Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formula Card Analytical Chemistry Prelim Exam
Uploaded by
Hans Gabriel RomanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formula Card Analytical Chemistry Prelim Exam
Uploaded by
Hans Gabriel RomanCopyright:
Available Formats
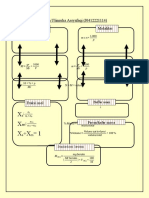
ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY
PRELIMINARY EXAM FORMULA CARD
LECTURE TOPICS
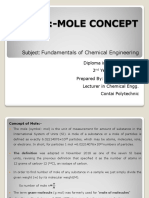
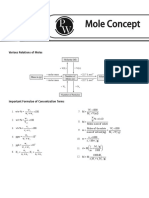
MOLE CONCEPT
Millimole
Depending on the dimensional analysis, the Mole Formula Pyramid
Avogadro’s following conversion factors can be used: Where: m
m = mass of given element (Unit: g)
number 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 1000 𝑚𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑜𝑟 1𝑚𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 10−3 𝑚𝑜𝑙
mm = molar mass of given element (Unit: g/mol)
= 6.02 × 10 23 In fraction: mm mol
1000 𝑚𝑚𝑜𝑙 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 mol = number of moles of given element (Unit: mol)
𝑜𝑟
1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 1000 𝑚𝑚𝑜𝑙
Conversion of moles to formula units/atoms/molecules
Conversion of formula units/atoms/molecules to moles
𝐹𝑜𝑟𝑢𝑚𝑢𝑙𝑎 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑠/𝑎𝑡𝑜𝑚𝑠/𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑒𝑠 =
𝑀𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑢𝑏𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 (𝑚𝑜𝑙) =
𝐴𝑣𝑜𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑜 ′ 𝑠 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟
𝐺𝑖𝑣𝑒𝑛 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑢𝑏𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 × 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑜𝑓 𝑔𝑖𝑣𝑒𝑛 𝑠𝑢𝑏𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒
1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑜𝑓 𝑔𝑖𝑣𝑒𝑛 𝑠𝑢𝑏𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝐹𝑜𝑟𝑚𝑢𝑙𝑎 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑢𝑏𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 ×
𝐴𝑣𝑜𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑜 ′ 𝑠 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟
NOTE: Unit dependent on given problem
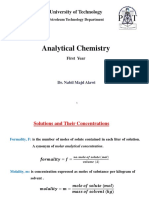
CONCENTRATIONS OF SOLUTIONS
𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 (𝑛)
Molarity 𝑀= % 𝑏𝑦 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 =
𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 (𝐿) % by 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 (𝑔)
(Molar
Where: mass × 100
Concentration) 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 (𝑔) + 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡(𝑔)
M = Molarity of solution (Unit: M or mol/L)
% 𝑏𝑦 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 = % by % 𝑏𝑦 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠/ 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 =
% by volume 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 (𝑚𝐿) mass / 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 (𝑔)
× 100 × 100
𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 (𝑚𝐿) + 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡 (𝑚𝐿) volume 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 (𝑚𝐿)
𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝐴 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 (𝑚𝑜𝑙. )
𝑋𝐴 = × 100 𝑚=
𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑎𝑙𝑙 𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑝𝑜𝑛𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡 (𝑘𝑔)
Mole Fraction Where: Molality Where:
XA = Mole Fraction of A m = Molality of solution (Unit: m or mol/kg)
A = Given substance
𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 (𝑚𝑔) 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 (𝑚𝑔)
𝑝𝑝𝑚 = × 106 Parts 𝑝𝑝𝑏 = × 109
Parts per 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 (𝑚𝑔) 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 (𝑚𝑔)
per
million Where: Where:
billion
ppm (Unit representation) = parts per million ppb (Unit representation) = parts per billion
𝑝𝑋 = −log [𝑋]
Where:
p-Functions
Px = p-Value of the species
X = Molar concentration of the species
ERRORS AND STATISTICAL DATA IN CHEMICAL ANALYSIS
𝐸 = 𝑋𝑖 − 𝑋𝑡 𝑋 −𝑋
𝐸 = 𝑖 𝑡 × 100
𝑋𝑡
Where:
E = Absolute Error Where:
Absolute E = Relative Error
Xi = Measured value Relative Error
Error Xi = Measured value
Xt = True value
NOTE: Unit dependent on given Xt = True value
problem NOTE: No unit for this, only percentage
∑|𝑋𝑖 − 𝑋̅ | 2
𝑑̅ = ∑(𝑋𝑖 − 𝑋̅ )
𝑛 𝑠= √
Where: 𝑁−1
Regular
𝑑̅ = Average deviation Where:
Average Standard
Xi = Measured value s = Regular Standard Deviation
Deviation Deviation (If n ≤
𝑋̅ = Mean of the data set 30)
Xi = Each measured value
n = Total number of data values 𝑋̅ = Mean of the data set
NOTE: Unit dependent on given N = Total number of data values
problem NOTE: No unit for this
2
∑(𝑋𝑖 − 𝑋̅)
∑(𝑋𝑖 − 𝜇)2 𝑠2 =
𝜎= √ 𝑁−1
𝑁 Where:
Population
Where: s2 = Regular Variance
Standard Regular Variance
𝜎 = Population Standard Deviation Xi = Each measured value
Deviation (If n ≤ 30)
Xi = Each measured value 𝑋̅ = Mean of the data set
(If n ≥ 30)
𝜇 = Mean of the population N = Total number of data values
N = Total number of data values NOTE: No unit for this
NOTE: No unit for this
∑(𝑋𝑖 − 𝜇)2 𝑠
𝜎2 = 𝑅𝑆𝐷 = × 1000 𝑝𝑝𝑡
𝑁 𝑋̅
Where: Where:
Population Relative RSD = Relative standard deviation
Variance 𝜎 2 = Population Variance Standard ppt = parts per thousand
(If n ≥ 30) Xi = Each measured value Deviation s = standard deviation of the data
𝜇 = Mean of the population
𝑋̅ = mean of the data set
N = Total number of data values
NOTE: No unit for this NOTE: No unit for this
𝑠 𝑤 =𝐻−𝐿
𝐶𝑉 = × 100%
𝑋̅ Where:
Coefficient Where: w = Spread or Range
of CV = Coefficient of variation Spread or Range H = Highest value
Variation s = standard deviation of the data L = Lowest value
𝑋̅ = mean of the data set NOTE: No unit for this
NOTE: No unit for this
LABORATORY TOPICS
LABORATORY TECHNIQUES IN ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY – MEASURING VOLUME
𝑣= 𝑎3 𝑣 = 𝑙𝑤ℎ
Where: Where:
Volume of a
Volume of a v = volume of cube (Unit: cm3) v = volume of rectangular box (Unit: cm3)
rectangular
cube a = area of cube (Unit: cm) l = length of cube (Unit: cm)
box
w = width of cube (Unit: cm)
h = height of cube (Unit: cm)
Volume of 𝑣 = 𝑣𝑓 − 𝑣𝑖 𝑚
𝑣=
irregular- Where: 𝑎
shaped solid v = volume of solid (Unit: mL) Volume of Where:
(via Water vf = Final volume (Unit: mL) liquid v = volume of liquid (Unit: mL)
Displacement Vi = Initial volume (Unit: mL)
a = density of liquid (Unit: kg/mL)
Method) m = mass of liquid (Unit: kg)
LABORATORY SAFETY AND TECHNIQUES
𝑀𝑒𝑎𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑒𝑑 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 − 𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒
% Error % 𝐸𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟 = ( ) × 100
𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒
NOTE: No unit for this, only percentage
𝐼𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑣𝑖𝑑𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑤𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡 = 𝐼𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑤𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡 − 𝐹𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑤𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡
Individual Weight by
(𝐴𝑓𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝑟𝑒𝑚𝑜𝑣𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑤𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡)
Subtraction
NOTE: Unit dependent on given problem
PREPARATIONS OF SOLUTIONS
𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 (𝑛) 𝐶𝑂 𝑉𝑂 = 𝐶𝑑 𝑉𝑑
𝑀=
𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 (𝐿) Where:
Molarity (Molar Where: Dilution Co = Stock solution’s concentration (Unit: M or mol/L)
Concentration) M = Molarity of solution (Unit: M or Formula Vo = Volume of stock solution being diluted (Unit: L)
mol/L) Cd = Dilute solution’s concentration (Unit: M or mol/L)
Vd = Volume of dilute solution (Unit: L)
You might also like
- Day - 5: Chemistry Class Notes: Biomentors Classes Online, MumbaiDocument4 pagesDay - 5: Chemistry Class Notes: Biomentors Classes Online, MumbaiSmit PatelNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER SolutionDocument26 pagesCHAPTER SolutionGoD Rusher Gaming YTNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Formula: Clinical ChemistryDocument4 pagesCompilation of Formula: Clinical ChemistryJillan MarieNo ratings yet
- Formula Chapter - SolutionDocument6 pagesFormula Chapter - SolutionSuraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Sammary and DefinitionsDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Sammary and DefinitionsRaneem AshrafNo ratings yet
- Biomentors Classes Online, Mumbai Day - 2 Chemistry Class NotesDocument4 pagesBiomentors Classes Online, Mumbai Day - 2 Chemistry Class NotesSmit PatelNo ratings yet
- ملخص اخر ٤ شباترDocument6 pagesملخص اخر ٤ شباترمحمد الخنينNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3 2022-2023 SolutionsDocument7 pagesProblem Set 3 2022-2023 SolutionskittypowerNo ratings yet
- Mean Standard Deviation: Antonio Mirano - 2018Document8 pagesMean Standard Deviation: Antonio Mirano - 2018jNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesChemistry Cheat SheetEJ FelisildaNo ratings yet
- Vapro 3-Concentration of SolutionDocument15 pagesVapro 3-Concentration of SolutionBakhitah NurulNo ratings yet
- لكجر 3Document22 pagesلكجر 3أمير حامدNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document6 pagesSession 3THE SEZARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-MeasurementDocument1 pageChapter 1-MeasurementantonstefanbiehlerNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Chemical Ngineering Unit IIDocument7 pagesFundamentals of Chemical Ngineering Unit IISk Jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 HW Sheet Answer KeyDocument23 pagesChapter 1 HW Sheet Answer Keyjaivalpatel4226No ratings yet
- Herbicide Concentration Quick Guide 2018Document2 pagesHerbicide Concentration Quick Guide 2018Ashvin DhirubhaiNo ratings yet
- Herbicide Concentration Quick Guide 2018Document2 pagesHerbicide Concentration Quick Guide 2018Ashvin DhirubhaiNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Equations To MemoriseDocument3 pagesGCSE Maths Equations To MemoriseexxclaimNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Atoms & MoleculesDocument30 pages2.1 Atoms & MoleculeschirebvutawandaNo ratings yet
- 05 Ohms Law - PresentationDocument9 pages05 Ohms Law - PresentationM.SNo ratings yet
- Last+Minute+Revision +chemistry+ (Abhinav+Sir+ +10!03!2021)Document303 pagesLast+Minute+Revision +chemistry+ (Abhinav+Sir+ +10!03!2021)AISHA AHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- Summary of Sk016 Define/ State Calculation Remark: Consant Avogadro Particles of NumberDocument8 pagesSummary of Sk016 Define/ State Calculation Remark: Consant Avogadro Particles of NumbertimNo ratings yet
- Baconga - Chem 80 Exercise 3A (Lecture 3. Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions I)Document3 pagesBaconga - Chem 80 Exercise 3A (Lecture 3. Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions I)Mary Kate BacongaNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثانيةDocument18 pagesالمحاضرة الثانيةbeiguiiuirrNo ratings yet
- Original PDF Us Solutions Manual To Accompany Elements of Physical Chemistry 7th PDFDocument41 pagesOriginal PDF Us Solutions Manual To Accompany Elements of Physical Chemistry 7th PDFclarence.barcia711100% (38)
- Department of Mathematics & Physics Mariam Zaarour Supervised By: Dr. Hussein FakihDocument1 pageDepartment of Mathematics & Physics Mariam Zaarour Supervised By: Dr. Hussein FakihMariam ZaarourNo ratings yet
- Resumen Formulas SolucionesDocument1 pageResumen Formulas SolucionesJorge DanielNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document12 pagesLesson 1merveNo ratings yet
- Solutions (Chapter 1)Document2 pagesSolutions (Chapter 1)PREET'S KITCHENNo ratings yet
- Sheet III PDFDocument2 pagesSheet III PDFGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FormulasDocument3 pagesChemistry FormulasAlondraNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document29 pagesCH 1Anteneh TarikuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FormulaeDocument285 pagesChemistry FormulaeBadri MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Physical Quantities Units and DimensionsDocument4 pagesChapter 1-Physical Quantities Units and Dimensionsprasad walteNo ratings yet
- 6495375ce254fb00182cacfa ## Mole Concept Short Notes Yakeen 2 0Document2 pages6495375ce254fb00182cacfa ## Mole Concept Short Notes Yakeen 2 0s.yagyan prasad acharyNo ratings yet
- Penentuan Bilangan PeroksidaDocument1 pagePenentuan Bilangan Peroksidasyawal12345No ratings yet
- Formulas and Concept in ChecalDocument3 pagesFormulas and Concept in Checaljillea mendozaNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Decay - DerivationDocument3 pagesRadioactive Decay - DerivationW-d DomNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Mixtures and SolutionsDocument9 pagesLesson 3 - Mixtures and SolutionsMelvyn DarauayNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concept of Chemistry - Short Notes - Arjuna NEET Fastrack 2024Document2 pagesSome Basic Concept of Chemistry - Short Notes - Arjuna NEET Fastrack 2024barnikbanerjee11No ratings yet
- 1.16 Converting UnitsDocument2 pages1.16 Converting Unitswabusb2sNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Solutions UST TemplateDocument15 pagesUnit 2 Solutions UST TemplateCess MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Solution Methodology: FLUENT That Has Been Used in The Study. Details About The Computational ApproachDocument9 pagesSolution Methodology: FLUENT That Has Been Used in The Study. Details About The Computational ApproachSouvik BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Comparison The Experimental Diffusivity and Literature Diffusivity Value of Cobalt (II) ChlorideDocument2 pages5.2 Comparison The Experimental Diffusivity and Literature Diffusivity Value of Cobalt (II) Chloridemiza adlinNo ratings yet
- Probability and Random Processes (15B11MA301)Document17 pagesProbability and Random Processes (15B11MA301)Aditya gaurNo ratings yet
- USTETReviewerScience PDFDocument5 pagesUSTETReviewerScience PDFFrancesca LuisaNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer-DESKTOP-TMOCD0EDocument20 pagesMass Transfer-DESKTOP-TMOCD0EAshna WaseemNo ratings yet
- AplkDocument1 pageAplknuhaNo ratings yet
- L17: Quasi-Fermi Levels and Steady State: EE203 Semiconductor DevicesDocument19 pagesL17: Quasi-Fermi Levels and Steady State: EE203 Semiconductor Devicesabdul ahadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document5 pagesLecture 14RajeevNo ratings yet
- Question 5Document3 pagesQuestion 5i 3l3jNo ratings yet
- Pharm 213L Unit 9 HandoutDocument8 pagesPharm 213L Unit 9 HandoutJazlyn RzelleNo ratings yet
- Turorial 4 Solutions (5769) PDFDocument2 pagesTurorial 4 Solutions (5769) PDFshubhamNo ratings yet
- Driving Force Can Be Expressed As Difference in Mole Fraction AlsoDocument4 pagesDriving Force Can Be Expressed As Difference in Mole Fraction Alsosarthak tripathiNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Methods of Microeconomics: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMethods of Microeconomics: A Simple IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Understanding Vector Calculus: Practical Development and Solved ProblemsFrom EverandUnderstanding Vector Calculus: Practical Development and Solved ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Virtual Verde Release Plan Emails: Email 1Document4 pagesVirtual Verde Release Plan Emails: Email 1Violet StarNo ratings yet
- Unsworth - Re-Branding The City - Changing The Images of PlacesDocument45 pagesUnsworth - Re-Branding The City - Changing The Images of PlacesNatalia Ney100% (2)
- Extraction of Non-Timber Forest Products in The PDFDocument18 pagesExtraction of Non-Timber Forest Products in The PDFRohit Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Read Online 9789351199311 Big Data Black Book Covers Hadoop 2 Mapreduce Hi PDFDocument2 pagesRead Online 9789351199311 Big Data Black Book Covers Hadoop 2 Mapreduce Hi PDFSonali Kadam100% (1)
- Paper 2Document8 pagesPaper 2Antony BrownNo ratings yet
- The Acceptability of Indian Mango Leaves Powdered As A Tea: (Mangifera Indica Linn.)Document22 pagesThe Acceptability of Indian Mango Leaves Powdered As A Tea: (Mangifera Indica Linn.)Marissa M. DoriaNo ratings yet
- Baby Brianna Andrew WaltersDocument14 pagesBaby Brianna Andrew WaltersBaby Brianna50% (2)
- Gianna Pomata (Editor), Nancy G. Siraisi (Editor) - Historia - Empiricism and Erudition in Early Modern Europe (Transformations - Studies in The History of Science and Technology) (2006)Document493 pagesGianna Pomata (Editor), Nancy G. Siraisi (Editor) - Historia - Empiricism and Erudition in Early Modern Europe (Transformations - Studies in The History of Science and Technology) (2006)Marcelo Rizzo100% (1)
- Neuromarketing EssayDocument3 pagesNeuromarketing Essayjorge jmzNo ratings yet
- Introductory EconomicsDocument22 pagesIntroductory Economicswedjefdbenmcve100% (1)
- Chapter 10: Third Party Non-Signatories in English Arbitration LawDocument13 pagesChapter 10: Third Party Non-Signatories in English Arbitration LawBugMyNutsNo ratings yet
- Mohit Maru 4th Semester Internship ReportDocument11 pagesMohit Maru 4th Semester Internship ReportAdhish ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Partnership & Corporation: 2 SEMESTER 2020-2021Document13 pagesPartnership & Corporation: 2 SEMESTER 2020-2021Erika BucaoNo ratings yet
- Ghosh, D. P., 1971, Inverse Filter Coefficients For The Computation of Apparent Resistivity Standard Curves For A Horizontally Stratified EarthDocument7 pagesGhosh, D. P., 1971, Inverse Filter Coefficients For The Computation of Apparent Resistivity Standard Curves For A Horizontally Stratified EarthCinthia MtzNo ratings yet
- The Newton-Leibniz Book Research - Gate - 06!12!2023Document17 pagesThe Newton-Leibniz Book Research - Gate - 06!12!2023Constantine KirichesNo ratings yet
- Practical Interpretation and Application of Exoc Rine Panc Rea Tic Tes Ting in Small AnimalsDocument20 pagesPractical Interpretation and Application of Exoc Rine Panc Rea Tic Tes Ting in Small Animalsl.fernandagonzalez97No ratings yet
- Victor Nee (Editor) - Richard Swedberg (Editor) - The Economic Sociology of Capitalism-Princeton University Press (2020)Document500 pagesVictor Nee (Editor) - Richard Swedberg (Editor) - The Economic Sociology of Capitalism-Princeton University Press (2020)Tornike ChivadzeNo ratings yet
- Early Pregnancy and Its Effect On The Mental Health of Students in Victoria Laguna"Document14 pagesEarly Pregnancy and Its Effect On The Mental Health of Students in Victoria Laguna"Gina HerraduraNo ratings yet
- Porn Sex Versus Real Sex: How Sexually Explicit Material Shapes Our Understanding of Sexual Anatomy, Physiology, and BehaviourDocument23 pagesPorn Sex Versus Real Sex: How Sexually Explicit Material Shapes Our Understanding of Sexual Anatomy, Physiology, and Behaviourzyryll yowNo ratings yet
- ( (LEAD - FIRSTNAME) ) 'S Spouse Visa PackageDocument14 pages( (LEAD - FIRSTNAME) ) 'S Spouse Visa PackageDamon Culbert0% (1)
- Skin DseDocument9 pagesSkin DsePapitas FritasNo ratings yet
- Feb 1 - ScottDocument17 pagesFeb 1 - ScottNyannnNo ratings yet
- Sample ProposalDocument2 pagesSample ProposaltoupieNo ratings yet
- Course Hand Out Comm. Skill BSC AgDocument2 pagesCourse Hand Out Comm. Skill BSC Agfarid khanNo ratings yet
- End-To-End Lung Cancer Screening With Three-Dimensional Deep Learning On Low-Dose Chest Computed TomographyDocument25 pagesEnd-To-End Lung Cancer Screening With Three-Dimensional Deep Learning On Low-Dose Chest Computed TomographyLe Vu Ky NamNo ratings yet
- AVEVA Work Permit ManagerDocument2 pagesAVEVA Work Permit ManagerMohamed Refaat100% (1)
- Diverse Narrative Structures in Contemporary Picturebooks: Opportunities For Children's Meaning-MakingDocument11 pagesDiverse Narrative Structures in Contemporary Picturebooks: Opportunities For Children's Meaning-MakingBlanca HernándezNo ratings yet
- 10 Fonts For A Better WebsiteDocument3 pages10 Fonts For A Better WebsiteAlyzza Kara AcabalNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Commission: Non-Holding of Annual MeetingDocument2 pagesSecurities and Exchange Commission: Non-Holding of Annual MeetingBea AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Mus Culo SkeletalDocument447 pagesMus Culo SkeletalKristine NicoleNo ratings yet