Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acid-base disorders summary
Uploaded by
Pau SorianoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acid-base disorders summary
Uploaded by
Pau SorianoCopyright:
Available Formats
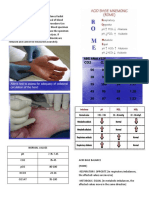
Normal values:
pH = 7.35-7.45
PCO2 = 35-45
HCO2 = 22-26
Anion gap < 16
Acid Base Primary Compensatory
PaCO2 pH Etiology
Disorder Change Change
Hypoventilation
Respiratory Increased
Increased Decreased Increased HCO3 Airway
Acidosis CO2
obstruction
Respiratory Decreased Anxiety
DecreasedIncreased Decreased HCO3
Alkalosis CO2 PE
Lactic acidosis
Metabolic Decreased
DecreasedDecreased Decreased CO3 DKA
Acidosis HCO3
Poisons
Vomiting (pyloric
Metabolic Increased
Increased Increased Increased CO2 stenosis)
Alkalosis HCO3
Diuretic therapy
Primary Disorder Expected Changes
Metabolic Acidosis PCO2 = 1.5 x HCO3 + (8 +/- 2)
Metabolic Alkalosis PCO2 = 0.7 x HCO3 + (21 +/- 2)
Acute Respiratory Acidosis Change in pH = 0.008 x (PCO2 - 40)
Chronic Respiratory Acidosis Change in pH = 0.003 x (PCO2 - 40)
Change in pH = 0.008 X (40 -
Acute Respiratory Alkalosis
PCO2)
Chronic Respiratory AlkalosisChange in pH = 0.017 x (40 - PCO2)
Caveats
Metabolic acid base problem exists if
pH is abnormal and pH and PCO2 change in same direction (both up or
down)
Respiratory compensation is intact if PCO2 resembles last 2 digits of pH
Respiratory acid base problem exisits if:
PCO2 is abnormal
pH and PCO2 change in opposite directions
Mixed acid base problem exists if:
PCO2 is abnormal and pH has not changed as expected or normal
pH is abnormal and PCO2 has not changed as expected or is normal
pH 7.46, CO2 32mmHg, HCO3- 23mEq/L
Respiratory alkalosis, Uncompensated
Feedback:
if HCO3- caused the acidosis or the alkalosis, it is METABOLIC
if CO2 caused the acidosis or alkalosis, it is RESPIRATORY
if CO2 and HCO3- caused the imbalanced, it is COMBINED
To determine compensation:
Uncompensated= abnormal pH and change in one blood parameter
Partially compensated= all 3 values of pH, HCO3-, CO2 are abnormal
Fully compensated= pH is normal, both HCO3- and CO2 are abnormal
Corrected= all parameters are normal
Normal ranges:
pH is 7.35-7.45
HCO3- is 22-26
CO2 is 35-45
pH 7.30, CO2 46 mmHg, HCO3 16 mEq/L
Combined, Partially compensated
If the CO2 caused the acidosis or alkalosis, it is what?
Respiratory
What is the normal range of bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) in arterial blood?
22-26
Ben has anxiety attack. His ABGs results show he is in respiratory alkalosis. He has
just had a car accident. What is your next nursing intervention?
Have him breathe into paper bag
What is the normal range of carbon dioxide (CO2) in arterial blood?
35-45
pH 7.31, CO2 50mmHg, HCO3- 22mEq/L
Respiratory acidosis, Uncompensated
If HCO3- caused the acidosis or the alkalosis, it is what?
Metabolic
What is the normal range of pH in the body?
7.35-7.45
If the CO2 and the HCO3- caused the imbalance, it is what?
Combined
pH 7.47, CO2 48 mmHg, HCO3 30 mEq/L
Metabolic alkalosis, partially compensated
When all 3 values--- pH, HCO3-, CO2 are abnormal. It is
Partially compensated
pH 7.30, CO2 46 mmHg, HCO3 16 mEq/L
Combined, partially compensated
pH 7.31, CO2 44 mmHg, HCO3 20 mEq/L
Metabolic acidosis, Uncompensated
When there is an abnormal pH and change in one blood parameter. It is
Uncompensated
When pH is normal, both HCO3 and CO2 are abnormal. It is
Fully compensated
When all parameters of pH, HCO3-, and CO2 are normal. It is
Corrected
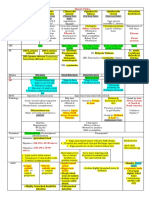
ORGAN REGULATES DISTURBANC CAUSES COMPENSATION
E
LUNGS pCO2 ↑ acidosis HYPOVENTALATION ↑ HCO3
(Respiratory) (acid) (↑ CO2 in blood) (metabolic
alkalosis)
↓ alkalosis HYPERVENTALATION ↓ HCO3
(increased breathing) (metabolic
acidosis)
KIDNEYS HCO3 ↑ alkalosis BICARBONATE ↑ pCO2
(Metabolic) (alkaline) REABSORPTION (respiratory
(back to blood) acidosis)
↓ acidosis BICARBONATE ↓ pCO2
EXCRETION (respiratory
(urine) alkalosis)
(excrete alkaline ex
diarrhea remaining is
acid)
pH pCO2 HCO3
Compensated NORMAL Abnormal Abnormal
Partially compensated Abnormal Abnormal Abnormal
Uncompensated Abnormal Either pCO2 or HCO3 is Abnormal
One is normal & other is Abnormal
You might also like
- Blood Gas AnalysisDocument52 pagesBlood Gas AnalysisKresna Dharma SuryanaNo ratings yet
- EKG Quick Reference ChartDocument4 pagesEKG Quick Reference ChartMildaNo ratings yet
- Understand Acid-Base DisordersDocument89 pagesUnderstand Acid-Base DisordersEdouinaNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument16 pagesImmunologyShyenNo ratings yet
- Blood Doping PPT PresentationDocument26 pagesBlood Doping PPT Presentationee4254100% (1)
- Respiratory & Circulatory Systems Activity SheetDocument7 pagesRespiratory & Circulatory Systems Activity SheetalexNo ratings yet
- How To Read Arterial Blood Gas .PTDocument36 pagesHow To Read Arterial Blood Gas .PTMohd Erham bin JonohNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalanceDocument40 pagesAcid Base Balancemohdmaghyreh100% (1)
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q2 Week 2 Module 4 - Significant Events of The Calvin CycleDocument19 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q2 Week 2 Module 4 - Significant Events of The Calvin CycleRomel Bayaban100% (1)
- ABG Arterial Blood Gas: Interpretation .. Simplified ApproachDocument62 pagesABG Arterial Blood Gas: Interpretation .. Simplified ApproachPrasanna Kumar100% (1)
- Concepts For Nursing Practice 3rd Edition Giddens Full-53-56Document4 pagesConcepts For Nursing Practice 3rd Edition Giddens Full-53-56هدوء النسمةNo ratings yet
- Exercise PhysiologyDocument8 pagesExercise PhysiologyJulie-Mar Valleramos LabacladoNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument94 pagesVital Signsglennm68100% (5)
- Abg PPT NewDocument69 pagesAbg PPT NewMalaka Atapattu100% (2)
- Acid-Base BalanceDocument38 pagesAcid-Base BalanceNym Angga SantosaNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance: Acidosis & AlkalosisDocument30 pagesAcid-Base Balance: Acidosis & AlkalosisrathanNo ratings yet
- Cchm2 MidtermsDocument22 pagesCchm2 MidtermsMACOB, ETHELHYN JHANE100% (1)
- Arterial Blood Gas: AnalysisDocument51 pagesArterial Blood Gas: Analysisnaven100% (2)
- Arterial Blood Gas: IM 2013 (AVM)Document66 pagesArterial Blood Gas: IM 2013 (AVM)Wilsonne ChuaNo ratings yet
- Marc D. Berg, MD - Devos Children'S Hospital Rita R. Ongjoco, Do - Sinai Hospital of BaltimoreDocument41 pagesMarc D. Berg, MD - Devos Children'S Hospital Rita R. Ongjoco, Do - Sinai Hospital of BaltimoreAhmed KamalNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Imbalance (Rubina)Document98 pagesAcid Base Imbalance (Rubina)Parvathy R Nair100% (1)
- Blood Gas InterpretationDocument28 pagesBlood Gas InterpretationgjdbfiuvaNo ratings yet
- Julienne Anjeli J. Cabradilla, MD: First Year, Department of Pediatrics ItrmcDocument42 pagesJulienne Anjeli J. Cabradilla, MD: First Year, Department of Pediatrics ItrmcKristine Boholst100% (1)
- Acid base disorders simplified/TITLEDocument48 pagesAcid base disorders simplified/TITLEAGUNG SETIADI NUGROHONo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Management: Presented byDocument38 pagesAcid-Base Management: Presented byNina NinaNo ratings yet
- Acid Based BalanceDocument11 pagesAcid Based BalanceAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- Keseimbangan Asam Basa: Prof. Dr. Achsanuddin Hanafie, Span, Kic, KaoDocument47 pagesKeseimbangan Asam Basa: Prof. Dr. Achsanuddin Hanafie, Span, Kic, KaorosidahhanumNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gases 1Document36 pagesArterial Blood Gases 1Husson GhalyaNo ratings yet
- Gangguan Asam BasaDocument51 pagesGangguan Asam BasaYudhistira YuliandraNo ratings yet
- ABGsDocument3 pagesABGsc hNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Compensated and Uncompensated Blood Gas AnalysisDocument30 pagesInterpreting Compensated and Uncompensated Blood Gas AnalysisJadie Barringer IIINo ratings yet
- Blood Gases (Abgs) Interpretation Dr/Baha Eldin Hassan Ahmed Fellow Paediatric Critical CareDocument48 pagesBlood Gases (Abgs) Interpretation Dr/Baha Eldin Hassan Ahmed Fellow Paediatric Critical Carehagir alhajNo ratings yet
- ABGs InterpretationDocument33 pagesABGs InterpretationHamza DossaNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Disorders: Blood PH Acidoses Alkaloses Arterial Blood Gas ABG Metabolic Acidosis Anion GapDocument5 pagesAcid-Base Disorders: Blood PH Acidoses Alkaloses Arterial Blood Gas ABG Metabolic Acidosis Anion GapMaryam RazaNo ratings yet
- Keseimbangan Asam-Basa (2) : Sudarno, DR M.KesDocument47 pagesKeseimbangan Asam-Basa (2) : Sudarno, DR M.Kesanny lusheniaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalaneceDocument11 pagesAcid Base BalaneceHAMMYER ALROKHAMINo ratings yet
- Acid Base InterpretationDocument46 pagesAcid Base InterpretationshikhaNo ratings yet
- ABG InterpertationDocument14 pagesABG Interpertationapi-3757039100% (1)
- ABG and DisturbancesDocument53 pagesABG and DisturbancesHenry Joseph Lizardo AlunesNo ratings yet
- Acid Base DisordersDocument33 pagesAcid Base DisordersShre RanjithamNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Balance 2B - 3.05.2021Document56 pagesAcid Base Balance 2B - 3.05.2021Kavya FouzdarNo ratings yet
- 2016 Acid Base DisordersDocument48 pages2016 Acid Base DisordersbellabelbonNo ratings yet
- ABG made simple: A 4-step approachDocument19 pagesABG made simple: A 4-step approachBimantoko Hadi Sriyono100% (1)
- Acid Base DisordersDocument66 pagesAcid Base DisordersIvan HensonNo ratings yet
- 295 - Renal Pathology) Acid Base Disorders and ABG Interpretation - IntroductionDocument6 pages295 - Renal Pathology) Acid Base Disorders and ABG Interpretation - IntroductionMuhammadR1No ratings yet
- 3 Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases Seminar 4 yDocument18 pages3 Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases Seminar 4 yPrasenjit SarkarNo ratings yet
- 5-Step Approach to Acid-Base DisordersDocument4 pages5-Step Approach to Acid-Base DisordersJose Carlos Guerrero AcostaNo ratings yet
- BLOOD-GASESDocument51 pagesBLOOD-GASESrbm121415chyNo ratings yet
- 4-Acid-Base 06-1 - 3Document134 pages4-Acid-Base 06-1 - 3api-19916399No ratings yet
- Acid Base: Prep by Clement UWASE PGY2Document48 pagesAcid Base: Prep by Clement UWASE PGY2TWISUNGANE PROTOGENENo ratings yet
- Analisa BGADocument45 pagesAnalisa BGAZara Yupita AzraNo ratings yet
- ABG Interpretation GuideDocument55 pagesABG Interpretation GuidetommyNo ratings yet
- Keseimbangan Asam Basa CMDocument47 pagesKeseimbangan Asam Basa CMsyakurNo ratings yet
- Acid Based Disorders Med07Document28 pagesAcid Based Disorders Med07Salem Ali BawazeerNo ratings yet
- Pengaturan Asam-Basa & ElektrolitDocument40 pagesPengaturan Asam-Basa & ElektrolitArifuddinZrNo ratings yet
- Abg InterpretationDocument1 pageAbg InterpretationMohd Johari Mohd ShafuwanNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base and Electrolyte DisordersDocument41 pagesAcid-Base and Electrolyte Disordersaantoxx84No ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: Interpreting Acid-Base ImbalancesDocument6 pagesArterial Blood Gas Analysis: Interpreting Acid-Base ImbalancesOrhan AsdfghjklNo ratings yet
- Abg Interpreter Lecture Bukas Sa Rle ShutaDocument3 pagesAbg Interpreter Lecture Bukas Sa Rle ShutaElaine Marie SeraficaNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Arterial Blood Gas ReportsDocument44 pagesInterpreting Arterial Blood Gas Reportsraed faisalNo ratings yet
- Understanding Acid-Base ImbalancesDocument47 pagesUnderstanding Acid-Base ImbalancesMilikPremiumstock90No ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument37 pagesAcid Basechngwq93100% (1)
- Acids BasedDocument5 pagesAcids BasedAngeline TaghapNo ratings yet
- Alteration of Acid-Base Balance: Metabolic and Respiratory Acidosis and AlkalosisDocument14 pagesAlteration of Acid-Base Balance: Metabolic and Respiratory Acidosis and Alkalosiscipriano2No ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument6 pagesAcid BaseCarol Solanyi Gacha QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalanceDocument44 pagesAcid Base BalanceKenny JapNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Fall 2008Document34 pagesAcid Base Fall 2008anon-252165No ratings yet
- Specimen Collection, Processing & Chain of Custody GuideDocument4 pagesSpecimen Collection, Processing & Chain of Custody GuidePau SorianoNo ratings yet
- MYCOVIRODocument11 pagesMYCOVIROPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Differentiating Staphylococcus and Micrococcus with BacitracinDocument13 pagesDifferentiating Staphylococcus and Micrococcus with BacitracinPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Biological Safety CabinetDocument9 pagesBiological Safety CabinetPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Donor BloodDocument2 pagesDonor BloodPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document30 pagesChapter 1Pau SorianoNo ratings yet
- DecalcificationDocument7 pagesDecalcificationPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- We Need To Be Fit To Fight The VirusDocument2 pagesWe Need To Be Fit To Fight The VirusPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Sample: Practicum PortfolioDocument21 pagesSample: Practicum PortfolioPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- How Can We Live A World Like ThisDocument2 pagesHow Can We Live A World Like ThisPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- AttendanceDocument1 pageAttendancePau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Hepatic FlukesDocument3 pagesHepatic FlukesPaul Avila SorianoNo ratings yet
- Identification of Bacteria (40Document11 pagesIdentification of Bacteria (40Pau SorianoNo ratings yet
- TLE Menu Performance TaskDocument23 pagesTLE Menu Performance TaskPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- National Training Service Program (NSTP) : Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University La Union, PhilippinesDocument24 pagesNational Training Service Program (NSTP) : Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University La Union, PhilippinesPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Major OrgansDocument20 pagesMajor OrgansPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Virtual Learning Among Medical Laboratory Science Students in Their Academic PerformancesDocument13 pagesEffects of Virtual Learning Among Medical Laboratory Science Students in Their Academic PerformancesPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- A Message From 2080Document1 pageA Message From 2080Pau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Schistosoma Japonicum: Schistosoma Japonicum or The Oriental Blood Fluke Causes Schistosomiasis Japonica. It IsDocument7 pagesSchistosoma Japonicum: Schistosoma Japonicum or The Oriental Blood Fluke Causes Schistosomiasis Japonica. It IsPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Bernabe Q Biagtan Elementary School property reportDocument19 pagesBernabe Q Biagtan Elementary School property reportPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- A Warning From 2080Document2 pagesA Warning From 2080Pau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Report 1Document12 pagesReport 1Pau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Acid-base disorders summaryDocument6 pagesAcid-base disorders summaryPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- STS Module 1 Lesson 1-2Document38 pagesSTS Module 1 Lesson 1-2Pau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Instrumentati ON Lesson: Group 6Document39 pagesInstrumentati ON Lesson: Group 6Pau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid-CC Group6Document35 pagesThyroid-CC Group6Pau SorianoNo ratings yet
- NSTP 1 MODULE 2 Drug EducationDocument12 pagesNSTP 1 MODULE 2 Drug EducationPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- STS Module 1 Lesson 1-2Document38 pagesSTS Module 1 Lesson 1-2Pau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Explore the heritage and culture of Calasiao, Pangasinan through its people, churches, and foodDocument5 pagesExplore the heritage and culture of Calasiao, Pangasinan through its people, churches, and foodPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Post Op CareDocument21 pagesPost Op Careahmadkhanmansoor09No ratings yet
- 651 PROCONNECT Blood Pressure Monitor: UA-651CNDocument2 pages651 PROCONNECT Blood Pressure Monitor: UA-651CNJean-Roch JacquesNo ratings yet
- H-V Intervals: Bundle-BranchDocument7 pagesH-V Intervals: Bundle-BranchRanda TabbahNo ratings yet
- Chronic Pain ManagementDocument44 pagesChronic Pain ManagementTomBramboNo ratings yet
- HEMODINAMIKADocument42 pagesHEMODINAMIKAIndraYudhiNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Body TemperatureDocument108 pagesAlterations in Body TemperatureJosephine George JojoNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Beta OxidationDocument59 pagesFatty Acid Beta OxidationEve YapNo ratings yet
- Soal MAYO Yg KeluarDocument8 pagesSoal MAYO Yg KeluardoktersaktiNo ratings yet
- General Pathology - Topical Past Papers-1Document21 pagesGeneral Pathology - Topical Past Papers-1RazaNo ratings yet
- Model Nursing Early Warning System Score (Newss) Dengan Aplikasi Tehnologi Informasi Sebagai Pengkajian Deteksi Kegawatan Pada Klien Stroke Di Rs Kabupaten TangerangDocument12 pagesModel Nursing Early Warning System Score (Newss) Dengan Aplikasi Tehnologi Informasi Sebagai Pengkajian Deteksi Kegawatan Pada Klien Stroke Di Rs Kabupaten Tangeranganggita putriNo ratings yet
- CABAGNOT, Karl Jasper Atherosclerosis Case StudyDocument2 pagesCABAGNOT, Karl Jasper Atherosclerosis Case StudyKasper CabagnotNo ratings yet
- U804173 Id No: Haematology ReportDocument1 pageU804173 Id No: Haematology ReportTB AhmedNo ratings yet
- U N I T I I Diseases of Organ Systems 1 4 8: Escherichia ColiDocument25 pagesU N I T I I Diseases of Organ Systems 1 4 8: Escherichia ColiHerbert YNo ratings yet
- Pedia 1 SGDDocument5 pagesPedia 1 SGDCarla GajoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To BotanyDocument11 pagesModule 1 Introduction To BotanyCEEJAY P. PATAWARANNo ratings yet
- Health Effects of Sleep DeprivationDocument7 pagesHealth Effects of Sleep DeprivationEmily KajlaNo ratings yet
- PN Comprehensive Review CD Questions 1001-1100 (COMP: No Equations/formulas No Questions)Document54 pagesPN Comprehensive Review CD Questions 1001-1100 (COMP: No Equations/formulas No Questions)Kaye PatanindagatNo ratings yet
- 14.respiration New BioHackDocument8 pages14.respiration New BioHackAnush KhillareNo ratings yet
- 200L FON PRESENTATION Group 1Document13 pages200L FON PRESENTATION Group 1jonaNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument5 pagesNCP Deficient Fluid VolumeCHRISTINE GRACE ELLONo ratings yet
- Energy Pathways ExplainedDocument6 pagesEnergy Pathways Explainedshirwen ClamNo ratings yet
- Research Article on Characteristics of Coronary Heart Disease Patients in North MalukuDocument10 pagesResearch Article on Characteristics of Coronary Heart Disease Patients in North MalukuAbduNo ratings yet