Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometry m1 Topic B Lesson 8 Teacher
Uploaded by
Yuli LiangOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geometry m1 Topic B Lesson 8 Teacher
Uploaded by
Yuli LiangCopyright:
Available Formats
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 8 M1
GEOMETRY
Lesson 8: Solve for Unknown Angles—Angles in a Triangle
Student Outcome
Students review formerly learned geometry facts and practice citing the geometric justifications regarding
angles in a triangle in anticipation of unknown angle proofs.
Lesson Notes
In Lesson 8, the unknown angle problems expand to include angles in triangles. Knowing how to solve for unknown
angles involving lines and angles at a point, angles involving transversals, and angles in triangles, students are prepared
to solve unknown angles in a variety of diagrams.
Check the justifications students provide in their answers. The next three lessons on unknown angle proofs depend even
more on these justifications.
Classwork
Opening Exercise (5 minutes)
Review the Problem Set from Lesson 7; students also attempt a review question from Lesson 7 below.
Opening Exercise
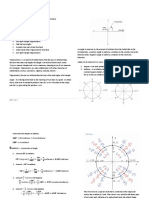
Find the measure of angle 𝒙 in the figure to the right. Explain your
calculations. (Hint: Draw an auxiliary line segment.)
MP.7 𝒎∠𝒙 = 𝟑𝟕°
The angle with the measure of 𝟕𝟐° can be divided two angles. One
measures 𝟑𝟓° (corresponding angles). Then the other angle has a
measure of 𝟑𝟕° (partition property).
Discussion (5 minutes)
Review facts about angles in a triangle.
Discussion
The sum of the 𝟑 angle measures of any triangle is 𝟏𝟖𝟎° .
INTERIOR OF A TRIANGLE: A point lies in the interior of a triangle if it lies in the interior of each of the angles of the triangle.
In any triangle, the measure of the exterior angle is equal to the sum of the measures of the opposite interior angles.
These are sometimes also known as remote interior angles.
Base angles of an isosceles triangle are equal in measure.
Each angle of an equilateral triangle has a measure equal to 𝟔𝟎°.
Lesson 8: Solve for Unknown Angles—Angles in a Triangle
70
This work is licensed under a
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org
This file derived from GEO-M1-TE-1.3.0-07.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 8 M1
GEOMETRY
Relevant Vocabulary (2 minutes)
Relevant Vocabulary
ISOSCELES TRIANGLE: An isosceles triangle is a triangle with at least two sides of equal length.
ANGLES OF A TRIANGLE: Every triangle △ 𝑨𝑩𝑪 determines three angles, namely, ∠𝑩𝑨𝑪, ∠𝑨𝑩𝑪, and ∠𝑨𝑪𝑩. These are called
the angles of △ 𝑨𝑩𝑪.
⃡ such that 𝑩 is
EXTERIOR ANGLE OF A TRIANGLE: Let ∠𝑨𝑩𝑪 be an interior angle of a triangle △ 𝑨𝑩𝑪, and let 𝑫 be a point on 𝑨𝑩
between 𝑨 and 𝑫. Then ∠𝑪𝑩𝑫 is an exterior angle of the triangle △ 𝑨𝑩𝑪.
Use a diagram to remind students that an exterior angle of a triangle forms a linear pair with an adjacent interior angle
of the triangle.
Exercises 1–11 (28 minutes)
Students try an example based on the Discussion and review as a whole class.
Exercises 1–11
1. Find the measures of angles 𝒂 and 𝒃 in the figure to the right. Justify your
results.
𝒎∠𝒂 = 𝟓𝟑°
𝒎∠𝒃 = 𝟒𝟎°
In each figure, determine the measures of the unknown (labeled) angles. Give reasons for your calculations.
2.
𝒎∠𝒂 = 𝟑𝟔°
The exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of the
two interior opposite angles.
3. 𝒎∠𝒃 = 𝟏𝟑𝟔°
The base angles of an isosceles triangle are equal
in measure.
The sum of the angle measures in a triangle is 𝟏𝟖𝟎°.
Linear pairs form supplementary angles.
4. 𝒎∠𝒄 = 𝟐𝟔°
The sum of the angle measures in a triangle is 𝟏𝟖𝟎°.
𝒎∠𝒅 = 𝟑𝟏°
Linear pairs form supplementary angles.
The sum of the angle measures in a triangle is 𝟏𝟖𝟎°.
Lesson 8: Solve for Unknown Angles—Angles in a Triangle
71
This work is licensed under a
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org
This file derived from GEO-M1-TE-1.3.0-07.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 8 M1
GEOMETRY
5.
𝒎∠𝒆 = 𝟓𝟏°
Linear pairs form supplementary angles.
The sum of the angle measures in a triangle is 𝟏𝟖𝟎°.
6.
𝒎∠𝒇 = 𝟑𝟎°
If parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then
corresponding angles are equal in measure.
Linear pairs form supplementary angles.
The sum of the angle measures in a triangle is 𝟏𝟖𝟎°.
7.
𝒎∠𝒈 = 𝟏𝟒𝟑°
If parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then alternate
interior angles are equal in measure.
Linear pairs form supplementary angles.
The sum of the angle measures in a triangle is 𝟏𝟖𝟎°.
8.
𝒎∠𝒉 = 𝟏𝟐𝟕°
Draw an auxiliary line, and then use the facts that linear
pairs form supplementary angles and the sum of the
angle measures in a triangle is 𝟏𝟖𝟎°.
9.
𝒎∠𝒊 = 𝟔𝟎°
If parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then alternate
interior angles are equal in measure.
Linear pairs form supplementary angles (twice).
The sum of the angle measures in a triangle is 𝟏𝟖𝟎°.
Lesson 8: Solve for Unknown Angles—Angles in a Triangle
72
This work is licensed under a
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org
This file derived from GEO-M1-TE-1.3.0-07.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 8 M1
GEOMETRY
10.
𝒎∠𝒋 = 𝟓𝟎°
If parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then alternate
interior angles are equal in measure.
Linear pairs form supplementary angles.
11.
𝒎∠𝒌 = 𝟓𝟔°
Closing (1 minute)
What is the sum of angle measures of any triangle?
The sum of angle measures of any triangle is 180°.
Describe the relationship between an exterior angle and the remote interior angles of a triangle.
The measure of the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the opposite
interior angles.
Exit Ticket (4 minutes)
Lesson 8: Solve for Unknown Angles—Angles in a Triangle
73
This work is licensed under a
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org
This file derived from GEO-M1-TE-1.3.0-07.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 8 M1
GEOMETRY
Name Date
Lesson 8: Solve for Unknown Angles—Angles in a Triangle
Exit Ticket
Find the value of 𝑑 and 𝑥.
𝑑 = ________
𝑥 = ________
Lesson 8: Solve for Unknown Angles—Angles in a Triangle
74
This work is licensed under a
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org
This file derived from GEO-M1-TE-1.3.0-07.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 8 M1
GEOMETRY
Exit Ticket Sample Solutions
Find the value of 𝒅 and 𝒙.
𝒅 = 𝟒𝟏
𝒙 = 𝟑𝟔
Problem Set Sample Solutions
Find the unknown (labeled) angle in each figure. Justify your calculations.
1.
𝒎∠𝒂 = 𝟒𝟒°
If parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then alternate
interior angles are equal in measure.
Linear pairs form supplementary angles.
The sum of the angle measures in a triangle is 𝟏𝟖𝟎°.
2.
𝒎∠𝒃 = 𝟓𝟖°
If parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then alternate
interior angles are equal in measure.
3.
𝒎∠𝒄 = 𝟒𝟕°
The base angles of an isosceles triangle are equal in
measure.
The sum of the angle measures in a triangle is 𝟏𝟖𝟎°.
The exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of the
two interior opposite angles.
The sum of the angle measures in a triangle is 𝟏𝟖𝟎°.
Lesson 8: Solve for Unknown Angles—Angles in a Triangle
75
This work is licensed under a
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org
This file derived from GEO-M1-TE-1.3.0-07.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
You might also like
- Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect An Angle: Student OutcomesDocument9 pagesLesson 3: Copy and Bisect An Angle: Student OutcomesKhristabel BenitoNo ratings yet
- DLP 33Document6 pagesDLP 33Pablo JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Triangle Inequality Theorem ExplainedDocument5 pagesTriangle Inequality Theorem ExplainedLorenzo Cohen100% (2)
- DLP 33Document3 pagesDLP 33Pablo Jimenea100% (1)
- Activity Sheet in Math 8 4th QuarterDocument11 pagesActivity Sheet in Math 8 4th QuarterDI AN NENo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Lesson 3 Presentation Course 2Document18 pagesChapter 7 Lesson 3 Presentation Course 2Sally SamirNo ratings yet
- Q4-Math-8-Week-1 (APRIL 24-28, 2023)Document5 pagesQ4-Math-8-Week-1 (APRIL 24-28, 2023)Teacher Vircie VlogNo ratings yet
- Lesson 25: Incredibly Useful Ratios: Student OutcomesDocument15 pagesLesson 25: Incredibly Useful Ratios: Student OutcomesPERLA Casiano OrtizNo ratings yet
- Angles, Polygons and Geometrical Proof: Stage 3 Mixed Selection 1Document1 pageAngles, Polygons and Geometrical Proof: Stage 3 Mixed Selection 1Manikantan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Math g7 m6 Topic B Lesson 15 TeacherDocument7 pagesMath g7 m6 Topic B Lesson 15 TeacherAnji KaringuNo ratings yet
- DLP TrianglesDocument4 pagesDLP TrianglesAngie A. DerialNo ratings yet
- MATH 113 Module Week 9-11Document14 pagesMATH 113 Module Week 9-11Elmar JuegoNo ratings yet
- G8 Term+3 AnglesDocument20 pagesG8 Term+3 AnglesRam AthreyapurapuNo ratings yet
- Mathematics7 Q3 M46 V4-Edited-2Document9 pagesMathematics7 Q3 M46 V4-Edited-2Yasha Antonio MaghanoyNo ratings yet
- 250-256!4!5 Isosceles and Equilateral TrianglesDocument7 pages250-256!4!5 Isosceles and Equilateral TrianglesAref Dahabrah100% (1)
- Triangle Centres in An Isosceles Triangle PDFDocument5 pagesTriangle Centres in An Isosceles Triangle PDFShikhar WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Math g8 m2 Topic C Lesson 12 Teacher PDFDocument9 pagesMath g8 m2 Topic C Lesson 12 Teacher PDFIsmail AbariNo ratings yet
- Trigo Module 1. Angles and Their Measurements Final PDFDocument6 pagesTrigo Module 1. Angles and Their Measurements Final PDFhppalapusNo ratings yet
- Math 8-Q3-L2-Postulates on AnglesDocument31 pagesMath 8-Q3-L2-Postulates on AnglesPearl De CastroNo ratings yet
- MELC 1: Illustrate The Six Trigonometric Ratios: Sine, Cosine, TangentDocument3 pagesMELC 1: Illustrate The Six Trigonometric Ratios: Sine, Cosine, TangentRolando Jr SabangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Preliminary Concepts in TrigonometryDocument6 pagesLesson 1 Preliminary Concepts in TrigonometryMARIA ELIZA LOMUNTADNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - 33Document2 pagesKami Export - 33Solomon FloresNo ratings yet
- 4 1 Guided NotesDocument2 pages4 1 Guided Notesapi-271136925No ratings yet
- Module 1 - Triangle CongruenceDocument25 pagesModule 1 - Triangle CongruenceJuan Lorenzo50% (2)
- Geometry m2 Topic C Lesson 18 TeacherDocument12 pagesGeometry m2 Topic C Lesson 18 TeacherNestor Bong Bordaje NemeñoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Leeson Plan ,MATH 8Document10 pagesDetailed Leeson Plan ,MATH 8Angeline BordajeNo ratings yet
- Math g7 m6 Topic A Lesson 4 TeacherDocument11 pagesMath g7 m6 Topic A Lesson 4 TeacherENo ratings yet
- Lesson 21Document7 pagesLesson 21Jeany Pearl EltagondeNo ratings yet
- Triangle Trigonometry and Circles TeacherDocument7 pagesTriangle Trigonometry and Circles TeacherClauciane Dias de LimaNo ratings yet
- Math-8 Q4 M1Document7 pagesMath-8 Q4 M1LADY ANN GRACE LAGAS100% (1)
- Demo JoyDocument20 pagesDemo JoyRizalie ComillasNo ratings yet
- SLM 4 Trigonometric Ratios of Special Angles 22 23Document10 pagesSLM 4 Trigonometric Ratios of Special Angles 22 23Kate Megan ApuliNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7Document4 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics 7angeline vacalaresNo ratings yet
- G7 DLP Day 5Document5 pagesG7 DLP Day 5Shiela Marie Cris AradoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Identical Triangles: Student OutcomesDocument11 pagesLesson 5: Identical Triangles: Student OutcomesJaselle NamuagNo ratings yet
- Math 8 q4 Week 1 FinalDocument9 pagesMath 8 q4 Week 1 FinalMillet CastilloNo ratings yet
- Math g7 m3 Topic C Lesson 22 TeacherDocument12 pagesMath g7 m3 Topic C Lesson 22 TeacherAzwa NadhiraNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 9Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 9Rena EtucagNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus For non-STEM (Algebra & TrigonometryDocument18 pagesPre-Calculus For non-STEM (Algebra & TrigonometryAlfeo DucejoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Illustrating Triangle CongruenceDocument5 pagesDLL - Illustrating Triangle CongruenceLovely CorpuzNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Geometry in Mathematis 8Document7 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Geometry in Mathematis 8Renan PaculanangNo ratings yet
- Math g8 m2 Topic C Lesson 14 TeacherDocument13 pagesMath g8 m2 Topic C Lesson 14 Teacherbelmin_zeNo ratings yet
- Math8_Q3_W6_LASDocument16 pagesMath8_Q3_W6_LASAmelita TupazNo ratings yet
- MATH8 Q4 LAS1 Week1-NoDocument14 pagesMATH8 Q4 LAS1 Week1-NoJohn gabriel SebuanNo ratings yet
- Circle Geometry Revision Booklet-1Document33 pagesCircle Geometry Revision Booklet-1lulamangwenya67No ratings yet
- Additional Practice: Another Look!Document2 pagesAdditional Practice: Another Look!Moaz KhursheedNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN ON TRIANGLE CONGRUENCE APPLICATIONSDocument7 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN ON TRIANGLE CONGRUENCE APPLICATIONSCleah Jane MonterolaNo ratings yet
- Ls Maths8 2ed TR Lesson Plan Sample 1Document4 pagesLs Maths8 2ed TR Lesson Plan Sample 1AJNo ratings yet
- t3 M 4443 Secondary Maths Unit Overview Trigonometry Worded Problems Unit Overview English Ver 1Document3 pagest3 M 4443 Secondary Maths Unit Overview Trigonometry Worded Problems Unit Overview English Ver 1Fanender AroraNo ratings yet
- Angles Formed By Parallel Lines Cut By A TransversalDocument5 pagesAngles Formed By Parallel Lines Cut By A TransversalNur ZannahNo ratings yet
- Triangle Inequality Theorems ExplainedDocument18 pagesTriangle Inequality Theorems ExplainedJuliet Macaraeg Añes33% (3)
- Week 2 Trigonometric RatiosDocument5 pagesWeek 2 Trigonometric RatiosEdwin CastanedaNo ratings yet
- CPCTC Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesCPCTC Lesson PlanNathalie Cordial100% (2)
- Hazel Chapter 4Document20 pagesHazel Chapter 4Hazel Grace Cabanos ArbanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Lesson 1 Notes Angle Relationships in TrianglesDocument4 pagesUnit 3 Lesson 1 Notes Angle Relationships in Trianglesapi-264764674No ratings yet
- Q4W1 Triangle InequalityDocument30 pagesQ4W1 Triangle InequalityElaine RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Geometry Snacks: Bite Size Problems and How to Solve ThemFrom EverandGeometry Snacks: Bite Size Problems and How to Solve ThemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- LPDocument5 pagesLPHeizyl ann VelascoNo ratings yet
- PqdifsdkDocument2 pagesPqdifsdkrafaelcbscribdNo ratings yet
- E - Program Files (x86) - Schneider - sft2841 - sft2841 Serie 80 - Notice - en - Manual - Sepam - Series80 - Operation - ENDocument180 pagesE - Program Files (x86) - Schneider - sft2841 - sft2841 Serie 80 - Notice - en - Manual - Sepam - Series80 - Operation - ENJuan Cristóbal Rivera PuellesNo ratings yet
- IAS Mains Electrical Engineering 1994Document10 pagesIAS Mains Electrical Engineering 1994rameshaarya99No ratings yet
- FINAL Please Be Informed That Your Termination From Office Is Not Intended To Be PersonalDocument9 pagesFINAL Please Be Informed That Your Termination From Office Is Not Intended To Be PersonalShareff ChamplainNo ratings yet
- BID 2021 046 6913 VendorList3. (237110)Document1 pageBID 2021 046 6913 VendorList3. (237110)JAGUAR GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Electric Machine Design 01 Electric Machine DesignDocument10 pagesElectric Machine Design 01 Electric Machine Designkhodabandelou100% (1)
- Agricrop9 ModuleDocument22 pagesAgricrop9 ModuleMaria Daisy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Perkins Engine Number Guide PP827Document6 pagesPerkins Engine Number Guide PP827Muthu Manikandan100% (1)
- Lesson 4 - Nature of The Speech Communication ProcessDocument4 pagesLesson 4 - Nature of The Speech Communication ProcessDon Miguel SpokesNo ratings yet
- Ooplabmanual 150412132629 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocument146 pagesOoplabmanual 150412132629 Conversion Gate01 PDFyawerjs33% (6)
- Sa Sem Iv Assignment 1Document2 pagesSa Sem Iv Assignment 1pravin rathodNo ratings yet
- KiaOptima Seccion 002Document7 pagesKiaOptima Seccion 002Luis Enrique PeñaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument12 pagesPhysics ProjectRita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fuel Equivalent Factor - Marine Services PDFDocument9 pagesFuel Equivalent Factor - Marine Services PDFMax Kolonko100% (1)
- MA 7 TranscriptDocument82 pagesMA 7 TranscriptBob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- Lun Mapping DisksDocument11 pagesLun Mapping DisksKarn GusainNo ratings yet
- TMF1014 System Analysis & Design Semester 1, 2020/2021 APPENDIX C: Group Assignment Assessment RubricDocument4 pagesTMF1014 System Analysis & Design Semester 1, 2020/2021 APPENDIX C: Group Assignment Assessment RubricWe XaNo ratings yet
- Daily DAWN News Vocabulary With Urdu Meaning (05 April 2020) PDFDocument6 pagesDaily DAWN News Vocabulary With Urdu Meaning (05 April 2020) PDFAEO Begowala100% (2)
- Memo-on-Orientation and Submission of PNPKIDocument5 pagesMemo-on-Orientation and Submission of PNPKICoronia Mermaly LamsenNo ratings yet
- A Is Called The Base and N Is Called The Exponent: Grade 7 Math Lesson 21: Laws of Exponents Learning GuideDocument4 pagesA Is Called The Base and N Is Called The Exponent: Grade 7 Math Lesson 21: Laws of Exponents Learning GuideKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Crankcase Pressure SM019901095211 - en PDFDocument5 pagesCrankcase Pressure SM019901095211 - en PDFDavy GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Captiva 2013 Systema Electric 3.0Document13 pagesCaptiva 2013 Systema Electric 3.0carlos martinez50% (2)
- Four Process StrategyDocument10 pagesFour Process StrategyChandria FordNo ratings yet
- Cosmos Carl SaganDocument18 pagesCosmos Carl SaganRabia AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Batch RecordDocument11 pagesBatch RecordInes Concepcion TupasNo ratings yet
- Hanix h15b 2 h15b Plus 2 Service Manual Sept 09Document10 pagesHanix h15b 2 h15b Plus 2 Service Manual Sept 09vickie100% (41)
- Intro To Factor AnalysisDocument52 pagesIntro To Factor AnalysisRawnak JahanNo ratings yet
- The World in Which We Believe in Is The Only World We Live inDocument26 pagesThe World in Which We Believe in Is The Only World We Live inYusufMiddeyNo ratings yet
- Word ShortcutsDocument3 pagesWord ShortcutsRaju BNo ratings yet