Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Sampling
Types of Sampling
Uploaded by
Rachel VinarcikOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Sampling
Types of Sampling
Uploaded by
Rachel VinarcikCopyright:
Available Formats
Terms:
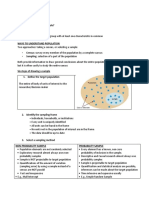
• Sampling
o Tool used to learn about a population
o Used even if units are not individuals
o Represents the population
• Population Value
o What % of voters approve of Trump
• Sample Value
o What % of voters in a sample approve of the President
• Margin of error
o Range of values within which the population value is likely to fall
o About 3% for a sample of 1000
o Margin of error is 1 over sqrt(n)
• Challenges for survey sampling
o Drawing an unbiased sample of the population
o Getting people to respond
• Sampling frame
o List from which units are randomly sampled to be included in the survey
• Biased sampling frame
o One in which some members of the population are more likely to be selected than
others
o Volunteer sample
▪ Call-in or website surveys
o Convenience or haphazard sample
o Network sample
▪ Referrals from participants to collect more people for the sample
Biased Samples:
• Generalize only if we have an unbiased sample of that population
Methods to get unbiased sample:
• Simple random sampling
o Every unit has an equal chance of being selected
▪ Start with a list of everyone in the population
▪ Generate the list of random numbers
▪ Select individuals corresponding with random numbers
• Systematic sampling
o Get a list of everyone
o Calculate skip interval
▪ population size/sample size
▪ pick a random number starting point between 1 and skip interval number
▪ every person has an equal chance of being selected
• Stratified random sampling
o Break population into relevant groups
o Conduct simple random sample among each subgroup
• Challenges
o Costly
o Hard to get a list of all people in the population
• Cluster sampling
o If no list is available or too expensive
o Specify groups of individuals
o Randomly select
o Interview everyone in those groups
1980 Court Case:
• Domino's Pizza vs Domino Sugar
• Sugar
o Sampled 10 cities that did not have Domino's Pizza
o Called people during the day (women at home)
• Domino's Pizza
o Asked people literally in Domino's
Why use?
• Cost
• Hard-to-collect populations
• No theory that indicates that these samples are unbiased
o But better to have biased data than none at all
Types of sampling:
Effectiveness:
You might also like
- Private Preschool Teachers' Understanding and Implementation of Learning Through Play According To Malaysia's National Preschool Standard CurriculumDocument18 pagesPrivate Preschool Teachers' Understanding and Implementation of Learning Through Play According To Malaysia's National Preschool Standard CurriculumJessmyn JmNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Sampling DistributionsDocument78 pagesSampling and Sampling DistributionsASHISH100% (22)
- No One Makes You Shop at Wal-Mart: The Surprising Deceptions of Individual ChoiceFrom EverandNo One Makes You Shop at Wal-Mart: The Surprising Deceptions of Individual ChoiceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- The One and Only Ivan Novel Study PreviewDocument12 pagesThe One and Only Ivan Novel Study Previewsuchi ravalia33% (3)
- Electricity in Agriculture LemströmDocument111 pagesElectricity in Agriculture LemströmScopulus100% (1)
- USSD Gateway SymSoftDocument8 pagesUSSD Gateway SymSoftLubega Charles LwangaNo ratings yet
- Sampling MethodDocument32 pagesSampling MethodGaurav100% (1)
- Sampling Methods PDFDocument20 pagesSampling Methods PDFCyndy Villapando100% (1)
- Presentation On Sampling: Group MembersDocument42 pagesPresentation On Sampling: Group MembersShahid Ali DurraniNo ratings yet
- Sample and Population: Heni Purnama, MnsDocument35 pagesSample and Population: Heni Purnama, MnsRobiNo ratings yet
- DataExtractor UDMA NewDocument175 pagesDataExtractor UDMA Newfuck_off_scribdNo ratings yet
- Carbon Peel Laser Technique To Improve Skin QualitDocument2 pagesCarbon Peel Laser Technique To Improve Skin QualitSarah Albaladejo VerezNo ratings yet
- Bannertail: The Story of A Gray SquirrelDocument302 pagesBannertail: The Story of A Gray SquirrelVeronika Czippelová100% (1)
- Folk ArchitectureDocument8 pagesFolk Architectureカズト桐ケ谷No ratings yet
- The Everyday Enneagram: A Personality Map For Enhancing Your Work, Love, and Life...Every DayFrom EverandThe Everyday Enneagram: A Personality Map For Enhancing Your Work, Love, and Life...Every DayNo ratings yet
- Theory of Sampling: Unit-IiiDocument41 pagesTheory of Sampling: Unit-IiiRachna MGMTNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Other Future FormsDocument4 pagesWorksheet - Other Future FormsJose ParNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument23 pagesSampling119936232141No ratings yet
- MKTG 4110 Class 14Document5 pagesMKTG 4110 Class 14JSNo ratings yet
- Concepts of SamplingDocument23 pagesConcepts of SamplingSharmila ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Statistics Chapter 5.1Document17 pagesStatistics Chapter 5.1thepikawuNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument21 pagesSamplinggaspol davidNo ratings yet
- 1.sampling Methods and Sample Size DeterminationDocument80 pages1.sampling Methods and Sample Size Determinationkebede jifaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Sample and Sampling Techniques.V1Document37 pagesLecture 4 - Sample and Sampling Techniques.V1YeshaelNo ratings yet
- Sampling Procedures/Designs/Methods/ Techniques: Dr. Hemal PandyaDocument109 pagesSampling Procedures/Designs/Methods/ Techniques: Dr. Hemal PandyaHemal PandyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document23 pagesLecture 4thomasNo ratings yet
- Sampling Techniques TULIO JO GABRIELDocument35 pagesSampling Techniques TULIO JO GABRIELIVY FAULVENo ratings yet
- 9 Sample DesignDocument42 pages9 Sample Designcesar suarezNo ratings yet
- RM 2Document22 pagesRM 2Sheikh MashuqueNo ratings yet
- Research and Analysis Skills Lecture 3Document20 pagesResearch and Analysis Skills Lecture 3ahmedehab1772002No ratings yet
- Afifah Ikrimah-5ba-Sampling-Reseacrh MethodologyDocument37 pagesAfifah Ikrimah-5ba-Sampling-Reseacrh MethodologyAfifah IkrimahNo ratings yet
- Sample and Sampling Techniques: By: Dr. Sohail Saadat Community Dentistry DepartmentDocument28 pagesSample and Sampling Techniques: By: Dr. Sohail Saadat Community Dentistry DepartmentShaheryar Ahmed Khan100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - Sampling Lecture Slides 2011-2012Document67 pagesLecture 2 - Sampling Lecture Slides 2011-2012Ismadth2918388No ratings yet
- MRM Mod 3Document121 pagesMRM Mod 3Mamatha NUNo ratings yet
- VII - Sampling MethodsDocument49 pagesVII - Sampling MethodsBehar AbdurahemanNo ratings yet
- Probability Sampling: BY Bhanuteja V.RDocument12 pagesProbability Sampling: BY Bhanuteja V.RPradip MehtaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 SamplingDocument22 pagesLesson 11 SamplingshayndelamagaNo ratings yet
- Chap12 Sample SurveysDocument48 pagesChap12 Sample SurveysCatalina Sabogal OrtegónNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 SamplingDocument41 pagesUnit 3 SamplingDr-Mukesh S TomarNo ratings yet
- Sampling MethodsDocument27 pagesSampling MethodsRehman ytNo ratings yet
- PR1 Lesson 10 SamplingDocument27 pagesPR1 Lesson 10 Samplingdhentiman933No ratings yet
- CH04 SamplingDocument33 pagesCH04 SamplingkinzaNo ratings yet
- Ch5 SamplingDocument10 pagesCh5 SamplingBCA SY 63 Aaditi RanawareNo ratings yet
- Sampling & Sampling Distribution: by Asif HanifDocument25 pagesSampling & Sampling Distribution: by Asif Hanifsadia245No ratings yet
- Sampling Design: By: Kris Joy D. DesembranaDocument18 pagesSampling Design: By: Kris Joy D. Desembranafrancisco macatugobNo ratings yet
- Lect8 SamplingTechniquesDocument21 pagesLect8 SamplingTechniquesKanwal KhanNo ratings yet
- Sampling: - Sampling Methods Are Classified As Either - Probability Sampling - Non-Probability SamplingDocument12 pagesSampling: - Sampling Methods Are Classified As Either - Probability Sampling - Non-Probability SamplingHaider MalikNo ratings yet
- 2006 - Philosophy, Methodology and Action ResearchDocument43 pages2006 - Philosophy, Methodology and Action ResearchnurleennaNo ratings yet
- Sampling 8.3.16Document40 pagesSampling 8.3.16Arham SheikhNo ratings yet
- 0UHB - Quantitative Analysis NumericalDocument71 pages0UHB - Quantitative Analysis NumericalNikhil PawarNo ratings yet
- Lec. 7 SamplingDocument55 pagesLec. 7 SamplingSarvesh JP NambiarNo ratings yet
- Sampling Techniques & Samples TypesDocument55 pagesSampling Techniques & Samples TypesRajan SahNo ratings yet
- Business Data Analytics Students-07-Sampling PDFDocument50 pagesBusiness Data Analytics Students-07-Sampling PDFSiddharth KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 Tecniche Di Campionamento (English)Document16 pages2 Tecniche Di Campionamento (English)marco sponzielloNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document33 pagesWeek 6Sedie PrempsNo ratings yet
- Sampling AssignmentDocument9 pagesSampling AssignmentAdibaNo ratings yet
- Sampling MRDocument51 pagesSampling MRTanisha SinghNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument21 pagesSamplingreffatnizamNo ratings yet
- Week 12Document22 pagesWeek 12lilywhite786No ratings yet
- Sampling - 2019Document38 pagesSampling - 2019Kudzy MatadiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05Document29 pagesLecture 05Yashodara WijekoonNo ratings yet
- Sampling Techniques Ali 2014Document43 pagesSampling Techniques Ali 2014sadamNo ratings yet
- Sampling Lecture SlideDocument27 pagesSampling Lecture SlideLEHLABILE OPHILIA TSHOGANo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesNota 7 SamplingDocument22 pagesLecture NotesNota 7 SamplingPrakash NakarajNo ratings yet
- Research METHODS 1Document33 pagesResearch METHODS 1EUNICE DARKONo ratings yet
- Target Population: Rely On Probability and Non ProbabilityDocument15 pagesTarget Population: Rely On Probability and Non ProbabilityNoufal Asif0% (1)
- Presentación Ingles EstadisticaDocument7 pagesPresentación Ingles EstadisticaAlexis TaveraNo ratings yet
- SIA 2101 - Lecture 8 - Sampling PopulationDocument58 pagesSIA 2101 - Lecture 8 - Sampling Populationmotihama12No ratings yet
- Introduction To Biostatistics: Associate Professor Georgi Iskrov, PHD Department of Social MedicineDocument60 pagesIntroduction To Biostatistics: Associate Professor Georgi Iskrov, PHD Department of Social MedicineKARTHIK SREEKUMARNo ratings yet
- Gis CatDocument7 pagesGis CatMARK KIPKORIR MARITIMNo ratings yet
- They Are Both User InterfaceDocument3 pagesThey Are Both User InterfaceSophia JaposNo ratings yet
- V5 Digital Health Experience-ICT Award Presentation SlideDocument16 pagesV5 Digital Health Experience-ICT Award Presentation SlideJhon KevinNo ratings yet
- General Mental Ability ClassificationDocument6 pagesGeneral Mental Ability ClassificationIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan. 31.01.2023Document4 pagesLesson Plan. 31.01.2023SanjayDominique100% (1)
- Esws at 8edDocument7 pagesEsws at 8edAddy The humanNo ratings yet
- Crackers ListDocument8 pagesCrackers ListrvijayabaskaranNo ratings yet
- New Magic Grammar 3ADocument34 pagesNew Magic Grammar 3AYume ZhuNo ratings yet
- 06 Assurance of SalvationDocument5 pages06 Assurance of SalvationDaniel MagcalasNo ratings yet
- Dav Public School: Art Integrated Project (Social Science)Document17 pagesDav Public School: Art Integrated Project (Social Science)siaNo ratings yet
- EMG ProtocolDocument11 pagesEMG ProtocolWayo Asakura100% (2)
- "The First Man in The Philippinee": Excerpt From Relacion de Las Islas FilipinasDocument1 page"The First Man in The Philippinee": Excerpt From Relacion de Las Islas FilipinasSTAR CHINEMANo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Write Your Answer On The Space ProvidedDocument4 pagesActivity 1: Write Your Answer On The Space ProvidedEki OmallaoNo ratings yet
- Tonsillitis and Adenoiditis: Islamic University Nursing CollegeDocument15 pagesTonsillitis and Adenoiditis: Islamic University Nursing CollegeNinaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Syllabus Kurukshetra UniversityDocument22 pagesMechanical Engineering Syllabus Kurukshetra Universityjasvindersinghsaggu100% (1)
- Online Assignment: TOPIC: Informal Learning ContextsDocument8 pagesOnline Assignment: TOPIC: Informal Learning ContextsMurali SambhuNo ratings yet
- Installation & Maintenance Information IF 1721: ApplicationDocument12 pagesInstallation & Maintenance Information IF 1721: ApplicationAndres VillacisNo ratings yet
- Local Media2381286157614080542Document13 pagesLocal Media2381286157614080542Junie carla GazaNo ratings yet
- (Studies in International Law) Andrea Bianchi - Enforcing International Law Norms Against Terrorism - Hart Publishing (2004)Document572 pages(Studies in International Law) Andrea Bianchi - Enforcing International Law Norms Against Terrorism - Hart Publishing (2004)Abhimanyu SinghNo ratings yet
- DPWH Standard Specification on:COMPACTION AND STABILIZATIONDocument7 pagesDPWH Standard Specification on:COMPACTION AND STABILIZATIONAldever BretanaNo ratings yet
- HP 20.04 Image InstallationDocument9 pagesHP 20.04 Image Installationjon san vicenteNo ratings yet