0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views7 pagesCentrifugal Pump Performance Testing
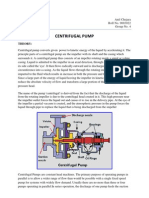
The document describes an experiment to determine the performance characteristics of a centrifugal pump. Key details include:
- Readings of discharge, total head, input and output power were taken at varying delivery valve positions.
- Efficiency, discharge, input and output power were calculated and graphs were plotted.
- The maximum efficiency was found to be 34.29% at a discharge of 0.987 x 10-2 m3/s.
- Total head decreases with increasing discharge due to increased friction losses in the system.
Uploaded by
Amisha SharonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views7 pagesCentrifugal Pump Performance Testing
The document describes an experiment to determine the performance characteristics of a centrifugal pump. Key details include:
- Readings of discharge, total head, input and output power were taken at varying delivery valve positions.
- Efficiency, discharge, input and output power were calculated and graphs were plotted.
- The maximum efficiency was found to be 34.29% at a discharge of 0.987 x 10-2 m3/s.
- Total head decreases with increasing discharge due to increased friction losses in the system.
Uploaded by
Amisha SharonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd