Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes Ch-12 Reproduction in Plants
Uploaded by
Bobby NoharaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes Ch-12 Reproduction in Plants
Uploaded by
Bobby NoharaCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Ch-12 Notes
Monday, April 12, 2021 12:40 PM
Notes Ch-12
Reproduction in Plants
All living organisms have a characteristic that they can produce their own kind. This
production of the offspring from the parents is called Reproduction.
Modes of Reproduction in Plants
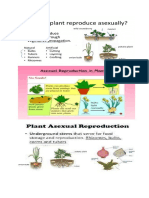
• Asexual Reproduction – The new plants are produced without using the seeds. In this
process, generally, the leaves, stems and roots participate in reproduction.
• Sexual Reproduction – The new plants are produced with the help of the seeds of a
plant. In this process, the flowers of the plants participate in reproduction.
Shoot – A young plant is often termed as a shoot. Generally, a shoot is regarded as a part of
the plant which has stems, leaves and flowers.
Node – It is a part of the stem or branch of a plant from where the leaf arises.
Vegetative Buds – Sometimes buds are present in the leaves that are capable of developing
into shoots. These are called Vegetative Buds.
Figure 1: Roots and Shoot in a Plant
Different types of Asexual Reproduction:
1. Vegetative Propagation
This type of reproduction takes place with the help of the vegetative parts of the plant. Only
one parent can produce the identical offspring in vegetative propagation.
Natural means of Vegetative Propagation:
a) Vegetative Propagation by Roots
Figure 2: Vegetative propagation by roots in Sweet Potato
• Plants that have tuberous roots, that is, roots which are used as a storage organ in plants
participate in vegetative propagation. In order to grow new plants, these tuberous roots are
sown in the soil.
• Example: Sweet potato and dahlia
b) Vegetative Propagation by Stem
• Stem Tubers: Just like tuberous roots, some plants have tuberous stems. These stem
tubers store the nutrients and bear nodes. These nodes bear buds that form the new plants.
Example: Potato
Figure 3: Vegetative propagation by stem in Potato
Some plants can also grow from when a portion of their stem is sown in the soil (cutting). For
e.g. The rose plant, moneyplant etc
Figure 6: Cutting
c) Vegetative Propagation by Leaves
• Some plants have leaves that contain buds that can develop into a new plant. Example:
Bryophyllum
Figure 5: Vegetative propagation by leaves of Bryophyllum
Advantages of Vegetative Propagation
• The plants that are produced with vegetative propagation grow faster than those that are
produced with sexual reproduction.
• The plants that reproduce with vegetative reproduction have fruits and flowers ahead of
time.
• The plants that are produced have exactly the same characteristics as that of their
parents.
2. Budding
• Yeast is an organism that contains a single cell. It is a fungi. It can propagate every few
hours if the proper amount of nutrients are available to it. As the yeast finds favourable
conditions, a small bulb-like projection produces from the yeast called Bud.
The bud grows gradually and then gets detached from the parent yeast. This new cell then
grows measures and produces more cells. Sometimes a chain of buds is formed which leads
to the production of a large number of yeasts altogether.
3. Fragmentation
• Algae like Spirogyra generally reproduce by the process of fragmentation in which they
divide themselves into multiple parts. As soon as the algae find enough water and nutrients, it
fragments and grows into new individuals.
• This process continues and algae multiply quickly in a short period of time.
4. Spore Formation
• Some plants contain spores that float in the air and cause asexual reproduction. A spore
has a hard protective cover which protects it from the unfavourable environmental conditions
like temperature and humidity. As a result, the spores can travel long distances and survive
for a long duration of time.
• As soon as they find favourable conditions such as moisture and nutrients, they germinate
and form new plants. For Example, Moss and ferns propagate in this way.
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
• The flowers of a plant are its reproductive organs that participate in the sexual
reproduction process. The male reproductive parts of a plant are called Stamen. The female
reproductive parts of a plant are called Pistil.
• Some flowers contain both stamen and pistil and are called Bisexual Flowers. Eg. Lily,
rose, brinjal, hibiscus, petunia, mustard etc. Some flowers contain either the statement or the
pistil and hence are called Unisexual Flowers. Eg. papaya, watermelon, cucumber, coconut
etc.
• The stamen consists of Anther that has pollen grains. These pollen grains produce male
gametes.
Figure 11: Stamen
• The pistil consists of three parts:
• Stigma – It is a sticky surface where pollen grains get attached.
• Style – It is a tube-like structure which connects the stigma and the ovary.
• Ovary – It contains eggs in which the female gametes or eggs are formed.
Figure 12: Pistil
How the male gametes reach the female gametes in plants?
• The male gametes reach the female gametes by the process of pollination. The pollen
grains have a tough covering which allows them in surviving the different climatic conditions.
• Due to their lightweight, winds and water often carry them away to different plants.
Sometimes the pollen grains also get attached to insects which carry them to different flowers.
This process of transfer of pollen grains from one stigma to another is called Pollination.
Figure 13: Pollination
Figure 14: Self-pollination and Cross-pollination
The Fertilization Process
• A zygote is formed as the fusion between the male and female gametes occurs. This
process of formation of the zygote is called Fertilization. Then the zygote develops and turns
in an embryo.
How fruits and seeds are formed?
• After the fertilization process, the ovary of the flowers grows and develops into a fruit. The
remaining parts of the flower fall off. The ovules develop and form the seeds of the fruits. The
embryo is enclosed inside the seeds.
• Some fruits are fleshy and juicy such as mango, apple and orange. Some fruits are hard
like almonds and walnuts
Figure 16: Formation of Fruits and Seeds
NCERT QUESTIONS
Q3. Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Ans: The mode of reproduction in which new plants are produced with the help of seeds is
known as sexual reproduction. The reproduction happens by the fusion of male and female
gametes.
In plants, the stamen is the male reproductive part. It consists of anthers and filaments. The
pollen grains found inside the anther produces male gamete.
The female reproductive part, pistil consists of stigma, style and ovary. Ovary contains ovules
which produce female gametes. The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilization.
Q7. How does the process of fertilisation take place in flowers?
Ans: When the pollen grain from the anther lands on the stigma of a plant by pollination, it
begins to germinate. The pollen grain extends a pollen tube through the style.
The male gamete travels in the pollen tube and reaches the ovule inside the ovary. There it
fuses with the female gamete and a zygote is formed. This process is called fertilisation. The
zygote then develops into an embryo.
You might also like
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants: Modes, Types and ProcessesDocument15 pagesReproduction in Plants: Modes, Types and ProcessesPta PNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants 7th GradeDocument14 pagesReproduction in Plants 7th Grade5545116.shreyastammeneniNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants Notes: Asexual and Sexual ProcessesDocument13 pagesReproduction in Plants Notes: Asexual and Sexual ProcessesAdnan SathikNo ratings yet
- Gr12 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument14 pagesGr12 - Reproduction in PlantsZelNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsrichie2885No ratings yet
- Reproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)Document10 pagesReproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)richelyn navalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12 Reproduction in PlantsDocument5 pagesChapter - 12 Reproduction in Plantsanju singhNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants - The Processes of Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument9 pagesReproduction in Plants - The Processes of Asexual and Sexual Reproductionmr. unknownNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterDocument7 pagesScience 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterHoneylet Alberto Castro ArilloNo ratings yet
- Reproduction PLANTDocument48 pagesReproduction PLANTmonamoikoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesReproduction in PlantsRenuNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Seeds and Its GerminationDocument18 pagesParts of The Seeds and Its GerminationNova Estrada KionisalaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesReproduction in PlantsRajeevSangam0% (1)
- Plant Reproduction - Sexual and Asexual Methods ExplainedDocument30 pagesPlant Reproduction - Sexual and Asexual Methods ExplainedShvet MahajanNo ratings yet
- Bio 3Document4 pagesBio 3sumitverma78929.svNo ratings yet
- Notes Chappter REPRODUCTIONDocument8 pagesNotes Chappter REPRODUCTIONKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument62 pagesPlant ReproductionAdonis BesaNo ratings yet
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Reproduction in Plants – RBSE GuideDocument3 pagesRBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Reproduction in Plants – RBSE GuideAlpine AcademiaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction of PlantsDocument19 pagesReproduction of PlantsYash Vardhan MundhraNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants PPT1Document17 pagesReproduction in Plants PPT1Hardik GulatiNo ratings yet
- Flowers, fruits and seeds: A morphological continuityDocument4 pagesFlowers, fruits and seeds: A morphological continuityJobadzNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument21 pagesReproduction in Plantsrani bloriaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument4 pagesReproduction in PlantsYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants 2020Document22 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants 2020Kestina MillerNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument6 pagesReproductionzainahNo ratings yet
- Vegetative Propagation and Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument19 pagesVegetative Propagation and Sexual Reproduction in PlantsPalak Singh0% (1)
- CBSE Class 7 science chapter on plant reproductionDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 7 science chapter on plant reproductionGiteshNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Lessons 2.0Document97 pages2nd Quarter Lessons 2.0Jean Zyrelle AuronNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document21 pagesPresentation 2Maro Ridhwan RidhiwaniNo ratings yet
- BryophytesDocument5 pagesBryophytesGilbert DullerNo ratings yet
- Plants Reproduction Class NotesDocument7 pagesPlants Reproduction Class NotesrupeshNo ratings yet
- Handbook Plant Reproduction of Small Chilli Pepper Flowers IZZUDDIN ISHAK (D20191088261)Document14 pagesHandbook Plant Reproduction of Small Chilli Pepper Flowers IZZUDDIN ISHAK (D20191088261)Izzuddin IshakNo ratings yet
- Modes of Reproduction in PlantsDocument15 pagesModes of Reproduction in Plantsjudy andrade100% (1)
- Reproduction in Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 12 - Learn CBSEDocument13 pagesReproduction in Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 12 - Learn CBSEPrateek Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Sexual reproduction in flowering plants explainedDocument23 pagesSexual reproduction in flowering plants explainedHeba AliNo ratings yet
- University Search: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesUniversity Search: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsNathan LeeNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Part 2Document6 pagesReproduction Part 2KELVIN CHIBINDANo ratings yet
- Biology Notes For Grade Week 9-10 For Grade 12Document25 pagesBiology Notes For Grade Week 9-10 For Grade 12Adeola YusufNo ratings yet
- Pollination, Fertilisation and GerminationDocument41 pagesPollination, Fertilisation and GerminationMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- A. Objective Type QuestionsDocument5 pagesA. Objective Type QuestionsPOONAM SHARMANo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Science How Plants ReproduceDocument41 pagesGrade 5 Science How Plants ReproduceJulie Mae Sajulga JacobeNo ratings yet
- Examining Fruits and FlowersDocument45 pagesExamining Fruits and Flowerscarlos monteaNo ratings yet
- How Do Plants Reproduce? Lesson 1: I. Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesHow Do Plants Reproduce? Lesson 1: I. Sexual Reproduction in PlantsJulliena BakersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Plant Growth and Reproduction: 5 Grade Science Teacher Imarlys CajigasDocument26 pagesChapter 3: Plant Growth and Reproduction: 5 Grade Science Teacher Imarlys CajigasSNOWCHILL VINESNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction: Biology For MajorsDocument35 pagesPlant Reproduction: Biology For MajorsPotato ManNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument19 pagesSexual ReproductionjojopebblesNo ratings yet
- Self-Incompatibility Lecture Outlines Flower Structure and ReproductionDocument30 pagesSelf-Incompatibility Lecture Outlines Flower Structure and ReproductionlkokodkodNo ratings yet
- MLP HLP Class 7 Reproduction in PlantsDocument5 pagesMLP HLP Class 7 Reproduction in Plantsbose baraniNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument16 pagesPlant Reproduction and Developmentits james de guzmanNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument6 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproduceAlok YadavNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument22 pagesPerpetuation of Lifemarizel salcedoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants 7 SDDocument7 pagesReproduction in Plants 7 SDAnupama NarayananNo ratings yet
- Ppt.x.reproduction 10 23Document83 pagesPpt.x.reproduction 10 23ammara hyderNo ratings yet
- Growing Food MaterialDocument3 pagesGrowing Food MaterialWajeea Asif - 76826/Coordinator/HSPRNo ratings yet
- Angels Project PlantsDocument6 pagesAngels Project Plantsmarycris gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Mode of ReproductionDocument21 pagesMode of ReproductionGian CabayaoNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Plants - 5 Stages + Fun Facts - Science4FunDocument8 pagesLife Cycle of Plants - 5 Stages + Fun Facts - Science4FunMasthankhan PatanNo ratings yet
- Class X Reproduction Notes 1Document13 pagesClass X Reproduction Notes 1vratNo ratings yet
- Gess303 PDFDocument12 pagesGess303 PDFSivaramakrishna SobhaNo ratings yet
- Top International Rankholders in CREST Science Olympiad (CSODocument12 pagesTop International Rankholders in CREST Science Olympiad (CSOBobby NoharaNo ratings yet
- M8 MT Linear Equation QuestionsDocument4 pagesM8 MT Linear Equation QuestionsBobby NoharaNo ratings yet
- NstseDocument46 pagesNstseBobby NoharaNo ratings yet
- NSTSE 2022 OnlineTestSeries (Class I To X) - SyllabusDocument1 pageNSTSE 2022 OnlineTestSeries (Class I To X) - SyllabusBobby NoharaNo ratings yet
- Pronouns WorksheetDocument2 pagesPronouns WorksheetBobby NoharaNo ratings yet
- DiaryDocument1 pageDiaryBobby NoharaNo ratings yet
- Modals and AuxiliariesDocument1 pageModals and AuxiliariesBobby NoharaNo ratings yet
- Grade - VII Subject: Mathematics Worksheet-1 Topic: Integers .Document2 pagesGrade - VII Subject: Mathematics Worksheet-1 Topic: Integers .Bobby Nohara100% (1)
- MesosphereDocument6 pagesMesosphereBobby NoharaNo ratings yet
- Pronouns Worksheet Revision Class 7Document2 pagesPronouns Worksheet Revision Class 7Bobby Nohara100% (1)
- Adverbs WorksheetDocument1 pageAdverbs WorksheetBobby NoharaNo ratings yet
- Unicus UNRMO QuestionsDocument4 pagesUnicus UNRMO QuestionsBobby NoharaNo ratings yet
- Paper SchemeDocument8 pagesPaper SchemeDev MaanNo ratings yet
- Amazing Math Facts: Magic 9s, Norse Hundreds & MoreDocument10 pagesAmazing Math Facts: Magic 9s, Norse Hundreds & MoreBobby NoharaNo ratings yet
- New Images CB-6 Ch1-3 With TOCDocument28 pagesNew Images CB-6 Ch1-3 With TOCBobby NoharaNo ratings yet
- The Mediaval History Saw The Major Development of ReligionsDocument4 pagesThe Mediaval History Saw The Major Development of ReligionsBobby NoharaNo ratings yet
- The Book Choice FernsDocument788 pagesThe Book Choice FernsSaibal ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy of Cassia Alata LeavesDocument6 pagesPharmacognosy of Cassia Alata LeavesMohd Afiq AizatNo ratings yet
- Kompos + Asam Humat MNDocument9 pagesKompos + Asam Humat MNHermanNo ratings yet
- FLORA NEOTROPICA Cecropiaceae - Coussapoa and PouroumaDocument211 pagesFLORA NEOTROPICA Cecropiaceae - Coussapoa and PouroumaSebastián Martínez LlanosNo ratings yet
- Horticulture in India Economics.Document27 pagesHorticulture in India Economics.Muskan KhatriNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Management For Sustainable Groundnut ProdDocument17 pagesNutrient Management For Sustainable Groundnut Proddesai nilimaNo ratings yet
- SBI3U:Plant Unit Review: Non-Vascular PlantsDocument2 pagesSBI3U:Plant Unit Review: Non-Vascular PlantsPavni ChandaniNo ratings yet
- ASESMEN DIAGNOSIS KOGNITIF - Bhs Inggris Kls 9Document2 pagesASESMEN DIAGNOSIS KOGNITIF - Bhs Inggris Kls 9Friska Mahyudin Syah100% (18)
- Biomass, Organic Carbon and Mineral Matter Contents of Abaca (Musa Textilis Nee) at Different Stages of GrowthDocument6 pagesBiomass, Organic Carbon and Mineral Matter Contents of Abaca (Musa Textilis Nee) at Different Stages of GrowthWladimir EncaladaNo ratings yet
- Anale I.C.A.S., 46 - Afforestation degraded lands VranceaDocument2 pagesAnale I.C.A.S., 46 - Afforestation degraded lands VranceagusaNo ratings yet
- Enhancing The Productivity and Profitability in Rice Cultivation by Planting MethodsDocument3 pagesEnhancing The Productivity and Profitability in Rice Cultivation by Planting MethodsSheeja K RakNo ratings yet
- The Living World: Plant Taxonomy and ClassificationDocument17 pagesThe Living World: Plant Taxonomy and ClassificationDébàshis DashNo ratings yet
- Report On Pest and Disease ManagementDocument3 pagesReport On Pest and Disease ManagementIkuzwe Aime PacifiqueNo ratings yet
- 4-Plant Structure and FunctionDocument7 pages4-Plant Structure and FunctionfebrimetrinNo ratings yet
- SlideDoc - Us-Diagnostic Natural Science 4 Primary Byme - Plants - TreesDocument2 pagesSlideDoc - Us-Diagnostic Natural Science 4 Primary Byme - Plants - TreesJuanA.RodriguezGonzalez100% (7)
- AcanthaceaeDocument109 pagesAcanthaceaeAnantha Krishna K SNo ratings yet
- Greeeen - Sakura Color Lyric + TranslationDocument3 pagesGreeeen - Sakura Color Lyric + TranslationLuluk Atul AzizahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantssuryababaNo ratings yet
- Smoakland Menu 420 SpecialsDocument1 pageSmoakland Menu 420 SpecialsACNo ratings yet
- Dragon Fruit Plant CareDocument72 pagesDragon Fruit Plant CareLiza Cabalquinto Lorejo100% (2)
- Final Report On Nursery Establishment (Report 2)Document87 pagesFinal Report On Nursery Establishment (Report 2)woubshetNo ratings yet
- f048m ForagingCalifornia Tut2uDocument257 pagesf048m ForagingCalifornia Tut2uKyle WatsonNo ratings yet
- Sweet Potato SEM IndonesiaDocument8 pagesSweet Potato SEM IndonesiaGalhaadisNo ratings yet
- EVS - Plants Around UsDocument16 pagesEVS - Plants Around UsRenu SyamNo ratings yet
- Yamadori ARTS 344Document5 pagesYamadori ARTS 344Ron GermanoNo ratings yet
- Posttest - CROP SCIDocument7 pagesPosttest - CROP SCIChryselleNo ratings yet
- Management of Phytophthora Diseases of DurianDocument58 pagesManagement of Phytophthora Diseases of DurianLushunQuon100% (4)
- Coffee Nursery Management Guide for Seed Germination, Polybag Planting, and Seedling MaintenanceDocument2 pagesCoffee Nursery Management Guide for Seed Germination, Polybag Planting, and Seedling MaintenanceDelfin AcayNo ratings yet
- 1st Summ AgriDocument3 pages1st Summ AgriShoby Carnaje TingsonNo ratings yet
- Chronic DiseasesDocument12 pagesChronic DiseasesanburajjNo ratings yet