Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment No. 2: To Obtain V-I Characteristics of PN Junction Diode. Lab Objective
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No. 2: To Obtain V-I Characteristics of PN Junction Diode. Lab Objective
Copyright:
Available Formats
EXPERIMENT NO.
To obtain V-I characteristics of PN junction diode.
Lab objective:
To know about the diode and how it can pass the current, and also know about the relationship
between V-I characteristics of PN junction diode.
Apparatus:
Variable DC power supply, PN junction Diode, Resistor, Multimeter and connecting wires.
Theory:
The semiconductor diode is formed by doping P-type impurity in one side and N-type of
impurity in another side of the semiconductor crystal forming a p-n junction as shown in the
following figure.
At the junction initially free charge carriers from both side recombine forming negatively
charged ions in P side of junction(an atom in P-side accept electron and becomes negatively
charged ion) and positively charged ion on n side(an atom in n-side accepts hole i.e. donates
electron and becomes positively charged ion)region. This region deplete of any type of free
charge carrier is called as depletion region. Further recombination of free carrier on both side is
Electronics Lab, Spring-2020 semester, Electrical Engineering Department
prevented because of the depletion voltage generated due to charge carriers kept at distance by
depletion (acts as a sort of insulation) layer as shown dotted in the above figure.
Working principle:
When voltage is not applied across the diode, depletion region forms as shown in the
above figure. When the voltage is applied between the two terminals of the diode (anode and
cathode) two possibilities arises depending on polarity of DC supply.
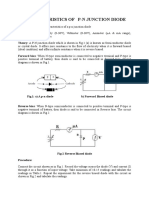
Forward-Bias Condition:
When the +Ve terminal of the battery is connected to P-type material & -Ve terminal to
N-type terminal as shown in the circuit diagram, the diode is said to be forward biased. The
application of forward bias voltage will force electrons in N-type and holes in P-type material to
recombine with the ions near boundary and to flow crossing junction. This reduces width of
depletion region. This further will result in increase in majority carriers flow across the junction.
If forward bias is further increased in magnitude the depletion region width will continue to
decrease, resulting in exponential rise in current as shown in ideal diode characteristic curve.
Reversed-Bias Condition:
If the negative terminal of battery (DC power supply) is connected with P-type terminal
of diode and +Ve terminal of battery connected to N type then diode is said to be reverse biased.
In this condition the free charge carriers (i.e. electrons in N-type and holes in P-type) will move
away from junction widening depletion region width. The minority carriers (i.e. –ve electrons in
p-type and +ve holes in n-type) can cross the depletion region resulting in minority carrier
current flow called as reverse saturation current(Is). As no of minority carrier is very small so the
magnitude of Is is few microamperes. Ideally current in reverse bias is zero.
Electronics Lab, Spring-2020 semester, Electrical Engineering Department
In short, current flows through diode in forward bias and do not flow through diode in reverse
bias. Diode can pass current only in one direction.
Experiment Procedure:
1. Connect the power supply, voltmeter, current meter with the diode as shown in the figure
for forward bias diode. You can use two multi meter (one to measure current through
diode and other to measure voltage across diode)
2. Increase voltage from the power supply from 0V to 20V in step as shown in the
observation table
3. Measure voltage across diode and current through diode. Note down readings in the
observation table.
4. Reverse DC power supply polarity for reverse bias
5. Repeat the above procedure for the different values of supply voltage for reverse bias
6. Draw VI characteristics for forward bias and reverse bias in one graph
Circuit diagram (forward bias)
Electronics Lab, Spring-2020 semester, Electrical Engineering Department
Circuit diagram (reverse bias)
WORKSHEET
Observation table: (Forward bias)
Electronics Lab, Spring-2020 semester, Electrical Engineering Department
Observation table: (Reverse bias)
Draw V-I characteristics of PN junction diode:
Conclusion:
We will write it after practical performance.
Electronics Lab, Spring-2020 semester, Electrical Engineering Department
You might also like
- Lab Report 1Document6 pagesLab Report 1jif 131067% (3)
- Gas Laws Phet Lab 2021Document8 pagesGas Laws Phet Lab 2021C INo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument14 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectAbhishek Raja88% (16)
- Characterisation and diagenetic transformation of silica mineralsDocument20 pagesCharacterisation and diagenetic transformation of silica mineralsde aris lukman100% (1)
- EPD Lab#6Document11 pagesEPD Lab#6Muhammad ShaheerNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode VI CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesPN Junction Diode VI CharacteristicsSyed Suleman Ayub - Section-BNo ratings yet
- 2054359797-BASIC ELNS-UNIT-1 NOTES-DiodesDocument18 pages2054359797-BASIC ELNS-UNIT-1 NOTES-Diodesajey002hegdeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 02Document4 pagesExperiment 02S sarkerNo ratings yet
- Electrical ProjectDocument24 pagesElectrical Projectghimiredipesh072No ratings yet
- OST.ana214Document96 pagesOST.ana214princekumar13785No ratings yet
- OST de-44Document84 pagesOST de-44princekumar13785No ratings yet
- PN Diode LabDocument4 pagesPN Diode LabAbhishekh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Semiconductor Diodes & ApplicsDocument31 pagesChapter 1-Semiconductor Diodes & Applicsramya hegdeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Semiconductor Diodes ApplicsDocument27 pagesChapter 1-Semiconductor Diodes ApplicsRamyaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10Document7 pagesExperiment 10Deepan AdakNo ratings yet
- Diodes and ApplicationsDocument55 pagesDiodes and ApplicationsIgnited IndianNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document2 pagesLab 2Daniel MakahlehNo ratings yet
- Exp5 2K20CO153Document7 pagesExp5 2K20CO153divye guptaNo ratings yet
- Module - 1 18ELN14Document38 pagesModule - 1 18ELN14DaisyQueen100% (1)
- Lab ManualDocument7 pagesLab ManualMm MNo ratings yet
- 4: Basic Electronics: Compare Between Intrinsic and Extrinsic SemiconductorDocument13 pages4: Basic Electronics: Compare Between Intrinsic and Extrinsic SemiconductorPavankumar GosaviNo ratings yet
- PN Diode Characteristics ExperimentDocument4 pagesPN Diode Characteristics Experimentamitkumar423No ratings yet
- Be8253 - Unit 4Document28 pagesBe8253 - Unit 4balajiNo ratings yet
- To Study and Plot The I-V Characteristics of A P-N JunctionDocument2 pagesTo Study and Plot The I-V Characteristics of A P-N Junctionamuhammadahsan73No ratings yet
- Expirement - 1: Name-Dev Summi SAP ID-1000014710 ROLL NO. - 200103900Document15 pagesExpirement - 1: Name-Dev Summi SAP ID-1000014710 ROLL NO. - 200103900Dev AabhroyNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeDocument15 pagesCharacteristics of P-N Junction Diodehybe07jiminNo ratings yet
- Eee Exp 3Document14 pagesEee Exp 3Shaswat kumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Study V-I Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeDocument7 pagesExperiment 4 Study V-I Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeTushar Sharma100% (1)
- Module1 RMYDocument28 pagesModule1 RMYpushpaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: Arunai Engineering College TiruvannamalaiDocument56 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits: Arunai Engineering College TiruvannamalaiKannan TindivanamNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 PHYELC - 2Document5 pagesExperiment 1 PHYELC - 2owronrawan74No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Circuits Lab, IIIT Chittoor: Part A. Forward & Reverse Bias Characteristics of PN Junction DiodeDocument5 pagesBasic Electronics Circuits Lab, IIIT Chittoor: Part A. Forward & Reverse Bias Characteristics of PN Junction DiodeSavithaGnNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesPN Junction Diode CharacteristicsheheheNo ratings yet
- Study of P-N Diodes: Us ManikandaDocument9 pagesStudy of P-N Diodes: Us ManikandaUS MANIKANDANo ratings yet
- PN Diode and Zener Diode AS PER BEEE NOTES MainDocument17 pagesPN Diode and Zener Diode AS PER BEEE NOTES MainMohd AbrarNo ratings yet
- 21EE32 AEC& OpAmps Module-1Document218 pages21EE32 AEC& OpAmps Module-1Antheesh RNo ratings yet
- Theory of PN Junction Diode: DiffusionDocument40 pagesTheory of PN Junction Diode: DiffusionGanesh RathnamNo ratings yet
- Experiment No:3: AIM: To Plot The V-I Characteristics of A PN Junction Diode in Both ForwardDocument3 pagesExperiment No:3: AIM: To Plot The V-I Characteristics of A PN Junction Diode in Both ForwardsanjuNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode: A Guide to Its Structure and OperationDocument5 pagesPN Junction Diode: A Guide to Its Structure and OperationVickeyNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Gautam Exp2Document13 pagesAbhishek Gautam Exp2Abhishek Mishra GautamNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction & Zener DiodeDocument8 pagesP-N Junction & Zener DiodeDeepali PolepalliNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics (ES-112)Document45 pagesBasic Electronics (ES-112)Bharat LalNo ratings yet
- Online - Bai 2 - Mach Ban DanDocument15 pagesOnline - Bai 2 - Mach Ban DanThất VọngNo ratings yet
- Bee IiiDocument68 pagesBee IiiTapobroto ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument20 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsjesudosssNo ratings yet
- 3.3 IV Characteristics of PN Junction Diode-ModifiedDocument18 pages3.3 IV Characteristics of PN Junction Diode-Modifiedraunak guptaNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction DiodeDocument4 pagesP-N Junction DiodeSanskarNo ratings yet
- DiodesDocument27 pagesDiodesamanuelfitsum589No ratings yet
- Unit-1 Analog ElectronicsDocument45 pagesUnit-1 Analog ElectronicsLodhaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - Analog Electronics CBDocument47 pagesUnit-1 - Analog Electronics CBNagesh BhaviNo ratings yet
- P-N Diode CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesP-N Diode Characteristicsrajesh.v.v.kNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of P-N Junction Dioderajesh.v.v.kNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument142 pagesBasic ElectronicsHarshitha CHALUMURI100% (1)
- PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesPN Junction Diode CharacteristicssrinathlalNo ratings yet
- The Junction Diode: Junction Diode Symbol and Static I-V CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesThe Junction Diode: Junction Diode Symbol and Static I-V CharacteristicsNithya MohanNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DiodesDocument9 pagesSemiconductor Diodessitaram rajNo ratings yet
- Experiment-2 (A) Objectives:-: Name:-Chhavi Ojha SCHOLAR NUMBER: - 2100208Document17 pagesExperiment-2 (A) Objectives:-: Name:-Chhavi Ojha SCHOLAR NUMBER: - 2100208Abhishek Mishra GautamNo ratings yet
- Lab ProjectDocument20 pagesLab ProjectTanveerNo ratings yet
- Publication 12 4795 82Document12 pagesPublication 12 4795 82Saud AloufiNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode Fundamentals, Rectifier Circuits & Transistor BasicsDocument46 pagesPN Junction Diode Fundamentals, Rectifier Circuits & Transistor Basicsoijhgvcx100% (1)
- JNTUA College Electronics Devices & Circuits Exam ReviewDocument21 pagesJNTUA College Electronics Devices & Circuits Exam ReviewRiyaz PashaNo ratings yet
- ECE 301 Electronics 1: Measurement TolerancesDocument17 pagesECE 301 Electronics 1: Measurement TolerancesVince Hugo GutibNo ratings yet
- Viva Attendance ElectronicsDocument1 pageViva Attendance ElectronicsMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- TimeDocument4 pagesTimeMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission & Distribution Lab (EE436L) : Total Marks 20Document2 pagesPower Transmission & Distribution Lab (EE436L) : Total Marks 20Mohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Smart Vision Cap For Visually Impaired People: Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument9 pagesSmart Vision Cap For Visually Impaired People: Electrical Engineering DepartmentMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- CLO-1 Describe The Concepts of PLC Programming and Ladder Logic. C2 PLO1 CLO-2 Analyze The Working of Multiple Electrical Drives. C4 PLO2Document1 pageCLO-1 Describe The Concepts of PLC Programming and Ladder Logic. C2 PLO1 CLO-2 Analyze The Working of Multiple Electrical Drives. C4 PLO2Mohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System Lab MarksDocument6 pagesLinear Control System Lab MarksMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System: Instructor ManualDocument3 pagesLinear Control System: Instructor ManualMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System Lab MarksDocument6 pagesLinear Control System Lab MarksMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument1 pageDepartment of Electrical EngineeringMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- EMS - DLD - Email VersionDocument2 pagesEMS - DLD - Email VersionMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge Rectifier: Experiment No. 6Document5 pagesFull Wave Bridge Rectifier: Experiment No. 6Mohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System Lab MarksDocument6 pagesLinear Control System Lab MarksMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 3: To Obtain V-I Characteristics of Zener Diode. Lab ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 3: To Obtain V-I Characteristics of Zener Diode. Lab ObjectiveMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Diode Limiter: Experiment No. 7Document9 pagesDiode Limiter: Experiment No. 7Mohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 3: To Obtain V-I Characteristics of Zener Diode. Lab ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 3: To Obtain V-I Characteristics of Zener Diode. Lab ObjectiveMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Three Phase RectificationDocument10 pagesThree Phase RectificationMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Sarhad University of Science & Information Technology, Peshawar Daily Class Attendance (ONLINE FALL-2020 SEMESTER)Document1 pageSarhad University of Science & Information Technology, Peshawar Daily Class Attendance (ONLINE FALL-2020 SEMESTER)Mohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Centre Tapped Rectifier: Experiment No. 5Document4 pagesFull Wave Centre Tapped Rectifier: Experiment No. 5Mohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Triac and Diac Control AC CircuitsDocument9 pagesTriac and Diac Control AC CircuitsMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Topics: Semiconductor Devices Week: 4 Program: Be Electrical EngineeringDocument20 pagesPower Electronics: Topics: Semiconductor Devices Week: 4 Program: Be Electrical EngineeringMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Measure Waveforms and Parameters Using DSODocument3 pagesMeasure Waveforms and Parameters Using DSOMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical Engineering100% (1)
- Sarhad University of Science & Information Technology, Peshawar Daily Class Attendance (ONLINE FALL-2020 SEMESTER)Document1 pageSarhad University of Science & Information Technology, Peshawar Daily Class Attendance (ONLINE FALL-2020 SEMESTER)Mohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- And Chopper Circuits Since No Commutation Circuits Are: RequiredDocument20 pagesAnd Chopper Circuits Since No Commutation Circuits Are: RequiredMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Topics: Firing Circuits For Thyristor Week: 3 Program: Be Electrical EngineeringDocument11 pagesPower Electronics: Topics: Firing Circuits For Thyristor Week: 3 Program: Be Electrical EngineeringMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Parallel CircuitDocument26 pagesWeek 2 Parallel CircuitMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Sarhad University of Science & Information Technology, Peshawar Daily Class Attendance (ONLINE FALL-2020 SEMESTER)Document1 pageSarhad University of Science & Information Technology, Peshawar Daily Class Attendance (ONLINE FALL-2020 SEMESTER)Mohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Topics: Semiconductor Devices Week: 4 Program: Be Electrical EngineeringDocument20 pagesPower Electronics: Topics: Semiconductor Devices Week: 4 Program: Be Electrical EngineeringMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Sarhad University of Science & Information Technology, Peshawar Daily Class Attendance (ONLINE FALL-2020 SEMESTER)Document1 pageSarhad University of Science & Information Technology, Peshawar Daily Class Attendance (ONLINE FALL-2020 SEMESTER)Mohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Boost Converter Simulation in PSPICEDocument4 pagesBoost Converter Simulation in PSPICEMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- 389-Article Text-1590-1-10-20230129Document6 pages389-Article Text-1590-1-10-20230129wahyu satriaNo ratings yet
- TDJ2Document248 pagesTDJ2nmtien1985No ratings yet
- Molecular DeviceDocument26 pagesMolecular Device7semNo ratings yet
- 纺纱学双语Document653 pages纺纱学双语Gizachew Zeleke100% (1)
- Astm B 134 B134M-08Document7 pagesAstm B 134 B134M-08Chung LeNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Force, Torque and SpeedDocument18 pagesMeasurement of Force, Torque and SpeedErxDNo ratings yet
- Thermal TestDocument11 pagesThermal TestBhavani GujjariNo ratings yet
- Mec-003 EngDocument58 pagesMec-003 EngnitikanehiNo ratings yet
- Me8491 em Unit - IIDocument119 pagesMe8491 em Unit - IIParameswara Raja100% (1)
- CHAYANIKA MTech 2013-15Document62 pagesCHAYANIKA MTech 2013-15Maher TolbaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document7 pagesLab Report 2HarwinderNo ratings yet
- MPX2053 MPXV2053G DatasheetDocument12 pagesMPX2053 MPXV2053G DatasheetkurmakkNo ratings yet
- MEMS Assignment On Crystal Structure of Silicon: R.Vijayaraghavan - 11MMT0002Document6 pagesMEMS Assignment On Crystal Structure of Silicon: R.Vijayaraghavan - 11MMT0002Vijayraghavan RameshNo ratings yet
- DPP 2Document3 pagesDPP 2DHRUV WORLDNo ratings yet
- N Conlan J Casey Comparing Predicted and On Site Performance of CLT Partitions and Flanking ElementsDocument8 pagesN Conlan J Casey Comparing Predicted and On Site Performance of CLT Partitions and Flanking ElementsGengaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Newton Vs LeibnizDocument21 pagesCalculus Newton Vs LeibnizAhmad Hakimi OthmanNo ratings yet
- Design & Analysis of HPDC Process For Aluminum Alloy ADC12Document5 pagesDesign & Analysis of HPDC Process For Aluminum Alloy ADC12GautamNo ratings yet
- Xpm2Electrical SchematicsDocument59 pagesXpm2Electrical SchematicsKleber DalasNo ratings yet
- Design and Application of FeederDocument35 pagesDesign and Application of Feederbgn10101977No ratings yet
- Module 2 Thermochemistry - CalorimetryDocument34 pagesModule 2 Thermochemistry - CalorimetryBro KingNo ratings yet
- Regression analysis for transport planningDocument15 pagesRegression analysis for transport planningHussein OmranNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry CBSE Exam Papers 2016 Foreign Set 1 AnswerDocument10 pages12 Chemistry CBSE Exam Papers 2016 Foreign Set 1 AnswerAlagu MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Charge in Zwitterions and Isoelectric Point MCAT Tutorial PDFDocument12 pagesAmino Acid Charge in Zwitterions and Isoelectric Point MCAT Tutorial PDFKHURT MICHAEL ANGELO TIU100% (1)
- Powerpoint DoseDocument16 pagesPowerpoint DoselcsmfoxNo ratings yet
- JCAMECH Volume 52 Issue 1 Pages 102-125Document24 pagesJCAMECH Volume 52 Issue 1 Pages 102-125Subodh KumarNo ratings yet
- Inc Germanium Phosphide: Features.Document4 pagesInc Germanium Phosphide: Features.MatNo ratings yet
- 4wrte Mannesmann RexrothDocument16 pages4wrte Mannesmann RexrothRuben Torres100% (1)