutorial - Bones, Joints and Proximal Muscles of The Upper Limb (David)Tony NgNo ratings yet
- Topic Overview Week 3Document5 pagesTopic Overview Week 3laurenNo ratings yet
- All Bat NotesDocument1,048 pagesAll Bat NotesAfk SystemNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Musculoskeletal System: AppendagesDocument16 pagesAnatomy of The Musculoskeletal System: AppendagesRyzeNo ratings yet
- Femur and PatellaDocument15 pagesFemur and PatellaaroojNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Forearm and Hand ULNA - Longer Proximally, Pinky SideDocument3 pagesBones of The Forearm and Hand ULNA - Longer Proximally, Pinky SideJeanne Waldo ReminajesNo ratings yet
- Cat SkeletonDocument10 pagesCat SkeletonJefferson TanNo ratings yet
- Muscle Chart Upper ExtremityDocument3 pagesMuscle Chart Upper Extremitykep1313100% (1)
- Tendon Transfers For Radial Nerve PalsyDocument62 pagesTendon Transfers For Radial Nerve Palsyavinashrao39No ratings yet
- Origin No JutsuuuuuuuuuDocument6 pagesOrigin No Jutsuuuuuuuuukristel amadaNo ratings yet
- Subclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)Document6 pagesSubclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)馮素琴No ratings yet
- DVT at Ortho 2020Document49 pagesDVT at Ortho 2020srijankbhatiaNo ratings yet
- Lec 11 UL Forarm Anterior CompartmentDocument32 pagesLec 11 UL Forarm Anterior CompartmenthusseinNo ratings yet
- A&p - All Files in One PDFDocument201 pagesA&p - All Files in One PDFandreeaNo ratings yet
- Coronoid FractureDocument38 pagesCoronoid FractureRamin MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Gross Comparative Anatomy of Domestic AnimalsDocument51 pagesGross Comparative Anatomy of Domestic AnimalsLila Loureen AlkuinoNo ratings yet
- Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex: Fundamental AnatomyDocument9 pagesTriangular Fibrocartilage Complex: Fundamental AnatomyManiDeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- Exp-4, To Study The General Features of Axial and Appendicular Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesExp-4, To Study The General Features of Axial and Appendicular Skeletal SystemKeshab KapoorNo ratings yet
- FixinCatalog PDFDocument44 pagesFixinCatalog PDFWedoeditor Fast100% (1)
- Open Reduction Internal FixationDocument7 pagesOpen Reduction Internal FixationalcojonicNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology Flashcards, 3E - Lippert, Lynn S., Minor, Mary Alice Duesterhause PDFDocument219 pagesKinesiology Flashcards, 3E - Lippert, Lynn S., Minor, Mary Alice Duesterhause PDFOrNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy Avian, Thoracic and Hind Limbs (VetBooks - Ir)Document83 pagesSurgical Anatomy Avian, Thoracic and Hind Limbs (VetBooks - Ir)LorrayneNo ratings yet
- Snell Muscle TablesDocument8 pagesSnell Muscle TablesSmallppNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument9 pagesANATOMYAndrassy Twinkle AlineaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy QuestionDocument22 pagesAnatomy Questionشاجوان عباس محمد احمدNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Human Body (Origin, Insertion, Innervation, Action)Document9 pagesMuscles of The Human Body (Origin, Insertion, Innervation, Action)Alyssa LumaadNo ratings yet
- Fracture Treatment - Quick Reference PosterDocument1 pageFracture Treatment - Quick Reference PosterTingting GeNo ratings yet
- 17 - Distal Radius FracturesDocument78 pages17 - Distal Radius FracturesFlorin Panduru100% (1)
- Vet Science-1Document51 pagesVet Science-1Fira'ol BogalaNo ratings yet
- Muscle Extremitas SuperiorDocument57 pagesMuscle Extremitas SuperiorDewi NurpratiwiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The ArmDocument38 pagesAnatomy of The ArmAkomolede AbosedeNo ratings yet
- Traumatology Orthopaedic EXAMDocument219 pagesTraumatology Orthopaedic EXAMElo GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Operative Treatment of Elbow Injuries PDFDocument169 pagesOperative Treatment of Elbow Injuries PDFBogdan SerbanNo ratings yet
- Bones of Limbs - Pharmacy - 12-9Document41 pagesBones of Limbs - Pharmacy - 12-9安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Upper and Lower Limb X Rays QeytgvDocument83 pagesUpper and Lower Limb X Rays Qeytgvغايتى رضاك والجنهNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MCQS Part 4 PDFDocument20 pagesAnatomy MCQS Part 4 PDFSamer Qusay100% (1)
- Anatomy of The ForearmDocument2 pagesAnatomy of The ForearmAmal LadNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy 1 Laboratory: Labelling ReportDocument22 pagesGeneral Anatomy 1 Laboratory: Labelling ReportMigz BolivarNo ratings yet
- The Small Intestine Channel of Hand TaiyangDocument165 pagesThe Small Intestine Channel of Hand TaiyangGeeta SajjanNo ratings yet
- Elbow: Posterior ApproachDocument5 pagesElbow: Posterior Approachhaitham alkhamaisehNo ratings yet