Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 38
Uploaded by
Hany ShaltootOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 38
Uploaded by
Hany ShaltootCopyright:
Available Formats
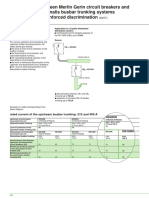
Coordination between circuit breakers and Telemecanique
Canalis busbar trunking systems
Cascading and reinforced discrimination
Circuit breaker selection taking The use of current-limiting circuit breakers Coordination techniques are described and
coordination into account makes it possible to implement coordination recognised by the following standards:
techniques. This improves circuit breaker c product standards IEC 947-1 and 947-2;
performance in terms of breaking capacity c installation standards IEC 364,
and continuity of service. NF C15-100, etc.
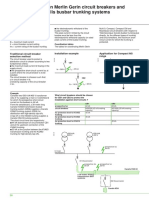
Cascading Principle Application for Compact NS range
The use of a current-limiting circuit breaker Cascading Cascading
upstream to reinforce the breaking capacity
E40703E
E40702E
of a downstream circuit breaker.
CB1
CB1 = NS400H
Renforced
break. cap.
70 kA
CB2 = NS160N
CB2
(Breaking
Isc = 65 kA cap. = 35 kA)
CB2 breaking capacity ➚
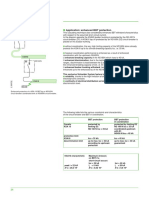
Discrimination Principle Application for Compact NS range
In the event of an electrical fault on one Cascading and reinforced discrimination Cascading and reinforced discrimination
outgoing circuit, discrimination is the ability
of the electrical installation to maintain the
E40704E
E40702E
continuity of electrical power supplied to the
CB1 = NS400H
other circuits not concerned by the fault. CB1
As a general rule, cascading and
discrimination techniques are applied
independently.
Schneider has developed an exclusive Break. cap. +
system to conciliate cascading and discrimination
discrimination. reinforced 70 kA
This system ensures discrimination up to the CB2
reinforced breaking capacity of the Isc = 65 kA CB2 = NS160N
association of circuit breakers CB1 and CB2 . Isc = 65 kA
CB 2 breaking capacity ➚
Discrimination ensured up to the reinforced
breaking capacity of CB2 ➚
37
You might also like
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 31Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 31Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 22Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 22Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- Système de Distribution Répartie: Application: Enhanced BBT ProtectionDocument1 pageSystème de Distribution Répartie: Application: Enhanced BBT ProtectionHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- Système de Distribution Répartie: 2.1 Telemecanique BBT/Merlin Gerin Circuit-Breaker CoordinationDocument1 pageSystème de Distribution Répartie: 2.1 Telemecanique BBT/Merlin Gerin Circuit-Breaker CoordinationHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- LS BKN-BDocument54 pagesLS BKN-Bashraf hafiziNo ratings yet
- Selection Manual - EN PDFDocument394 pagesSelection Manual - EN PDFkhuzaimNo ratings yet
- MCB eDocument56 pagesMCB eAnonymous 2M6rRGKKWNo ratings yet
- CIBSE WM CPD Seminar Cascading Discrimination by Schneider PDFDocument33 pagesCIBSE WM CPD Seminar Cascading Discrimination by Schneider PDF3238NDNo ratings yet
- C60N Marine PDFDocument2 pagesC60N Marine PDFViorel CatalinNo ratings yet
- Ais Nxair Onepager 40ka en Screen HighresDocument2 pagesAis Nxair Onepager 40ka en Screen HighresAltafNo ratings yet
- MPS2222A: Elektronische Bauelemente NPN SiliconDocument6 pagesMPS2222A: Elektronische Bauelemente NPN SiliconJose CordovaNo ratings yet
- KYN61-40.5 Indoor Removable AC Metal-Clad SwitchgearDocument1 pageKYN61-40.5 Indoor Removable AC Metal-Clad SwitchgearCLAVOTNo ratings yet
- Limitation: ConclusionDocument7 pagesLimitation: ConclusionAshirvad RathNo ratings yet
- KYN61-40.5 (Z) KYN61-40.5 (Z) : Metalclad AC Enclosed Switchgear Metalclad AC Enclosed SwitchgearDocument5 pagesKYN61-40.5 (Z) KYN61-40.5 (Z) : Metalclad AC Enclosed Switchgear Metalclad AC Enclosed SwitchgearCLAVOTNo ratings yet
- Low Voltage Circuit Breaker Designing: Compiled By: Er. SADIQ HUSSAIN - INDIADocument16 pagesLow Voltage Circuit Breaker Designing: Compiled By: Er. SADIQ HUSSAIN - INDIAsaleh gazi100% (1)
- Lec.01 - Building Design Concept - SE Sponsor 2021Document20 pagesLec.01 - Building Design Concept - SE Sponsor 2021moosuhaibNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker DesigningDocument16 pagesCircuit Breaker DesigningSadiq HussainNo ratings yet
- 2P Circuit Breakers P&ADocument11 pages2P Circuit Breakers P&AparyonoNo ratings yet
- DPC47F Yb01 G0100 Ed001 - 001 SectionDocument1 pageDPC47F Yb01 G0100 Ed001 - 001 SectionSUSOVAN BISWASNo ratings yet
- MetalClad Outdoor VCBEnglish PDFDocument2 pagesMetalClad Outdoor VCBEnglish PDFdip461No ratings yet
- COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Virtual Campus IslamabadDocument38 pagesCOMSATS Institute of Information Technology Virtual Campus IslamabadIan BagunasNo ratings yet
- Energypac Engineering's Outdoor VCBDocument12 pagesEnergypac Engineering's Outdoor VCBAnley NigissieNo ratings yet
- Disjuntores TemBreak TerasakiDocument4 pagesDisjuntores TemBreak TerasakiEuflasio MouraNo ratings yet
- Système de Distribution Répartie: Short-Circuit Protection by Circuit-BreakerDocument1 pageSystème de Distribution Répartie: Short-Circuit Protection by Circuit-BreakerHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- Bi-Directional Isolated DC-DC Converter For Next-Generation Power Distribution - Comparison of Converters Using Si and Sic DevicesDocument10 pagesBi-Directional Isolated DC-DC Converter For Next-Generation Power Distribution - Comparison of Converters Using Si and Sic DevicesPrasad SolasaNo ratings yet
- Cascading PDFDocument8 pagesCascading PDFNitinKhareNo ratings yet
- Merged Capacitor Switching Based SAR ADC With Highest Switching Energy-EfficiencyDocument2 pagesMerged Capacitor Switching Based SAR ADC With Highest Switching Energy-EfficiencyalphabetagammathetaNo ratings yet
- Catalog LSDocument52 pagesCatalog LSlethanhtu0105No ratings yet
- Havells MCCB PDFDocument39 pagesHavells MCCB PDFvkcomputer_bhiwadiNo ratings yet
- GCB HVR BrochureDocument8 pagesGCB HVR BrochureHan HuangNo ratings yet
- Mismatch AnalysisDocument4 pagesMismatch AnalysisSav ThaNo ratings yet
- BC639Document9 pagesBC639abolfazlNo ratings yet
- Generator Circuit-Breaker Systems: Product BrochureDocument5 pagesGenerator Circuit-Breaker Systems: Product Brochurehamza shahzadNo ratings yet
- MCB S 1205Document52 pagesMCB S 1205hermanNo ratings yet
- Mini Interruptores Termomagnéticos e Interruptores DiferencialesDocument52 pagesMini Interruptores Termomagnéticos e Interruptores DiferencialesJay SantanNo ratings yet
- 08 COMPACT Prekidaci 80-3200ADocument469 pages08 COMPACT Prekidaci 80-3200AThông NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Xlpe Cable PDFDocument18 pagesXlpe Cable PDFAlapon BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Upgraded With New Spring Drive Operating Mechanism MSD: LTB 420E2 Live Tank Circuit BreakerDocument2 pagesUpgraded With New Spring Drive Operating Mechanism MSD: LTB 420E2 Live Tank Circuit BreakerChiranjeev SahooNo ratings yet
- Unisec SBC-W: Air-Insulated Medium-Voltage Secondary Distribution SwitchgearDocument8 pagesUnisec SBC-W: Air-Insulated Medium-Voltage Secondary Distribution Switchgearjoko setiawanNo ratings yet
- 2N6178 RcaDocument8 pages2N6178 RcaJohnnysNo ratings yet
- Chong Set Van SA - 110kV Nam Tra MyDocument3 pagesChong Set Van SA - 110kV Nam Tra MyPhước Khang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chong Set Van SA - 110kV Nam Tra MyDocument3 pagesChong Set Van SA - 110kV Nam Tra MyPhước Khang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Page 47Document1 pagePage 47Abhishek ShatagopachariNo ratings yet
- Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB and RCB, RCD or RCCBDocument21 pagesDifference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB and RCB, RCD or RCCBRahel Sorri100% (1)
- Hensel PDFDocument1 pageHensel PDFigorNo ratings yet
- 33kv Indoor Gas Insulated Switchgear - Rev 0Document8 pages33kv Indoor Gas Insulated Switchgear - Rev 0Koushik BhaumikNo ratings yet
- 2021 10 28 Lecture 5 SicmosfetssoftswitchingDocument36 pages2021 10 28 Lecture 5 SicmosfetssoftswitchingYves DuforezNo ratings yet
- Chong Set SA Drawings - 110kV Tra MyDocument3 pagesChong Set SA Drawings - 110kV Tra MyPhước Khang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Selecting and Deciding On Circuit Breakers Made Easy With IEC SpecificationsDocument36 pagesSelecting and Deciding On Circuit Breakers Made Easy With IEC SpecificationsSun TzuNo ratings yet
- Chong Set SA Drawings - 110kV Tra MyDocument3 pagesChong Set SA Drawings - 110kV Tra MyPhước Khang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chong Set SA Drawings - 110kV Tra MyDocument3 pagesChong Set SA Drawings - 110kV Tra MyPhước Khang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- (Device) Electric Product Catalog en 202106Document68 pages(Device) Electric Product Catalog en 202106Trọng Trương NgọcNo ratings yet
- RPP - Sup403mDocument4 pagesRPP - Sup403mLivNo ratings yet
- 11 - Neobreak Distribution System CatalougeDocument30 pages11 - Neobreak Distribution System CatalougeHisham AL-OmariNo ratings yet
- Kondezatorske BaterijeDocument26 pagesKondezatorske BaterijeMareHCNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: BC635 BC637 BC639Document8 pagesData Sheet: BC635 BC637 BC639Jose M PeresNo ratings yet
- Fahrleitung Datenblatter Lasttrennschalter EN Web PDFDocument6 pagesFahrleitung Datenblatter Lasttrennschalter EN Web PDFtaarak143No ratings yet
- Schneider MCCB Typs:: SR. NO - Name Type Size in Amp. Brea King Capac ITY Specifications 1 NSXMDocument6 pagesSchneider MCCB Typs:: SR. NO - Name Type Size in Amp. Brea King Capac ITY Specifications 1 NSXMAnkitaNo ratings yet
- LEC # 20 Ratings CBsDocument14 pagesLEC # 20 Ratings CBsSyeda TanzilaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 23Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 23Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- Week-11-Testing-And-Inspection-C-G-2391 4Document1 pageWeek-11-Testing-And-Inspection-C-G-2391 4Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 29Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 29Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- Système de Distribution Répartie: 2.4 Advantages of The Schneider SystemDocument1 pageSystème de Distribution Répartie: 2.4 Advantages of The Schneider SystemHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 17Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 17Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 24Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 24Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 39Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 39Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 33Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 33Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 37Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 37Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- The Different Types of Telemecanique Busbar TrunkingDocument1 pageThe Different Types of Telemecanique Busbar TrunkingHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 45Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 45Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 42Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 42Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 41Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 41Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 43Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 43Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 14Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 14Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- Rated Current of The Upstream Busbar Trunking: 500 and 630 ADocument1 pageRated Current of The Upstream Busbar Trunking: 500 and 630 AHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 9Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 9Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 16Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 16Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 11Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 11Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 12Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 12Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 7Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 7Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- Busbar Distribution System: 1.3 IEC 439.2 StandardsDocument1 pageBusbar Distribution System: 1.3 IEC 439.2 StandardsHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- DRS Rev.0 GTP-TR1!01!002 Condensate RecyclingDocument4 pagesDRS Rev.0 GTP-TR1!01!002 Condensate RecyclingBalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- FlazasulfuronDocument2 pagesFlazasulfuronFenologiaVinhaNo ratings yet
- Sop Toh Engine PT MarminDocument5 pagesSop Toh Engine PT MarminBeni WantaraNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document1 pageBook 1PES SAFETYNo ratings yet
- Cracked Tooth Syndrome. Part 1 Aetiology and DiagnosisDocument17 pagesCracked Tooth Syndrome. Part 1 Aetiology and Diagnosisfloressam2000No ratings yet
- Schrodinger Wave EquationsDocument6 pagesSchrodinger Wave EquationsksksvtNo ratings yet
- Reprint: Digital HVDC Partial Discharge TestingDocument6 pagesReprint: Digital HVDC Partial Discharge TestingcisnatelNo ratings yet
- Ligamentele LargiDocument2 pagesLigamentele LargiIoana IonicaNo ratings yet
- Gastritis: Department of Gastroenterology General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University Si Cen MDDocument82 pagesGastritis: Department of Gastroenterology General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University Si Cen MDAvi Themessy100% (1)
- Wind Load CompututationsDocument31 pagesWind Load Compututationskim suarezNo ratings yet
- Truong Quang Tuong ITITIU20130 Lab 2 CDocument6 pagesTruong Quang Tuong ITITIU20130 Lab 2 CTrương Quang TườngNo ratings yet
- WEG CTM Dwb400 10004024165 Installation Guide EnglishDocument1 pageWEG CTM Dwb400 10004024165 Installation Guide Englishjeffv65No ratings yet
- Mohd Mopti Bin Yassin V Lembaga Kemajuan Perusahaan Pertanian Negeri Pahang (LKPP) Corp SDN BHD & AnorDocument12 pagesMohd Mopti Bin Yassin V Lembaga Kemajuan Perusahaan Pertanian Negeri Pahang (LKPP) Corp SDN BHD & AnorA random humanNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The IEEE Color BooksDocument6 pagesAn Overview of The IEEE Color BooksOhm666No ratings yet
- Bar Tending TerminologyDocument3 pagesBar Tending TerminologySiska WangNo ratings yet
- Pottery Making May06 Poi0506dDocument52 pagesPottery Making May06 Poi0506dMadeleineNo ratings yet
- 08 A330 Ata 35Document32 pages08 A330 Ata 35Owen100% (1)
- Pahlavi PoemDocument9 pagesPahlavi PoemBatsuren BarangasNo ratings yet
- Environmental and Sustainability Issues - 1Document21 pagesEnvironmental and Sustainability Issues - 121. PLT PAGALILAUAN, EDITHA MNo ratings yet
- 06ESL37 Analog Electronics Lab MANUALDocument70 pages06ESL37 Analog Electronics Lab MANUALSan AngadiNo ratings yet
- Blank BPSU TemplateDocument6 pagesBlank BPSU TemplateClarina Alviz BerganteNo ratings yet
- Substation Battery ChargerDocument2 pagesSubstation Battery Chargercadtil0% (1)
- Website Catalog MOTORS v2 PDFDocument8 pagesWebsite Catalog MOTORS v2 PDFИгорь КернякевичNo ratings yet
- Pastor O. I. Kirk, SR D.D LIFE Celebration BookDocument63 pagesPastor O. I. Kirk, SR D.D LIFE Celebration Booklindakirk1100% (1)
- RestrictedDocument51 pagesRestrictedsridharpalledaNo ratings yet
- Mold Maintenance StepDocument0 pagesMold Maintenance StepMonica JoynerNo ratings yet
- Definition of Logistics ManagementDocument4 pagesDefinition of Logistics ManagementzamaneNo ratings yet
- X Glo LED Strip Lighting For Tunnelling BrochureDocument6 pagesX Glo LED Strip Lighting For Tunnelling BrochureJOSE HUAMANINo ratings yet
- BHS Inggris 2021Document6 pagesBHS Inggris 2021Muhammad FirmanNo ratings yet
- Staff Code Subject Code Subject Data FromDocument36 pagesStaff Code Subject Code Subject Data FromPooja PathakNo ratings yet