Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochem CH 2 Quiz
Uploaded by
Shiri BlaiseOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biochem CH 2 Quiz
Uploaded by
Shiri BlaiseCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOCHEMISTRY
CHAPTER 2 QUIZ
SHIRI BLAISE LIM
1. How to make soap? What do we call its process? What is the connection of lipids to making
soap?
Mix together Caster Oil & Ethanol and speed it up with hot water then mix it with Saturated
Sodium Chloride Solution in an ice cold water to precipitate. Filler off by means of mixing
distilled water in the formation of soap to test if it is a success. When Lather (foam/forth) is
visible then your detergent is done. And this process is called SAPONIFICATION. From the
word SAPO which means soap in Latin. A soap is a by-product of cholesterol which is a type of
lipid that digests as it functions. Also, bile salt is capable of emulsifying fats and oils while the
enzymes present in it may break them down making a soap very effective in cleaning.
2. How do soaps clean our dirty clothes?
Soap acts as an Emulsifying or Surfactant agent which means a surface-active material that
absorbs oil-water intervention. Every detergent has a Hydrophobic Tail which is attached to
grime & dirt and a Hydrophilic Head which is affixed to water molecules. So, the dirt is pulled
away and washed in water, leaving it clean.
3. Differentiate Phospholipid and Glycolipid in terms of structure.
Phospholipid is composed of 2 Hydrophobic Tails of fatty acids & 1 Hydrophilic Head that is
joint by Glycerol Molecule meanwhile Glycolipid is sugar-containing compound lipid which is
also called Glycosphingolipids that contains carbohydrate groups that is attached to the lipid
residue.
4. What is the importance of Glycolipid to our cells?
Glycolipid is a complex lipid that contains carbohydrates sugar (Glucose & Galactose) which
maintains the stability of cell membrane. It is said to ease cellular intervention and also allows
them to connect with one another to form tissues.
5. Describe the molecule transports across the membrane.
There are three (3) transports across the membrane namely the Passive, Facilitated and Active
Transport. A Passive transport doesn’t require the cell to expand energy and only small
molecules can pass through the pore such as Ions, Sugar, Amino Acids and Nucleotides. And is
said to be a Gap Junction which are channels that connect cells and facilitate the exchange of
small molecules. Facilitated Transport is an interaction between transporter and the
transported molecule. It moves from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration
and moves with concentration gradient. And lastly, the Active Transport moves from a region
of lower to higher concentration against concentration gradient. Needs to expand energy to
change protein shape and exchange one substance for another. And in our Anatomy and
Physiology lesson, the malfunction of active transport can lead to serious health conditions.
6. Why is Cholesterol important to us?
Cholesterol is said to be an abundant steroid (group of plant/animal lipids) in our body.
Precedes all steroid hormones and bile acids and also an important component in the animal
plasma membrane. According to other’s research, the body uses this to build the structure of
a cell membrane. It is also an ingredient to produce vitamin D that is why it is very essential to
the human body.
7. When will Cholesterol be associated with the disease Atherosclerosis? Describe the cause of
increase in numbers of Cholesterol in the blood.
When cholesterol is unbelievably high, it builds up or forms plaque deposits on the walls of
arteries causing it to become narrowed and this disease is called Atherosclerosis (thickening
or hardening of arteries). Narrowed blood vessels reduce blood flow to the heart causing the
person to have higher risk of heart attack, stroke, kidney dis-function or other problems.
Smoking, Unhealthy diet, Lack of exercise and having an underlying condition (high blood
pressure & diabetes) are the causes of the increase of cholesterol in our body.
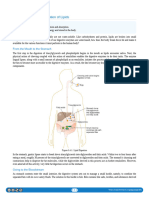
8. What is the role of Bile Salt?
Bile Salt is the product of oxidation of cholesterol. It is stored in the Gallbladder when they’re
not used. Produced in our liver and is excreted in our intestine in order to emulsify fats and
aids in digestion of fats. Absorbs important Vitamins and eliminates toxins.
You might also like
- HW Lipids ARLOSDocument3 pagesHW Lipids ARLOSyan100% (1)
- PHARMACOKINETICS MCQDocument10 pagesPHARMACOKINETICS MCQyan219100% (1)
- Answers To Eocqs: Notes About Mark SchemesDocument3 pagesAnswers To Eocqs: Notes About Mark Schemespukhtoon92No ratings yet
- Molecular Organization of The Plasma MembraneDocument53 pagesMolecular Organization of The Plasma MembraneJD100% (1)
- Lipid MetabolismDocument21 pagesLipid MetabolismTooba GhummanNo ratings yet
- Tsi NewDocument7 pagesTsi NewMarkos sitotawNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument20 pagesBIOLOGYBlaire ReyesNo ratings yet
- Advanced Biology Q3Document3 pagesAdvanced Biology Q3MARITHE ROJIANNE MERCADONo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: 1. What Do You Understand by The Term "Health"?Document7 pagesCarbohydrates: 1. What Do You Understand by The Term "Health"?Fatima SalmanNo ratings yet
- (Assignment 1)Document5 pages(Assignment 1)Zahid HridoyNo ratings yet
- PJK Project 2011 Form 2 (Word 2010)Document30 pagesPJK Project 2011 Form 2 (Word 2010)Charmaine Yeo Shern LiNo ratings yet
- ContentsDocument24 pagesContentsBrandon LohNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption of Lipids-1Document3 pagesDigestion and Absorption of Lipids-1Samuel AgulueNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate IGCSE Guide To BiologyDocument53 pagesThe Ultimate IGCSE Guide To BiologyAbdul Raheem100% (1)
- Lipids Answered Review F 07Document7 pagesLipids Answered Review F 07song flamesNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Its Various TypesDocument8 pagesBiomolecules and Its Various TypesJALAL JAMINo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Written Report LipidsDocument17 pagesGen Bio Written Report LipidsKerenloise Keziah CawasNo ratings yet
- Biokimia LipidDocument6 pagesBiokimia Lipiddimensi warnaNo ratings yet
- Chem 113 Lipid ActivityDocument3 pagesChem 113 Lipid ActivityAlliah MendozaNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate IGCSE Guide To BiologyDocument53 pagesThe Ultimate IGCSE Guide To BiologyMashrafe Aslam100% (3)
- Why Does The Camel Have A Hump?Document20 pagesWhy Does The Camel Have A Hump?Zhao Xuan TanNo ratings yet
- 2.LIPIDS DigestionDocument21 pages2.LIPIDS DigestionAlaa Hisham100% (1)
- Lipids NotesDocument4 pagesLipids NoteskatNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document30 pagesAssignment 2Michelle prouteNo ratings yet
- Unit 8Document55 pagesUnit 8Rediat GossayeNo ratings yet
- Biochem Q.B III Sess Mar 2020Document39 pagesBiochem Q.B III Sess Mar 2020Jinal Jyoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Sp14 10lipidsDocument20 pagesSp14 10lipidsqubituNo ratings yet
- Lipid MetabolismDocument52 pagesLipid MetabolismDr.P.NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Review For Science 10 4TH PERIODICALDocument19 pagesAsynchronous Review For Science 10 4TH PERIODICALchristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- ClinChem Digestion and Absorption of LipidsDocument3 pagesClinChem Digestion and Absorption of LipidsVincent ReyesNo ratings yet
- Biochem 8Document4 pagesBiochem 8Jamila RaniNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculeDocument14 pagesBiological MoleculeRaidioactiveguyNo ratings yet
- Module 3-4Document26 pagesModule 3-4yeoflittlefaithNo ratings yet
- NoteDocument9 pagesNotevarel rcNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument12 pagesBIOLOGYIshrat Hussain JagiraniNo ratings yet
- Biology Capitolo 4 Riassunto PDFDocument5 pagesBiology Capitolo 4 Riassunto PDFEdoardo ColucciNo ratings yet
- Written Report in Biochemistry (Lipids) : Submitted byDocument9 pagesWritten Report in Biochemistry (Lipids) : Submitted byWayne David C. PadullonNo ratings yet
- Fat TranscriptDocument4 pagesFat TranscriptDhruv CVNo ratings yet
- Lipids Project 1Document9 pagesLipids Project 1api-296126866No ratings yet
- Bio 270 Lecture 10 University of TorontoDocument24 pagesBio 270 Lecture 10 University of TorontoJD BaruaNo ratings yet
- Al Biology Carbohydrate LipidsDocument8 pagesAl Biology Carbohydrate LipidsDr.CharinNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Discussion Questions and AnswersDocument2 pagesCarbohydrates Discussion Questions and AnswerslolstudentNo ratings yet
- Lapurga BSES27 Assignment4Document5 pagesLapurga BSES27 Assignment4jerico.lapurgaNo ratings yet
- bIOLOGICAL CHO, CHONDocument82 pagesbIOLOGICAL CHO, CHONgalauraaprilrose96No ratings yet
- Module 9: LipidsDocument2 pagesModule 9: LipidsMariam EskandariNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument10 pagesBiochemWaseem Abbas ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Why Can Glycerophospholipids Form Membranes, While Triacylglycerols Cannot?Document7 pagesWhy Can Glycerophospholipids Form Membranes, While Triacylglycerols Cannot?JunjunNo ratings yet
- Lipids ProteinsDocument5 pagesLipids ProteinsRuchie Ann Pono BaraquilNo ratings yet
- Mirador Kiana Anaphyact3Document4 pagesMirador Kiana Anaphyact3Kiana MiradorNo ratings yet
- Nutrients and Their Importance: M.ANAB 11-TDocument28 pagesNutrients and Their Importance: M.ANAB 11-TAnab ArifNo ratings yet
- BCH 401 Note 2-1Document25 pagesBCH 401 Note 2-1idriscognitoleadsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 LipidDocument36 pagesLecture 3 Lipidaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Name - Digestive System Worksheet: Salivary GlandsDocument5 pagesName - Digestive System Worksheet: Salivary GlandsRJ CamarilloNo ratings yet
- The Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinDocument64 pagesThe Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinSayhidoen CepexNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Introductory BiochemistryDocument17 pagesLecture 2 - Introductory BiochemistryKevonSingh1No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates - Hmhub - Perfect ? Hub For 66K+ ? Hospitality ? StudentsDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates - Hmhub - Perfect ? Hub For 66K+ ? Hospitality ? StudentsPulkit SinghNo ratings yet
- Biology ReportDocument64 pagesBiology ReportChelo IlagNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument37 pagesReviewer in BiologyMICHELLE DE GUZMAN SOTTONo ratings yet
- Cog 13 LipidsDocument27 pagesCog 13 LipidsTahpehs PhiriNo ratings yet
- HivDocument9 pagesHivAamirkhan AamirkhanNo ratings yet
- نسخة من المحاضرة الرابعة.docxDocument5 pagesنسخة من المحاضرة الرابعة.docxربيع مراد ميشو موسىNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1From EverandAQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Question PaperDocument16 pagesQuestion PaperAashi AkterNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMDocument6 pagesBIOCHEMLili M.No ratings yet
- Full Download Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manual PDF Full Chaptersugarysestine.fllo5z100% (18)
- General Biology Chapter8Document272 pagesGeneral Biology Chapter8Lemma Deme ResearcherNo ratings yet
- Difference of Animal and Plant Cells (Onion and Cheek Cells) NotesDocument7 pagesDifference of Animal and Plant Cells (Onion and Cheek Cells) NotesAnjehyn ElleNo ratings yet
- General Biology Mid Exam Summary Semester OneDocument26 pagesGeneral Biology Mid Exam Summary Semester OneDeborah ShirleenNo ratings yet
- Micropara: Chapter 5 NotesDocument8 pagesMicropara: Chapter 5 NotesPatrick JuacallaNo ratings yet
- Sbi4u Ontario CurriculumDocument14 pagesSbi4u Ontario CurriculumqueenmemecaraNo ratings yet
- BIOCELLDocument81 pagesBIOCELLAchraf RbNo ratings yet
- Cho Rio ChitDocument3 pagesCho Rio ChitRisma S PNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document34 pagesChapter 7muhammad yaseenNo ratings yet
- Boron Intrebari Pentru Evaluare enDocument42 pagesBoron Intrebari Pentru Evaluare enAna0% (1)
- Ganong Compiled QuestionsDocument24 pagesGanong Compiled QuestionsFrancisco Casio MataNo ratings yet
- CHPT 12 Intracellular Compartments Anddfd Protein SortingDocument59 pagesCHPT 12 Intracellular Compartments Anddfd Protein SortingSaurabh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Journal 5 - Sugar and Salt Tolerant Yeasts PDFDocument10 pagesJournal 5 - Sugar and Salt Tolerant Yeasts PDFYoanda AlisaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Cell Biology Practice 1: (72 Marks)Document17 pagesUnit 1 Cell Biology Practice 1: (72 Marks)Rita LimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1,2 - Plant Cell Structure - DFQDocument10 pagesLecture 1,2 - Plant Cell Structure - DFQUmarNo ratings yet
- Biology For CAPE Unit 1 Chapter 3 Answers PDFDocument8 pagesBiology For CAPE Unit 1 Chapter 3 Answers PDFGerrald RamoutarNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 NotesDocument36 pagesExam 2 NotesClara PianaltoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Cell BiologyDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Cell Biologyjahp_13625% (4)
- Cell Theory, Parts and FunctionsDocument30 pagesCell Theory, Parts and FunctionsSab IbarretaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exam Science 7Document2 pages2nd Quarter Exam Science 7Franklin John SargadoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document13 pagesExercise 1Estephen FortelaNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Biologi SelDocument81 pagesPengantar Biologi SeldiesNo ratings yet
- 15 CH110 Lipids TimberlakeDocument96 pages15 CH110 Lipids TimberlakeSumit TatedNo ratings yet
- Zoology NotesDocument42 pagesZoology NotesNolour de los SantosNo ratings yet