Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan 25 Jan 2022
Uploaded by
Faadiyah RoojeeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adobe Scan 25 Jan 2022
Uploaded by
Faadiyah RoojeeCopyright:
Available Formats
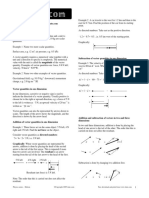
Two forces, of
3 magnitudes 1 N and
3 N, act on a 1N
shown in the diagram. Calculate the magnitude particle in the directions
particle and the of the resultant force on the
angle between this resultant force and the
3N. force of magnitude
40 >3N
(J98/P2/5)
Ans: 3.82 N, 10°
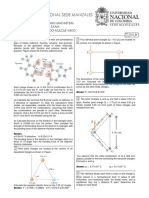
A particle is free to move on a horizontal table. It is acted on by constant forces P ,P+Q
P and Q. The force P has
magnitude 5 N and acts due to north. The resultant
P+Qhas magnitude 9 N and acts in the direction 060°. Calculate the magnitude
and direction of Q.
60
(UCLES)
Ans: 61 N, 093.7o
5. Two forces, P and Q, of 2 N and 6 N respectively have a resultant of 5 N. Calculate the anglebetween Pand
Ans: 128.70
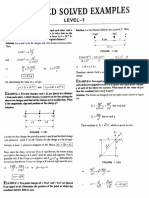
6. Forces P and Q act on a particle, and are inclined at 40° to each other. The
resultant of P and Q makes an angle of 10° with P and 30° with Q, as shown
diagram.
in the The magnitude of P is 2N. Find the magnitude ofQ and the
magnitude of the resultant. ---
(J99/P2/6)
Ans: 0.69, 2.6
(+3) N
QN and (Q+3) N acting in directions
7. The diagram shows two forces of magnitude
Find
N
another.
th:at are at angle 6 to one
an
6 and 0 60°
two forces when Q =
i) the magnitude of the resultant of the
120° and the magnitude ofthe resultant ofthe two forces
ii) the value of Q when 6= Ans 13.1 N, 5 N
is 7 N.
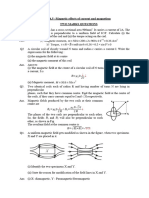
P N and Q N. The resultant of
the two forces has
forces have magnitudes PN
wo
in a direction 40° clockwise from the force of 12N
magnitude 12 N and acts N (see
anticlockwise from the force of magnitude O
agnitude PN and 80°
iagram). Find the value of Q.
(N09/3) ON
Ans : 8.91
QN, are inclined at
an angle 0 to each other. When P= V12 andO =2, the resultant has
9. Two forces, P N and
the resultant in the case when P= v12 and Q =4. Find the value of 0 and of R.
the same magnitude, RN, as
(UCLES)
Ans 150°,2
a force XN and a force of 6 N IS I20". It the resultant ofthe two forces has magnitude 14 N
10. The angle between Ans 16
X.
find the value of
(M1) 6A. 2
You might also like
- Gini Coefficient Formula Excel TemplateDocument9 pagesGini Coefficient Formula Excel TemplateAmanNo ratings yet
- Vector Practice 3Document2 pagesVector Practice 3api-292550476No ratings yet
- Course Outline Math 221C Advanced AlgebraDocument1 pageCourse Outline Math 221C Advanced Algebraherbertjohn2450% (2)
- Drew Marine Tank Cleaning ManualDocument102 pagesDrew Marine Tank Cleaning ManualStasio8090% (10)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Progression From RCM2 To RCM3 V0Document4 pagesProgression From RCM2 To RCM3 V0Fernando César Lima de Souto100% (1)
- Daily Practice Problems-01Document2 pagesDaily Practice Problems-01Motivational LifeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Ankit KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 MCQ-mergedDocument30 pagesUNIT 1 MCQ-mergedRohit Ghere100% (1)
- Vector NumericalsDocument4 pagesVector NumericalsAnwita JhaNo ratings yet
- M1-06 - Resultant ForcesDocument9 pagesM1-06 - Resultant ForcesHawraa HawraaNo ratings yet
- Scoe em Unit 1 To 4 MCQ BankDocument105 pagesScoe em Unit 1 To 4 MCQ BankVishwanath Naikwade -49100% (2)
- Electrostatics TH XIIDocument28 pagesElectrostatics TH XIIDark gaming liveNo ratings yet
- SITS EM Que BankDocument84 pagesSITS EM Que Bankrashmi kenvatNo ratings yet
- EME (U1 + U2) Insem EditionDocument97 pagesEME (U1 + U2) Insem EditionRohit Ghere100% (1)
- Eng Mechanics Unit 1-4 MCQS: Unit 1 - Resolution and Composition ofDocument106 pagesEng Mechanics Unit 1-4 MCQS: Unit 1 - Resolution and Composition ofAtul SheñdeNo ratings yet
- Problems On Resultant of Two Forces Acting at A Point (Parallelogram Law of Forces) Tutorial ProblemsDocument2 pagesProblems On Resultant of Two Forces Acting at A Point (Parallelogram Law of Forces) Tutorial ProblemsSudhakar UppalapatiNo ratings yet
- 8 VectorDocument6 pages8 VectorXoss ChannelNo ratings yet
- Scalars and VectorsDocument3 pagesScalars and VectorsnaylinaungNo ratings yet
- 7 - Statics & Dynamics Ex. Module-6-BDocument24 pages7 - Statics & Dynamics Ex. Module-6-BRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - Final Exams Revision: Electrical ChargeDocument19 pagesElectrostatics - Final Exams Revision: Electrical ChargeThabelo NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Vectors and ScalarsDocument8 pagesVectors and Scalarsdbigboss5050No ratings yet
- Physics Notes MotionDocument17 pagesPhysics Notes MotionDwomoh Richard AddoNo ratings yet
- PanPearl2016 Solutions 1Document8 pagesPanPearl2016 Solutions 1tanNo ratings yet
- ME 1 06 Resultant of ForcesDocument2 pagesME 1 06 Resultant of ForcesMuhammad SamyNo ratings yet
- Taller Parcial 1 - Fisica IiiDocument6 pagesTaller Parcial 1 - Fisica IiiJorge CañetesNo ratings yet
- Ecko Diaz g12 Stem C Gp2 w1Document4 pagesEcko Diaz g12 Stem C Gp2 w1brownywhitey22No ratings yet
- L1 - Assignment On Superposition Principle and Equilibrium of ChargesDocument2 pagesL1 - Assignment On Superposition Principle and Equilibrium of ChargesdynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- 9709 Teacher Tutorial 4 1 ForcesInEquilibrium v1Document9 pages9709 Teacher Tutorial 4 1 ForcesInEquilibrium v1salwasheikh800No ratings yet
- Selected Solved Examples: 2x10 - K (8+x) K (16x10-) - K (9x10Document17 pagesSelected Solved Examples: 2x10 - K (8+x) K (16x10-) - K (9x10manu patankarNo ratings yet
- As 123Document4 pagesAs 123anurag kumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering MechanicsDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Engineering Mechanicsmondalrohan8828No ratings yet
- Solutions 2 PHYSICS 2Document6 pagesSolutions 2 PHYSICS 2MARIAMA SILLAHNo ratings yet
- Pan Pearl River Delta Physics Olympiad 2016Document5 pagesPan Pearl River Delta Physics Olympiad 2016Bhawna SharmaNo ratings yet
- SEQUENCE-2, Application of Addition and Subtraction of VectorDocument3 pagesSEQUENCE-2, Application of Addition and Subtraction of VectorManthan PatelNo ratings yet
- Scan Jul 03, 2023Document3 pagesScan Jul 03, 2023jackdish18No ratings yet
- Projectile Motion - JP03 INTEGARDocument3 pagesProjectile Motion - JP03 INTEGARhimanshuNo ratings yet
- Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 04Document3 pagesCh-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 04Gurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1ShreyJain100% (1)
- Chapter 14 Circular FunctionsDocument50 pagesChapter 14 Circular FunctionsPhuong Ngan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 5 MagnetismDocument7 pagesCh-4 5 Magnetismgkgthe1No ratings yet
- 2020 HCI Prelim H2 Physics 9749 P1 SolnDocument6 pages2020 HCI Prelim H2 Physics 9749 P1 SolnYi QinNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - VectorsDocument16 pagesWeek 4 - VectorsSherryl MontalboNo ratings yet
- Physics: Sample Question PaperDocument8 pagesPhysics: Sample Question PaperShobhit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Department of Electrical Engineering Air University, IslamabadDocument40 pagesElectricity and Magnetism: Department of Electrical Engineering Air University, IslamabadIshmaal KhanNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Exercises3Document14 pagesWuolah Free Exercises3Don José Antonio García-Trevijano ForteNo ratings yet
- Spotlight - Phase-2 - (2022-23) - Week-1 - Paper-2 - Compile (2020-P-2) - (Only Que.)Document12 pagesSpotlight - Phase-2 - (2022-23) - Week-1 - Paper-2 - Compile (2020-P-2) - (Only Que.)Suryansh DummyNo ratings yet
- 9 SF I0 Un JJ7 PGu YPs GH 8 JDocument23 pages9 SF I0 Un JJ7 PGu YPs GH 8 JYeri KhaNo ratings yet
- 3H Electromagnetism 2008-2009: Solutions 4 - Mostly Faraday and MaxwellDocument14 pages3H Electromagnetism 2008-2009: Solutions 4 - Mostly Faraday and MaxwellkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Electrostat Extra QuestionsDocument4 pagesElectrostat Extra QuestionsPristy JoyisNo ratings yet
- Task Vectors and Scalars Moment of ForceDocument4 pagesTask Vectors and Scalars Moment of ForceDavina MoralezNo ratings yet
- EM Unit-I MCQDocument34 pagesEM Unit-I MCQgakelNo ratings yet
- Theory Trigonometric Ratio 34292Document28 pagesTheory Trigonometric Ratio 34292Tanay DwivediNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-03-14 203546Document1 pageScreenshot 2023-03-14 203546AkhileshNo ratings yet
- 6 April Evening Shift - 2 PhysicsDocument5 pages6 April Evening Shift - 2 PhysicsSHAKTI SWARUP SAHOONo ratings yet
- Daily Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesDaily Practice ProblemsHarshitNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2Abhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Hand Written NotesDocument97 pagesEngineering Mechanics Hand Written Notessunilkumarvss395No ratings yet
- Vector AssignmentDocument1 pageVector AssignmentNarenthran RameshNo ratings yet
- MechanicsDocument24 pagesMechanicsKeerthiNo ratings yet
- EM3 Suppl Examples 2013 07 19 PDFDocument181 pagesEM3 Suppl Examples 2013 07 19 PDFsuudfiinNo ratings yet
- Milon: Circular Motion (Chap.7)Document20 pagesMilon: Circular Motion (Chap.7)mmilon07No ratings yet
- Random Fourier Series with Applications to Harmonic Analysis. (AM-101), Volume 101From EverandRandom Fourier Series with Applications to Harmonic Analysis. (AM-101), Volume 101No ratings yet
- Compound Light MicroscopeDocument6 pagesCompound Light MicroscopeAselleNo ratings yet
- Binomial Distribution Powerpoint 1Document17 pagesBinomial Distribution Powerpoint 1kailash100% (1)
- Microsoft Word - Monografia - Diagnostico Do Escoamento Pluvial em Luanda - Maio 2013Document40 pagesMicrosoft Word - Monografia - Diagnostico Do Escoamento Pluvial em Luanda - Maio 2013Vivaldo Palanga100% (1)
- On Pro - A Powerful App For HDL Control SystemsDocument10 pagesOn Pro - A Powerful App For HDL Control SystemsRicardo GerdesNo ratings yet
- Towards A Vision of A Sustainable University - 2000Document21 pagesTowards A Vision of A Sustainable University - 2000Ihsan MarwatNo ratings yet
- Columban College, Inc.: The Impacts of Social Media Influencers in The Decision Making of The YouthDocument4 pagesColumban College, Inc.: The Impacts of Social Media Influencers in The Decision Making of The YouthJohn Joshua Pentecostes OliNo ratings yet
- Solid State 2022 by Bharat PanchalDocument21 pagesSolid State 2022 by Bharat PanchalRudraksh SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Bus 173 ProjectDocument12 pagesBus 173 Projectsyed abm AffanNo ratings yet
- Dumpsite Rehabilitation ManualDocument149 pagesDumpsite Rehabilitation ManualMwagaVumbiNo ratings yet
- IBC High Precision Angular Contact Ball Bearings DTB (Driven Tool Bearing)Document2 pagesIBC High Precision Angular Contact Ball Bearings DTB (Driven Tool Bearing)kizzie1No ratings yet
- L3b Reactor Sizing Example ProblemsDocument15 pagesL3b Reactor Sizing Example ProblemsNaniNeijieNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motors Step Up For Machine Automation: DON PHAM, Product Manager, IDECDocument4 pagesStepper Motors Step Up For Machine Automation: DON PHAM, Product Manager, IDECSolikinSolehNo ratings yet
- C1 Editable Progress Test 6 - 0Document5 pagesC1 Editable Progress Test 6 - 0Марія БарнаNo ratings yet
- THE PRESENT PERFECT TenseDocument16 pagesTHE PRESENT PERFECT TenseNguyễn Thị Ngọc ÁnhNo ratings yet
- DLP-16 Safety Measures in Arc WeldingDocument6 pagesDLP-16 Safety Measures in Arc WeldingChinelle Joseph Sollano TinoyNo ratings yet
- MAIN Electrical Parts List: FirmwareDocument8 pagesMAIN Electrical Parts List: FirmwareWilliam SequeraNo ratings yet
- Ec3058D-Vlsi Circuits and Systems Winter Semester-2020-21: DD Ton TopDocument2 pagesEc3058D-Vlsi Circuits and Systems Winter Semester-2020-21: DD Ton TopGamer AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Unit: 1 Complex Numbers: Department of MathematicsDocument4 pagesUnit: 1 Complex Numbers: Department of Mathematicsvidhya_bineeshNo ratings yet
- Barone R., 2010.: Fourth EditionDocument2 pagesBarone R., 2010.: Fourth EditionAbdelMonem Ben KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Tanginang ES PaimportanteDocument3 pagesTanginang ES PaimportantegutierrezyoofclaridethNo ratings yet
- Self-Instruct Aligning Language Model With Self GeDocument19 pagesSelf-Instruct Aligning Language Model With Self GeTere OliverosNo ratings yet
- Assignment Pages 12Document7 pagesAssignment Pages 12Rheia TangonanNo ratings yet
- DLM PaqueteDocument37 pagesDLM PaqueteBASTI APNo ratings yet
- 13 Impact of Tillage Plant Populationa and Mulches On WeedDocument4 pages13 Impact of Tillage Plant Populationa and Mulches On WeedHaidar AliNo ratings yet
- NM TotalDocument163 pagesNM TotalPrashant PrasarNo ratings yet
- Geography Lesson NotesDocument3 pagesGeography Lesson Notesteju.ganeshcNo ratings yet