Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Cell Cycle and Describe Its Stages
Uploaded by
Jhon Marvin ArienzaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Cell Cycle and Describe Its Stages
Uploaded by
Jhon Marvin ArienzaCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
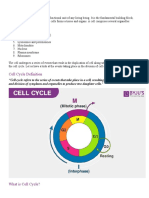
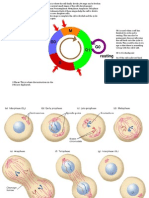
What is a Cell Cycle and describe its stages
A cell cycle is a sequence of events that occur in a cell as it develops and divides. A cell spends the
majority of its time in what is known as interphase, which is when it grows, duplicates its chromosomes,
and prepares for cell division. The cell then exits interphase, goes through mitosis, and divides
completely. The resultant daughter cells enter their own interphase and begin a new round of the cell
cycle.
Interphase
A cell doubles its cytoplasm and synthesizes DNA at this stage of the cell cycle. A dividing cell is thought
to spend 90-95 percent of its time in this phase.
G1 phase: The time interval preceding DNA synthesis. In this phase, the cell's bulk and organelle
number rise in preparation for cell division. This phase of animal cells is diploid, which means
they have two sets of chromosomes.
S phase: The time frame in which DNA is produced. In most cells, DNA replication happens only
within a certain time period. In this phase, the chromosomal content is doubled.
G2 phase: The time between the completion of DNA synthesis and the onset of mitosis. The cell
continues to grow in size as it synthesizes more proteins.
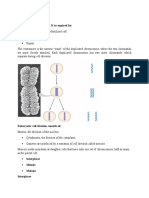
Stages of Mitosis
The contents of the dividing cell are divided evenly across two daughter cells during mitosis and
cytokinesis. Mitosis is divided into four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Prophase: Changes occur in both the cytoplasm and nucleus of the dividing cell at this stage.
Chromosomes are formed when chromatin condenses. The chromosomes start to move toward
the cell center. The nuclear membrane degrades, and spindle fibers develop at the cell's
opposing poles.
Metaphase: At this point, the nuclear membrane has entirely vanished. At the metaphase plate,
the spindle completely develops and the chromosomes align.
Anaphase: Pairs of chromosomes split and begin migrating to opposing ends of the cell at this
stage. The cell is lengthened and elongated by spindle fibers that are not linked to chromatids.
Telophase: The chromosomes are partitioned off into independent new nuclei at this point, and
the cell's genetic material is split evenly into two halves. Cytokinesis begins before mitosis ends
and ends shortly after telophase.
You might also like
- Cell Cycle: Prepared By: Ms. Charis D. Juanico, General Biology 1 TeacherDocument59 pagesCell Cycle: Prepared By: Ms. Charis D. Juanico, General Biology 1 TeacherTrisha Loise VillacampaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle NotesDocument12 pagesCell Cycle NotesMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- Cellular-Reproduction ScienceDocument43 pagesCellular-Reproduction ScienceMiel GaboniNo ratings yet
- Bio 1Document13 pagesBio 1Mary Ann FriasNo ratings yet
- Tle 7 Budget of WorkDocument7 pagesTle 7 Budget of WorkJhon Marvin Arienza100% (4)
- Cell Growth and DivisionDocument15 pagesCell Growth and DivisionJohn Lester BerdinNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionParth GoyalNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Assessment Tle 9Document3 pagesDiagnostic Assessment Tle 9Jhon Marvin Arienza100% (3)
- Arts Appreciation Reflection L 1-3Document4 pagesArts Appreciation Reflection L 1-3Jhon Marvin ArienzaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Cell Cycle by Javali.GDocument15 pagesOverview of Cell Cycle by Javali.GJavali.GNo ratings yet
- Tle 9&10 Second Quarter Summative TestDocument4 pagesTle 9&10 Second Quarter Summative TestJhon Marvin Arienza100% (4)
- DIAGNOSTIC ASSESSMENT IN TLE 7 Agricultural Crop Production SenenDocument2 pagesDIAGNOSTIC ASSESSMENT IN TLE 7 Agricultural Crop Production SenenJhon Marvin Arienza100% (10)
- Diagnostic Test Tle 9 Dressmaking-SenenDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Test Tle 9 Dressmaking-SenenJhon Marvin Arienza100% (9)
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 3Document7 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 3karyo eseymNo ratings yet
- Cell Growth and DivisionDocument15 pagesCell Growth and DivisionJohn Lester BerdinNo ratings yet
- DR - Anangwe-Cell DivisionDocument21 pagesDR - Anangwe-Cell DivisionStanley OdiraNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument10 pagesCell CycleFatima Tul zahraNo ratings yet
- m2 - Cell DivisionDocument40 pagesm2 - Cell DivisionDaisy RamaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument7 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionAicel AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument4 pagesCell CycleRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle in Multicellular Organism, It Is Required ForDocument9 pagesCell Cycle in Multicellular Organism, It Is Required Forwajiha raufNo ratings yet
- Principle of Genetics and Animal BreedingDocument49 pagesPrinciple of Genetics and Animal BreedingSuresh NepaliNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesDocument56 pagesMitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: Objectiveskaran79No ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument12 pagesCell CycleVega, Charles Gabriel G.No ratings yet
- CSEC Biology and HSB Cell Divsion NotesDocument10 pagesCSEC Biology and HSB Cell Divsion NotesAnasha Éttienne-Taylor100% (2)
- Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell DivisionMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- MITOSISMEIOSISDocument34 pagesMITOSISMEIOSISDiosa BakingNo ratings yet
- GENBIO1MOD3Document11 pagesGENBIO1MOD3Renzsoc JalmascoNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionEloisa MadrilenoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Worksheet AnswersDocument3 pagesCell Division Worksheet AnswersDanaNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument19 pagesCell CycleAnahita SuriNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer 2Document9 pagesBiology Reviewer 2John Arnel BunquinNo ratings yet
- 5 - Histology Lecture, Cell DivisionDocument50 pages5 - Histology Lecture, Cell DivisionAMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionVardan ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document48 pagesModule 1Saalif RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document4 pagesLesson 1catalancsj10No ratings yet
- Mystical Rose College of Science and Technology: Stage 1: InterphaseDocument4 pagesMystical Rose College of Science and Technology: Stage 1: InterphaseLaarni ToleteNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesDocument56 pagesMitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesANnur RAshidNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionDocument120 pagesCell Cycle & Cell DivisionGanesh Patil100% (1)
- Genbio1 LessonsDocument30 pagesGenbio1 Lessonsian rabagoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionDocument45 pagesCell Cycle & Cell DivisionAdyasha mishraNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Q4 L2Document5 pagesScience 8 Q4 L2Sheila mae CadiaoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - BST Notes FinalDocument6 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division - BST Notes FinalSanjeevi RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Cellular ReproductionDocument44 pagesCellular Reproductionellaine.garciaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division DNA Replication Bacteria Cell NucleusDocument2 pagesCell Division DNA Replication Bacteria Cell NucleusJhon Navarro SabordoNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument19 pagesCell Divisionapi-233187566No ratings yet
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationDocument22 pagesNew Microsoft PowerPoint Presentationsaramaktoof2No ratings yet
- Bio Cell Division 100106220037 Phpapp01Document35 pagesBio Cell Division 100106220037 Phpapp01PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Cell Reproduction HandoutDocument4 pagesCell Reproduction HandoutLenor TunacNo ratings yet
- Cell CicleDocument1 pageCell CiclediogoNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument39 pagesCell CycleBuyco, Nicole Kimberly M.No ratings yet
- Section 3 - The Mitotic Cycle 1Document36 pagesSection 3 - The Mitotic Cycle 1abielgtgNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document8 pagesWeek 2lilyrosemary.masilangNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle To MeiosisDocument13 pagesCell Cycle To MeiosisSOPHIA ALESNANo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument44 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionKILLER FFNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: MitosisDocument36 pagesThe Cell Cycle: MitosisEllen Jane RamosNo ratings yet
- Class - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionDocument13 pagesClass - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionANIRBAN PALNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument32 pagesCell Cycleproxima midnightxNo ratings yet
- CycleDocument7 pagesCycleAbbas TalibNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle.Document5 pagesCell Cycle.msmall123No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument19 pagesCell DivisionAl FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Class Notes: Cell CycleDocument9 pagesClass Notes: Cell CycleWhyNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument19 pagesThe Cell CycleShiba ShirzadNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument27 pagesCell CycleDNYANESHWAR BIRADARNo ratings yet
- Contemp Final NaDocument7 pagesContemp Final NaJhon Marvin ArienzaNo ratings yet
- Name: Arienza, Jhon Marvin A. Section: BSED 1D (SCIENCE) Schedule: 9:00-10:00 Am TTH UNIT TestDocument3 pagesName: Arienza, Jhon Marvin A. Section: BSED 1D (SCIENCE) Schedule: 9:00-10:00 Am TTH UNIT TestJhon Marvin ArienzaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document3 pagesAssignment 5Jhon Marvin ArienzaNo ratings yet
- Contemp PrefinalDocument10 pagesContemp PrefinalJhon Marvin ArienzaNo ratings yet
- Material SelfDocument3 pagesMaterial SelfJhon Marvin Arienza100% (2)
- Adv Tech.Document17 pagesAdv Tech.Jhon Marvin ArienzaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document3 pagesAssignment 5Jhon Marvin ArienzaNo ratings yet
- Arts Appreciation Reflection L 4-6Document4 pagesArts Appreciation Reflection L 4-6Jhon Marvin ArienzaNo ratings yet
- Physical SelfDocument2 pagesPhysical SelfJhon Marvin Arienza100% (1)
- Sexual SelfDocument1 pageSexual SelfJhon Marvin ArienzaNo ratings yet
- Name: Arienza, Jhon Marvin A. Section: BSED 1D (SCIENCE) Schedule: 9:00-10:00 Am TTH UNIT TestDocument3 pagesName: Arienza, Jhon Marvin A. Section: BSED 1D (SCIENCE) Schedule: 9:00-10:00 Am TTH UNIT TestJhon Marvin ArienzaNo ratings yet
- PEE M1 and M2Document13 pagesPEE M1 and M2Jhon Marvin Arienza100% (2)
- Contemporary MidtermDocument6 pagesContemporary MidtermJhon Marvin ArienzaNo ratings yet
- Tle 9 Las Q3 M1Document21 pagesTle 9 Las Q3 M1Jhon Marvin Arienza100% (1)
- Reflection Rubric Above Expectations Meet Expectations Approaching Expectations Below Expectations 4 3 2 1 Reflective ThinkingDocument1 pageReflection Rubric Above Expectations Meet Expectations Approaching Expectations Below Expectations 4 3 2 1 Reflective ThinkingJhon Marvin ArienzaNo ratings yet
- Q1 Summative Test Tle 9 2020Document8 pagesQ1 Summative Test Tle 9 2020Jhon Marvin Arienza100% (3)