Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EALS
Uploaded by
emarites ronquillo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesEALS
Uploaded by
emarites ronquilloCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE
Name : Rona Elaiza Campolio Date : Nov. 20 , 2021
Section and Strand : Humss 11 - 9 St. Titus Teacher : Sir. Jerome Razon
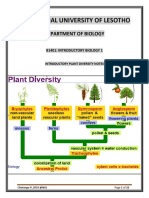
1. Jayson - MUNG BEANS - As the plant matures, small, pale yellow
flowers will appear in clusters of 12 to 15 toward the top of a mung
bean plant. The flowers are self-pollinating and do not require wind or
insects. Pollen, the male portion of the plant, forms as grains at the end
of an organ called the anther. When pollen comes in contact with the
female portion of the plant, known as the stigma, sperm is released. The
sperm travels down through the stigma into the ovary, where
fertilization occurs.
● As it matures, the plant will put forth stems that will grow either
as indeterminate plants that grow as vines or terminate plants that
grow in bush form.
2. Jenny - GRAPES - The male parts of the flower are the stamens, each
consisting of a pollen-bearing anther supported by a filament.
Generally, there are five anthers arranged around the ovary, but some
varieties may have more or less. Pollen is shed as the anther ripens and
are primarily transported by wind, though rarely more than 20 feet (7
meters) from the source. Pollination occurs when pollen lands on the
female parts of a flower. Each pollen grain grows a long tube towards
the eggs within the ovary, and sperm cells move down this tube.
● The female parts of the flower consisting of the ovary, the stigma,
and the style. The stigma and style provide the entrance to the
ovary for pollen. When a sperm cell in the pollen tube unites with
an egg cell in the ovary, an embryo (a new seedling plant) is
produced. The embryo grows within the developing seed, while
the entire ovary grows to become the grape berry itself with seeds
contained within.
3. Angelo - ROSE - The sexual reproduction in rose plants happens with
the fusion of male and female gametes produced by plants. The male
gametes are produced by the process of microsporogenesis which
occurs in anthers whereas the female gametes or eggs are produced in
the ovary of the flower. After the maturation of gametes, fertilization
between gametes occurs by pollination in which the male gametes
reach the female gamete for fertilization to give rise to a new rose plant.
The process of pollination is aided by many agents of pollination such
as wind or insects which take pollen grains to other rose plants (in case
of cross-pollination). After fertilization, embryo formation takes place.
This embryo is present in the seeds of the plant. The seed protects the
embryo and nourishes the embryo until it germinates in soil and
develops into a new plant.
● A seed consists of an embryo, which is surrounded by a
protective coat. The parent rose plant disperses the seeds into the
atmosphere. In favourable conditions, those seeds germinate and
the embryo grows into a new rose plant.
4. Janelle - PINE TREE - As a general rule, most trees pine trees
included – reproduce sexually. This means that both male and female
parts of the pine tree are required for fertilization and for a seed to
develop. Female pine cones use their woody structure to keep their
seeds safe. They keep their seeds safe so the seeds can hopefully be
pollinated and grow. Each female pine cone has numerous spirally
arranged scales, with two seeds on each fertile scale. Male pine cones
produce pollen, which is like a powder. The male cones release their
pollen, which is carried around the air by blowing wind and hopefully
to another female pine cone on a different pine tree. If the pollen
reaches a female pine cone, this process is called pollination.
● After pollination, and as time passes (usually about two to three
years), the pollinated pine seeds grow and eventually peel loose
and off of the cone and fall to the ground. If a good spot for the
seed is available, a new pine tree will grow! However, there are
many ways fertilized pine seeds can move from place to plac
5. Jerome - FERN - The fern "life cycle" refers to sexual reproduction.
However, ferns use asexual methods to reproduce, too. In apogamy, a
sporophyte grows into a gametophyte without fertilization occurring.
Ferns use this method of reproduction when conditions are too dry to
permit fertilization. Ferns can produce baby ferns at proliferous frond
tips. As the baby fern grows, its weight causes the frond to droop
toward the ground. Once the baby fern roots itself, it can survive
separate from the parent plant. The proliferous baby plant is genetically
identical to its parent. Ferns use this as a method of quick reproduction.
● The rhizomes (fibrous structures that resemble roots) can spread
through soil, sprouting new ferns. Ferns grown from rhizomes are
also identical to their parents. This is another method that permits
quick reproduction.
6. Erica - THYLLOPHYTA - The sexual reproduction in thallophyta is
isogamous, anisogamous and oogamous. In thallophyta, sexual
reproduction takes place through zygotic meiosis, therefore the embryo
is not formed.
You might also like
- Pollination NotesDocument6 pagesPollination Notesketki kamatNo ratings yet
- GR4 Science Plant ReproductionDocument35 pagesGR4 Science Plant ReproductionG09 Janelle Ivana Rose GoNo ratings yet
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Reproduction in Plants – RBSE GuideDocument3 pagesRBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Reproduction in Plants – RBSE GuideAlpine AcademiaNo ratings yet
- GRade 11 ScienceDocument3 pagesGRade 11 SciencePROx HUNTERzNo ratings yet
- Flowers, fruits and seeds: A morphological continuityDocument4 pagesFlowers, fruits and seeds: A morphological continuityJobadzNo ratings yet
- Essential Reproduction Process in All Living OrganismsDocument15 pagesEssential Reproduction Process in All Living Organismseugene_970418755No ratings yet
- The Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandThe Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Part Two of Your JourneyDocument3 pagesWelcome To The Part Two of Your JourneyRaphael Louis DacanayNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Science How Plants ReproduceDocument41 pagesGrade 5 Science How Plants ReproduceJulie Mae Sajulga JacobeNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 6 Perpetuation of LifeDocument23 pagesLECTURE 6 Perpetuation of LifeJemuel LuminariasNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument62 pagesPlant ReproductionAdonis BesaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12 Reproduction in PlantsDocument5 pagesChapter - 12 Reproduction in Plantsanju singhNo ratings yet
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- Reproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)Document10 pagesReproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)richelyn navalesNo ratings yet
- 3RD Grading ScienceDocument16 pages3RD Grading ScienceJohannah Eleiya CalimagNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument41 pagesFinal ReportMickeyNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Plants: Flower, Cone, and Spore-BearingDocument17 pagesLife Cycle of Plants: Flower, Cone, and Spore-Bearingmarc louise tipayNo ratings yet
- Spider Plant Reproduction MethodsDocument9 pagesSpider Plant Reproduction MethodsWorkout PrietoNo ratings yet
- Tracheophyte NotesDocument11 pagesTracheophyte NotesTracy Lou FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Reproduction ExplainedDocument53 pagesAnimal and Plant Reproduction ExplainedSheryl Osorio100% (1)
- Plant Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument16 pagesPlant Reproduction and Developmentits james de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction 4 1Document4 pagesPlant Reproduction 4 1Belen MartinezNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project (Class 12)Document14 pagesBiology Investigatory Project (Class 12)MAX Music77% (22)
- Plant Reproduction - Sexual and Asexual Methods ExplainedDocument30 pagesPlant Reproduction - Sexual and Asexual Methods ExplainedShvet MahajanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument5 pagesReproduction in OrganismsRenuNo ratings yet
- Self-Incompatibility Lecture Outlines Flower Structure and ReproductionDocument30 pagesSelf-Incompatibility Lecture Outlines Flower Structure and ReproductionlkokodkodNo ratings yet
- Flower Pollination NoteDocument5 pagesFlower Pollination NotejuliaNo ratings yet
- Science Synthesis II 5Document5 pagesScience Synthesis II 5lala0483No ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument20 pagesReproduction in PlantsAndrea AgustinNo ratings yet
- HOW Flowering Plants Reproduce: November 4, 2019Document29 pagesHOW Flowering Plants Reproduce: November 4, 2019Ligaya Orozco Bautista-GonzalesNo ratings yet
- CH # 9 Kingdom Plantae Class 11THDocument37 pagesCH # 9 Kingdom Plantae Class 11THJansher Ali ChohanNo ratings yet
- Module 5: Heredity: OutcomesDocument22 pagesModule 5: Heredity: OutcomesNavtej DeyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Plant Growth and Reproduction: 5 Grade Science Teacher Imarlys CajigasDocument26 pagesChapter 3: Plant Growth and Reproduction: 5 Grade Science Teacher Imarlys CajigasSNOWCHILL VINESNo ratings yet
- Q2 - W5 Science 5Document48 pagesQ2 - W5 Science 5Mac RamNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Development in OrganismsDocument3 pagesReproduction and Development in OrganismsOtot DaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsrichie2885No ratings yet
- Plant Propagation MethodsDocument4 pagesPlant Propagation MethodsimperialNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants Notes: Asexual and Sexual ProcessesDocument13 pagesReproduction in Plants Notes: Asexual and Sexual ProcessesAdnan SathikNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument17 pagesAsexual Reproduction in Plantswafa eliasNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Reproduction Processes ComparedDocument16 pagesPlant and Animal Reproduction Processes Comparedhellohelloworld100% (1)
- Plant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsDocument22 pagesPlant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsLebohang MakhanyaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantsAshraf ali palhNo ratings yet
- Modes of Reproduction in PlantsDocument15 pagesModes of Reproduction in Plantsjudy andrade100% (1)
- PRINTDocument10 pagesPRINT24 Rashi Anand JangdeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument80 pagesChapter 23 Plant Reproductionmain.15001068No ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument5 pagesPlant ReproductionFaizan ElahiNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterDocument7 pagesScience 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterHoneylet Alberto Castro ArilloNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingDocument34 pagesReproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingJulie BalogoNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTION-sexual in PlantsDocument7 pagesREPRODUCTION-sexual in Plantskmakabe78No ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants NotesDocument5 pagesReproduction in Plants Notesalviayaan807No ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument2 pagesAsexual ReproductionReshma MohabeirNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesReproduction in PlantsRenuNo ratings yet
- Flowers Fruit and SeedsDocument3 pagesFlowers Fruit and SeedsJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction PartsDocument2 pagesPlant Reproduction PartsIrish cambriNo ratings yet
- IS NotesDocument3 pagesIS Notesshanicewhyne05No ratings yet
- How Do Plants Grow? Botany Book for Kids | Children's Botany BooksFrom EverandHow Do Plants Grow? Botany Book for Kids | Children's Botany BooksNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument4 pagesReproduction in PlantsYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction Alevel Flowering Plants (3)Document5 pagesSexual Reproduction Alevel Flowering Plants (3)barasasamuel922No ratings yet
- The Queer Queen Quivers The Gays in Selected PhiliDocument13 pagesThe Queer Queen Quivers The Gays in Selected Philiemarites ronquilloNo ratings yet
- Final Chap 1 5 1 1Document33 pagesFinal Chap 1 5 1 1emarites ronquilloNo ratings yet
- Immaculate Conception Polytechnic Senior High SchoolDocument1 pageImmaculate Conception Polytechnic Senior High Schoolemarites ronquilloNo ratings yet
- Campolio, Rona Elaiza Lesson 6 Quiz 6Document1 pageCampolio, Rona Elaiza Lesson 6 Quiz 6emarites ronquilloNo ratings yet
- Campolio, Rona Elaiza Lesson 6 Activity 6Document2 pagesCampolio, Rona Elaiza Lesson 6 Activity 6emarites ronquilloNo ratings yet
- Campolio, Rona Elaiza Lesson 6 Quiz 6Document1 pageCampolio, Rona Elaiza Lesson 6 Quiz 6emarites ronquilloNo ratings yet
- Campolio, Rona Elaiza Lesson 6 Quiz 6Document1 pageCampolio, Rona Elaiza Lesson 6 Quiz 6emarites ronquilloNo ratings yet
- EALSDocument4 pagesEALSemarites ronquilloNo ratings yet
- 40 Lesson PlansDocument62 pages40 Lesson Plansadnan hashimNo ratings yet
- Tugas News Item KLS XiiDocument18 pagesTugas News Item KLS XiisuhaeniNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Reproduction & GrowthDocument3 pagesBiology Form 5 Reproduction & GrowthM I K R A MNo ratings yet
- Development Theories 1 2Document66 pagesDevelopment Theories 1 2Aaryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- F1b Project Description Part BDocument5 pagesF1b Project Description Part BBranislavPetrovicNo ratings yet
- Vertebrate Embryology - Randel PDFDocument399 pagesVertebrate Embryology - Randel PDFrandelNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Dr. Ma. Angelita S. Rabanal, RN, MSNDocument9 pagesPrepared By: Dr. Ma. Angelita S. Rabanal, RN, MSNAngie SaquingNo ratings yet
- Crop ScienceDocument108 pagesCrop ScienceJairus LampanoNo ratings yet
- Fertilisation and PregnancyDocument24 pagesFertilisation and PregnancyLopak TikeNo ratings yet
- General-Biology-2LAS MwaDocument31 pagesGeneral-Biology-2LAS MwaLance Liad100% (1)
- Insights into philosophy, history and nature from various passagesDocument24 pagesInsights into philosophy, history and nature from various passagesBhoomiNo ratings yet
- Developing Person Through Childhood Adolescence 10th Edition Berger Test BankDocument22 pagesDeveloping Person Through Childhood Adolescence 10th Edition Berger Test BankJefferyBowenkzdf100% (31)
- 3rd Laboratory Activity AnuraDocument7 pages3rd Laboratory Activity AnuraZia Ammarah SaripNo ratings yet
- Post Feb Mock Plan: Topics 1-4 PAPER 1 Assessment Focus RPDocument61 pagesPost Feb Mock Plan: Topics 1-4 PAPER 1 Assessment Focus RPEllisNo ratings yet
- Sts-Lesson 3 FinalsDocument2 pagesSts-Lesson 3 Finalsluisaalejandro993No ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 2Document58 pages08 - Chapter 2Bahadur BiswasNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument7 pagesStem Cellsdaccci0% (1)
- Rajvin Samuel PonrajDocument28 pagesRajvin Samuel PonrajPutri kartiniNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Animal DiversityDocument3 pagesAn Introduction To Animal DiversityJulia Elaine AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Developmental BiologyDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Developmental BiologyJovie Esquivias NicolasNo ratings yet
- Study Reveals How Egg Cells Get So Big: Date: Source: SummaryDocument2 pagesStudy Reveals How Egg Cells Get So Big: Date: Source: SummaryFred PascuaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Study Module - Lakshya NEET 2024Document60 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Study Module - Lakshya NEET 2024uditp7381No ratings yet
- Kenji SiratoriDocument23 pagesKenji SiratoriKazuAiriNo ratings yet
- Embryo Development SEDocument7 pagesEmbryo Development SEWWE FightsNo ratings yet
- Report On The Visit To National Dairy Research InstituteDocument15 pagesReport On The Visit To National Dairy Research InstitutemuhsinNo ratings yet
- GPB 316 Plant Biotechnology (2+1) - Online Study MaterialDocument150 pagesGPB 316 Plant Biotechnology (2+1) - Online Study MaterialadityaNo ratings yet
- Views of Orthodox Theology on Bioethical IssuesDocument24 pagesViews of Orthodox Theology on Bioethical IssuessilviustoiangalatiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 .ProfEd 601 Child & Adolescent Learners & Learning PrinciplesDocument19 pagesUNIT 1 .ProfEd 601 Child & Adolescent Learners & Learning PrinciplesHANEYZIL LARANGJONo ratings yet
- Fulltext 2Document10 pagesFulltext 2Ariana ChimiNo ratings yet
- THE ANGIOAPERMS (Part 1)Document5 pagesTHE ANGIOAPERMS (Part 1)PerrieNo ratings yet