Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Materials Science and Engineering (L) : New Era University
Uploaded by
malik aliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Materials Science and Engineering (L) : New Era University
Uploaded by
malik aliCopyright:
Available Formats
NEW ERA UNIVERSITY
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE
Department of Mechanical Engineering
MATERIALS SCIENCE
AND ENGINEERING (L)
A LABORATORY MANUAL
Compiled by
ERWIN T. STA. MARIA
Laboratory Exercise No. 8
Torsional Stress Test of A Galvanized Iron (GI) Pipe
NAME: Date Performed:
Program/Year: Date Submitted:
Day/Time/Group: Instructor:
Laboratory Exercise No. 8
Torsional Stress Test of A Galvanized Iron (GI) Pipe
Objectives :
Upon completion of this laboratory exercise, the students must be able to:
1. familiarize themselves on the principles of torsional stress,
2. get acquainted on the use of a torque wrench as an alternative equipment
or tool for testing
3. realize the significance of loads exerted on metallic materials,
4. identify actual applications in the field of mechanical engineering
Introduction :
In many engineering applications, engineering components are subjected to
torsion. So it is necessary for an engineer to understand the basics of torsion theory and
learn how an engineering material in mechanical components will act under torsion
stresses.
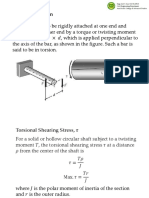
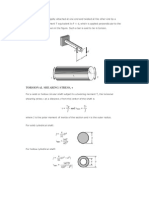
When an engineering component is subjected to twisting moment or torque then
it is said that the component is under torsion.. Stress produced as a result of torsion are
called torsional shear stress. Torsional shear stresses are maximum at outer surface
and minimum at its central axis.
In the exercise, one end of the pipe is fixed and the other is subjected to external
torque. As aid earlier, stresses produced by the torque will be at zero at its central axis
and maximum at the outer surface. The maximum value of this torsional stress can be
find by the formula :
Torsional Stress , τ = Torque applied (T) x radius (r)
Second Polar of Inertia (J)
Reference : Materials Science and Engineering, RS Khurmi & JK Gupta (2005)
List of Instruments, Apparatus and Materials
Pull-Push Steel Tape
Vernier Caliper
Steel Cutting Saw
Torque wrench set
GI Pipe ½ inch diameter x 3 inches
Procedures
1. Get reminders about safety of machines to be used.
2. Cut the galvanized iron pipe to a length of 3 inches
3. Measure the diameter of the pipe and its length
4. Prepare the torque wrench set
5. Place the GI Pipe to a table vice, and have it clamped.
6. Upon securing clamps, twist the pipe until an angle of twist is measured. This is
the angular displacement as a result of applied torque.
7. Take note of the load and measure it.
8. Compute for the torsional stress.
9. Clear the area of the used materials.
10. Secure the torque wrench and other tools after its usage.
Sample Computations :
1. Second Polar of Inertia, J =Πx D⁴
of the pipe 32
2. Torsional Shear , τ = Torque applied (T) x radius (r)
Stress Second Polar of Inertia (J)
3. Modulus of Rigidity, G = . Torque applied (T) x Length of Pipe (ɭ) .
Angular Displacement (Ө) x Polar of Inertia (J)
4. Torsional Shear Strain, γ = radius (r) x Angular Displacement (Ө)
Length of Pipe (ɭ)
Final Tabulation of Data TABLE
I
Sample Outside Inside Length
TRIAL Material Diameter Diameter (mm)
(mm) (mm)
1 GI Pipe
2
3
TABLE II
TRIAL Load, Angle of Polar Torsional Modulus of Torsional
No. T Displacement Moment of Stress Rigidity, G Shear Strain
(N-m) Ө, (radians) Inertia (mm²) (MPa) (N/mm²) (mm/mm or %)
1
2
3
TABLE III
Sample
TRIAL Material
ID
1
2
3
Questions to Answer :
1. What are the applications of torsional shear stress in mechanical
engineering practice?
2. How do torsional stresses of steel pipes compare to PVC pipes?
Name : Date Performed:
Day/Time:
Laboratory Exercise No. 8
Torsional Stress Test of A Galvanized Iron (GI) Pipe
PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET
TABLE I
TRIAL Sample Outside Inside Length Other Data Other Data
Material Diameter Diamete (mm) (mm)
(mm) r (mm)
1
2
TABLE
Reading Load, T Angle of Polar Torsional Modulus of Torsional
No. (N-m) Displacement Moment of Stress Rigidity, G Shear Strain
Ө, (radians) Inertia (mm²) (MPa) (N/mm²) (mm/mm or %)
1
2
3
TABLE III
TRIAL Sample
Material
ID
1
2
Group no. _
Approved for
Leader : _
finalization For
Members :
revision / correction
1. _
Remarks :
2. _
_
3. _
4. _
5. .
Instructor
You might also like
- DK. BMT Lab ManualDocument46 pagesDK. BMT Lab ManualPaviter SinghNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Ueme1132 Experiment 1Document11 pagesUeme1132 Experiment 1freeloadNo ratings yet
- The Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryFrom EverandThe Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryNo ratings yet
- ASM Lab Record BookDocument36 pagesASM Lab Record BookNandan HegdeNo ratings yet
- MT Lab Experiment 3Document13 pagesMT Lab Experiment 3Himmat Singh RawatNo ratings yet
- LabEx No. 4 Tensile Test of Reinforcing BarDocument4 pagesLabEx No. 4 Tensile Test of Reinforcing BarianzkieeNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 2 Title:: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesExperiment - 2 Title:: ObjectiveRushiL PateLNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Mechanic Division Spec. Laboratory - Torsion Lab. ReportDocument5 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Mechanic Division Spec. Laboratory - Torsion Lab. ReportBhanuka SamarakoonNo ratings yet
- 85-218-Lab 2-ManualDocument5 pages85-218-Lab 2-Manualjoseph0% (1)
- Ecs258 - Lab Report (Co4: Po4) : Faculty of Civil EngineeringDocument9 pagesEcs258 - Lab Report (Co4: Po4) : Faculty of Civil EngineeringSyafiq FauziNo ratings yet
- Gouasmi 2012 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 28 012015Document6 pagesGouasmi 2012 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 28 012015srinivas murthyNo ratings yet
- BMT LAB NEW Final111111 PDFDocument85 pagesBMT LAB NEW Final111111 PDFmohanNo ratings yet
- BMT ManualDocument72 pagesBMT ManualSuvam PatelNo ratings yet
- SOM 2 Lab ManualDocument52 pagesSOM 2 Lab ManualAnusha GNo ratings yet
- Quantity Estimation 1 Set 1: (E.g. Per Set/group of Student)Document11 pagesQuantity Estimation 1 Set 1: (E.g. Per Set/group of Student)Axel LeeNo ratings yet
- Bet2334 Infrstructural Project (Studio 3) : Faculty of Civil Engineering Technology Univerisiti Malaysia PahangDocument3 pagesBet2334 Infrstructural Project (Studio 3) : Faculty of Civil Engineering Technology Univerisiti Malaysia Pahangummi alyaNo ratings yet
- ESA211 Lab Sheet 2020 - 21 Exp 1 - 7Document31 pagesESA211 Lab Sheet 2020 - 21 Exp 1 - 7pantas cafeeNo ratings yet
- Technical Report - Torsion of BarDocument20 pagesTechnical Report - Torsion of BarGeo AyoubNo ratings yet
- LabEx No. 20 Flexural Strength of Concrete BeamDocument4 pagesLabEx No. 20 Flexural Strength of Concrete BeamGerman BarlisNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument19 pagesLab Manual: Department of Mechanical Engineeringhydromec_indiaNo ratings yet
- MDB 2034 Solid Mechanics: Experiment Sml2: Torsion of Bars Group IdDocument7 pagesMDB 2034 Solid Mechanics: Experiment Sml2: Torsion of Bars Group IdSaswindrran AnnadoraiNo ratings yet
- HW2 Mat e 202 W18Document5 pagesHW2 Mat e 202 W18TahirNo ratings yet
- Tensile TestDocument14 pagesTensile TestAysha AlNo ratings yet
- Mapua Institute of Technology School of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringDocument16 pagesMapua Institute of Technology School of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringJan Philip GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ecs258 - Lab Report (Co4: Po4) : Faculty of Civil EngineeringDocument10 pagesEcs258 - Lab Report (Co4: Po4) : Faculty of Civil EngineeringSyafwan Hafiz100% (1)
- Strength of Materials Laboratory ExperimentsDocument20 pagesStrength of Materials Laboratory Experimentskenneth iyahenNo ratings yet
- Me136p Exp2 Tensile Test of Reinforcing Steel BarsDocument15 pagesMe136p Exp2 Tensile Test of Reinforcing Steel BarsJohn Henry SalvadoNo ratings yet
- Me136p Exp2 Tensile Test of Reinforcing Steel BarsDocument15 pagesMe136p Exp2 Tensile Test of Reinforcing Steel BarsJohn Henry SalvadoNo ratings yet
- Sokoine University of Agriculture: Department of Engineering Sciences and TechnologyDocument16 pagesSokoine University of Agriculture: Department of Engineering Sciences and TechnologyEngr.Hamid Ismail CheemaNo ratings yet
- Fracture Behavior of 6061 Al Alloy PipesDocument6 pagesFracture Behavior of 6061 Al Alloy PipesbharatNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Chemtech Research: Pravin Pawar, Raj Ballav, Amaresh KumarDocument6 pagesInternational Journal of Chemtech Research: Pravin Pawar, Raj Ballav, Amaresh KumarMuhamad BaharudiantoNo ratings yet
- Standard Incercari MecaniceDocument35 pagesStandard Incercari Mecanicenicolicescu_claudiu5152No ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Lab Final Questions 2020Document3 pagesMechanical Engineering Lab Final Questions 2020jannatul ferdous provaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 (Tensile Test) JD23Document11 pagesLab 1 (Tensile Test) JD23M.Irfan MaasyirNo ratings yet
- Burulma Deneyi Calisma Notu - ENDocument5 pagesBurulma Deneyi Calisma Notu - ENNourTarekHassenNo ratings yet
- LabEx No. 3 Shear Test of WoodDocument4 pagesLabEx No. 3 Shear Test of WoodianzkieeNo ratings yet
- LabEx No. 3 Shear Test of WoodDocument4 pagesLabEx No. 3 Shear Test of WoodianzkieeNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test: Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringDocument10 pagesTensile Test: Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringMohd Danial HNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 ErianeDocument16 pagesExp 3 ErianeEriane GarciaNo ratings yet
- Praktikumsanleitung Ws16-17.de - enDocument28 pagesPraktikumsanleitung Ws16-17.de - enadhiprachNo ratings yet
- DETERMINATION OF OPTIMAL CUTTING CONDITIONS Chua Et Al 1991Document9 pagesDETERMINATION OF OPTIMAL CUTTING CONDITIONS Chua Et Al 1991ROZIKINNo ratings yet
- Experiment p1 Metal Cutting ProcessDocument13 pagesExperiment p1 Metal Cutting Processvipin_shrivastava25No ratings yet
- Torsion Lab Manual (Short) PDFDocument7 pagesTorsion Lab Manual (Short) PDFDonnell FrancisNo ratings yet
- 1 Tensile TestDocument10 pages1 Tensile TestAsadullahSafiNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test ReportDocument12 pagesTensile Test ReportMayowaNo ratings yet
- Drop-Weight Impact Studies of GLARE 5 Fiber-Metal LaminatesDocument13 pagesDrop-Weight Impact Studies of GLARE 5 Fiber-Metal LaminatesSharamito AkaritoNo ratings yet
- Ramkrishna Mahato Government Engineering College: S0Lid Mechanics LaboratoryDocument34 pagesRamkrishna Mahato Government Engineering College: S0Lid Mechanics LaboratoryMaynak DeyNo ratings yet
- LabEx No. 2 Flexural Strength of WoodDocument6 pagesLabEx No. 2 Flexural Strength of WoodianzkieeNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT NO 1. Tensile Strength TestDocument11 pagesEXPERIMENT NO 1. Tensile Strength TestAshley Justine RowanNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials LabDocument46 pagesStrength of Materials Labbaladani24No ratings yet
- Torsion Test Lab Report PDFDocument40 pagesTorsion Test Lab Report PDFengkuNo ratings yet
- Realiability of Corrosion DeffectsDocument20 pagesRealiability of Corrosion DeffectsJavier Gualdrón PlataNo ratings yet
- Mostafa Qasim (Lab Report)Document6 pagesMostafa Qasim (Lab Report)Mostafa HamawandyNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual For Engrd 202, Virtual Torsion Experiment Aluminum ModuleDocument10 pagesLab Manual For Engrd 202, Virtual Torsion Experiment Aluminum ModuleJd RhapsodyNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation of Nozzle Junction Based On ASME Pressure Vessel Design CodeDocument7 pagesDesign Calculation of Nozzle Junction Based On ASME Pressure Vessel Design CodebiniamNo ratings yet
- TENSILE Lab SheetDocument4 pagesTENSILE Lab SheetKerem Taha TekinNo ratings yet
- UTA016 Engineering Design Project-IDocument5 pagesUTA016 Engineering Design Project-IVishal SinghNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 StructrDocument6 pagesLab 1 Structriena razakNo ratings yet
- SM CH10 PDFDocument70 pagesSM CH10 PDFJuanJoseVelasquezNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design For TorsionDocument50 pagesAnalysis and Design For TorsionJin-hwan KimNo ratings yet
- Shaft Design and AnalysisDocument11 pagesShaft Design and AnalysisJagadish Mogaveera BNo ratings yet
- MDB Lesson 5 Torsion PDFDocument9 pagesMDB Lesson 5 Torsion PDFpoliman2017No ratings yet
- Strength of Material Chapter 5Document26 pagesStrength of Material Chapter 5naserunn100% (1)
- Mechanics of Solids - (Riveted and Welded Joints)Document37 pagesMechanics of Solids - (Riveted and Welded Joints)TusherNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Non-Circular Bars - Saint Venants - Prandle MethodDocument40 pagesTorsion of Non-Circular Bars - Saint Venants - Prandle MethodMathew JohnNo ratings yet
- Discussion I. Analyse and Differentiate Through A Brief Discussion Based On Data Obtained From Laboratory WorkDocument5 pagesDiscussion I. Analyse and Differentiate Through A Brief Discussion Based On Data Obtained From Laboratory WorkZariff ZakiNo ratings yet
- 1 Shaft Key and CouplingDocument3 pages1 Shaft Key and CouplingBryan Christian G. LambolotoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - TorsionDocument17 pagesChapter 3 - TorsionJohn DeerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Torsion Beams + SFD and BMD. (SOM-201)Document99 pagesChapter 4 Torsion Beams + SFD and BMD. (SOM-201)Raushan Jha100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - TorsionDocument38 pagesChapter 3 - TorsionJovy NotorioNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Circular ShaftsDocument26 pagesTorsion of Circular ShaftsNaveen Kumar0% (1)
- Simple Belt Conveyor Calculation ExampleDocument3 pagesSimple Belt Conveyor Calculation ExampleBerk Koç100% (6)
- Mit - 16.20Document3 pagesMit - 16.20vishalsinha9137No ratings yet
- 4 Simple StressesDocument25 pages4 Simple StressesPRASAD326No ratings yet
- Shaft DesignDocument33 pagesShaft DesignMunawwar Abbas0% (1)
- Chapter 4 TorsionDocument20 pagesChapter 4 Torsionشكار حسينNo ratings yet
- Som MCQDocument17 pagesSom MCQShiva KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- CouplingsDocument15 pagesCouplingshudaperistesNo ratings yet
- 3 TorsionDocument26 pages3 TorsionataNo ratings yet
- Unit III TorsionDocument7 pagesUnit III TorsionVirtusEstoestaNo ratings yet
- TorsionDocument46 pagesTorsionVenkata Kiran MullapudiNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials 4th Ed by Ferdinand L Singer Andrew Pytel Www07MettkDocument21 pagesStrength of Materials 4th Ed by Ferdinand L Singer Andrew Pytel Www07Mettkvjereme100% (3)
- M 452 ContentDocument65 pagesM 452 ContentISsa Qafa'itiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials: TorsionDocument51 pagesMechanics of Materials: Torsionpaul loganNo ratings yet
- Structural Sections: To BS4: Part 1: 1993 and BS EN10056: 1999Document48 pagesStructural Sections: To BS4: Part 1: 1993 and BS EN10056: 1999Gammal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document14 pagesWeek 1Mohammed AlryaniNo ratings yet
- Solutions Chapter 5 (WǪ) PDFDocument34 pagesSolutions Chapter 5 (WǪ) PDF黃羿傑No ratings yet
- CE6306-Strength of Materials NotesDocument16 pagesCE6306-Strength of Materials NotesTrishul SampathNo ratings yet
- The Cyanide Canary: A True Story of InjusticeFrom EverandThe Cyanide Canary: A True Story of InjusticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (52)
- Slow Violence and the Environmentalism of the PoorFrom EverandSlow Violence and the Environmentalism of the PoorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Rights of Nature: A Legal Revolution That Could Save the WorldFrom EverandThe Rights of Nature: A Legal Revolution That Could Save the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Waste: One Woman’s Fight Against America’s Dirty SecretFrom EverandWaste: One Woman’s Fight Against America’s Dirty SecretRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Art of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionFrom EverandArt of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- 3rd Grade Science: Life Sciences in Eco Systems | Textbook EditionFrom Everand3rd Grade Science: Life Sciences in Eco Systems | Textbook EditionNo ratings yet
- Desperate: An Epic Battle for Clean Water and Justice in AppalachiaFrom EverandDesperate: An Epic Battle for Clean Water and Justice in AppalachiaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Environmental Education in Practice: Concepts and ApplicationsFrom EverandEnvironmental Education in Practice: Concepts and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Exposure: Poisoned Water, Corporate Greed, and One Lawyer's Twenty-Year Battle Against DuPontFrom EverandExposure: Poisoned Water, Corporate Greed, and One Lawyer's Twenty-Year Battle Against DuPontRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Busted!: Drug War Survival Skills and True Dope DFrom EverandBusted!: Drug War Survival Skills and True Dope DRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Exposure: Poisoned Water, Corporate Greed, and One Lawyer's Twenty-Year Battle against DuPontFrom EverandExposure: Poisoned Water, Corporate Greed, and One Lawyer's Twenty-Year Battle against DuPontRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- The Intersection of Intellectual Property Law and the “Green” Movement: RIPL’s Green Issue 2010From EverandThe Intersection of Intellectual Property Law and the “Green” Movement: RIPL’s Green Issue 2010Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Down to the Wire: Confronting Climate CollapseFrom EverandDown to the Wire: Confronting Climate CollapseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Reduce, Reuse and Recycle : The Secret to Environmental Sustainability : Environment Textbooks | Children's Environment BooksFrom EverandReduce, Reuse and Recycle : The Secret to Environmental Sustainability : Environment Textbooks | Children's Environment BooksNo ratings yet
- Fighting Westway: Environmental Law, Citizen Activism, and the Regulatory War That Transformed New York CityFrom EverandFighting Westway: Environmental Law, Citizen Activism, and the Regulatory War That Transformed New York CityNo ratings yet
- Land Divided by Law: The Yakama Indian Nation as Environmental History, 1840-1933From EverandLand Divided by Law: The Yakama Indian Nation as Environmental History, 1840-1933No ratings yet
- New Paradigms in Environmental Biomonitoring Using PlantsFrom EverandNew Paradigms in Environmental Biomonitoring Using PlantsSupriya TiwariNo ratings yet
- Dawn at Mineral King Valley: The Sierra Club, the Disney Company, and the Rise of Environmental LawFrom EverandDawn at Mineral King Valley: The Sierra Club, the Disney Company, and the Rise of Environmental LawRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (334)
- Ecosystem Facts That You Should Know - The Forests Edition - Nature Picture Books | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandEcosystem Facts That You Should Know - The Forests Edition - Nature Picture Books | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet