Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ESAS-SAMPLE PROBLEM AND SOLUTIONS-Final
Uploaded by
Arnel AguasCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ESAS-SAMPLE PROBLEM AND SOLUTIONS-Final
Uploaded by
Arnel AguasCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS)
PROBLEM SOLVING AND SOLUTIONS
1. A 10 grams block slides with a velocity of 20 cm/s on a smooth level surface and
makes a collision with a 30 grams block moving in the opposite direction with a
velocity of 10 cm/s. If the collision is perfectly elastic, what is the velocity of the
30 gram block after the collision?.
A. 5 cm/s
B. 10 cm/s
C. 15 cm/s
D. 25 cm/s
SOLUTION:
Formula is: Initial momentum = Final Momentum
Therefore: m1V1 + m2+V2 = m1V1' + m2V2'
Given:
m1 = 10 grams
V1 = 20 cm/s
m2 = 30 grams
V2 = 10 cm/s
m1V1 + m2+V2 = m1V1' + m2V2'
10(20) + 30(-10) = 10(-V1') + 30V2'
- 100 = -10V1' + 30V2' Equation 1
Note: For a perfectly elastic collision, coefficient of restitution (e) is equal to 1.
V2' + V1'
e = = 1
V1 - V2
V1 - V2 = V2' - V1'
20 - (-10) = V2' - (-V1')
V1' = 30 - V2' Equation 2
Substitute (Equation 2) in (Equation 1):
- 100 = -10 (30 -V2') + 30V2'
- 100 = 300 + 10V2' + 30V2'
V2' = 5 cm/s
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS) Page 1
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS)
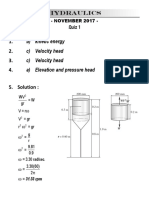
2. A block of wood floats in water with 5 cm projecting above the water surface.
When placed in glycerine of specific gravity of 1.35, the block projects 7.5 cm
above the liquid. Determine its specific gravity.
A. 0.514
B. 0.704
C. 0.836
D. 0.658
SOLUTION:
Let: A = base area
h = height of the wood
W = BF1
(sp. gr.w) (ωwater) (Vt) = (ωwater) (VD)
sp. gr.w (Ah) = A (h-5)
h-5
sp. gr.w = Equation 1
h
W = BF2
(sp. gr.w) (ωwater) (Vt) = (sp. gr.g) (ωwater) (VD)
sp. gr.w (Ah) = (1.35) (A) (h - 7)
1.35 (h - 7.5)
sp. gr.w = Equation 2
h
Equate (Equation 1) to (Equation 2)
h-5 1.35 (h - 7.5)
=
h h
h-5 = 1.35h - 10.125
h = 14.64 cm
Substitute in (Equation 1)
14.64 - 5
sp. gr.w =
14.64
sp. gr.w = 0.658
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS) Page 2
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS)
3. A 600 N block rests in a surface inclined at 30⁰. Determine the horizontal force P
required to prevent the block from sliding down. Angle of friction between the
block and the inclined plane is 15⁰.
A. 160.75 N
B. 164.60 N
C. 190.45 N
D. 198.55 N
SOLUTION:
ƩFx 0=
P cos θ + F =
W sin θ
P cos θ + μ N =
W sin θ
P cos 30° + tan 15⁰ N 600 sin 30⁰
=
300 – 0.866 P
P = Equation 1
0.268
ƩFx = 0
N = W cos θ + P sin θ
N = 600 cos 30⁰ + P sin 30⁰
N = 519.6 + 0.5 P Equation 2
Equate (Equation 1) to (Equation 2)
300 – 0.866 P
= 519.6 + 0.5 P
0.268
P = 160.75 Newtons
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS) Page 3
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS)
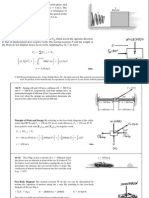
4. Determine the sag of a flexible wire cable weighing 60 N/m over two frictionless
pulleys 100 m apart and carrying one 10 kN weight at each end. Assume the
weight of the cable to be uniformly distributed horizontally. The cable extends
5 m beyond each pulley to the point they are attached to the weights.
A. 7.2 m
B. 7.4 m
C. 7.6 m
D. 7.8 m
SOLUTION:
60N
T = 10,000 + (5m) = 10,300 N
m
ωL 2
T2 = + H2
2
60 (100)
(10,300) 2 = + H2
2
H = 9853.42 N
ωL2
H =
8d
60 (100) 2
9853.42 =
8d
d = 7.6 m
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS) Page 4
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS)
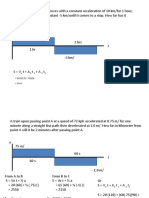
5. A train passing point A at a speed of 72 kph accelerates at 0.75 m/s2 for one
minute along a straight path then decelerates at 1.0 m/s2. How far in km from
point A will it be 2 minutes after passing point A?
A. 3.60 km
B. 4.65 km
C. 6.49 km
D. 7.30 km
SOLUTION:
72 km 1hr 1000 m
Vo = x x
hr 60 min sec
Vo = 20 m/s
1
S1 = Vo t1 + a t 12
2
1
S1 = 20 (60) + (0.75) (60) 2
2
2550
S1 = 2550 m = = 2.55 km
1000
V1 = Vo + a t1
V1 = 20 + 0.75 (60) = 65 m/sec
1
S2 = V1 t2 - a t 22
2
1 2100
S2 = 65 (60) - (1) (60) 2 = 2100 m = = 2.10 km
2 1000
Solving for total distance
S = S1 + S2 = 2.55 + 2.10
S = 4.65 km
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS) Page 5
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS)
6. An automobile moving at a constant velocity of a 15 m/sec passes a gasoline
station. Two seconds later, another automobile leaves the gasoline station and
accelerates at a constant rate of 2 m/sec2. How soon will the second automobile
overtake the first?
A. 13.5 sec
B. 15.3 sec
C. 16.8 sec
D. 18.6 sec
SOLUTION:
S1 = V1 t1
S1 = 15 ( t2 + 2 )
S1 = 15 t2 + 30 Equation 1
1
S2 = V2 t2 + a t 22
2
1
S2 = 0 (t2) + (2) t22
2
S2 = t22 Equation 2
Equate (Equation 1) to (Equation 2):
S1 = S2
15 t2 + 30 = t 22
t 22 - 15t2 – 30 = 0
By quadratic formula:
15 ± √ (15)2 – 4 (1) (-30) 15 ± 18.574
t2 = =
2 (1) 2
Take + sign, t2 = 16.8 seconds
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS) Page 6
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS)
7. Using a powerful air gun, a steel ball is shot vertically upward with a velocity of
80 meters per second, followed by another shot after 5 seconds. Find the initial
velocity of the second ball in order to meet the first ball 150 meters from the
ground.
A. 45.1 m/sec
B. 56.2 m/sec
C. 61.3 m/sec
D. 65.3 m/sec
SOLUTION:
V12 = Vo2 - 2gh1
0 = (80) 2 - 2 ( 9.81 ) h1
h1 = 326.2 m
V1 = Vo - gt1
0 = 80 - ( 9.81 ) t1
t1 = 8.155 sec
1
h2 = V1 t2 + gt22
2
h2 = h1 - h3 = 326.2 - 150
1
176.2 = 0 (t2) + (9.81) t22
2
t2 = 6 sec
t 3 = t 1 + t2 - 5
t3 = 8.155 + 6 - 5
t3 = 9.155 sec
1
h3 = V3 t3 - gt32
2
1
150 = V3 (9.155) - (9.81) (9.155)2
2
V3 = 61.3 m/s
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS) Page 7
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS)
8. A 100 gram of water is mixed to 150 gram of alcohol (ρ = 790 kg/m3). Calculate
the specific volume of the solution, assuming that it is mixed completely.
A. 0.63 cm3/g
B. 0.82 cm3/g
C. 0.88 cm3/g
D. 1.20 cm3/g
SOLUTION:
m t = m 1 + m2
mt = 100 + 150
mt = 250 g
m1 m2
Vt = V1 + V2 = +
ρ1 ρ2
Note: The density of water (ρ1) is 1000 kg/m3
Therefore:
3
0.100 0.150 -4 3
1000 cm
Vt = + = 2.8987 x 10 m x
1000 790 1m
Vt = 289.87 cm3
Vt 289.87
V = =
mt 250
V = 1.20 cm3/g
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS) Page 8
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS)
9. The pressure of the nitrogen gas thermometer is 76 cm at 0°C. What is the
temperature of a liquid in which the bulb of the thermometer is immersed when
the pressure is seen to be 87.7 cm.
A. 34°C
B. 45°C
C. 60°C
D. 90°C
SOLUTION:
Formula:
P1 V1 P2 V2
= , Note: V1 = V2
T1 T2
Therefore:
78 87.7
=
0 + 273 T2
T2 = 306.95 °K
T2 = 306.95 - 273
T2 = 34 °C
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS) Page 9
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS)
10. An iron column of annular cross-section has an outer diameter of 200 mm and is
subjected to a force of 74 kN. Find the thickness of the wall if the allowable
compressive stress is 10 MPa.
A. 12.57 mm
B. 12.75 mm
C. 15.75 mm
D. 17.75 mm
SOLUTION:
Formula:
P P
σ = ; A =
A σ
Therefore:
75,000
A = = 0.0075 m2
10 x 106
π π
A = D2 - d2
4 4
π π
0.0075 = (0.20)2 - d2
4 4
d = 0.1745 m
Solving for t:
D = d + 2t
0.2 = 0.1745 + 2t
t = 0.01275 m x 1000
t = 12.75 mm
ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND ALLIED SUBJECTS (ESAS) Page 10
You might also like
- Electrical Circuits Ii: DIRECTIONS: Solve For The Unknown Values For Each Problem, With Complete SolutionsDocument8 pagesElectrical Circuits Ii: DIRECTIONS: Solve For The Unknown Values For Each Problem, With Complete SolutionsJean Kimberly AgnoNo ratings yet
- Problemario 2° DepDocument8 pagesProblemario 2° DepDulce GoveaNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Engr. Besavilla - Lecture 02 - 08 Nov 2023Document14 pagesEngr. Besavilla - Lecture 02 - 08 Nov 2023Rhowelle TibayNo ratings yet
- Ion Beams for Materials AnalysisFrom EverandIon Beams for Materials AnalysisR. Curtis BirdNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document123 pagesCH 02kgallolvieerNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Problem Set 2Document7 pagesChapter 6 Problem Set 2Vyomika TewaryNo ratings yet
- 5 - Flow With Pumps and TurbinesDocument7 pages5 - Flow With Pumps and TurbinesMarshall james G. RamirezNo ratings yet
- Particle motion analysis and jet plane braking distanceDocument11 pagesParticle motion analysis and jet plane braking distanceSaad AhmadNo ratings yet
- PhysDocument7 pagesPhysCristine Gen HernandezNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 1 18 SolDocument125 pagesHydraulics 1 18 SolPrances Pabillore CloribelNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2Document8 pagesAssignment-2RICHELLE NESTORNo ratings yet
- 086 - 2004 Nov O Level Physics (5052) P1 P2 - Suggested Answers (PDF Library)Document4 pages086 - 2004 Nov O Level Physics (5052) P1 P2 - Suggested Answers (PDF Library)McDonald Whites JonesNo ratings yet
- As Answers Camb 2003 June A Level Paper 1 2 9702-1-2Document3 pagesAs Answers Camb 2003 June A Level Paper 1 2 9702-1-2jmok92100% (1)
- Curve Banking AngleDocument11 pagesCurve Banking AngleRiver RunNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument136 pagesExamMichael Vincent MirafuentesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Examples 2Document12 pagesChapter 14 Examples 2Wednesday SharonNo ratings yet
- EE 521 Assignment 1Document10 pagesEE 521 Assignment 1Suwilanji MoombaNo ratings yet
- =F sinθ : R= F F R= F F R= FDocument46 pages=F sinθ : R= F F R= F F R= FYhelly27No ratings yet
- EE420 Problem Set 1: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering SolutionsDocument11 pagesEE420 Problem Set 1: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering SolutionsWingel LullabyNo ratings yet
- EEE3405Tut1 5QSDocument10 pagesEEE3405Tut1 5QSArjunneNo ratings yet
- DrillsDocument93 pagesDrillsjulioNo ratings yet
- S12 P2 BChap 28 SolutionsDocument10 pagesS12 P2 BChap 28 SolutionsAlbert TregalNo ratings yet
- SGCL 2020Document5 pagesSGCL 2020এম. ডি. মামুনNo ratings yet
- Ds VDT Ds DT S 27 T T S 27 (3) (3) S 54 M:: Rectilinear MotionDocument15 pagesDs VDT Ds DT S 27 T T S 27 (3) (3) S 54 M:: Rectilinear MotionAndrea MagtutoNo ratings yet
- Objective:: C E L Sig B C e Supply in LDocument14 pagesObjective:: C E L Sig B C e Supply in LMuhammad SameerNo ratings yet
- Homework Problems on Forces, Motion and EnergyDocument7 pagesHomework Problems on Forces, Motion and EnergyQuinnNgo100% (1)
- Current and Resistance: Answers To QuestionsDocument20 pagesCurrent and Resistance: Answers To QuestionsSamuel González MoralesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Exercise AnswersDocument14 pagesChapter 3 Exercise AnswersHenok DerejeNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Equation of Motion - Curvilinear Motion ProblemsDocument21 pagesDynamics Equation of Motion - Curvilinear Motion ProblemsDiana VegaNo ratings yet
- P=γh P=9.81 (1.849) P=18.139 kn /m F= Ph: Structural Analysis Of Bench FlumeDocument16 pagesP=γh P=9.81 (1.849) P=18.139 kn /m F= Ph: Structural Analysis Of Bench FlumeAllyssa OpantoNo ratings yet
- BREB Recruitment Question ME (8th June 2018) 'S Solution As On 26.06.2018Document6 pagesBREB Recruitment Question ME (8th June 2018) 'S Solution As On 26.06.2018Shahriar AlamNo ratings yet
- B Answers MomentumDocument33 pagesB Answers MomentumRyan TanNo ratings yet
- Phase 4 2024 Adv 2 SoluDocument19 pagesPhase 4 2024 Adv 2 Solutribewhitedevil123No ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 1: Ee 420: Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument16 pagesProblem Set No. 1: Ee 420: Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringWingel Lullaby100% (1)
- PHYSICS-25-2-11th (PQRS & J) Partial MarkingDocument9 pagesPHYSICS-25-2-11th (PQRS & J) Partial MarkingRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Answer Control SystemDocument8 pagesAnswer Control Systemjethro kimandeNo ratings yet
- MEG 207 Dynamics Solutions CompilationDocument253 pagesMEG 207 Dynamics Solutions CompilationRoberto MongeNo ratings yet
- Ce1 Diff - CalculusDocument8 pagesCe1 Diff - Calculuslakr lamaNo ratings yet
- Post Task - Cristian Leonardo PiragauraDocument11 pagesPost Task - Cristian Leonardo PiragauraGERMANEDU2000No ratings yet
- 05 WEP Tutorial SolutionsDocument6 pages05 WEP Tutorial SolutionsMe4d SHiV23No ratings yet
- Unit A - Activity 5 - Notes 2023Document3 pagesUnit A - Activity 5 - Notes 2023Sara AboueiNo ratings yet
- 2018 Board Part 1Document20 pages2018 Board Part 1Ira MejiaNo ratings yet
- URS Civil Engineering Project Math & Surveying ProblemsDocument16 pagesURS Civil Engineering Project Math & Surveying ProblemsRomelNo ratings yet
- Cive327 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Assignment No. 4Document9 pagesCive327 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Assignment No. 4Hajar BaarabeNo ratings yet
- Class22 Ex3Document2 pagesClass22 Ex3Nazakat HussainNo ratings yet
- SLOPE STABILITY AND PILE DESIGN FOR Ø=30Document10 pagesSLOPE STABILITY AND PILE DESIGN FOR Ø=30NoobNoobNo ratings yet
- Nov'23 Math 01 - 07 Nov 2023Document33 pagesNov'23 Math 01 - 07 Nov 2023Rhowelle TibayNo ratings yet
- NCESQ 2015 Answer KeyDocument10 pagesNCESQ 2015 Answer KeyKenneth Joy SorianoNo ratings yet
- Nov23 Hydraulics 01 06 Nov 2023Document16 pagesNov23 Hydraulics 01 06 Nov 2023Jayson Mari100% (1)
- Beam 3 Design and AnalysisDocument5 pagesBeam 3 Design and AnalysisCelsoRapiNo ratings yet
- Problem - 3A PDFDocument14 pagesProblem - 3A PDFMonicaNo ratings yet
- Physics Solutions 2016Document28 pagesPhysics Solutions 2016Xavian EdwardsNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument6 pagesMotionNikka FerrerNo ratings yet
- Let The Vector Be Written As - Given That: I J + R 1 1 2 2 + R 1 3 - 4 + ÞDocument45 pagesLet The Vector Be Written As - Given That: I J + R 1 1 2 2 + R 1 3 - 4 + ÞE84091079羅筠笙No ratings yet
- ELE 201 Assignment #1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesELE 201 Assignment #1 SolutionssedarNo ratings yet
- Plates # 3Document9 pagesPlates # 3Joshua Perez AlbayNo ratings yet
- Simbawa Oliver Task 2 Reading Report Calculus and Its Application To PhysicsDocument3 pagesSimbawa Oliver Task 2 Reading Report Calculus and Its Application To PhysicsOliver SimbawaNo ratings yet
- Use of The Ultrasonic Time of Flight Diffraction (TOFD) TechniqueDocument12 pagesUse of The Ultrasonic Time of Flight Diffraction (TOFD) TechniqueWilson Alexander SantoNo ratings yet
- Explosive SC Penetration Into Tuff RockDocument69 pagesExplosive SC Penetration Into Tuff RockBAYE JBPNo ratings yet
- Kennametal - Tungsten Carbide Composite Brazing Rods DatasheetDocument1 pageKennametal - Tungsten Carbide Composite Brazing Rods DatasheetsakthiNo ratings yet
- Conductor Ampacity Based On The 2017 National Electrical Code®Document1 pageConductor Ampacity Based On The 2017 National Electrical Code®Ira Jane LosañezNo ratings yet
- P and H Chapter 3Document42 pagesP and H Chapter 3Noor UL AaienNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics Mcqs and Fill in The Blanks 2023Document8 pagesModern Physics Mcqs and Fill in The Blanks 2023LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Construction and Working Principles of BLDC MotorDocument24 pagesConstruction and Working Principles of BLDC Motormahadeva prasad m sNo ratings yet
- MCQs Question of Surveying 1Document9 pagesMCQs Question of Surveying 1jamil ahmedNo ratings yet
- Product Line Up 2018: World Class ComfortDocument41 pagesProduct Line Up 2018: World Class ComfortHashirama tobiramaNo ratings yet
- Galileoscope Optics Guide 1.1Document46 pagesGalileoscope Optics Guide 1.1Fernando P Mancebo CampilloNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Study For In-Plane Cyclic Behavior of Low Aspect-Ratio Steel-Concrete Composite WallsDocument11 pagesAn Experimental Study For In-Plane Cyclic Behavior of Low Aspect-Ratio Steel-Concrete Composite Wallsci_balaNo ratings yet
- Laprak Fixed and Fluidized BedDocument12 pagesLaprak Fixed and Fluidized BedIchsan ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- FOR Approval Specification: 32.0" Wxga TFT LCD TitleDocument42 pagesFOR Approval Specification: 32.0" Wxga TFT LCD TitleJulio Alberto Cabrera RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Experimentno.4 Uniform Motion I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesExperimentno.4 Uniform Motion I. ObjectivesStephanie AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Research of The Inverse Time Characteristic Curve For The Electronic Thermal RelayDocument4 pagesResearch of The Inverse Time Characteristic Curve For The Electronic Thermal RelayGeorge MateiNo ratings yet
- PLU Civil Engineering Department Midterm Exam ReviewDocument7 pagesPLU Civil Engineering Department Midterm Exam ReviewhaniiramosNo ratings yet
- Mech Micromachining ReportDocument21 pagesMech Micromachining ReportSWAPNALI KHANDARENo ratings yet
- BEE Assignment Even 2020Document5 pagesBEE Assignment Even 2020Aditya PatelNo ratings yet
- 11 WLAN Antenna TechnologyDocument53 pages11 WLAN Antenna TechnologyPaidamoyo ChimukaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Composite Materials-4 ModuleDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Composite Materials-4 Modulegagan devarajNo ratings yet
- A World Without Cause and Effect: Logic-Defying Experiments Into Quantum Causality Scramble The Notion of Time ItselfDocument3 pagesA World Without Cause and Effect: Logic-Defying Experiments Into Quantum Causality Scramble The Notion of Time ItselfWalterHuNo ratings yet
- Adv Mat14, 1857 (Natural To Artifitial)Document4 pagesAdv Mat14, 1857 (Natural To Artifitial)chirag sabhayaNo ratings yet
- CE Module 21 - Fluid Flow in Pipes (Answer Key)Document7 pagesCE Module 21 - Fluid Flow in Pipes (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- DC Inverter VRF Systems C VRFDocument50 pagesDC Inverter VRF Systems C VRFMd Saddam HossainNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science 7Th Edition Bill W Tillery full chapterDocument51 pagesIntegrated Science 7Th Edition Bill W Tillery full chapterwilliam.berry830100% (4)
- Digital thermometer guide with LED and LCD displaysDocument6 pagesDigital thermometer guide with LED and LCD displaysmohamed lamine elbiskriNo ratings yet
- JKSSB Je Me 2015 103 A Series 470e8f91Document17 pagesJKSSB Je Me 2015 103 A Series 470e8f91ZAFFAR GANINo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Motion in A Straight LineDocument36 pagesLecture 3 - Motion in A Straight LineMaitha AlhosaniNo ratings yet
- Journal of Building Engineering: SciencedirectDocument11 pagesJournal of Building Engineering: Sciencedirectr3dh34rtNo ratings yet