Professional Documents
Culture Documents
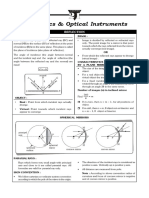
Reflection of Light Total Internal Reflection Refraction of Light
Uploaded by
Gaming X YTOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reflection of Light Total Internal Reflection Refraction of Light
Uploaded by
Gaming X YTCopyright:
Available Formats
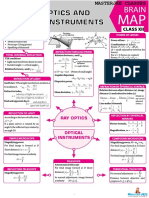
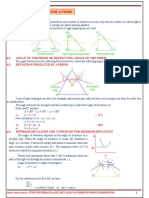
RAY OPTICS
PART-1
RAY OPTICS
REFLECTION OF LIGHT TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION REFRACTION OF LIGHT
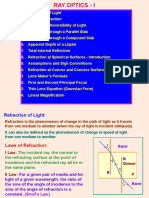
TIR CONDITIONS
Normal
According to the laws of reflec�on,
∠i = ∠r •Light must travel from denser Rarer
to rarer, i Medium
If a plane mirror is rotated
by an angle of �, the reflected rays •Incident angle i>cri�cal angle ie
Denser
Medium r
rotates by an angle 2�. 1
Rela�on between μ & ie : μ =
Sin ie
APPLICATION OF TIR SNELL’S LAW
Normal
•Fiber op�cs Communica�on When light travels from
In
y
ra
cid
•Medical endoscopy medium a to medium b,
ed
en
ct
μ
tr
fle
i r •Periscope (using prism) Sin i
ay
a
Re
μ = =
•Sparkling of diamond ab μ Sin r
b
Refrac�ve index,
c
REFLECTION BY SPHERICAL P μ=
v
MIRROR
1 1 1 2 A Real & apparent depth
Mirror formula, δ
+ = = i1 real depth (x)
u v f R i2 μ=
r1 r2 Apparent depth (y)
v h
Magnifica�on, m = - = i
u ho REFRACTION BY
Q R SPHERICAL SURFACE
REFRACTION THROUGH Rela�on between object
PRISM distance (u), image distance (v)
and refrac�on index (μ)
Rela�on between μ and δm δm μ2 μ μ - μ1
- 1 = 2
ght
Sin [ (A+δm) / 2 ] R v u R
μ= li O
Sin (A/2) W hite Y
G Lens maker’s formula
B
[ ]
I
V 1 1 1
or , δ = (μ-1)A = (μ-1) -
f R R
Screen 1 2
Angular dispersion,
= δv - δR = ( μV - μR )A THIN SPHERICAL LENS POWER OF LENS
Thin lens formula, Power of lens,
Dispersive power, 1
1 1 1 P=
δ v - δR μV - μR f (in m)
w= = - =
μ-1 v u f Combina�on of lenses,
δ
Mean devia�on, Magnifica�on, Power : P = P1 + P2 - dP1P2
(d=small separa�on between the lenses )
δ +δ v h
δ= v R m= = i For d = 0 ( lenses in contact)
2 u ho
Power : P = P1 + P2 + P3 +......
SCATTERING OF LIGHT
The process of re-emission of absorbed light in all direc�ons with different intensi�es by atoms or
molecules , is called sca�ering of light.
DAILY LIFE APPLICATIONS
•Blue colour of the sky.
•Reddening of the sun at sunrise and sunset.
You might also like
- RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS CLASS NOTESDocument1 pageRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS CLASS NOTESMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- Laws of Refraction:: I LawDocument4 pagesLaws of Refraction:: I LawhareeshNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light through Prism ExplainedDocument17 pagesRefraction of Light through Prism Explainedthe SkulptorNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics - IDocument68 pagesRay Optics - IsmrutirekhaNo ratings yet
- 2 Ray Optics 2Document15 pages2 Ray Optics 2royal ghostNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics FormulasDocument8 pagesRay Optics Formulassamueljoshuah2004No ratings yet
- Pooja 12Document19 pagesPooja 12arthiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Refraction of Light at A Plane SurfaceDocument56 pagesChapter 4 - Refraction of Light at A Plane SurfaceHehe BunbunNo ratings yet
- P10 - RefractionDocument7 pagesP10 - RefractionAdib ShaheenNo ratings yet
- Chap1 Waves WatermarkDocument22 pagesChap1 Waves WatermarkIng Ding LonNo ratings yet
- 2 Ray Optics 2Document18 pages2 Ray Optics 2kdNo ratings yet
- Ch-9 Ray_Optics_2Document15 pagesCh-9 Ray_Optics_2examkv1cuttackNo ratings yet
- Created by C. Mani and Modified by N.K.TyagiDocument19 pagesCreated by C. Mani and Modified by N.K.TyagiNadeem AijazNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics ExplainedDocument29 pagesRay Optics ExplainedsmrutirekhaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ray Optics 1Document46 pages1 Ray Optics 1kd100% (1)
- 6 OpticsDocument68 pages6 OpticsNathanianNo ratings yet
- Huygens Principle and Laws of Rfraction and ReflectionDocument6 pagesHuygens Principle and Laws of Rfraction and Reflectionmahimamg2003No ratings yet
- Ch-9 Ray_Optics_1Document19 pagesCh-9 Ray_Optics_1examkv1cuttackNo ratings yet
- Ray 5Document5 pagesRay 5shreyashenoy03No ratings yet
- Created by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreDocument19 pagesCreated by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreNirmala Devi100% (1)
- Optics Refraction Snell's LawsDocument7 pagesOptics Refraction Snell's LawsUmesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Optical InstrumentsDocument9 pagesRay Optics Optical InstrumentsEternalChronosNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Light - Reflection and Refraction Notes, Important Questions & Practice PaperDocument1 pageClass 10 Science Light - Reflection and Refraction Notes, Important Questions & Practice Papermangawallah07No ratings yet
- Understanding Optics &optical CommunicationsDocument44 pagesUnderstanding Optics &optical CommunicationsWondimu KenateNo ratings yet
- Chap 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument7 pagesChap 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsAryan ZutshiNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction For PodcastDocument74 pagesOptics and Refraction For PodcastKittithep Sukkhong100% (1)
- Formula Sheet 2022Document10 pagesFormula Sheet 2022Prakhyat 19No ratings yet
- Prism Refractive IndexDocument60 pagesPrism Refractive IndexAnik ManojNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024Document4 pagesRay Optics and Optical Instruments - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024bhaveshkumarbijaniNo ratings yet
- Physics Book 2 FormulasDocument12 pagesPhysics Book 2 FormulasMrs. NishaNo ratings yet
- Prism Refraction and DeviationDocument7 pagesPrism Refraction and Deviationashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics - Reflection Important QuestionsDocument58 pagesRay Optics - Reflection Important QuestionsRuchirNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics: Snell's Law &Document68 pagesGeometrical Optics: Snell's Law &Mr. X100% (1)
- (L6) Ray Optics - Reflection 8th SeptDocument54 pages(L6) Ray Optics - Reflection 8th SeptRajkeshwar SahuNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Understanding Refraction of LightDocument13 pages5.2 Understanding Refraction of LightkhodijahaminNo ratings yet
- sadsddsadwaddwdaDocument23 pagessadsddsadwaddwdaredlegend606No ratings yet
- Wjec Gce Mathematics Unit 3 5 Trigonometry AbDocument2 pagesWjec Gce Mathematics Unit 3 5 Trigonometry AbSubiraj RamanjoolooNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument19 pagesDownloadHooria AlyNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Chapter SummaryDocument37 pagesRay Optics Chapter SummaryANMOLNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics: Key Concept Exercise Exercise Exercise Answer KeyDocument19 pagesGeometrical Optics: Key Concept Exercise Exercise Exercise Answer KeyRoN100% (1)
- XII Wave OpticsDocument16 pagesXII Wave OpticsMeenal BansalNo ratings yet
- Waves Optics 1Document16 pagesWaves Optics 1WarishaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Refraction at Plane Surface Theory Module-5-1Document8 pages3 - Refraction at Plane Surface Theory Module-5-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics PDFDocument44 pagesGeometrical Optics PDFSukesh Subaharan100% (1)
- Applications of Trigonometry To WavesDocument13 pagesApplications of Trigonometry To WavesSylvia WilsonNo ratings yet
- LENSDocument20 pagesLENSA PNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 2Document1 pagePdfa5 2aizatNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics: Raman Niwas (Near Aakashwani), Mahmoorganj, Varanasi. Ph. (0542) - 2363455, WWW - Catjee.inDocument100 pagesRay Optics: Raman Niwas (Near Aakashwani), Mahmoorganj, Varanasi. Ph. (0542) - 2363455, WWW - Catjee.inaloneguy251No ratings yet
- Refraction of Light: SyllabusDocument35 pagesRefraction of Light: SyllabusGomesNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument24 pagesPhysics ProjectP Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023-24 Optics Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument18 pagesJEE Main 2023-24 Optics Revision Notes - Free PDF Downloadbalwannain1977No ratings yet
- Medical Imaging Techniques SPECTPETDocument51 pagesMedical Imaging Techniques SPECTPETMSNo ratings yet
- Optics PDFDocument23 pagesOptics PDFabhishekNo ratings yet
- Ometrical Optics ExerciseDocument59 pagesOmetrical Optics ExerciseMojisola OluwatunbiNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics PPT 1Document16 pagesWave Optics PPT 1Bhupesh100% (1)
- Refraction of Light For NTSEDocument65 pagesRefraction of Light For NTSEKrishna KishoreSarva100% (1)
- Introduction to Applied Optics for EngineersFrom EverandIntroduction to Applied Optics for EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Practical Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy: Industrial and laboratory chemical analysisFrom EverandPractical Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy: Industrial and laboratory chemical analysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- AESL April KB Class-10 Reduced SizeDocument39 pagesAESL April KB Class-10 Reduced SizeGaming X YTNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Atomic Mass ColorDocument1 pagePeriodic Table Atomic Mass ColorGaming X YTNo ratings yet
- Collection of Geometry ProblemsDocument8 pagesCollection of Geometry Problemsaopssnorlax100% (3)
- 72097Document7 pages72097Gary SynthosNo ratings yet
- M01 Exam: Geometry, Numbers and Algebra QuestionsDocument8 pagesM01 Exam: Geometry, Numbers and Algebra QuestionsAnupamNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers: For For For For ForDocument12 pagesQuestions & Answers: For For For For ForRaghav guptaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - Mat: Time: 1:00 HoursDocument11 pagesSample Paper - Mat: Time: 1:00 Hoursbrm1shubhaNo ratings yet
- NSEJS 2015 Answer Key PDFDocument5 pagesNSEJS 2015 Answer Key PDFPremMehtaNo ratings yet
- Nco Class 10Document2 pagesNco Class 10purntripathiNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Symmetry 13 00442 v2Document102 pagesSymmetry 13 00442 v2Gaming X YTNo ratings yet
- Nco Class 10Document2 pagesNco Class 10purntripathiNo ratings yet
- Artemis Plan PDFDocument74 pagesArtemis Plan PDFMystery WireNo ratings yet
- At A Glance/ Pharmacy Calculations: Mixing ConcentrationsDocument2 pagesAt A Glance/ Pharmacy Calculations: Mixing ConcentrationsGaming X YTNo ratings yet
- Professional Diploma in Artificial Intelligence Starter PackDocument8 pagesProfessional Diploma in Artificial Intelligence Starter PackGaming X YTNo ratings yet
- Thermographic TestingDocument14 pagesThermographic TestingArluky NovandyNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text About RainbowDocument4 pagesExplanation Text About RainbowNeyHafniiCyuwCyu25% (4)
- Micromachines 11 00666 v2Document25 pagesMicromachines 11 00666 v2Paola GongoraNo ratings yet
- Hollow Core Fiber Optic Ring Resonator For Rotation Sensing: ME6 PDFDocument4 pagesHollow Core Fiber Optic Ring Resonator For Rotation Sensing: ME6 PDFSebastian Soto PerdomoNo ratings yet
- ASTM E1672-12 Standard Guide For Computed Tomography (CT) System SelectionDocument10 pagesASTM E1672-12 Standard Guide For Computed Tomography (CT) System SelectiondaiweijueNo ratings yet
- IR IntroductionDocument48 pagesIR IntroductionMuhammad Erik Rezakola Ahnaf100% (1)
- Physics Investigatory FinalDocument19 pagesPhysics Investigatory FinalsrishtiNo ratings yet
- Classification of Analytical TechniquesDocument8 pagesClassification of Analytical TechniquesAmais AslamNo ratings yet
- Optical Properties of Solids Prof. Mark Fox: Autumn SemesterDocument81 pagesOptical Properties of Solids Prof. Mark Fox: Autumn SemesterInuk YouNo ratings yet
- Efek Radiasi Dan Proteksi RadiasiDocument56 pagesEfek Radiasi Dan Proteksi RadiasiMargana SitumorangNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Examination: Standard Guide ForDocument13 pagesRadiographic Examination: Standard Guide ForLuis JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics - : BPHY101LDocument7 pagesEngineering Physics - : BPHY101LVenkat BalajiNo ratings yet
- Maser Theory TownesDocument10 pagesMaser Theory TownesMauricio Alfredo Fuentes FloresNo ratings yet
- School BookDocument114 pagesSchool BookNeelambal SeeranganNo ratings yet
- User Manual PDFDocument139 pagesUser Manual PDFvschintapalliNo ratings yet
- Design of Anti-Reflection Coatings For Application in The Infrared Region (10.6 Micron)Document6 pagesDesign of Anti-Reflection Coatings For Application in The Infrared Region (10.6 Micron)Anurak OnnnoomNo ratings yet
- Em SpectrumDocument3 pagesEm SpectrumMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Radiation Safety Test Study GuideDocument9 pagesRadiation Safety Test Study GuideVon A. Damirez100% (1)
- Low-Profile Wideband Dual-Polarized Antenna For Millimeter-Wave Beam Steering ApplicationsDocument11 pagesLow-Profile Wideband Dual-Polarized Antenna For Millimeter-Wave Beam Steering ApplicationsSuman NelaturiNo ratings yet
- Space Radiation EnvironmentDocument110 pagesSpace Radiation EnvironmentBulut100% (1)
- Ict in Disaster Management in IndiaDocument27 pagesIct in Disaster Management in IndiaTransform Healthcare ITNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/12Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/12Nisha zehraNo ratings yet
- Extra NumericalsDocument2 pagesExtra NumericalsDeep KambleNo ratings yet
- Decreasing Wavelength Increasing Increasing Frequency Decreasing Increasing Energy DecreasingDocument3 pagesDecreasing Wavelength Increasing Increasing Frequency Decreasing Increasing Energy DecreasingShielo Marie CardinesNo ratings yet
- Srestha ADocument108 pagesSrestha ARounak GhoshNo ratings yet
- Mobile Mobile Radiography Radiography Gpy GpyDocument10 pagesMobile Mobile Radiography Radiography Gpy GpyPaulNo ratings yet
- Refraction TestDocument3 pagesRefraction TestVaishakh VarierNo ratings yet
- Antenna 4800 2L 4M 1.5m: Capacity Compact CoverageDocument6 pagesAntenna 4800 2L 4M 1.5m: Capacity Compact CoverageMARCO OLIVERIONo ratings yet
- Convection AnswersDocument5 pagesConvection AnswersShakerMahmoodNo ratings yet
- Huygens' Theory of Double Refraction: PrincipalDocument13 pagesHuygens' Theory of Double Refraction: PrincipalGokul Subramanyan100% (1)