Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity 1: Break It Down Activity 3: The Nerves!!!
Uploaded by
Jia Capati0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Science10_Q3W3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views2 pagesActivity 1: Break It Down Activity 3: The Nerves!!!
Uploaded by
Jia CapatiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Jia Lianne Y.
Capati Science 10 (3rd Quarter – Week 3)
10 – Maxwell Mr. Jake Kok
Activity 1: Break It Down Activity 3: The Nerves!!!
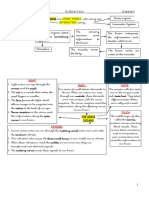
1. The two major divisions of the Nervous
System are the Central Nervous System
(CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous
System (PNS).
2. The parts under the CNS are the brain
and the spinal cord.
3. The CNS functions as the control center
that receives data and feedback from
sensory organs and nerves throughout
the body, processes the information,
and sends commands back out. On the
other hand, the PNS is composed of
nerves, outside the brain and spinal
cord, that connect the CNS to other Activity 5: The Nervous Trip!
parts of the body. 1. Thirst
4. The sensory (afferent) division is 2. Tongue
composed of somatic and visceral 3. The receptor receives the stimulus and
sensory nerve fibers, located near the converts it into an impulse. The nerves
brain and spinal cord, that transmit pass the impulse to the next nerve cell.
impulses from stimuli toward the CNS. Then, the brain receives the information
The motor (efferent) division is through the sensory neurons.
composed of motor nerve fibers, 4. As soon as the brain receives the
located within the CNS, that transmit information from the sensory neurons, it
impulses from the CNS out to the processess a response to send to the
peripheral organs (muscles and glands) motor neurons.
to cause an effect or action. 5. The brain processes the information and
5. If one part of the nervous system fails to delivers a response to an effector, such
carry out its function properly, all other as organs, muscles, and glands, through
parts of the system will be affected and the motor neurons. The effector will then
may be unable to perform their usual perform the response given.
tasks. 6. Muscles (triceps)
7. Arms will be used to assist in fetching a
glass of water.
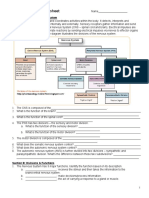
Activity 2: What’s in Your Brain? 8. The sensory (afferent) division is
1. Brain stem composed of somatic and visceral
2. Cerebrum sensory nerve fibers that transmit
3. Cerebellum impulses from stimuli toward the CNS.
The motor (efferent) division is
composed of motor nerve fibers that
transmit impulses from the CNS out to
the peripheral organs (muscles and
glands) to cause an effect or action.
Jia Lianne Y. Capati Science 10 (3rd Quarter – Week 3)
10 – Maxwell Mr. Jake Kok
Activity 6: The BALANCE Inside!
1. Homeostasis is the process by which the
internal environment regulates itself to
maintain stability while adjusting to
different conditions.
2. When the temperature of the
environment increases, the body
regulates its temperature by
perspiration; when it decreases, the
body triggers the shivering reflex. In the
presence of light, the pupil constricts to
adjust to the brightness; in its absence,
the pupil dilates to take in more light.
These are achieved when when each
part of the body functions in equilibrium
with other parts.
3. Homeostasis usually involves negative
feedback that act to oppose the
stimulus that triggers them; for example,
when the body temperature is too high,
a negative feedback will be triggered
to bring it back down and regulate it.
4. Positive feedback intensifies a change
in the body's physiological condition
rather than reversing it; for example,
when the body temperature is too low,
a positive feedback will be triggered to
bring it back up and regulate it.
Post Test
1. D
2. A
3. A
4. C
5. B
You might also like
- Comparison Chart of Four Developmental TheoriesDocument1 pageComparison Chart of Four Developmental Theoriescarpe diemNo ratings yet
- The New Science of Learning For StudentsDocument95 pagesThe New Science of Learning For StudentsTerry Doyle100% (1)
- Assignment 2 Case StudyDocument6 pagesAssignment 2 Case Studyapi-427319867No ratings yet
- The Master Disorder Document SPR 2015Document6 pagesThe Master Disorder Document SPR 2015api-261267976100% (1)
- My Favorite Rapid and Instant InductionsDocument27 pagesMy Favorite Rapid and Instant Inductionstrueflownow85% (13)
- Nervous Endocrine SystemsDocument44 pagesNervous Endocrine SystemsChristine Pinton BahianNo ratings yet
- The Neuromuscular System and ExerciseDocument20 pagesThe Neuromuscular System and ExercisenofriNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ActivityDocument1 pageNervous System ActivityMark Owen BaldoNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy and Physiology of The Masticatory System: MAJ Joseph Lowe October 15, 2010Document76 pagesNeuroanatomy and Physiology of The Masticatory System: MAJ Joseph Lowe October 15, 2010joeylowetylerNo ratings yet
- G-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- GR 10 ReviewerDocument292 pagesGR 10 Revieweradrianigop29No ratings yet
- Major Divisions and Parts of The Nervous System The Nerve CellDocument6 pagesMajor Divisions and Parts of The Nervous System The Nerve CellAllysa Mae MoraNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Document5 pagesScience-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsDocument13 pagesUnit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsIrene Caballero PicazoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System and Coordination of Nervous and Endocrine System To Achieve HomeostasisDocument65 pagesNervous System and Coordination of Nervous and Endocrine System To Achieve HomeostasisJoseph yvannNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesHuman Nervous SystemI Kadek Adi Putra Suandana 2005No ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument6 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorLyanna MormontNo ratings yet
- At The Base of The Brain Stimulates Growth and Controls The Functions of Other Glands Below The Voice Box Thyroxin, CalcitoninDocument8 pagesAt The Base of The Brain Stimulates Growth and Controls The Functions of Other Glands Below The Voice Box Thyroxin, CalcitoninAubrey Jen MañasNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology: Explain The Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology: Explain The Functions of The Nervous SystemJay-ar BarquerosNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: by Dr. K. Sumangala BhatDocument37 pagesNervous System: by Dr. K. Sumangala BhatanushkaNo ratings yet
- Sight Smell Taste: Unit 2 InteractionDocument3 pagesSight Smell Taste: Unit 2 InteractionmarcNo ratings yet
- PE NeuronDocument3 pagesPE Neuronlucy ocampoNo ratings yet
- SCience Group 1 q3 Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesSCience Group 1 q3 Nervous Systemapolancos50713No ratings yet
- IM AnSci 111 Module 3Document21 pagesIM AnSci 111 Module 3Riza Mae Duran RangasNo ratings yet
- B Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 2 (Week 3)Document17 pagesB Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 2 (Week 3)Daisy Soriano PrestozaNo ratings yet
- Neuro-Network: A Presentation About The Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNeuro-Network: A Presentation About The Nervous Systemwellskyle891No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemsabanalgenneNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous Systemkmakabe78No ratings yet
- Unit 3 NotesDocument10 pagesUnit 3 Notesapi-300762638No ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3Document15 pagesScience 10 Quarter 3 Module 3Zahra Alexä DavidsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Biology of MindDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - The Biology of MindCindy AvendanoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 2023Document31 pagesNervous System 2023Rayjie G RuleNo ratings yet
- Biology 10Document3 pagesBiology 10Dwayne BaldozaNo ratings yet
- UNIT5 InteractionDocument8 pagesUNIT5 InteractionMairela miranda ausínNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemPatricia BonganayNo ratings yet
- Week 20 - Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesWeek 20 - Nervous SystemEraNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science 10 Q3 W3Document6 pagesLeaP Science 10 Q3 W3SHAIRA SOTOMAYORNo ratings yet
- 3.2.2.2. The Human Nervous System Conceptual Check UpDocument3 pages3.2.2.2. The Human Nervous System Conceptual Check UpJana De LiñaNo ratings yet
- Integration and Coordination - SG3Document180 pagesIntegration and Coordination - SG3Marcos AlbaridaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous Systemvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- Human Regulatory SystemDocument23 pagesHuman Regulatory SystemNina WirdiyanaNo ratings yet
- Module - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of BehaviorDocument11 pagesModule - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of Behavioraudree d. aldayNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Written Report 2Document24 pagesNervous System Written Report 2Noronisa PendalidayNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument3 pagesCoordination and ResponseclintonbogololephojaneNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - The Human Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesModule 2 - The Human Nervous SystemoyamaNo ratings yet
- Body System II 1 Nerv 1Document77 pagesBody System II 1 Nerv 1rrq8cwk2gnNo ratings yet
- AnscieDocument10 pagesAnscieEstephanie BusligNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Science Form 4Document26 pagesChapter 2 Science Form 4Shafie Buyamin100% (2)
- The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesThe Nervous Systemhajra0325No ratings yet
- Nervous System WorksheetDocument3 pagesNervous System WorksheetLiezel CauilanNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesThe Nervous SystemmalakbasahalNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response in Animals - 052037Document8 pagesCoordination and Response in Animals - 052037MosesNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument21 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviourSufian Khan100% (1)
- The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesThe Nervous SystemKristie Becker100% (1)
- L5 Controlling ProcessesDocument28 pagesL5 Controlling ProcessesMawadda AljawadiNo ratings yet
- q3 w2 Science 10Document63 pagesq3 w2 Science 10dejaveusNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesNervous Systemphoebecruz636No ratings yet
- Irritability Part IDocument18 pagesIrritability Part IYanique JonesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: 2 Quarter - Module 2Document2 pagesGeneral Biology 2: 2 Quarter - Module 2Veronica RojasNo ratings yet
- THE Nervou S System: "Explain How A Boy Is Able To React When He Comes Into Contact With A Hot Object"Document14 pagesTHE Nervou S System: "Explain How A Boy Is Able To React When He Comes Into Contact With A Hot Object"Sanjay VeerasammyNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Module 3Document32 pagesQuarter 3 Module 3Herbert DelacruzNo ratings yet
- PSY-105 Chapter # 03: Neuro Science and BehaviorDocument9 pagesPSY-105 Chapter # 03: Neuro Science and BehaviorSabbir AhammedNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument21 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorSyed Huzayfah FaisalNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemDeejay BeekayNo ratings yet
- Ambady Rosenthal 92 Thin Slices of Expressive Behavior As Predictors of Interpersonal ConsequencesDocument19 pagesAmbady Rosenthal 92 Thin Slices of Expressive Behavior As Predictors of Interpersonal Consequences22marbieNo ratings yet
- Mental Retardation Is Now Cadlled Intellectual Disability Which Is Characterized by BelowDocument16 pagesMental Retardation Is Now Cadlled Intellectual Disability Which Is Characterized by BelowxxxxxxxNo ratings yet
- Fs 1 (Episode 2) - Learner'S Characteristics and Needs: TargetDocument3 pagesFs 1 (Episode 2) - Learner'S Characteristics and Needs: TargetKC BernabeNo ratings yet
- David Grove Basic Clean Language QuestionsDocument2 pagesDavid Grove Basic Clean Language QuestionsAnonymous 2a1YI92k9L100% (4)
- UTSDocument25 pagesUTSAngelica TañedoNo ratings yet
- Ogranizational Behavior Course OutlineDocument9 pagesOgranizational Behavior Course Outlineqirat nadeemNo ratings yet
- Wellspring High School, Inc.: Chapter 2: Review of Related StudiesDocument4 pagesWellspring High School, Inc.: Chapter 2: Review of Related StudiesRaven Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Massive Shared Trauma and "Hot" PlacesDocument12 pagesMassive Shared Trauma and "Hot" PlacesEdwardNo ratings yet
- New - General Psy ModuleDocument20 pagesNew - General Psy ModuleMaria CrisalveNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Perception AttributionDocument15 pagesTopic 3 Perception AttributionSarvishnie MuniyandyNo ratings yet
- CV CmsDocument3 pagesCV Cmsapi-534472616No ratings yet
- Clinical Case Reports - 2020 - Oliveira - A Normal Motor Development in Congenital Hydrocephalus After Cuevas MedekDocument4 pagesClinical Case Reports - 2020 - Oliveira - A Normal Motor Development in Congenital Hydrocephalus After Cuevas MedekRonaldo Angel VelásquezNo ratings yet
- Model Answers: Chapter 12 Coordination and Response in HumansDocument5 pagesModel Answers: Chapter 12 Coordination and Response in HumansLaff IzzatulNo ratings yet
- Principles and Strategies of TeachingDocument15 pagesPrinciples and Strategies of TeachingJayson YanguasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10. Personality DisorderDocument21 pagesChapter 10. Personality Disordersherlin_de_wardanaNo ratings yet
- Treatment PlanDocument4 pagesTreatment Planworship himNo ratings yet
- WestbyDocument3 pagesWestbySwathi GNo ratings yet
- Self Compassion 1Document17 pagesSelf Compassion 1SoulyogaNo ratings yet
- Action Learning and Action Research Are Closely Related ProcessesDocument4 pagesAction Learning and Action Research Are Closely Related ProcessesmachevallieNo ratings yet
- SWAN Parkinson MRIDocument9 pagesSWAN Parkinson MRIulfi yunitaNo ratings yet
- Pex 02 03 PDFDocument6 pagesPex 02 03 PDFCourtney Sims83% (6)
- Categories of Disability Under IDEADocument6 pagesCategories of Disability Under IDEANational Dissemination Center for Children with DisabilitiesNo ratings yet
- Developing The Whole PersonDocument21 pagesDeveloping The Whole Personchikincat450No ratings yet
- The Material SelfDocument24 pagesThe Material SelfTripulca Annabelle0% (1)
- Lecture Refletive Practice in Nursing HSMDocument38 pagesLecture Refletive Practice in Nursing HSMelsiNo ratings yet