Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.5 Classificatio Answer
Uploaded by
mohamedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.5 Classificatio Answer
Uploaded by
mohamedCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
3 Features of organisms
Common Cell Structures
The cells of all living organisms contain the following:
o Cytoplasm
o Cell membrane
o DNA as genetic material (either found in the nucleus or free in the
cytoplasm)
Cell Composition & Structure
When viewed under an electron microscope (at a much higher
magnification), all cells also contain the following:
o Ribosomes for protein synthesis
o Enzymes for respiration (in many, but not all types of cells, found in
mitochondria
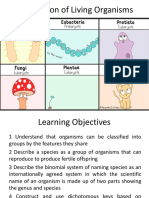
The Five Kingdoms
The first division of living things in the classification system is to put them
into one of five kingdoms. They are:
o Animals
o Plants
o Fungi
o Protoctists
o Prokaryotes (without nuclei)
Features of Viruses
Viruses are not part of any classification system as they are not considered
living things
They do not carry out the seven life processes for themselves, instead
they take over a host cell’s metabolic pathways in order to make multiple
copies of themselves
Virus structure is simply genetic material (RNA or DNA) inside a protein
coat
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 1 Tel. 00201023726242
Main features of all animals:
o they are multicellular
o their cells contain a nucleus but no cell walls or chloroplasts
o they feed on organic substances made by other living things
Main features of all plants:
o they are multicellular
o their cells contain a nucleus, chloroplasts and cellulose cell walls
o they all feed by photosynthesis
Fungi, Protoctists & Prokaryotes
Main features of all fungi (e.g. moulds, mushrooms, yeast)
o usually multicellular / yeast (single-celled)
o main fungus body is called mycelium, made up a branching network
of threads called hyphae.
o cells have nuclei and cell walls not made from cellulose made from
chitin
o no chlorophyll / do not photosynthesize but feed by
saprophytic (feed on dead or decaying material) or parasitic (on live
material) nutrition
Main features of all Protoctists (e.g. Amoeba, Paramecium,
Plasmodium that causes malaria / algea)
o most are unicellular (single celled) but some are multicellular
o all have a nucleus, some may have cell walls and chloroplasts
o meaning some protoctists photosynthesise and some feed on
organic substances made by other living things
Main features of all Prokaryotes (bacteria)
o often unicellular
o cells have cell walls (not made of cellulose) and cytoplasm but no
nucleus or mitochondria or chloroplast
o loops of DNA inside their cytoplasm (plasmid)
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 2 Tel. 00201023726242
1.4 Classifying Animals
Vertebrates
All vertebrates have a backbone. There are 5 classes of vertebrates:
Class Main features Examples
Mammals 1. Fur/hair on skin Horse
2. Have a placenta /dog
3. Young feed on milk from mammary glands /squirrel/
4. External ears (pinna) visible human/
5. Endothermic (warm blooded) cow
Birds 1. Skin covered in feathers Parrot/
2. Have 2 legs and 2 wings instead of forelimbs blue tit/
3. Lay eggs with hard shells on land eagle/
4. Have a beak swan
5. Endothermic (warm blooded)
Reptiles 1. Dry, fixed scales on skin Snake/
2. Lay eggs with rubbery shells on land turtle/
3. Cold blooded iguana/
crocodile
Amphibians 1. Smooth, moist slimy skin Frog/
2. Adults usually live on land (so have lungs), newt/
larvae live in water (so have gills) toad
3. Lay eggs without shells in water
4. Cold blooded
Fish 1. Loose, wet scales on skin Flounder/
2. Gills for breathing grouper/
3. Lay eggs without shells in water shark/
4. Cold blooded tuna
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 3 Tel. 00201023726242
Questions related to the topic of today from past papers/all variants
(2002 to 2021)
1-
2-
3-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 4 Tel. 00201023726242
4-
5-
6-
7-
8-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 5 Tel. 00201023726242
9-
10-
11-
12-
13-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 6 Tel. 00201023726242
14-
15-
16-
17-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 7 Tel. 00201023726242
18-
19-
20-
21
-
22-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 8 Tel. 00201023726242
23-
24-
25-
26-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 9 Tel. 00201023726242
27-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 11 Tel. 00201023726242
1.5 Classifying Animals
Invertebrates are animals that do not have a backbone or vertebral column.
Arthropods
1. From the largest of the groups in the animal kingdom.
(containing largest number of species)
2. Has segmented body.
3. External skeleton (exoskeleton)
4. Jointed legs.
Class Main features Examples
Crustaceans 1. Body is divided into 2 parts cephalothorax Crabs/
(head-thorax) and abdomen. woodlice/
2. Two pairs of antennae. / Compound eyes shrimps/
3. Between 5 and 20 pairs of legs. crayfish/
4. Breathe using gills. lobsters
Myriapods 1. Long body/many segments centipedes/
2. Total number of legs depends upon how millipedes
many segments there are.
3. Centipedes have 1 pair of legs on each
segment / fast-moving carnivores.
4. Millipedes have 2 pairs of legs on each
segment / slow-moving herbivores.
5. One pair of antennae
Insects 1. Body is divided into 3 parts: head, thorax beetles/
and abdomen. flies/
2. Three pairs of jointed legs on the thorax. locusts/
3. (some) Two pairs of wings. / Compound cockroaches
eyes. /dragonflies
4. One pair of antennae on the head. /butterflies/
5. Breathe through holes in the sides of the moths/bees/
thorax and abdomen called spiracles. wasps/
6. Covered by a waterproof cuticle that stops ladybird
them losing too much water / can fly
Arachnids 1. Body is divided into 2 parts cephalothorax scorpions/
(head-thorax) and abdomen. ticks/
2. Four pairs of jointed legs. mites/
3. No wings spiders
4. No antennae.
5. Have several pairs of simple eyes.
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 11 Tel. 00201023726242
Questions related to the topic of today from past papers/all variants
(2002 to 2021)
1-
2-
5-20 8 6
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 12 Tel. 00201023726242
3-
4-
6 legs 8 legs
5-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 13 Tel. 00201023726242
6-
arachnid crustacean
7-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 14 Tel. 00201023726242
8-
6 8
9-
10-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 15 Tel. 00201023726242
11-
12-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 16 Tel. 00201023726242
13-
14-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 17 Tel. 00201023726242
15-
16-
17-
18-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 18 Tel. 00201023726242
19-
20-
1.6 Classifying Plants
Ferns & Flowering Plants
Are multicellular.
Green in colour – chloroplasts contain green pigment (chlorophyll) –
absorbs light for photosynthesis.
Cell wall made of cellulose.
Have transport systems = xylem vessels (carry water and mineral ions)
= phloem tubes (transport dissolved substances
such as sugars)
Ferns:
Have strong stems, roots and leaves.
Leaves have a waxy layer (cuticle) helps to reduce water loss.
Have leaves called fronds.
Do not produce flowers but instead reproduce by spores on the underside
of fronds
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 19 Tel. 00201023726242
Flowering plants:
Reproduce by means of flowers which make seeds
Seeds are produced inside the ovary found at the base of the flower.
Stem = transport water from the soil up to the leaves and food from the
leaves to other parts of the plant.
Roots = absorb water and mineral ions from the soil and fix the plant in the
soil.
Can be divided into two groups – monocotyledons and dicotyledons
(one) Monocotyledons (two) Dicotyledons
Leaves Narrow leaves/Parallel Broad with a network of
veins branching veins.
Flowers Multiplies of 3 Multiplies of 4 or 5
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 21 Tel. 00201023726242
Questions related to the topic of today from past papers/all variants
(2002 to 2021)
1-
2-
3-
4-
5-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 21 Tel. 00201023726242
6-
7-
8-
9-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 22 Tel. 00201023726242
1.7 Dichotomous key
are used to identify organisms based on a series of questions about their
features.
Dichotomous means ‘branching into two’ and it leads the user through to
the name of the organism by giving two descriptions at a time and asking
them to choose.
Each choice leads the user onto another two descriptions.
Questions related to the topic of today from past papers/all variants
(2002 to 2021)
1-
2-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 23 Tel. 00201023726242
3-
4-
5-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 24 Tel. 00201023726242
6-
7-
more than 4 stamens
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 25 Tel. 00201023726242
5 petals
8-
jagged = toothed
9-
stamen
sepals
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 26 Tel. 00201023726242
10-
wings
scales
scales
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 27 Tel. 00201023726242
11-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 28 Tel. 00201023726242
12-
1 2 4
3
only 3
1/2/4
1/3
3/4
13-
14-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 29 Tel. 00201023726242
15-
4
16-
smooth
17-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 31 Tel. 00201023726242
18-
4 petals
6 stamens
19-
20-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 31 Tel. 00201023726242
21-
22-
23-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 32 Tel. 00201023726242
24-
25-
distinct = separate
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 33 Tel. 00201023726242
26-
27-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 34 Tel. 00201023726242
28-
29-
30-
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 35 Tel. 00201023726242
31-
32-
Next session on 18th of September, I will answer related questions paper 4 and 6
Mr. Ramy El-gebaly (IGCSE biology teacher) 36 Tel. 00201023726242
You might also like
- Al Rowad International School, Riyadh: Biology IGCSE CambridgeDocument154 pagesAl Rowad International School, Riyadh: Biology IGCSE CambridgeNicayne RamnarineNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology - Biology Notes - Al RowadDocument161 pagesIGCSE Biology - Biology Notes - Al RowadlawyuyuscribdNo ratings yet
- Workbook: Laboratory BIO32: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm) Branch Sabah Campus Kota KinabaluDocument6 pagesWorkbook: Laboratory BIO32: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm) Branch Sabah Campus Kota KinabaluMirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and Classification of OrganismsDocument7 pagesCharacteristics and Classification of Organismsmanarehab35No ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument58 pagesBiology NotesZeinab TalaatNo ratings yet
- Sicience CMDocument96 pagesSicience CMRana MurmuNo ratings yet
- Biology Topic: 1.1: Fill in The BlanksDocument4 pagesBiology Topic: 1.1: Fill in The Blanksazizul hasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2rida ikramNo ratings yet
- 2 ClassificationDocument6 pages2 ClassificationmeerzasarahNo ratings yet
- Classification CHP 2 BioDocument9 pagesClassification CHP 2 BioWAIT A MINNo ratings yet
- week 1 Learner'S Note Topic: Vertebrates - Characteristics and ExamplesDocument14 pagesweek 1 Learner'S Note Topic: Vertebrates - Characteristics and ExamplesTamuno MatthewNo ratings yet
- Must-Know Key Concepts in PSLE ScienceDocument30 pagesMust-Know Key Concepts in PSLE ScienceClarisa CynthiaNo ratings yet
- Organ System: Kingdom AnimaliaDocument18 pagesOrgan System: Kingdom AnimaliaTanishq AroraNo ratings yet
- Igcse BiologyDocument39 pagesIgcse BiologylordeNo ratings yet
- Ragab ClassificationDocument20 pagesRagab ClassificationlawyuyuscribdNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument27 pagesKingdom AnimaliaBlanche Mascarinas LaborteNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology Final Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesDevelopmental Biology Final Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsPearl PascuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Biodiversity: 3.1 Diversity of Living OrganismsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Biodiversity: 3.1 Diversity of Living OrganismsWJ LooNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument154 pagesBiology NotesMarwan YasserNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living Organisms FinalDocument13 pagesCharacteristics of Living Organisms FinalSunny x10No ratings yet
- Biology Igcse NOTESDocument46 pagesBiology Igcse NOTESJeremy Evans0% (1)
- Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsDocument8 pagesCharacteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsAmana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class Insecta and Compound EyeDocument13 pagesClass Insecta and Compound EyeHriNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument13 pagesBiology NotesHeinzNo ratings yet
- Living Things 22-23Document9 pagesLiving Things 22-23hiNo ratings yet
- Phylum Annelida PDFDocument9 pagesPhylum Annelida PDFIntolerable AlienNo ratings yet
- All ZnotesDocument158 pagesAll ZnotesaakashchandraniisNo ratings yet
- Classification PDFDocument34 pagesClassification PDFFaiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- What Is Morphology?Document26 pagesWhat Is Morphology?Michael Vincent P.No ratings yet
- Spark Science 5 KeybookDocument53 pagesSpark Science 5 Keybookmaryam arshad100% (1)
- Animal KingdomDocument22 pagesAnimal KingdomdellfrogNo ratings yet
- The Five-Kingdom System of ClassificationDocument9 pagesThe Five-Kingdom System of ClassificationliugirmayNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 7 Chapter 3 Classification of AnimalsDocument19 pagesSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 7 Chapter 3 Classification of AnimalsAKSHAJ AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- An Tech Insects ReviewDocument2 pagesAn Tech Insects ReviewLindsey KochanskiNo ratings yet
- g6 q2 Week 4-5 Vertebrates and Invertebrates 1Document18 pagesg6 q2 Week 4-5 Vertebrates and Invertebrates 1JAMES RUSSEL JAMANDRENo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse: BiologyDocument32 pagesCaie Igcse: BiologySamyuktha TIPSNo ratings yet
- Charactersitics of Living ThingsDocument69 pagesCharactersitics of Living Thingsrue pattinsonNo ratings yet
- Plus 2 PracticalDocument16 pagesPlus 2 Practicaljayantaroy783360No ratings yet
- Unit 7 (Invertebrates)Document7 pagesUnit 7 (Invertebrates)Simón Marín CrespoNo ratings yet
- 02 - Tree of Life and SystematicsDocument28 pages02 - Tree of Life and SystematicsJumiel VillamorNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument40 pagesKingdom AnimaliaraniNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument42 pagesKingdom AnimaliaGuffran septiahadiNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes: Cie IgcseDocument64 pagesBiology Notes: Cie Igcsehamza96No ratings yet
- ANIMALSDocument11 pagesANIMALSEman AbdellatifNo ratings yet
- Bio IGCSE (Chapter 1)Document3 pagesBio IGCSE (Chapter 1)SpablaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom of AnimaliaDocument6 pagesKingdom of AnimaliaBen ZerepNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 Tutorial Questions For 100lDocument2 pagesBio 101 Tutorial Questions For 100lAnthony DewayneNo ratings yet
- Bio System SummariesDocument52 pagesBio System Summariesxara zinkNo ratings yet
- 5 Kingdom ClasfificationDocument14 pages5 Kingdom ClasfificationDarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument61 pagesBiology NotesaliciasidikNo ratings yet
- Group Members (Surname, First Name, Middle Initial) : 1.ortigas, Ayessa Nicole M. 2. 3Document4 pagesGroup Members (Surname, First Name, Middle Initial) : 1.ortigas, Ayessa Nicole M. 2. 3Vladimyr EnriquezNo ratings yet
- 4.4.2017 The Five KingdomsDocument15 pages4.4.2017 The Five KingdomsZareiff ZareiffNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Test Paper Ch4 1Document4 pages11 Biology Test Paper Ch4 1Akhil AkhilNo ratings yet
- Aim of The ExperimentDocument10 pagesAim of The Experimentraktim BaruahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 BiodiversityDocument22 pagesCHAPTER 3 BiodiversityNur Hidayah AlawiNo ratings yet
- 5 KingdomDocument9 pages5 Kingdomdivine grace mesiasNo ratings yet
- IGCSE BIOLOGY REVIEW: Topics 1-8Document37 pagesIGCSE BIOLOGY REVIEW: Topics 1-8Jimena De Leon100% (1)
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- How Insects Work: An Illustrated Guide to the Wonders of Form and Function from Antennae to WingsFrom EverandHow Insects Work: An Illustrated Guide to the Wonders of Form and Function from Antennae to WingsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Weekly Plan For Social Studies Grade 5Document2 pagesWeekly Plan For Social Studies Grade 5mohamedNo ratings yet
- 2021 Online First Term Exam TimetableDocument3 pages2021 Online First Term Exam TimetablemohamedNo ratings yet
- Social Relationship Name: Subject: Islamic Culture Unit - 1Document6 pagesSocial Relationship Name: Subject: Islamic Culture Unit - 1mohamedNo ratings yet
- 2021 Online First Term Exam TimetableDocument3 pages2021 Online First Term Exam TimetablemohamedNo ratings yet
- Family Values Name: Subject: Islamic Culture Unit - 2Document7 pagesFamily Values Name: Subject: Islamic Culture Unit - 2mohamedNo ratings yet
- Social Studies - 5 Answer Sheet: Al-Reeyada International SchoolDocument3 pagesSocial Studies - 5 Answer Sheet: Al-Reeyada International SchoolmohamedNo ratings yet
- Social Relationship Name: Subject: Islamic Culture Unit - 1Document6 pagesSocial Relationship Name: Subject: Islamic Culture Unit - 1mohamedNo ratings yet
- Destination Holidays To Morocco: Exercise 1Document2 pagesDestination Holidays To Morocco: Exercise 1mohamedNo ratings yet
- Active N Passive Ws PDFDocument2 pagesActive N Passive Ws PDFmohamedNo ratings yet
- 2021 Online First Term Exam TimetableDocument3 pages2021 Online First Term Exam TimetablemohamedNo ratings yet
- Weekly Plan For Social Studies Grade 5Document1 pageWeekly Plan For Social Studies Grade 5mohamedNo ratings yet
- Printable Graph PaperDocument4 pagesPrintable Graph PapermohamedNo ratings yet
- 2021 Online First Term Exam TimetableDocument3 pages2021 Online First Term Exam TimetablemohamedNo ratings yet
- 111answer Key Worksheet Lesson 4 g5Document4 pages111answer Key Worksheet Lesson 4 g5mohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsmohamedNo ratings yet
- 04 Plant Nutrition Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFDocument24 pages04 Plant Nutrition Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFSiew Ming KongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsmohamedNo ratings yet
- Research & Resource Pack For Teachers (Key Stages 1 & 2) : Pack 1: The Mesozoic Era: A General History of DinosaursDocument42 pagesResearch & Resource Pack For Teachers (Key Stages 1 & 2) : Pack 1: The Mesozoic Era: A General History of DinosaursDMNo ratings yet
- The Platypus: Name - DateDocument2 pagesThe Platypus: Name - DateNadaFlorescuNo ratings yet
- Seen Only in JuvenilesDocument18 pagesSeen Only in JuvenilesshivrajsheoramNo ratings yet
- 7.) Khans of Tarkir - MultipleDocument203 pages7.) Khans of Tarkir - MultipleLilly Elise Garza VasquezNo ratings yet
- Victor Public School SESSION (2020 - 21) English Class - ViDocument1 pageVictor Public School SESSION (2020 - 21) English Class - ViNiyati RUSTAGINo ratings yet
- Sci CH - 7 Animal Kingdom (Final)Document10 pagesSci CH - 7 Animal Kingdom (Final)Vasoya ManojNo ratings yet
- Bridge To The Past - Animals and People of Madagascar (1961) by David AttenboroughDocument200 pagesBridge To The Past - Animals and People of Madagascar (1961) by David AttenboroughΦΩΤΗΣ ΛΑΜΠΡΙΑΝΟΣNo ratings yet
- Evolution of ManDocument2 pagesEvolution of ManHennessy Shania Gallera ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument5 pagesAnimal KingdomAngoruz Gohain BaruahNo ratings yet
- 6th English - Teachers ManualDocument32 pages6th English - Teachers ManualKINGNo ratings yet
- GiraffeDocument1 pageGiraffeaidon siskandarNo ratings yet
- Soal Report Text WritingDocument3 pagesSoal Report Text WritingAdeRNo ratings yet
- Little Giraffe With Big IdeaDocument1 pageLittle Giraffe With Big IdearaymondshirleyNo ratings yet
- Lion NicheDocument1 pageLion NicheJose Gregorio SuterNo ratings yet
- (Toxinology) P. Gopalakrishnakone, Anita Malhotra (Eds.) - Evolution of Venomous Animals and Their Toxins-Springer NetherlandsDocument361 pages(Toxinology) P. Gopalakrishnakone, Anita Malhotra (Eds.) - Evolution of Venomous Animals and Their Toxins-Springer NetherlandsJOHAN FELIPE NAVIA PIZONo ratings yet
- African ProverbsDocument4 pagesAfrican ProverbsRog DonNo ratings yet
- Modul Intensif Utbk BHS Inggris FixDocument36 pagesModul Intensif Utbk BHS Inggris FixMuhammad RidwansyahNo ratings yet
- Soal B Inggris L KLS 12Document6 pagesSoal B Inggris L KLS 12Endang kurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Pale On 02 ZittDocument304 pagesTextbook of Pale On 02 ZittMarco VazquezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Lots To Do A. Circle and Write The Correct Word.: (Answer Key)Document9 pagesUnit 1. Lots To Do A. Circle and Write The Correct Word.: (Answer Key)Adam AliNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Module 16Document3 pagesEarth & Life Module 16Emerald GreenNo ratings yet
- Screening Test, Grade 11Document4 pagesScreening Test, Grade 11Al Lhea Bandayanon Morales100% (1)
- Evolution, 4th EditionDocument1 pageEvolution, 4th EditionEbooks Cart100% (1)
- Parrot: Parrots Parrots, Also Known As PsittacinesDocument25 pagesParrot: Parrots Parrots, Also Known As PsittacinesozNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Elephant 1Document20 pagesEvolution of Elephant 1Saman NaseemNo ratings yet
- Janzen & Martin 1982 - Fruits For Extinct MegafaunaDocument9 pagesJanzen & Martin 1982 - Fruits For Extinct MegafaunaSara Helena Cardona ToroNo ratings yet
- Poemas Essenciais - Parte 1Document6 pagesPoemas Essenciais - Parte 1Halisson Wellame GranaNo ratings yet
- All About LeopardsDocument3 pagesAll About Leopardsapi-288441863No ratings yet
- Grade 3 ModulesDocument9 pagesGrade 3 ModulesHM Lumoya BalandangNo ratings yet
- Identifying Human Versus Non-Human Skeletal Remains in The FieldDocument24 pagesIdentifying Human Versus Non-Human Skeletal Remains in The FieldVasantha PhutaneNo ratings yet