Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Système de Distribution Répartie: Short-Circuit Protection by Circuit-Breaker
Uploaded by
Hany Shaltoot0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
1_Canalis_expert guide 13
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageSystème de Distribution Répartie: Short-Circuit Protection by Circuit-Breaker
Uploaded by
Hany ShaltootCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Système de distribution
répartie
In short Short-circuit protection by circuit-
breaker
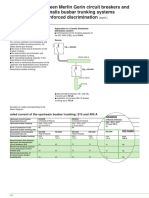
BBT sizing is determined ■ Inherent BBT characteristiques
by 3 types of
characteristics: BBT short-circuit sizing is determined by the following characteristics:
■ the maximum peak ■ the maximum peak current, peak l:
current, peak l This characteristic expresses the instantaneous electrodynamic withstand limits of
■ the maximum short-term the busbar trunking. Peak current value is often the most restrictive instantaneous
rms current, lcw characteristic for the protection device.
■ the thermal stress ■ maximum short-term rms current lcw:
(in A2s). This characteristic expresses the permissible temperature rise limit of conductors for
a given period of time (0.1 to 1 s).
■ the thermal stress in A2s:
This characteristic expresses the instantaneous thermal stress withstand of the BBT.
Normally, if the short-circuit generates fault conditions that are compatible with the
first two characteristics, this constraint is “ naturally satisfied ”.
The assumed short-circuit current to be considered for BBT protection is the one
found at supply box level.
■ Circuit-breaker characteristics
circuit-breaker Circuit-breaker D must meet the requirements of product construction standards
(IEC 947-2,...) and installation standards (IEC 364 or relevant country standards), i.e.
Isc at point A
its breaking capacity lcu* must be greater than short-circuit current Isc at the point
where it is installed.
A *installation standard IEC 364 and the construction standards specify that the breaking capacity
of a circuit-breaker is:
v the ultimate breaking capacity, lcu, if it is not coordinated with an upstream protection device
v the breaking capacity enhanced by cascading, if there is coordination with the upstream
E 36854E
BBT protection device.
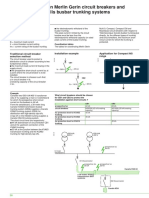
■ Applications
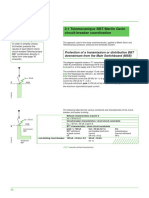
Directly protected BBT
■ Two cases must be considered :
v directely protected busbar trunking
circuit-breaker lcu > assumed Isc at point A
circuit-breaker
BBT peak l > asymmetrical assumed or limited Isc at point A
BBT thermal withstand in lcw > thermal stress passing through the BBT
'A
v busbar trunking protected downstream from a cable
cable
circuit-breaker lcu > assumed Isc at point A
BBT peak l > asymmetrical assumed or limited Isc at point B
BBT thermal withstand in lcw > thermal stress passing through the BBT
B
BBT
E 36855E
BBT protected downstream
from a cable
12
You might also like
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 16Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 16Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- A5 - Integral 63 - T - EN (Dgcat)Document26 pagesA5 - Integral 63 - T - EN (Dgcat)Martin GonzalezNo ratings yet
- CA908023E (Web) Ny - Koridnacija - Zastite PDFDocument8 pagesCA908023E (Web) Ny - Koridnacija - Zastite PDFjuka prazinaNo ratings yet
- SOCOMEC - 18013 - EN - Protection - Switching - Neutral - Issues - IECDocument21 pagesSOCOMEC - 18013 - EN - Protection - Switching - Neutral - Issues - IECAlexandru-Mihnea RaduNo ratings yet
- Système de Distribution Répartie: 2.1 Telemecanique BBT/Merlin Gerin Circuit-Breaker CoordinationDocument1 pageSystème de Distribution Répartie: 2.1 Telemecanique BBT/Merlin Gerin Circuit-Breaker CoordinationHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- CIBSE WM CPD Seminar Cascading Discrimination by Schneider PDFDocument33 pagesCIBSE WM CPD Seminar Cascading Discrimination by Schneider PDF3238NDNo ratings yet
- Bootstrap For IC PDFDocument5 pagesBootstrap For IC PDFDuc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker Fundamental CharacteristicDocument8 pagesCircuit Breaker Fundamental CharacteristicMaj RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Hensel PDFDocument1 pageHensel PDFigorNo ratings yet
- bcp56 0900766b80466693Document8 pagesbcp56 0900766b80466693Andrei StateNo ratings yet
- ABB Breakers Study Sharing 180911Document18 pagesABB Breakers Study Sharing 180911Marvin MarcaidaNo ratings yet
- Selectivity Presentation MH01Document85 pagesSelectivity Presentation MH01Abdelrahman shokryNo ratings yet
- Selecting and Deciding On Circuit Breakers Made Easy With IEC SpecificationsDocument36 pagesSelecting and Deciding On Circuit Breakers Made Easy With IEC SpecificationsSun TzuNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Các đặc điểm kỹ thuật của thiết bị đóng cắt hạ ápDocument19 pages3.1 Các đặc điểm kỹ thuật của thiết bị đóng cắt hạ ápNamNam LeeNo ratings yet
- MCB CurvesDocument1 pageMCB CurvesKasun PremarathnaNo ratings yet
- An-7006 IGBT Peak-Voltage and SnubberDocument8 pagesAn-7006 IGBT Peak-Voltage and SnubberdhruvNo ratings yet
- Abb MCBDocument20 pagesAbb MCBvr15847No ratings yet
- Fundamental Characteristics of Circuit BreakerDocument4 pagesFundamental Characteristics of Circuit Breakerdejanoski_aNo ratings yet
- 9AKK107992A9528 - Technical - Note - Site Planning ToolDocument14 pages9AKK107992A9528 - Technical - Note - Site Planning ToolKourosh52No ratings yet
- B ELSB Cat 2020 II 01 MCBs Preview 26-10-2020Document204 pagesB ELSB Cat 2020 II 01 MCBs Preview 26-10-2020tan yangNo ratings yet
- MCB For Generic Purposes: nxcuong-BMTBDDocument11 pagesMCB For Generic Purposes: nxcuong-BMTBDkhoaminh97No ratings yet
- Short Circuit StudyDocument45 pagesShort Circuit Studymohamad arifinNo ratings yet
- Schneider - ETC 5-Coordination of LV Protection Devices PDFDocument48 pagesSchneider - ETC 5-Coordination of LV Protection Devices PDFmanfredm6435No ratings yet
- BCP 51-BCP 52-BCP 53 - Transistor PNP PDFDocument8 pagesBCP 51-BCP 52-BCP 53 - Transistor PNP PDFTiago LeonhardtNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Design Revision - V2Document35 pagesBasic Circuit Design Revision - V2Rob PettitNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Substation ProtectionDocument19 pagesPresentation On Substation ProtectionSushil SharmaNo ratings yet
- B Elsb Cat 2021 01 McbsDocument190 pagesB Elsb Cat 2021 01 McbsCr1234512No ratings yet
- Topic - 4A-Overcurrent ProtectionDocument73 pagesTopic - 4A-Overcurrent ProtectionJoe ChengNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: BC635 BC637 BC639Document8 pagesData Sheet: BC635 BC637 BC639Jose M PeresNo ratings yet
- NextECMUpload 34264224 20201209145212Document14 pagesNextECMUpload 34264224 20201209145212karim_ouakliNo ratings yet
- BC639Document9 pagesBC639abolfazlNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 Distribution of Electric PowerDocument54 pagesMODULE 6 Distribution of Electric PowerSharapov Mechanic (Все просто)100% (2)
- H1Document39 pagesH1Dominic R. SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Characteristics of Circuit BreakerDocument7 pagesFundamental Characteristics of Circuit BreakerFlorin RaduNo ratings yet
- 550E2050 - Caract GralesDocument2 pages550E2050 - Caract GralesArturo Isidro Conde PérezNo ratings yet
- Silicon PNP Power Transistors: Savantic Semiconductor Product SpecificationDocument3 pagesSilicon PNP Power Transistors: Savantic Semiconductor Product SpecificationrolandseNo ratings yet
- DC Biasing-Bjts: Reference Book: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory (11th Edition) Robert F. BoylestadDocument24 pagesDC Biasing-Bjts: Reference Book: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory (11th Edition) Robert F. BoylestadfarukNo ratings yet
- UF3C065040B3 Data SheetDocument13 pagesUF3C065040B3 Data Sheetsultaniwahid240No ratings yet
- Indoor Voltage Transformer Fuses, WBP Outdoor Voltage Transformer Fuses, BRTDocument8 pagesIndoor Voltage Transformer Fuses, WBP Outdoor Voltage Transformer Fuses, BRTThi Huyen Trang VuNo ratings yet
- WBP - BRT - Catalogue Fuses (En) - 2005 PDFDocument8 pagesWBP - BRT - Catalogue Fuses (En) - 2005 PDFEdwin QuispeNo ratings yet
- BU2523Document6 pagesBU2523Ronald CastellarNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Characteristics of A Circuit-Breaker - ScheiderDocument7 pagesFundamental Characteristics of A Circuit-Breaker - Scheiderdavid_diaz_sNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: NPN Power TransistorDocument8 pagesData Sheet: NPN Power Transistoryuni supriatinNo ratings yet
- BU2506DXDocument7 pagesBU2506DXMARIPANo ratings yet
- BCP55Document6 pagesBCP55JlavieraNo ratings yet
- AN296133 DC Current Capability Fuse Characteristics Current Sensor ICs 50 200 ADocument4 pagesAN296133 DC Current Capability Fuse Characteristics Current Sensor ICs 50 200 Amamanca1No ratings yet
- Technical Bulletin Short Circuit and Back Up Cable ProtectionDocument4 pagesTechnical Bulletin Short Circuit and Back Up Cable ProtectionLSrakNo ratings yet
- Hager Residential Distribution Catalogue 1220Document44 pagesHager Residential Distribution Catalogue 1220lizukyNo ratings yet
- Design 30 Time Delayed RCCB Incomer: Consumer UnitDocument2 pagesDesign 30 Time Delayed RCCB Incomer: Consumer UnitTheDazzler420No ratings yet
- 1 Protection of FeedersDocument17 pages1 Protection of FeedersFake Acc99No ratings yet
- 6209 AdvancedCommercial DEW 20080829 WebDocument8 pages6209 AdvancedCommercial DEW 20080829 Webali ahmadNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Technical Data: Medium Power NPN Silicon High Current Transistor Surface MountDocument6 pagesSemiconductor Technical Data: Medium Power NPN Silicon High Current Transistor Surface MountIvanir Ferreira da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Biasing CircuitsDocument16 pagesBiasing CircuitsronaldbuijsNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric - Chapter G - Sizing and Protection of ConductorsDocument50 pagesSchneider Electric - Chapter G - Sizing and Protection of ConductorsRobert MarkovskiNo ratings yet
- Eee4227: Power System Protection Term: Mid-TermDocument41 pagesEee4227: Power System Protection Term: Mid-TermKazi ShahadatNo ratings yet
- Silicon NPN Power Transistors: Savantic Semiconductor Product SpecificationDocument3 pagesSilicon NPN Power Transistors: Savantic Semiconductor Product SpecificationSidienn MarceloNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 23Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 23Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 22Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 22Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- Week-11-Testing-And-Inspection-C-G-2391 4Document1 pageWeek-11-Testing-And-Inspection-C-G-2391 4Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 29Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 29Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- Système de Distribution Répartie: 2.4 Advantages of The Schneider SystemDocument1 pageSystème de Distribution Répartie: 2.4 Advantages of The Schneider SystemHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 17Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 17Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 24Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 24Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 39Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 39Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 31Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 31Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 38Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 38Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 37Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 37Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- Système de Distribution Répartie: Application: Enhanced BBT ProtectionDocument1 pageSystème de Distribution Répartie: Application: Enhanced BBT ProtectionHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- The Different Types of Telemecanique Busbar TrunkingDocument1 pageThe Different Types of Telemecanique Busbar TrunkingHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 41Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 41Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- Rated Current of The Upstream Busbar Trunking: 500 and 630 ADocument1 pageRated Current of The Upstream Busbar Trunking: 500 and 630 AHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 42Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 42Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 33Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 33Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 12Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 12Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 43Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 43Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 9Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 9Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 14Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 14Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 7Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 7Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 45Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 45Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 11Document1 page1 - Canalis - Expert Guide 11Hany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- Busbar Distribution System: 1.3 IEC 439.2 StandardsDocument1 pageBusbar Distribution System: 1.3 IEC 439.2 StandardsHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- 22 Thành NG Quen Thu C Trên Ielts - FirefighterDocument2 pages22 Thành NG Quen Thu C Trên Ielts - FirefighterNinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Sociology of Crimes and Ethics Suggested Answer "A"Document34 pagesSociology of Crimes and Ethics Suggested Answer "A"Bernabe Fuentes Jr.No ratings yet
- S25580 MSDS Corn Starch FisherchiDocument6 pagesS25580 MSDS Corn Starch FisherchiProcurement ProlineNo ratings yet
- ANNEXESDocument6 pagesANNEXESKyzer Calix LaguitNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps: Turbo Machines Amit Pathania Roll No:09309 Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesCentrifugal Pumps: Turbo Machines Amit Pathania Roll No:09309 Mechanical EngineeringAmit PathaniaNo ratings yet
- Caroline G Babin: Undergraduate Degree at Louisiana State University in Baton Rouge, Louisiana - Currently EnrolledDocument2 pagesCaroline G Babin: Undergraduate Degree at Louisiana State University in Baton Rouge, Louisiana - Currently EnrolledCaroline BabinNo ratings yet
- Piaggio MP3 300 Ibrido LT MY 2010 (En)Document412 pagesPiaggio MP3 300 Ibrido LT MY 2010 (En)Manualles100% (3)
- Headlight Washer System: Current Flow DiagramDocument3 pagesHeadlight Washer System: Current Flow DiagramLtBesimNo ratings yet
- Shift Registers NotesDocument146 pagesShift Registers NotesRajat KumarNo ratings yet
- Filling The Propylene Gap On Purpose TechnologiesDocument12 pagesFilling The Propylene Gap On Purpose Technologiesvajidqc100% (1)
- ToiletsDocument9 pagesToiletsAnonymous ncBe0B9bNo ratings yet
- Gates Crimp Data and Dies Manual BandasDocument138 pagesGates Crimp Data and Dies Manual BandasTOQUES00No ratings yet
- MGNM801 Ca2Document19 pagesMGNM801 Ca2Atul KumarNo ratings yet
- Changing Sentences in The Simple Present Tense Into PassiveDocument4 pagesChanging Sentences in The Simple Present Tense Into PassiveBernadette NarteNo ratings yet
- Waste Foundry Sand and Its Leachate CharDocument10 pagesWaste Foundry Sand and Its Leachate CharJanak RaazzNo ratings yet
- OPENING & CLOSING PROGRAM NARRATIVE REPORT (Grade 7)Document4 pagesOPENING & CLOSING PROGRAM NARRATIVE REPORT (Grade 7)Leo Jun G. Alcala100% (1)
- Optimizing Stata For Analysis of Large Data SetsDocument29 pagesOptimizing Stata For Analysis of Large Data SetsTrần Anh TùngNo ratings yet
- Bosch KE-Jetronic System DescriptionDocument3 pagesBosch KE-Jetronic System DescriptionJack Tang50% (2)
- CTRLX Automation BrochureDocument60 pagesCTRLX Automation BrochureNinja do SofáNo ratings yet
- Bombas KMPDocument42 pagesBombas KMPReagrinca Ventas80% (5)
- Manish Kumar: Desire To Work and Grow in The Field of MechanicalDocument4 pagesManish Kumar: Desire To Work and Grow in The Field of MechanicalMANISHNo ratings yet
- How To Install 64 Bits IDES On 32 Bits OSDocument1 pageHow To Install 64 Bits IDES On 32 Bits OSMuhammad JaveedNo ratings yet
- Schmidt Hammer TestDocument5 pagesSchmidt Hammer Testchrtrom100% (1)
- Energy BodiesDocument1 pageEnergy BodiesannoyingsporeNo ratings yet
- 20235UGSEM2206Document2 pages20235UGSEM2206Lovepreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Finding Targets PDFDocument9 pagesFinding Targets PDFSteve TangNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives Ii. Content Iii. Learning ResourcesDocument13 pagesI. Objectives Ii. Content Iii. Learning ResourcesZenia CapalacNo ratings yet
- Green ThumbDocument2 pagesGreen ThumbScarlet Sofia Colmenares VargasNo ratings yet
- Angle ModulationDocument26 pagesAngle ModulationAtish RanjanNo ratings yet
- 2011 Burris CatalogDocument56 pages2011 Burris CatalogMario Lopez100% (1)