Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Learning Layer 8: Weather and Climate
Uploaded by
swetha swithinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning Layer 8: Weather and Climate
Uploaded by
swetha swithinCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning Layer 8: Weather and Climate
Note- Checkpoint 1,2,3(Discussed in the class)
Word Buddy-Write from CB
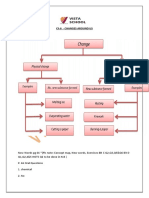
Concept Map:
Coursebook
I Connect
The plants that grow in hot climate are cactus, sage, sunflower dahlia, aloe vera and many more. The
plants that grow in cold climate are carrot, turnip, kale, broccoli and many more.
Checkpoint
1.
a. daily
b. sunlight
c. moderate
d. sea, land
e. humidity
2.
a.Tropical
b. Polar regions
c. moderate
I Think and Reflect
Natasha's city is located in the Temperate Zone.
I Discover
A rainbow is an are or semi-circular display of different colours visible in the sky. It appears in the sky after a
light rainfall. It is caused by the refraction and dispersion of sunlight by rain or water droplets present in the
atmosphere
I Link
1.see (meaning to use sight or eyes to look at something or watch something)
sea (meaning a salty water body)
2. pair (meaning two things of the same type) pear (meaning a fruit)
3. eye (meaning a body part)
I (meaning the first person)
I Extend
Two countries under each climatic zone are Kenya in Africa and Indonesia in Asia. These two countries lie in
the Torrid climatic zone.
I Learn for Life
1.Some wild animals like zebras migrate annually in search of food and water sources.
2.Some birds like Arctic terns migrate from Arctic to Antarctica each year due to changes in temperature and
for breeding
Learning Layer 8: Weather and
Climate
Application book B
Worksheet 8.1
1.Weather is the atmospheric condition of a place over a short period of time. It may change daily 2.
a. It describes the amount of hotness and coldness in the air over a short period of time. b.It describes
if an area is dry, wet, stormy, cloudy Or sunny
c. It tells about the daily temperature and the extent of rainfall an area experiences at that time.
Worksheet 8.2
A. 1. hot and humid climate. - b.
2. extreme cold climate. - c.
3. moderate climate. - a.
B. 1. b. cold
2. c. Frigid zone
3. d.weather
4. a.Humidity
5. b.Equator
Worksheet 8.3
Climate
1. Climate describes the weather pattern for a long period of time,
2.Climate changes hardly and may change in 25 or 30 years
3.Climate may be described in terms of yearly basis like this summer was hot and winter was cold etc.
4. Climate is influenced by factors like distance from the Equator, altitude, distance from the sea, direction of
wind and rainfall
Weather
1. Weather describes the atmospheric condition over a short period of time.
2. Weather may change daily
3. Weather describes hotness and coldness of air on everyday basis.
4. Weather is influenced by factors like wind, sunshine, rain, humidity, cloud etc.
Worksheet 8.4
A.1. three
2. Temperate Zone
3. sea
4. land, sea
5.sea, direction
B.Answers may very/Individual Response
C. 1. Cold. 2. Hot and dry
3. Maritime (neither too hot nor too cold)
Worksheet 8.5
Torrid Zone:-
This Zone lies in both side of the equator.It extends from tropic of Cancer to the tropic of Capricorn.This
zone experiences hot and humid climate through the year. EX-Mexico, Columbia.
Temperate Zone:-
This Zone lies in the middle of the torrid and Frigid Zone in both the hemispheres.It extends from tropic of
Cancer to the Arctic circle in the Northern hemisphere and tropic of Capricorn to the Antarctic circle in the
southern hemisphere.This zone has moderate climate.EX-Australia,
Japan southern hemisphere.
Frigid zone:-
This Zone lies in the North and South Poles. The North frigid zone lies between the Arctic Circle and North
Pole. The South Frigid Zone lies between the Antarctic Circle and the South Pole. This Zone has extreme cold
conditions.EX-Russia,Siberia.
Worksheet 8.6
1. Direction of wind like onshore winds or sea breeze that blows from sea to land brings rains to the coastal
areas and offshore winds or land breeze that blows from land to sea brings warm or cold air depending on the
land. Thus, these winds affect the climate of a region.
2.Equatorial region receives direct sun rays. So the areas near the Equator are hot and humid throughout the
year. But the areas away from the Equator receive slanting sun rays. So the regions away from the Equator
become colder and colder. Therefore, the Polar regions become the coldest regions. Thus, distance from the
Equator affects the climate of a place.
3. The vertical rays of the Sun fall on the Equator. Because of the Earth's spherical shape, areas other than the
Equator receive slanting sun rays. Polar regions being the farthest from the Equator receive very little sunlight.
You might also like
- Questions and Answers about: Planet EarthFrom EverandQuestions and Answers about: Planet EarthRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Factors that Determine ClimateDocument4 pagesFactors that Determine ClimateVanessa Rose Rota67% (3)
- 10.2 - Water's Influence On Weather and ClimateDocument3 pages10.2 - Water's Influence On Weather and Climateapi-251806635No ratings yet
- SST Class-V Ch.-4 Weather and Climate Q-ADocument4 pagesSST Class-V Ch.-4 Weather and Climate Q-AAnwar Hussain RaymaNo ratings yet
- 5 SST NewDocument10 pages5 SST NewakhijainNo ratings yet
- Meteorology Specific Objectives ActivityDocument3 pagesMeteorology Specific Objectives ActivityRhyza Labrada Balgos - CoEdNo ratings yet
- LN - 10 - 46 - Climate Science - ExtraTropicaDocument15 pagesLN - 10 - 46 - Climate Science - ExtraTropicaPantulu MurtyNo ratings yet
- 4q Elements of Weather Climate Quarter 4 Week 3 Day 1-Day 4Document89 pages4q Elements of Weather Climate Quarter 4 Week 3 Day 1-Day 4Winlyn B. Malazarte0% (1)
- CH 5 & 6 of GeoDocument3 pagesCH 5 & 6 of GeoTanu BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Elements of Weather Climate Quarter 4 Week 3 Day 1-Day 41Document89 pagesElements of Weather Climate Quarter 4 Week 3 Day 1-Day 41BENJ AMINNo ratings yet
- Crea, Read Me: Weather and ClimateDocument4 pagesCrea, Read Me: Weather and ClimateCreaNo ratings yet
- Class 5 - Social Studies ChapterDocument4 pagesClass 5 - Social Studies ChapterSharmistha KarNo ratings yet
- SHLT SCI 9 Q3 Wk5 6 1Document16 pagesSHLT SCI 9 Q3 Wk5 6 1irishangela789No ratings yet
- Basher Basics: Weather: Whipping up a storm!From EverandBasher Basics: Weather: Whipping up a storm!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Climate and Weather - Climate ZonesDocument6 pagesClimate and Weather - Climate Zonesmaria.sempere09No ratings yet
- For Module Chapter 3 PDF 1Document15 pagesFor Module Chapter 3 PDF 1secretzNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Q3 Module 4Document18 pagesGrade 9 Q3 Module 4Ma. Verinizie SangalangNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate Elements and ControlsDocument9 pagesWeather and Climate Elements and ControlsFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- ClimateDocument43 pagesClimateGabby VNo ratings yet
- BST161 1.0 - ClimateDocument48 pagesBST161 1.0 - ClimateNuriy NabihahNo ratings yet
- Modules Quarter 3 - Weeks 5 - 8: ScienceDocument41 pagesModules Quarter 3 - Weeks 5 - 8: ScienceEirene Irish OngpaucoNo ratings yet
- Climate and Distance From The Ocean ActivityDocument2 pagesClimate and Distance From The Ocean ActivityDanilo Reyes100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Pearl NecoleNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate-2ndDocument78 pagesWeather and Climate-2ndDwayne Lyndon GutierrezNo ratings yet
- For Module Chapter 5 Final PDFDocument25 pagesFor Module Chapter 5 Final PDFJanjesrey GallanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Factors Affecting The Climate of An Area PDF 2023Document7 pagesLesson 6 Factors Affecting The Climate of An Area PDF 2023Fritzgerald CarlinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ClimatologyDocument36 pagesIntroduction To ClimatologyMehak SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Geografía Tema 4Document12 pagesGeografía Tema 4Rocío MadolellNo ratings yet
- Environmental RegionsDocument63 pagesEnvironmental RegionsChalise SupremeNo ratings yet
- Important Approach To Climatic DesignDocument37 pagesImportant Approach To Climatic DesignJan Adrielle VeniceNo ratings yet
- GQA Science9 Q3 Wk5 Factors Affect The Climate of An Area - LrqaDocument11 pagesGQA Science9 Q3 Wk5 Factors Affect The Climate of An Area - LrqaBryce pandaanNo ratings yet
- Geography Session 3 MCQsDocument17 pagesGeography Session 3 MCQskalmeen583No ratings yet
- Factors affecting climate: latitude, altitude, distance from seaDocument5 pagesFactors affecting climate: latitude, altitude, distance from seaJezreel TanNo ratings yet
- Week 21 Learning PacketDocument12 pagesWeek 21 Learning PacketAizel Nova AranezNo ratings yet
- Class 5 Subject Social Studies Chapter 6 Weather and ClimateDocument4 pagesClass 5 Subject Social Studies Chapter 6 Weather and Climatemeera2k10No ratings yet
- S.St. Chapter-6 JULY-2020 Class-5 Q&Ans 18-6-20Document2 pagesS.St. Chapter-6 JULY-2020 Class-5 Q&Ans 18-6-20rasiawasthiNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Activity 1 1. The Equator 2. 3. 4. 5Document4 pagesWeek 5 Activity 1 1. The Equator 2. 3. 4. 5Katherine B. AbuanNo ratings yet
- How Latitude, Altitude, Bodies of Water and Wind Systems Impact ClimateDocument60 pagesHow Latitude, Altitude, Bodies of Water and Wind Systems Impact ClimateTeacher CarlaNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument3 pagesScriptNadhine MacalinaoNo ratings yet
- g6 Factors Affecting The ClimateDocument35 pagesg6 Factors Affecting The ClimateserwelaslebronNo ratings yet
- Factor Afffecting ClimateDocument38 pagesFactor Afffecting ClimatePrincess Alyssa BarawidNo ratings yet
- distance from the seaDocument8 pagesdistance from the seasteodoro012No ratings yet
- Living in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesLiving in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions Manualkhuongdiamond6h5100% (24)
- Living in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesLiving in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFFredMurphybgzr100% (14)
- Final Reviewer ClimateDocument17 pagesFinal Reviewer ClimateAprecio, Bryan C.No ratings yet
- S3 Geography Notes Topic 2 ClimateDocument25 pagesS3 Geography Notes Topic 2 ClimateOmel StephenNo ratings yet
- Week 2 AssignmentDocument12 pagesWeek 2 AssignmentKenneth Ryan EbaldoneNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate - WorksheetDocument4 pagesWeather and Climate - Worksheetlavender2x2No ratings yet
- S9 Q3 Enhanced Hybrid Module 3 Week 4 Final 2Document16 pagesS9 Q3 Enhanced Hybrid Module 3 Week 4 Final 2yeshNo ratings yet
- Group3 WriteUpDocument14 pagesGroup3 WriteUpWhinona FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chap12 MeteorologyDocument30 pagesChap12 MeteorologyopulitheNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Climate ExplainedDocument18 pagesFactors Affecting Climate ExplainedAkisha Jen Calicdan0% (1)
- Air Masses and Related Weather: Compilation of Project in MeteorologyDocument11 pagesAir Masses and Related Weather: Compilation of Project in MeteorologyAdnel Luis Robert GilhangNo ratings yet
- Science - Grade 9: (Elicit)Document13 pagesScience - Grade 9: (Elicit)G16 OLALIA LHYNISE MAE A.No ratings yet
- Weather and Climate PDFDocument9 pagesWeather and Climate PDFKashvi GoelNo ratings yet
- 5 - Q3 SciDocument21 pages5 - Q3 Scimaximo meridaNo ratings yet
- Incredible India Event DetailsDocument8 pagesIncredible India Event Detailsswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Sample Challenge Document For School LevelDocument4 pagesSample Challenge Document For School Levelswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Living Organisms and Their SurroundingsDocument8 pagesLiving Organisms and Their Surroundingsswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- GRADE 5-ENGLISH-HALFYEARLY-SET-2checkedDocument7 pagesGRADE 5-ENGLISH-HALFYEARLY-SET-2checkedswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Electricity NotesDocument6 pagesElectricity Notesswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- AY 21-22 Opening CircularDocument1 pageAY 21-22 Opening Circularswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- LEDGER ACCOUNTDocument17 pagesLEDGER ACCOUNTswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- CH 6.changes Around Us - NotesDocument5 pagesCH 6.changes Around Us - Notesswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Buddy Program - Break Out!! - CircularDocument1 pageBuddy Program - Break Out!! - Circularswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- MyPedia Science GR 5 CB Ch1-3 With TOCDocument33 pagesMyPedia Science GR 5 CB Ch1-3 With TOCswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Diary of A Wimpy Kid Book 5 - The Ugly TruthDocument226 pagesDiary of A Wimpy Kid Book 5 - The Ugly Truthswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Diary of A Wimpy Kid 8 - Hard LuckDocument213 pagesDiary of A Wimpy Kid 8 - Hard LuckBaraa Dawod50% (2)
- Murder in The Orient ExpressDocument137 pagesMurder in The Orient ExpressJose Luis Sanchez SotoNo ratings yet
- Hercule Poirots Christmas by Agatha ChristieDocument182 pagesHercule Poirots Christmas by Agatha ChristieYoginder Yadav100% (1)
- (Geronimo Stilton The Curse of The Cheese Pyramid PDFDocument136 pages(Geronimo Stilton The Curse of The Cheese Pyramid PDFSachin guptaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Transaction 6-Ay 2021-22-24!4!21Document2 pagesWeekly Transaction 6-Ay 2021-22-24!4!21swetha swithinNo ratings yet
- (Geronimo Stilton 1_ Geronimo Stilton - Original Italian Pub. Order 7_ Geronimo Stilton) Geronimo Stilton_ Matt Wolf_ Larry Keys_ Mark Nithael_ Kat Stevens - Lost Treasure of the Emerald Eye-Sch.pdfDocument138 pages(Geronimo Stilton 1_ Geronimo Stilton - Original Italian Pub. Order 7_ Geronimo Stilton) Geronimo Stilton_ Matt Wolf_ Larry Keys_ Mark Nithael_ Kat Stevens - Lost Treasure of the Emerald Eye-Sch.pdfTanvi Gupta49% (37)
- Art & Craft Summer Camp Planner for Grade 6Document2 pagesArt & Craft Summer Camp Planner for Grade 6swetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Easy Meals and Drinks for Grade 6Document1 pageEasy Meals and Drinks for Grade 6swetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know PlantsDocument8 pagesGetting To Know Plantsswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- L10-There Will Come Soft RainsDocument3 pagesL10-There Will Come Soft Rainsswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Exam Portion and TT - GR 6Document3 pagesHalf Yearly Exam Portion and TT - GR 6swetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Easy Meals and Drinks for Grade 6Document1 pageEasy Meals and Drinks for Grade 6swetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Weekly Transaction 6-Ay 2021-22 17 - 4 - 21Document1 pageWeekly Transaction 6-Ay 2021-22 17 - 4 - 21swetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 English Halfyearly Set 2checkedDocument7 pagesGrade 5 English Halfyearly Set 2checkedswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Weekly Transaction 6-Ay 2021-22 10 - 4 - 21Document1 pageWeekly Transaction 6-Ay 2021-22 10 - 4 - 21swetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 English Halfyearly Set 2checkedDocument7 pagesGrade 5 English Halfyearly Set 2checkedswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- Learning Layer 8: Weather and ClimateDocument4 pagesLearning Layer 8: Weather and Climateswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- MyPedia Science GR 5 CB Ch1-3 With TOCDocument33 pagesMyPedia Science GR 5 CB Ch1-3 With TOCswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- JPATS Aviation Weather Booklet GuideDocument182 pagesJPATS Aviation Weather Booklet GuideBarut BrkkNo ratings yet
- GCLA (La Palma)Document17 pagesGCLA (La Palma)adrianNo ratings yet
- Critical Review of Dyson's 2005 Article on Climate Change and its ImpactsDocument2 pagesCritical Review of Dyson's 2005 Article on Climate Change and its ImpactsRezza Petra100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7 GradeDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 7 GradeShamarie Love Maribao100% (3)
- Average Temperature Total Precipitation Thermal Altitude Hemisphere Climate Zone ClimateDocument2 pagesAverage Temperature Total Precipitation Thermal Altitude Hemisphere Climate Zone ClimateDiana AvilaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Chapter 4 WorkbookDocument19 pagesGrade 7 Chapter 4 WorkbookBrennan ColdwellNo ratings yet
- Duct Sizing and HVAC CalculationDocument21 pagesDuct Sizing and HVAC Calculationsardarmkhan80% (5)
- Chapter 16 - Atmosphere Part 1Document30 pagesChapter 16 - Atmosphere Part 1adingmarasigan0% (1)
- Thermal PhysicsDocument29 pagesThermal PhysicsAnonymous rn5Te9MwkNo ratings yet
- Science 3 - Q4 - L4 - Types of WeatherDocument13 pagesScience 3 - Q4 - L4 - Types of WeatherAira Shane LladaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Module 1Document12 pagesMidterm Module 1Geraldes IbañezNo ratings yet
- Process Equations PDFDocument1 pageProcess Equations PDFSatheesh ChandranNo ratings yet
- Mississippi Severe Weather Awareness Week: February 21 - 25, 2011Document16 pagesMississippi Severe Weather Awareness Week: February 21 - 25, 2011thereznewsNo ratings yet
- S8ES-IId-18 Understanding Typhoon IntroductionDocument7 pagesS8ES-IId-18 Understanding Typhoon IntroductionAsniah Takiri McrndsNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: An Inconvenient TruthDocument74 pagesUnit 5: An Inconvenient TruthEnglish TimeNo ratings yet
- "Rainmaker" Emmelie Deforest Esc2014 Official SongDocument2 pages"Rainmaker" Emmelie Deforest Esc2014 Official SongAlex LeirasNo ratings yet
- Humidity Unit Conversions-General PDFDocument10 pagesHumidity Unit Conversions-General PDFMachineryengNo ratings yet
- Weather Climate Change GuideDocument11 pagesWeather Climate Change Guidefailures12No ratings yet
- 2230 Insert ON 2011 P1 and P2 Brunei GeographyDocument3 pages2230 Insert ON 2011 P1 and P2 Brunei GeographyNadd Azis100% (1)
- NHC Report On Hurricane IanDocument72 pagesNHC Report On Hurricane IanABC Action NewsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HydrometeorologyDocument21 pagesIntroduction To HydrometeorologyApril JulianoNo ratings yet
- Apuntes GeophysicalDocument298 pagesApuntes GeophysicalGaby Vilchez RojasNo ratings yet
- Face Prep Wipro Slot Analysis 25th Sep 2021 Slot 1Document21 pagesFace Prep Wipro Slot Analysis 25th Sep 2021 Slot 1Aniket KaleNo ratings yet
- September 2000 PAMS Data Analysis Workbook: Data Validation 1Document36 pagesSeptember 2000 PAMS Data Analysis Workbook: Data Validation 1Bhanu Prakash SNo ratings yet
- Orlove 2002 - Ethnoclimatology en The AndesDocument8 pagesOrlove 2002 - Ethnoclimatology en The AndesreempeNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectDocument3 pagesGreen House EffectRavi Kanth M NNo ratings yet
- EVAPORATIVE COOLING: PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONSDocument3 pagesEVAPORATIVE COOLING: PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONSShaukat RafiNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar Pustakatuti azrizaNo ratings yet
- Ongc Patan of Different Cities From GujratDocument23 pagesOngc Patan of Different Cities From GujratRavindra VarmaNo ratings yet
- Task 1 AcademicDocument2 pagesTask 1 AcademicripanNo ratings yet