Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Ch.1: Keywords and End of Chapter Questions
Uploaded by
ar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Chemistry (Chapter 1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesChemistry Ch.1: Keywords and End of Chapter Questions
Uploaded by
arCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Chemistry Ch.
1: Keywords and End of Chapter Questions
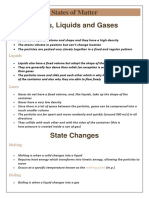
1. Atmospheric pressure: the pressure of the atmosphere. The pressure evaporated gas particles
create over a heating liquid.
2. Boiling point: the point where a heated liquid stops stays in the same temperature as all the
heat goes toward creating energy in the particles to overcome the attractive forces and break
free from the liquid. The liquid at this stage has gas bubbles forming in bulk on the liquid as the
particles are quickly trying to escape.
3. Condensation: the process in which water vapor turns into liquid water as it touches a cool
surface/ gets cooled. The gas particles lose energy, get closer together and build attractive
forces, turning into liquid droplets.
4. Diffusion: the process by which liquid or gas particles spread randomly and haphazardly
throughout an area to reach an equilibrium (be spread equally).
5. Evaporation: the process by which particles at the surface of the liquid break free after
overcoming attractive forces and escaping.
6. Kinetic theory: theory that all matter consists of tiny particles that cannot be seen with the
naked eye and which differ from substance to substance (i.e being an atom, molecule or ion)
and that particles have energy within them causing them to move differently based on their
state of matter and the movement can change based on temperature change.
7. Matter: all substances and materials that the physical universe is composed of.
8. Melting point: as a solid is heated, it’s temperature increases and the particles gain kinetic
energy and vibrate within their positions faster and faster. However, at one point the
temperature of the solid stops increasing and all the heat gained is used for the particles to build
energy to move further apart and overcome attractive forces to turn into a liquid. This point is
called the melting point and after the solid turns into a liquid, the temperature of the liquid
increases very quickly within a short amount of time (steep increase in temperature)
9. Solids, Liquids, Gases: the three states of matter. Solids are not compressible. Liquids are
relatively compressible and gases are highly compressible. Solids have a fixed shape and volume,
liquids have a fixed volume but they take the shape of the container they’re placed in and gases
have neither a fixed volume or shape but they take the shape of the container.
10. Sublimation: the direct change of matter of solids into gases without passing through the liquid
state. Dry ice is solid carbon dioxide which siblimes into a gas at any temperature above -78
degrees Celsius.
Questions: (correct with notebook when its returned)
1.c- Oxygen gas particles loose their energy as they cool down and the attractive forces between them
start to form as they get closer together.
4.a- When taken out of the fridge, the block of butter’s temperature is very cool and when left for 15
minutes it starts to lose it’s cool, gaining energy and the particles vibrate faster and faster pushing each
other away and weakening the attractive forces. This causes the butter to lose its firm structure.
4.c- The air particles in the football loose their heat by the evening, causing them to lose their energy
and move less inside the ball, thus it becomes softer. When they’re moving fast, the particles collide
with the surface of the wall so now that they’re moving with less energy, they don’t collide with the wall
as much.
5.a- The gas particles of the hydrochloric acid and ammonia solution diffused and reacted on the
position where they met.
6.e-
i. input of heat energy: melting (B)
ii. output of heat energy: freezing (A)
7. The particles of the nickel (II) sulfate solution take a while to diffuse throughout the liquid because the
particles of the liquid move more slowly as they collide more often and slow each other down.
You might also like
- Understanding the States of MatterDocument9 pagesUnderstanding the States of Mattervidya pmNo ratings yet
- G9-Chem-Matter 1-NotesDocument11 pagesG9-Chem-Matter 1-NotesvijahatNo ratings yet
- Heat_and_Matter_NotesDocument8 pagesHeat_and_Matter_NotesHwang ElyseNo ratings yet
- 2-Thermal PhysicsDocument26 pages2-Thermal PhysicsSamah Hafez100% (1)
- Thermal_physics_notesDocument26 pagesThermal_physics_notesantonettemosweu211No ratings yet
- Y9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesDocument10 pagesY9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesTeck TieNo ratings yet
- The States of MatterDocument26 pagesThe States of Mattertamim haqueNo ratings yet
- Chemistry for Cambridge IGCSE Grade 10Document192 pagesChemistry for Cambridge IGCSE Grade 10mohammed mahdyNo ratings yet
- U1 PN Mod 2Document16 pagesU1 PN Mod 2Puja DhawanNo ratings yet
- Changes in Matter/Phase Change: Phase Transition Liquid GasDocument1 pageChanges in Matter/Phase Change: Phase Transition Liquid GasMARISTELA MACARANASNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocument7 pagesTopic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter Notessteve KingNo ratings yet
- Solids: Notes 1 Chapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter Solids, Liquids and GasesDocument7 pagesSolids: Notes 1 Chapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter Solids, Liquids and GasesQfkjfksNo ratings yet
- 5 CH 2 Sec 2 Changes in State and Energy - UploadDocument74 pages5 CH 2 Sec 2 Changes in State and Energy - Uploadapi-270861823No ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument10 pagesStates of Matterm.umerfaizan1895No ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingDocument62 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingSumit ManeNo ratings yet
- مذكرة ساينس 6 ابتدائي ترم اول 2024 كاملة مدرسة جيل 2000Document160 pagesمذكرة ساينس 6 ابتدائي ترم اول 2024 كاملة مدرسة جيل 2000eadawi32No ratings yet
- 9th Matter in Our Sorounding Notes 2Document4 pages9th Matter in Our Sorounding Notes 2Santosh RaiNo ratings yet
- Changes of StatesDocument39 pagesChanges of StatesSalemah MeshalNo ratings yet
- Chemisty Igcse Updated Till SyllabusDocument97 pagesChemisty Igcse Updated Till Syllabusapi-181176018No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMDocument11 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMJay Bee83% (29)
- The Nature of MatterDocument26 pagesThe Nature of MatterEsma KurtanovićNo ratings yet
- Study Guide I TERMDocument3 pagesStudy Guide I TERMCristina BarahonaNo ratings yet
- Particle Theory Matter ExplainedDocument6 pagesParticle Theory Matter ExplainedMatthew ScherbatyNo ratings yet
- Foundation Chemistry 1Document60 pagesFoundation Chemistry 1Ivan OgwangNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lesson #1 - Kinetic Particle Theory Pre-TestDocument6 pagesChemistry Lesson #1 - Kinetic Particle Theory Pre-TestestherlimrhNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument7 pagesStates of MatterShubhra MoreNo ratings yet
- ExploreDocument3 pagesExploreLourdes Joy LibradoNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument6 pagesStates of MatterHadeel IbrahimNo ratings yet
- GQA Science 8 Q3 - Wk3 4 - Phase Change of Matter - LRQADocument12 pagesGQA Science 8 Q3 - Wk3 4 - Phase Change of Matter - LRQACobert RuhsterNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument8 pagesKinetic Particle TheoryShaikh IradNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Matter and The Atomic Structure: 2.1 Basic Concept of MatterDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Matter and The Atomic Structure: 2.1 Basic Concept of Matterforyourhonour wongNo ratings yet
- Matter Solid Liquid Gas: Page - 1Document5 pagesMatter Solid Liquid Gas: Page - 1Anonymous l309xEA6No ratings yet
- Handout # 2.4 Particle Model For MatterDocument5 pagesHandout # 2.4 Particle Model For MatterMr. KhanNo ratings yet
- Solids liquids and gasesDocument4 pagesSolids liquids and gasesAbdullah SalmanNo ratings yet
- SUMMER VACATION Chemistry 9Document7 pagesSUMMER VACATION Chemistry 9jshndNo ratings yet
- Melting Boiling and EvaporationDocument19 pagesMelting Boiling and EvaporationAnmol MalgotraNo ratings yet
- HEAT for F1A (Revision) ExplainedDocument61 pagesHEAT for F1A (Revision) ExplainedChrise RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - States of MatterDocument13 pagesChapter 4 - States of MatterAdam BeyNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory Explains Phases of MatterDocument9 pagesKinetic Theory Explains Phases of MatterPeterClomaJr.No ratings yet
- States of Matter: Explaining the Three PhasesDocument6 pagesStates of Matter: Explaining the Three PhasesDexter TorringtonNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument2 pagesStates of Matteralquran.queriesNo ratings yet
- O LVL Chem - Chap 1Document3 pagesO LVL Chem - Chap 1montyredNo ratings yet
- 2-2 Changes in StateDocument61 pages2-2 Changes in Stateapi-294483847No ratings yet
- Understanding the States of Matter and Particle TheoryDocument10 pagesUnderstanding the States of Matter and Particle TheoryAjitabh SinghNo ratings yet
- 2 States of Matter NotesDocument14 pages2 States of Matter Notesafnan.6556No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Sayantan ChakrabortyDocument9 pagesHeat Transfer: Sayantan ChakrabortySayantan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- JYOTI Chemistry IGCSE Revision NotesDocument16 pagesJYOTI Chemistry IGCSE Revision NotesJyoti MeenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Solid Liquid and GasesDocument36 pagesChapter 6 Solid Liquid and Gasestashnee pillayNo ratings yet
- Notes - Matter in Our Surroundings - ExpDocument6 pagesNotes - Matter in Our Surroundings - Expdeborah hildaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument33 pagesCHEMISTRYemiyaNo ratings yet
- cl9ch1Document5 pagescl9ch1Pankaj PathakNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument32 pagesThe Particulate Nature of MatterPritam CainNo ratings yet
- FTH 4Document14 pagesFTH 4melissaNo ratings yet
- CBE 9 SCDocument104 pagesCBE 9 SCd_narnolia0% (1)
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v12Document29 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v12Roshni ReddyNo ratings yet
- caie-igcse-chemistry-0620-theory-v13Document29 pagescaie-igcse-chemistry-0620-theory-v13Khoa DangNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- RADIOSS ElementDocument113 pagesRADIOSS ElementAmolNo ratings yet
- InTech-Mass and Heat Transfer During Thin Film Evaporation of Liquid SolutionsDocument17 pagesInTech-Mass and Heat Transfer During Thin Film Evaporation of Liquid SolutionsClarence AG YueNo ratings yet
- Shear Strength of Precast Prestressed Concrete Hollow Core SlabsDocument4 pagesShear Strength of Precast Prestressed Concrete Hollow Core SlabsMarkoGlamuzinaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics QBDocument4 pagesEngineering Mechanics QBAndrea DouglasNo ratings yet
- Skema Freezer Dan ChillerDocument2 pagesSkema Freezer Dan ChillerNurul AnnidaNo ratings yet
- 3.2. SMART Method For Crack-Growth SimulationDocument35 pages3.2. SMART Method For Crack-Growth SimulationAlexgh1993No ratings yet
- ME8595 - Thermal Engineering II - Unit IIIDocument50 pagesME8595 - Thermal Engineering II - Unit IIIommech2020No ratings yet
- Precise Temperature Control for Reactor ApplicationsDocument22 pagesPrecise Temperature Control for Reactor ApplicationsFernando Stuar Campos MendozaNo ratings yet
- Mulit Phase 3Document30 pagesMulit Phase 3sb aliNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Life Evaluation of Grab Ship UnloaderDocument6 pagesFatigue Life Evaluation of Grab Ship UnloaderflorinelvvNo ratings yet
- EXP 7 - Continuous Distillation-Bubble CapDocument19 pagesEXP 7 - Continuous Distillation-Bubble CapHamdan JasmiNo ratings yet
- Strenx 700 Brochure Square ENDocument6 pagesStrenx 700 Brochure Square ENEjang GutNo ratings yet
- HL200 48-2 Performaance Chart-1Document1 pageHL200 48-2 Performaance Chart-1MustafaNo ratings yet
- P-Toluene Sulfonic AcidDocument2 pagesP-Toluene Sulfonic AcidfitriNo ratings yet
- Cyclone Performance and Design PDFDocument23 pagesCyclone Performance and Design PDFIstván SzékelyNo ratings yet
- Week 12, Lecture 1 - Cyclones: Dr. Dave Dubois Division of Atmospheric Sciences, Desert Research InstituteDocument34 pagesWeek 12, Lecture 1 - Cyclones: Dr. Dave Dubois Division of Atmospheric Sciences, Desert Research Instituteshailesh pansareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24. Refrigerated Facility Loads: Transmission LoadDocument35 pagesChapter 24. Refrigerated Facility Loads: Transmission Loadroberto medinaNo ratings yet
- Phy Solution For (P, PTP, SMS, DPS, j1, JH, PH) Iit FFFFHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHDocument5 pagesPhy Solution For (P, PTP, SMS, DPS, j1, JH, PH) Iit FFFFHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHvishal110085No ratings yet
- Cast-in-place Pile and Column Design Based on ACI 318Document15 pagesCast-in-place Pile and Column Design Based on ACI 318John Carlo AbalaNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Characteristics of NACA 4412 AirfoilDocument20 pagesAerodynamic Characteristics of NACA 4412 AirfoilEmeka1987No ratings yet
- Rheology For Quality Control - Better Rheological ResultsDocument20 pagesRheology For Quality Control - Better Rheological ResultsPaulo FragaNo ratings yet
- DOCUMENTFUNDAMENTAL OF RESERVOIR FLUID FLOWDocument18 pagesDOCUMENTFUNDAMENTAL OF RESERVOIR FLUID FLOWFerdiNandoNo ratings yet
- Back Questions On Heat TransferDocument6 pagesBack Questions On Heat TransferASHUTOSH RAUTNo ratings yet
- NSCP Seismic DesignDocument59 pagesNSCP Seismic DesignJamielah Macadato85% (20)
- Homework-1 Fall 2021Document1 pageHomework-1 Fall 2021Elif HalıcıNo ratings yet
- CVG 2140 - Problem Set 8Document6 pagesCVG 2140 - Problem Set 8Ershad SarwarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 2: Fundamentals of Fluid FlowDocument37 pagesHydraulics 2: Fundamentals of Fluid FlowVincentNo ratings yet
- Product specifications and energy efficiency ratings for Daikin air conditionersDocument2 pagesProduct specifications and energy efficiency ratings for Daikin air conditionerssloba68No ratings yet
- The Use of Leak-Off Tests As Means of Predicting Minimum In-Situ StressDocument5 pagesThe Use of Leak-Off Tests As Means of Predicting Minimum In-Situ StressNguyen Cao KyNo ratings yet
- Vertical Pump EngineeringDocument49 pagesVertical Pump EngineeringKhaled GameaNo ratings yet