Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Physics 2 Reviewer
Uploaded by
Francia Mae0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views2 pagesThis document provides formulas and concepts for general physics 2, including:
1) Conductors allow free flow of electrons while insulators impede electron flow. Examples of each are given.
2) Formulas are presented for potential difference (V), electric field strength (E), distance (d), and relationships between these variables.
3) SI units for key variables like potential difference, electric field strength, distance, charge, and capacitance are defined.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides formulas and concepts for general physics 2, including:
1) Conductors allow free flow of electrons while insulators impede electron flow. Examples of each are given.
2) Formulas are presented for potential difference (V), electric field strength (E), distance (d), and relationships between these variables.
3) SI units for key variables like potential difference, electric field strength, distance, charge, and capacitance are defined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views2 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Reviewer
Uploaded by
Francia MaeThis document provides formulas and concepts for general physics 2, including:
1) Conductors allow free flow of electrons while insulators impede electron flow. Examples of each are given.
2) Formulas are presented for potential difference (V), electric field strength (E), distance (d), and relationships between these variables.
3) SI units for key variables like potential difference, electric field strength, distance, charge, and capacitance are defined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
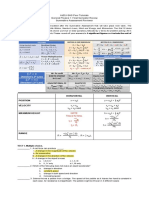
GENERAL PHYSICS 2
REVIEWER
Conductors FORMULAS
- a substance which anticipates LABEL
free flow of electrical charge or V- Potential difference
permits electrons to flow freely E- Electric field strength
d-distance
from particle to particle.
- Examples: Silver, gold, steel, SI UNIT
copper wire, or any metals, Potential difference (V)
human body, graphite and Electric field strength (V/m)
Distance (m)
aqueous solutions of salts
o To find potential difference
Insulators
between two plates
- materials that impede the free V=Ed
flow of electrons from atom to
o To find distance between two
atom and molecule to molecule. plates or to find separation
- Examples: plastics, Styrofoam, distance
Check the no.
paper, rubber, glass, dry air, V V
d= or d= 2 in week 6
E V/m
asphalt, oil, porcelain application
o To find Voltage (SI Unit is V)
𝑘𝑄
V= 𝑟
The value of k is always 8.99x 109
𝑁(𝑚2 )
, Q is the given charge, and r
𝐶2
is the distance.
SI UNIT of Q is C and for r is m
REMINDER: DISTANCE MUST BE In one micrcoulomb there is 1E-6
IN METER Coulumb
• mm to meter (divide the given In Scientific calculator,
number into 1000)
(Your answer) divided by (1E+6)
• cm to meter (divide the given
number into 100) C (capacitance) - F (Farad)
V (Voltage)- V
o To find the distance
To practice it, check the Application
𝑘𝑄
r= 𝑟 in week 5, you will use the
capacitance you found on No. 1
o To find the Capacitance (C) of a
parallel plate capacitor
εo A
C=
𝑑
SI UNIT
C (capacitance) - F (Farad)
εo (permittivity of free space)- F/m and
have a constant value of 8.85 x 10 -
12
F/m
A (area)- m2
d (distance)- m
o To know the charge
Q=CV
SI UNIT
Q- given charge Microcoulomb (μC)
and convert it into Coulumb (C)
You might also like
- Grade 12 General Physics 2 ExamDocument1 pageGrade 12 General Physics 2 ExamAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 Capacitance and DielectricsDocument14 pagesMODULE 4 Capacitance and DielectricsVenus CaringalNo ratings yet
- LAS RCP 12 MELC 1-2 WeeK 1-2PerfTaskDocument4 pagesLAS RCP 12 MELC 1-2 WeeK 1-2PerfTaskMonica SolomonNo ratings yet
- General Physics Ii Week 1-8 PDFDocument34 pagesGeneral Physics Ii Week 1-8 PDFDarey ApostolNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan in General Chemistry 2: Write YourDocument3 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan in General Chemistry 2: Write YourAshanty Cruz100% (1)
- General Physics 2 W 5-6Document12 pagesGeneral Physics 2 W 5-6NOEMI AMADORNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Module 1Document32 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Module 1GNC Tricia Faye DeleonNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Quarter 3: Week 2: Module 2: Gauss's LawDocument11 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Quarter 3: Week 2: Module 2: Gauss's LawBryan OndajareNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Hich Among The Given Particles Will Complete CNO Cycle?Document4 pagesDepartment of Education: Hich Among The Given Particles Will Complete CNO Cycle?adrian lozanoNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Q3W4Document3 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Q3W4Beverly Ventanilla NevadoNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1.2b Moment of InertiaDocument42 pagesGeneral Physics 1.2b Moment of InertiaLADY SUZETTE LANDICHONo ratings yet
- Game ShowDocument52 pagesGame ShowDaisy OrbonNo ratings yet
- The BigbangDocument23 pagesThe BigbangTrisha MagtibayNo ratings yet
- School Grading Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date Quarter Teaching Time No. of DaysDocument9 pagesSchool Grading Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date Quarter Teaching Time No. of DaysHeilene Ethel AngcayaNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Quarter 3 Module 5Document53 pagesPhysics 2 Quarter 3 Module 5Bea Lha Zandra BesingaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Third Quarter-Module 2Document17 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Third Quarter-Module 2Jaime DimariaNo ratings yet
- Formation of Heavy Elements' John Patrick Carl R. Hermosura Instructor 1-Institute of EducationDocument17 pagesFormation of Heavy Elements' John Patrick Carl R. Hermosura Instructor 1-Institute of EducationJohn Patrick Carl Hermosura100% (1)
- Physics MidtermDocument14 pagesPhysics MidtermPrecious015100% (1)
- Gen Chem 1finalsDocument6 pagesGen Chem 1finalsMaricarDimasNo ratings yet
- D.C Circuits Class TestDocument1 pageD.C Circuits Class TestShinde JayakrishnaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Western Leyte CollegeDocument15 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Western Leyte CollegeDaniela Grace Mata100% (1)
- GeneralPhysics2 Week 1Document9 pagesGeneralPhysics2 Week 1Altea EvaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice ReviewerDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice ReviewerVeronicaNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Quarter 3Document35 pagesPhysics 2 Quarter 3Aaron Justin BeltranNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Genral Physics 2Document4 pagesLesson Plan Genral Physics 2Ron Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Electric Flux & Gauss's Law: Physics 16Document23 pagesElectric Flux & Gauss's Law: Physics 16clndneNo ratings yet
- Coulomb's LawDocument17 pagesCoulomb's LawChristine Jade MonteraNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 Midterm Examinations ReviewerDocument5 pagesPhysics 1 Midterm Examinations ReviewerWylie Thomas PeNo ratings yet
- Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument24 pagesLaws of ThermodynamicsMYBNG SHPPRNo ratings yet
- Name: - AP Physics Worksheet - Mechanical Waves ReviewDocument5 pagesName: - AP Physics Worksheet - Mechanical Waves ReviewMarcial Aguilar BarahonaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document4 pagesModule 1welpNo ratings yet
- GNPHYS 2 - WORKTEXT - Week 7 - Unit 7Document8 pagesGNPHYS 2 - WORKTEXT - Week 7 - Unit 7Nad dlanyer LatigidadNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2Document22 pagesGeneral Physics 2Kian SabordoNo ratings yet
- Puerto Galera National High School: Daily Lesson LogDocument2 pagesPuerto Galera National High School: Daily Lesson LogJennifer MagangoNo ratings yet
- Natsci 101.1: Physical Science: O O O ODocument5 pagesNatsci 101.1: Physical Science: O O O OMatthew Alison ApostolNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 LessonDocument170 pagesGeneral Physics 1 LessonEunice AquinoNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge and Electric Fields: General Physics IIDocument25 pagesElectric Charge and Electric Fields: General Physics IIJoie LastimosaNo ratings yet
- GeneralPhysics1 Q1 ChapterTest1Document2 pagesGeneralPhysics1 Q1 ChapterTest1Jasmin Soriano100% (1)
- ES Module 3 - Quarter 1 - Types of SolidsDocument13 pagesES Module 3 - Quarter 1 - Types of SolidsAnalynAsuncionAtaydeNo ratings yet
- Electric Forces and Electric FieldsDocument24 pagesElectric Forces and Electric FieldsLara WadiNo ratings yet
- Test For AteDocument4 pagesTest For AteZyra Barbin MaglabeNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of... The Learners Are Able To... The Learners..Document24 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of... The Learners Are Able To... The Learners..Mark Francis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their PropertiesDocument39 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their PropertiesSTANNo ratings yet
- LP Chemistry CONCENTRATION UNITSDocument4 pagesLP Chemistry CONCENTRATION UNITSErica De VeraNo ratings yet
- Electric Force & Electric Field IDocument60 pagesElectric Force & Electric Field IImran ParvezNo ratings yet
- POP32i-Sheet230316-re TH en PDFDocument28 pagesPOP32i-Sheet230316-re TH en PDFGenInfo ServicesNo ratings yet
- How Energy Is Produced and ManagedDocument1 pageHow Energy Is Produced and ManagedSonoko Suzuki100% (1)
- General Chemistry 1 - STEM 11: Quarter 1: Week 1-8Document49 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 - STEM 11: Quarter 1: Week 1-8lui yangyangNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Nature and Inquiry of Research: Kaneesha Mei S. LancinDocument4 pagesUnit 1: Nature and Inquiry of Research: Kaneesha Mei S. LancinKaneesha Sobreviñas100% (1)
- IB Electrostatics11Document111 pagesIB Electrostatics11Shankara Lakshmi GanapathyNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Module 4 1Document16 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Module 4 1Mary Rose DomingoNo ratings yet
- Without Key Gen Physics 1 QRT 1Document83 pagesWithout Key Gen Physics 1 QRT 1CRISTINE ANNE RINONo ratings yet
- Universal GravitationDocument46 pagesUniversal GravitationNurulWardhani11No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan PhysicsDocument35 pagesLesson Plan Physicsare fiqsNo ratings yet
- GenPhysics1 - Q1MELC1-5W1 MeasurementDocument10 pagesGenPhysics1 - Q1MELC1-5W1 MeasurementShane Ureta100% (1)
- 11 Module 11 - Q1 - GENERAL PHYSICS 1Document14 pages11 Module 11 - Q1 - GENERAL PHYSICS 1RoyNo ratings yet
- Gen. Physics 1 Summative ReviewerDocument3 pagesGen. Physics 1 Summative ReviewerMARIELLE ANDREA ZAMORASNo ratings yet
- General Physics2 Lesson 2 PDFDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics2 Lesson 2 PDFJohn Renzo MolinarNo ratings yet
- 05 Electrostatics 1005Document68 pages05 Electrostatics 1005ccsingNo ratings yet
- 2 SSF CurrentDocument66 pages2 SSF Currentkuharujjwal79No ratings yet
- How To Write Chapter 2: Review of Related Literature and StudiesDocument18 pagesHow To Write Chapter 2: Review of Related Literature and StudiesFrancia MaeNo ratings yet
- RESORT No. 5Document1 pageRESORT No. 5Francia MaeNo ratings yet
- UP College Admissions 2021 AR 1211241732Document1 pageUP College Admissions 2021 AR 1211241732Francia MaeNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 13 09953 v2Document20 pagesSustainability 13 09953 v2Francia MaeNo ratings yet
- Paras, Mae BernadetteDocument2 pagesParas, Mae BernadetteFrancia MaeNo ratings yet
- CETVDocument6 pagesCETVFrancia MaeNo ratings yet
- Os TP Owe Rful Love Is The: Lie Vet HattheDocument2 pagesOs TP Owe Rful Love Is The: Lie Vet HattheFrancia MaeNo ratings yet
- UNDP - Dialogue Bullet PointsDocument6 pagesUNDP - Dialogue Bullet Pointsvlad panfiliiNo ratings yet
- LCFAITH - Peer Review: Name of Member Score Contributions CommentsDocument1 pageLCFAITH - Peer Review: Name of Member Score Contributions CommentsFrancia MaeNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - HemocytometryDocument7 pagesLab Manual - HemocytometryFrancia MaeNo ratings yet
- Ceprofiles MagazineDocument4 pagesCeprofiles MagazineFrancia MaeNo ratings yet
- Truth As Determinant of Religious Faith: Global Journal of Humanities Vol 8, No. 1&2, 2009: 57-61Document6 pagesTruth As Determinant of Religious Faith: Global Journal of Humanities Vol 8, No. 1&2, 2009: 57-61Francia MaeNo ratings yet
- UNDP - Dialogue Bullet PointsDocument6 pagesUNDP - Dialogue Bullet Pointsvlad panfiliiNo ratings yet
- A R T I C L E S: Reason and Faith in GodDocument16 pagesA R T I C L E S: Reason and Faith in GodFrancia MaeNo ratings yet
- Bright: Insidecrochet - Co.ukDocument100 pagesBright: Insidecrochet - Co.ukЕкатерина Матушинец100% (2)
- Ass AsDocument25 pagesAss AsMukesh BishtNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SamplexDocument12 pagesPharmacology SamplexLiezel Dejumo BartolataNo ratings yet
- Acetaldehyde Solution SDSDocument10 pagesAcetaldehyde Solution SDSJuan Carlos Blanco LeónNo ratings yet
- Zeroing Neural Networks, An Introduction To, A Survey Of, and Predictive Computations For Time-Varying Matrix ProblemsDocument24 pagesZeroing Neural Networks, An Introduction To, A Survey Of, and Predictive Computations For Time-Varying Matrix ProblemsgoatcockNo ratings yet
- Start Up Slug Catcher and Train 1Document43 pagesStart Up Slug Catcher and Train 1Larbi HammounNo ratings yet
- Aviation Fuel Quality Control Manual - Rev.2015Document56 pagesAviation Fuel Quality Control Manual - Rev.2015Aswin Lorenzo Gultom100% (1)
- SC3 User Manual - V1.06 PDFDocument196 pagesSC3 User Manual - V1.06 PDFJoeNo ratings yet
- Tugas Basing MandaDocument5 pagesTugas Basing MandaSalman AlfariziNo ratings yet
- Principle of Virtual Work and Its ApplicationDocument7 pagesPrinciple of Virtual Work and Its Applicationprem adhikari100% (1)
- Classification of AntibioticsDocument5 pagesClassification of AntibioticsdenaNo ratings yet
- MSDS Matrix Diluent-2 LISSDocument4 pagesMSDS Matrix Diluent-2 LISSLaboratorium RSI PekajanganNo ratings yet
- Dyneema Vs SteelDocument5 pagesDyneema Vs SteelSaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Origin of Khmer Land and PeopleDocument16 pagesWeek 3 - Origin of Khmer Land and PeopleAlienNo ratings yet
- Lower Motor Neuron LesionsDocument29 pagesLower Motor Neuron LesionsLoshi ChandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Eagle: This Article Is About The Bird. For Other Uses, See - "Eagles" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument12 pagesEagle: This Article Is About The Bird. For Other Uses, See - "Eagles" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeMegaEkaSetiawanNo ratings yet
- Methodology and Specifications Guide: Crude OilDocument34 pagesMethodology and Specifications Guide: Crude Oil066709No ratings yet
- Plant InvitroDocument219 pagesPlant InvitroMD Nassima100% (4)
- Vo 1263 AaDocument8 pagesVo 1263 Aa801400No ratings yet
- Previews 2502414 PreDocument9 pagesPreviews 2502414 PreAlex Andre RojasNo ratings yet
- Forklift Bucket 1400B - ManualDocument4 pagesForklift Bucket 1400B - ManualVie LiesnaNo ratings yet
- Spek Dental Panoramic Rotograph EVODocument2 pagesSpek Dental Panoramic Rotograph EVOtekmed koesnadiNo ratings yet
- GDPDocument6 pagesGDPBenedetta NardiNo ratings yet
- Magic HRC Scarf 1: by Assia BrillDocument6 pagesMagic HRC Scarf 1: by Assia BrillEmily HouNo ratings yet
- Manual of Esco 201 S+G Gas AnlyzerDocument5 pagesManual of Esco 201 S+G Gas Anlyzerikhsan_priambodoNo ratings yet
- ISolutions Lifecycle Cost ToolDocument8 pagesISolutions Lifecycle Cost ToolpchakkrapaniNo ratings yet
- QuantorVet Plus User Manual - EN - 130815Document83 pagesQuantorVet Plus User Manual - EN - 130815rtr electronicaNo ratings yet
- Vray MaterialsDocument206 pagesVray MaterialsDodeptrai BkNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 Workbook BussinessDocument45 pagesUnit 14 Workbook BussinessAna Victoria DíazNo ratings yet
- EAU2 - I - 04 - Ruins of The Lost RealmDocument127 pagesEAU2 - I - 04 - Ruins of The Lost RealmHache73% (15)