Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review Notes
Uploaded by
Ashley0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesThe document provides review notes on various topics related to geology and astronomy. It defines key terms like continental and oceanic crust, the Moho, foliated rock, rotation and revolution. It also summarizes concepts such as how sedimentary, metamorphic and volcanic rocks form. Additionally, it lists the regions of the solar system from the sun and provides information on properties of minerals like hardness, luster and streak.
Original Description:
Original Title
REVIEW-NOTES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides review notes on various topics related to geology and astronomy. It defines key terms like continental and oceanic crust, the Moho, foliated rock, rotation and revolution. It also summarizes concepts such as how sedimentary, metamorphic and volcanic rocks form. Additionally, it lists the regions of the solar system from the sun and provides information on properties of minerals like hardness, luster and streak.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesReview Notes
Uploaded by
AshleyThe document provides review notes on various topics related to geology and astronomy. It defines key terms like continental and oceanic crust, the Moho, foliated rock, rotation and revolution. It also summarizes concepts such as how sedimentary, metamorphic and volcanic rocks form. Additionally, it lists the regions of the solar system from the sun and provides information on properties of minerals like hardness, luster and streak.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
REVIEW NOTES
CONTINENTAL & OCEANIC CRUST are the two types of crust
Moho is the upper boundary that separates the crust and the mantle
Why does the atmosphere float above the crust?
- Air is denser than the crust
Foliated rock is a type of metamorphic rock having identifiable layers,
textures, and patterns.
What is the difference between rotation and revolution?
- Rotation moves on its own axis while revolution moves around the sun
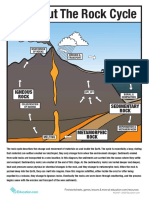
How does the sedimentary rock form?
- The rock forms through the accumulation, compaction and cementation
What happens when the pre-existing rocks get in contact with the heat source
(magma)
- It will transform into a Metamorphic rock
What occurs when rocks tend to break into pieces?
- Weathering
Which of the following minerals can scratch by a fingernail?
- Gypsum
Basalt is an example of what types of rocks?
- Volcanic or Extrusive Rocks
The word “metamorphic” means?
- Made of living matter
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS created when pieces of other rocks, plant and
animal matter, or dissolved minerals collect to form layers.
Meteoroids are thought of as remnants of a “failed planet”. What does “failed
planet” mean in astronomy from Asteroid Belts?
- A planet that is smaller than Pluto.
Sediment is solid material that is moved and deposited in a new location.
Which of the following lies beyond Neptune and comprises numerous rocky or
icy bodies a few meters to hundreds of kilometers in size?
- Kuiper belt
Which of the following has lower density because it is mostly composed of
granitic rock?
- Continental Crust
A collection of rocks is used to model the kinds of materials found in Earth.
Which rock should be labeled “core” rocks?
- Iron and Nickel
Which of the following correctly lists the various regions of our solar system in
increasing distance from the sun?
- Inner planets, asteroid belt, Outer planet, Kuiper belt, Oort cloud
In order to predict whether a star will eventually fuse oxygen into a heavier
element, what do you need to know about the star?
- Its mass
Doppler Effect refers to the change in wave frequency during the relative
motion between a wave source and its observer.
Streak, the color of a mineral in its powdered form.
Luster is the quality and intensity of reflected light exhibited by the mineral.
Hardness is a measure of the resistance of a mineral (not specifically surface)
to abrasion
Specific gravity is the ratio of the density of the mineral and the density of
water.
Cleavage is the property of some minerals to break along specific planes of
weakness to form smooth, flat surfaces.
These native elements are commonly divided into three groups—
namely, metals (platinum, iridium, osmium, iron, zinc, tin, gold, silver, copp
er, mercury, lead,
chromium); semimetals (bismuth, antimony, arsenic, tellurium, selenium);
and nonmetas (sulfur, carbon).
STUDY THE MOHS HARDNESS SCALE
The steady-state theory is a view that the universe is always expanding but
maintaining a constant average
GODBLESS ON YOUR EXAM! FIGHTINGGGGG
You might also like
- Oil and Gas AccountingDocument81 pagesOil and Gas Accountingmike8895100% (1)
- Basic Civil Engineering PDFDocument348 pagesBasic Civil Engineering PDFDeependra100% (1)
- Desert Magazine 1963 MayDocument40 pagesDesert Magazine 1963 Maydm1937No ratings yet
- Structure and Composition of The EarthDocument20 pagesStructure and Composition of The EarthgengkapakNo ratings yet
- GEOSPHEREDocument18 pagesGEOSPHEREPennie KoscaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Comets, Meteros and AsteroidsDocument88 pagesLesson 6 Comets, Meteros and AsteroidsApril Rose GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Geology by Carla Montgomery - 10e, TEST BANK 0073524115Document12 pagesEnvironmental Geology by Carla Montgomery - 10e, TEST BANK 0073524115jksnmmmNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Review KEYDocument2 pagesRock Cycle Review KEYShelamarey MallillinNo ratings yet
- Comets Meteors and AsteroidsDocument56 pagesComets Meteors and AsteroidsJeal Amyrrh Caratiquit100% (2)
- Ways To Elucidate A Concept PaperDocument20 pagesWays To Elucidate A Concept PaperAshleyNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 3Document40 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 3ARIANE I. LAGATIC100% (11)
- C1528 Guide For Selection of Dimension Stone For Exterior Use PDFDocument14 pagesC1528 Guide For Selection of Dimension Stone For Exterior Use PDFwerewaro100% (1)
- Eals ReviewerDocument13 pagesEals Reviewerbubwit2No ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study Guide GEOL 1014 24534Document6 pagesExam 1 Study Guide GEOL 1014 24534Jason WolfeNo ratings yet
- Soil Science MergeDocument135 pagesSoil Science MergeSajeebChandraNo ratings yet
- Types of Rock Lesson ObjectivesDocument2 pagesTypes of Rock Lesson ObjectivesKring-kring GumanaNo ratings yet
- Geography of East AfricaDocument84 pagesGeography of East AfricaMatabaro Benjamin50% (2)
- Minerals and Rocks Lecture NotesDocument22 pagesMinerals and Rocks Lecture NotesOyedotun Tunde67% (3)
- AAPG MEMOIR 28 SandstonesDocument202 pagesAAPG MEMOIR 28 SandstonesJhan Carlos C100% (1)
- Full Report Thin Section and Petrography ExperimentDocument17 pagesFull Report Thin Section and Petrography ExperimentNabil Imran50% (2)
- Geography CSS and PMS Chapter 1 and 2Document25 pagesGeography CSS and PMS Chapter 1 and 2Ismail BarakzaiNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Hand OutDocument3 pagesRock Cycle Hand Outrufino delacruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Universe and The Solar SystemDocument11 pagesLesson 1: The Universe and The Solar SystemKesia CruzNo ratings yet
- Group Three (Petrology)Document7 pagesGroup Three (Petrology)thea4bermejoNo ratings yet
- Summary Guide in Earth ScienceDocument7 pagesSummary Guide in Earth ScienceMeriam WebsterNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science 1ST Quarter NotesDocument5 pagesEarth and Life Science 1ST Quarter Notesanaira wahabNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Small Bodies - MineralsDocument4 pagesReviewer - Small Bodies - MineralsMARC CASSEY AYUDTUDNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience ReviewerRhylee Mae Vel DemegilloNo ratings yet
- Earth's Materials and ResourcesDocument51 pagesEarth's Materials and ResourcesChrist Joseph QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Earth'S Internal Structure and SubsystemsDocument37 pagesEarth'S Internal Structure and SubsystemsAj OrtileNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Reviewer (G-12)Document9 pagesEarth Science Reviewer (G-12)D-Jay LigotNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Lesson 2Document4 pagesEarth and Life Science Lesson 2Grace Alexandra AngaraNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument12 pagesEarth ScienceKelly Misha NoolNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Rock-Forming Minerals Ore-Forming MineralsDocument3 pagesMinerals: Rock-Forming Minerals Ore-Forming MineralsDarcy EvansNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument8 pagesGeologic Time ScaleLily DaniaNo ratings yet
- 5 Rock CycleDocument70 pages5 Rock Cycleapi-251060011No ratings yet
- Earthscience ReviewerDocument31 pagesEarthscience ReviewerAryan Daniel TayagNo ratings yet
- Environmental LithosphereDocument44 pagesEnvironmental LithosphereRichard II RemisNo ratings yet
- EARTH SCIENCE - Q1 Lesson 2Document6 pagesEARTH SCIENCE - Q1 Lesson 2hannah calamiganNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER-for-First-Quarter FilipinoDocument13 pagesREVIEWER-for-First-Quarter FilipinoHera RinNo ratings yet
- The Petrology Displays: Rocks in The MuseumDocument8 pagesThe Petrology Displays: Rocks in The MuseumtwmailinatorNo ratings yet
- Lithosphere and Soil PollutionDocument102 pagesLithosphere and Soil PollutionPranav MittalNo ratings yet
- UD2 - THE GEOSPHERE TierraDocument91 pagesUD2 - THE GEOSPHERE TierraJorge Ramiro PatiñoNo ratings yet
- SPLM #2 (Copy 2) Mineral & PetrologyDocument7 pagesSPLM #2 (Copy 2) Mineral & Petrologyadel antegraNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography 2ndDocument21 pagesPhysical Geography 2ndAwais BakshyNo ratings yet
- 23 Meteorites, Impacts, and Mass ExtinctionDocument13 pages23 Meteorites, Impacts, and Mass ExtinctionLuisa LouisaNo ratings yet
- Science 11 ReviewerDocument10 pagesScience 11 ReviewerArgie MabagNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 8 January 14Document6 pagesSCIENCE 8 January 14jameelacabordaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Earth Science and Earth and Life Science: Universe and Solar SystemDocument3 pagesReviewer in Earth Science and Earth and Life Science: Universe and Solar SystemJunica urbodaNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument10 pagesEarth ScienceJAS MAGHARINo ratings yet
- Synopsis On The Topics in Earth and Space Science: Submitted By: Enguito, Damsel F. MasterandDocument11 pagesSynopsis On The Topics in Earth and Space Science: Submitted By: Enguito, Damsel F. MasterandmjuhngtegNo ratings yet
- Rocks & Minerals ExploitationDocument15 pagesRocks & Minerals ExploitationuibikunNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Q1 Week 1 8Document54 pagesEarth and Life Science Q1 Week 1 8carldagayloan818No ratings yet
- 4 - Plate Tectonics Part 1 - Ch03 04Document43 pages4 - Plate Tectonics Part 1 - Ch03 04Jordan RixNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument4 pagesEarth and Life SciencehyunNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals - 063744Document34 pagesRocks and Minerals - 063744gomezrian20No ratings yet
- Different Types of Rocks Unit 3Document27 pagesDifferent Types of Rocks Unit 3Mahan JamalNo ratings yet
- The Solid RockDocument12 pagesThe Solid RockKimberly Rose MallariNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials and ProcessesDocument1 pageEarth Materials and ProcessesJemarjo SalandananNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Handouts 2Document3 pagesEarth Science Handouts 2Juvelyn Kyle GugmaNo ratings yet
- Easc Mta Sem 1 ReviewerDocument26 pagesEasc Mta Sem 1 ReviewerHeart DordasNo ratings yet
- Olps Earth Science Lesson 2 Minerals and RocksDocument8 pagesOlps Earth Science Lesson 2 Minerals and RocksJoseph MansionNo ratings yet
- Rocks Minerals Notes Kean UniversityDocument38 pagesRocks Minerals Notes Kean Universityapi-323312952No ratings yet
- Geology: What Is Petrology?Document8 pagesGeology: What Is Petrology?Anjanette ManubayNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Fortest2 Geology 101 Lab Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesStudy Guide Fortest2 Geology 101 Lab Midterm ExamTyler MroskoNo ratings yet
- Meteorite Characteristics Reporting Meteorite Finds: Meteorites@ess - Ucla.eduDocument2 pagesMeteorite Characteristics Reporting Meteorite Finds: Meteorites@ess - Ucla.eduAnonymous pgWs18GDG1No ratings yet
- Earth Rocks (All Notes)Document86 pagesEarth Rocks (All Notes)Rex TranquilliNo ratings yet
- Materia - para - Teste - 01 - CN - InglesDocument5 pagesMateria - para - Teste - 01 - CN - InglesMargarida OliveiraNo ratings yet
- 2Document32 pages2Jin ALfred Coliao IIINo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ELSDocument2 pagesReviewer in ELSMary Rhodelyn FerminNo ratings yet
- Contribution-Matrix-GROUP-3 CHAPTER 1Document8 pagesContribution-Matrix-GROUP-3 CHAPTER 1AshleyNo ratings yet
- As4 Q3 English10 Mejica FinalDocument8 pagesAs4 Q3 English10 Mejica FinalAshleyNo ratings yet
- Foreign StudiesDocument7 pagesForeign StudiesAshleyNo ratings yet
- Poetry Comprehension: "No Sick Note"Document9 pagesPoetry Comprehension: "No Sick Note"AshleyNo ratings yet
- Concept 5Document3 pagesConcept 5AshleyNo ratings yet
- Concept 4Document4 pagesConcept 4AshleyNo ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument10 pagesPhysical EducationAshleyNo ratings yet
- WRDTHDSHFJEJEVEJEIDocument21 pagesWRDTHDSHFJEJEVEJEIAshleyNo ratings yet
- DLP 2 (Ashley Abad)Document2 pagesDLP 2 (Ashley Abad)AshleyNo ratings yet
- Contribution-Matrix GROUP 3Document8 pagesContribution-Matrix GROUP 3AshleyNo ratings yet
- JJDocument14 pagesJJAshleyNo ratings yet
- Tle - Cookery: A Measuring Cup or Measuring Jug Is A Kitchen Utensil Used Primarily ToDocument2 pagesTle - Cookery: A Measuring Cup or Measuring Jug Is A Kitchen Utensil Used Primarily ToAshleyNo ratings yet
- Music 10: Quarter 4 - Week 1Document6 pagesMusic 10: Quarter 4 - Week 1AshleyNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Learning Plan: Arellano University SeniorDocument3 pagesDynamic Learning Plan: Arellano University SeniorAshleyNo ratings yet
- Non - Fiction WritingDocument9 pagesNon - Fiction WritingAshleyNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Pointers To ReviewDocument7 pagesPersonal Development Pointers To ReviewAshleyNo ratings yet
- Physical Education and Health 1 Points To Review: Against Resistance For A Prolonged Period of TimeDocument2 pagesPhysical Education and Health 1 Points To Review: Against Resistance For A Prolonged Period of TimeAshleyNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 2 (Senior High School)Document15 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 2 (Senior High School)JAY ELLNo ratings yet
- Types of MetamorphismDocument4 pagesTypes of MetamorphismMike Mor'zNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals of Pa Edr318Document13 pagesRocks and Minerals of Pa Edr318api-455032847No ratings yet
- Pyroxene GrupDocument24 pagesPyroxene GrupSamuel TangkaNo ratings yet
- CE6301 Engineering Geology Part A CombDocument20 pagesCE6301 Engineering Geology Part A CombElakiya RajanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Rock Mechanics: Introduction and Course OutlineDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Rock Mechanics: Introduction and Course OutlineAlina RafeeqNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics-Lecture Notes With CoverDocument237 pagesSoil Mechanics-Lecture Notes With CoverShashank TiwariNo ratings yet
- Petrography and Rock FormationDocument48 pagesPetrography and Rock FormationApril EspiñaNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle QuizDocument2 pagesRock Cycle QuizKizzi Kye Edelweiss BalmoresNo ratings yet
- GDG 7 Batuan MatamorfDocument53 pagesGDG 7 Batuan MatamorfFandy MuhammadNo ratings yet
- 3 ANTIPAROS Kervekidis 2015 PDFDocument24 pages3 ANTIPAROS Kervekidis 2015 PDFDiego JerezNo ratings yet
- Week 2 AssessmentDocument3 pagesWeek 2 Assessmentjanice alquizarNo ratings yet
- Geology ReviewerDocument8 pagesGeology ReviewerAnthony LoñezNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 12 Lesson 3: The Three Main Categories of RocksDocument9 pagesEarth Science 12 Lesson 3: The Three Main Categories of Rocksana mae mancillaNo ratings yet
- Maryknoll School of Lupon Inc.: Kambing Baratua Street, Lupon, Davao OrientalDocument23 pagesMaryknoll School of Lupon Inc.: Kambing Baratua Street, Lupon, Davao OrientalJoshua James Sanguenza RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Q2.1Document6 pagesEarth Science Q2.1Eian InganNo ratings yet
- Learning Target: Earth Is One Special PlanetDocument20 pagesLearning Target: Earth Is One Special Planetpetraz cabahugNo ratings yet
- Apinke Field ReportDocument20 pagesApinke Field ReportDaniel timileyinNo ratings yet
- Geo101 FINALSDocument8 pagesGeo101 FINALSCn cnNo ratings yet