Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ionic Compounds: Did You Know?
Uploaded by
MOHAMMAD WAAIZ ALAM SAADOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ionic Compounds: Did You Know?
Uploaded by
MOHAMMAD WAAIZ ALAM SAADCopyright:
Available Formats
Ionic Compounds
Summary
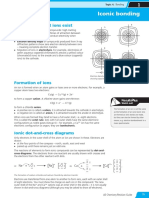
Ionic bonding occurs from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. Ionic bonds
require an electron donor and an electron acceptor. The electron donor is typically a metal,
which transfers its electrons and forms a positively charged ion (cation). The electron acceptor
is typically a nonmetal, which accepts the metal's electrons to form a negatively charged ion
(anion).
Thus, an ionic bond is composed
of cations (typically metals) and Na Cl Na1+ Cl1-
anions (typically non metals)
that sum up to a net charge of 0.
- + -
Everyday Ionic Compounds - +
+
- + -
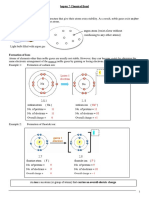
Ionic compounds are formed from ionic bonds that hold
+ - +
them together. Check out the ionic compounds that you
- + -
probably use every day! + - +
- + -
+ - +
NaF Ingredient in toothpaste, added to -
- +
water supplies to promote healthy teeth
Table salt Ionic compounds are composed of
KI If your salt label reads "iodized table salt," cations and anions. These
it contains KI. Promotes healthy thyroid
oppositely charged ions form a
function.
crystal lattice structure to optimize
NaHCO3 Otherwise known as "baking soda."
Used for all purpose cooking and cleaning. their attractionto one another. This
results in a highly stable compound
Properties of Ionic Compounds when in its solid form. When
immersed in water, this crystal
Form a crystal lattice structure due to strong lattice structure breaks apart, and
attraction between cations and anions
the ions separate.
High melting and boiling points due to crystal
lattice structure Did you know?
Form strong electrolytes in water (conduct The melting point of NaCl (table salt)
electricity) is 1,472 F! Why? Because the cations
Opposite charges cause the compounds to be polar and anions form a strong crystal
Dissolve easily in water (because water is also lattice structure, which increases the
polar) bond strength, which increases the
Hard and brittle as a solid amount of energy to break apart their
Act as good insulators when in solid state
crystal lattice structure!
Designed by Rachel Beckham
Ionic Compounds
How to Name
Ionic compounds are named in the following fashion:
Name of cation (metal) + Name of anion (nonmetal), but remove ending and change to "-ide"
Ex: Sr3N2
Strontium Nitrogen Nitride
As shown above, the cation (the metal) is named first, followed by the anion (the nonmetal).
The cation's name is not changed in any way, but the anion's name ending is replaced with
"-ide". This replacing of the name ending always occurs for anions. For example, O 2- is an
oxygen atom, but it is referred to as "oxide" because it is in its anion state.
How to Name Transition Metals
Ionic compounds that contain cations with varying charges must include the charge of that
cation using roman numerals in parenthesis. Because most transition metals have varying
charges, roman numeral typically must be added. This means that you will have to identify
the charge that the cation must have for the net charge to be 0!
For example, write the name of FeO.
Since Fe is a transition metal, we need to find out the charge of Fe for this compound.
We know that:
(number of Fe atoms) (charge of Fe) + (number of O atoms) (charge of O) = 0
Nitrogen's charge is -3. (If you don't know this, go back to the charges of families and
memorize!). When we plug this in along with the number of Fe and N atoms, we get:
(1)(x) + (1)(-2) = 0
x = +2
When we solve for x, we see that Fe = +3.
Therefore, the name of FeO will be iron (II) oxide.
Let's try naming Cu2(CO3)3!
(2)(x) + (3)(-2) = 0
x = +3
When we solve for x, we see that Cu = +3. Thus, the name of Cu2(CO3)3 will be copper (III) oxide.
You Try It!
1. Name the following substances:
a. MgCl2 b. NiBr2 c. Fe2O3 d. Al2O3
Designed by Rachel Beckham
Ionic Compounds
Writing Formulas
Writing formulas for ionic compounds is simple! The total positive charge must equal the total
negative charge so that the net charge is zero. For example, consider lithium and chlorine.
Lithium has 1 valence electron and will donate its outer electron to form a +1 charge, or Li 1+.
Chlorine has 7 valence electrons and will accept lithium's extra electron to form a -1 charge, or
Cl1-. One lithium ion and one chlorine ion will result in a net charge of 0. Thus, the resulting
formula is LiCl. Now consider an ionic compound between Mg and Cl. Mg will donate its two
outer electrons to form a Mg2+ charge. Cl will form a Cl1- ion. In order to have a net charge of 0,
we will need two chloride ions and one magnesium ion. The resulting formula will therefore be
MgCl2. Note that the subscript "2" indicates the number of chloride ions present in that
compound. *Note: In order to write formulas for ionic compounds, you must know the specific
charges of each group on the periodic table. If you don't, go back and review!
The Cross Over Rule
Write symbols Cross over charges Reduce Confirm net charge = 0
and charges
Mg2+ Cl1- = MgCl2 = MgCl2 +2 + [2(-1)] = 0 ✓
Al3+ P3- = Al3P3 = AlP 1(+3) + 1(-3) = 0 ✓
Be2+ Se2- = Be2Se2 = BeSe 1(+2) + 1(-2) = 0 ✓
Ga3+ CO32- = Ga2(CO3)3 = Ga2(CO3)3 2(+3) + 3(-2) = 0 ✓
* Note: NEVER change the subscripts on polyatomic ions. Make sure to put
parenthesis around the polyatomic ion before crossing over the charge!
1. Write out the 2. cross over the 3. reduce to the 4. Do the math to
symbols and magnitudes (remove simplest ratio of confirm that the
charges of the the + or - sign) ions if needed net charge is zero
atoms of the charges.
You Try It!
1. An unknown compound is tested and found to 3. Write formulas for the following
have a low melting point and does not dissolve compounds:
readily in water. Based on this information, is a. Sodium fluoride
this substance an ionic compound? b. Rubidium hydroxide
c. Calcium nitrate
2. Which of the following substances are ionic
d. Copper (II) chloride
compounds?
e. Iron (III) nitrate
MgS, Be3(PO4)2 ,H2SO4, H2O, CH4, Rb2O, CF4
Designed by Rachel Beckham
You might also like
- Unit 4 Chemical Bonding & Molecular StructureDocument29 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Bonding & Molecular StructureVighnesh0% (1)
- Grade 9 - Chemistry - Ionic BondingDocument23 pagesGrade 9 - Chemistry - Ionic BondingPathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Ionic Bonding & Structure: Mrs. Page IB Chem. 2015-2016Document38 pages4.1 Ionic Bonding & Structure: Mrs. Page IB Chem. 2015-2016api-546066323No ratings yet
- Ions - Ionic BondingDocument35 pagesIons - Ionic BondingAmjadNo ratings yet
- Binary Ionic CompoundsDocument26 pagesBinary Ionic CompoundsMaxine de la Torre100% (1)
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding 1 1Document46 pagesIonic and Covalent Bonding 1 1Ivan LazaroNo ratings yet
- AS Level Chemistry Notes: BondingDocument12 pagesAS Level Chemistry Notes: BondingAyesha Ahmed100% (1)
- G 11 BondingDocument11 pagesG 11 BondingTarek FaramawyNo ratings yet
- Stability of Atoms and Formation of IonsDocument10 pagesStability of Atoms and Formation of Ions4A10 HUI OI YU KATRINANo ratings yet
- STD Ionic BondingDocument40 pagesSTD Ionic BondingSergio Casado Payá Year 10No ratings yet
- CH 8 Ionic CompoundsDocument36 pagesCH 8 Ionic CompoundseherrerahghsNo ratings yet
- 05 Chem Bond - Modul - ChemistryDocument11 pages05 Chem Bond - Modul - Chemistryrudi_z100% (1)
- A Closer Look at Silicon - Chemistry Book for Elementary | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandA Closer Look at Silicon - Chemistry Book for Elementary | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- I Graphite As An Electrical Conductor: Si Atoms O AtomsDocument3 pagesI Graphite As An Electrical Conductor: Si Atoms O AtomsAykhan DamirliNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondDocument35 pagesIonic Bondirma.javashviliNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Bonds: Prof. H. K. Khaira Hod, Msme Deptt. Manit, BhopalDocument81 pagesInteratomic Bonds: Prof. H. K. Khaira Hod, Msme Deptt. Manit, Bhopalraj kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic BondingDocument56 pagesChapter 7 Ionic and Metallic BondingCharles GibbsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Presentation - RevisionDocument24 pagesChemical Bonding Presentation - RevisionKnk SeriesNo ratings yet
- 002 Ionic BondingDocument23 pages002 Ionic BondingDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Bonding and StructureDocument4 pagesRevision Notes Bonding and StructureSomeRandomDude - Tutorials - TechNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding 2Document16 pagesIonic Bonding 2Bira NoNo ratings yet
- Ionic Compounds NKCSDDocument28 pagesIonic Compounds NKCSDRalph Bryan HidalgoNo ratings yet
- 13 Ionicnotes ModDocument40 pages13 Ionicnotes ModMara MarianNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure revision cardDocument1 pageBonding and Structure revision cardagentdog175No ratings yet
- Ionic Compounds NKCSDDocument28 pagesIonic Compounds NKCSDRalph Bryan HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Bonding bookletDocument11 pagesBonding bookletAfridxDominatorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Semester 1 SK 026Document36 pagesChemistry: Semester 1 SK 026kjj7760No ratings yet
- Practice Problem: RevisionDocument133 pagesPractice Problem: RevisionJerry Sumok WalterNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding and StructureDocument20 pagesIonic Bonding and StructureKaren OrlanskiNo ratings yet
- 7-8 NSS Chemical BondingDocument16 pages7-8 NSS Chemical Bonding黃淑敏No ratings yet
- Core Bonding - Ionic BondingDocument21 pagesCore Bonding - Ionic BondingMarin PesicNo ratings yet
- 4A Ionic Bonding Edrolo Study Notes AnnotatedDocument17 pages4A Ionic Bonding Edrolo Study Notes AnnotatedMr FiddleNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonds.1Document42 pagesIonic Bonds.1Chad Laurence Vinson CandelonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Ionic BondDocument56 pagesChemical Bonding - Ionic BondFianna GalleroNo ratings yet
- 9 Grade (2022) - Bonding and StructureDocument59 pages9 Grade (2022) - Bonding and StructureTarun PNo ratings yet
- Y10B (AP) Bonding 2022Document41 pagesY10B (AP) Bonding 2022Mulki MohamedNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonds Notes: Essential Question: What Are Ions and How Are They Formed?Document31 pagesIonic and Covalent Bonds Notes: Essential Question: What Are Ions and How Are They Formed?Gerlie VelascoNo ratings yet
- Ionic bonding and structureDocument49 pagesIonic bonding and structureJuan Fernando Velasco ForeroNo ratings yet
- Intro To Ionic CompoundsDocument23 pagesIntro To Ionic Compoundsapi-483662721No ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 4 Atoms Combining PresentationDocument73 pagesChemistry Chapter 4 Atoms Combining Presentationchitminthu560345No ratings yet
- 4.chemzone - Formulas and Names of CompoundsDocument14 pages4.chemzone - Formulas and Names of CompoundsIANo ratings yet
- G9 Science Q2-Week 2 - Types of CompoundsDocument79 pagesG9 Science Q2-Week 2 - Types of CompoundsKarina GentonNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Ionic BondsDocument6 pages5.2 Ionic BondspapajahatNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Types of Chemical BondsDocument12 pages4.1 Types of Chemical BondsNeha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonds Chemistry Mrs Coyle Part ADocument35 pagesIonic Bonds Chemistry Mrs Coyle Part AthetlpxNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Chemistry Section 1 Lesson 4Document45 pagesiGCSE Chemistry Section 1 Lesson 4Marin PesicNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument72 pagesIonic BondingibanathinkomboniNo ratings yet
- Covalent & Ionic Bonding: NotesDocument11 pagesCovalent & Ionic Bonding: NotesArfaan WaheedNo ratings yet
- Stalagmites and Stalactites Are Composed of Ionic Compounds Calcium Carbonate and Magnesium CarbonateDocument50 pagesStalagmites and Stalactites Are Composed of Ionic Compounds Calcium Carbonate and Magnesium CarbonateAustin GirardNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Products TH 4.0 Molten PPT (Converted To PDFDocument73 pagesElectrolysis Products TH 4.0 Molten PPT (Converted To PDFT HanslaNo ratings yet
- Ions and Ionic BondDocument21 pagesIons and Ionic Bondchickuwa pawawawaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry: Chapter OutlineDocument68 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry: Chapter OutlineMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Chem - MIST Sec A - Chem BondingDocument102 pagesChem - MIST Sec A - Chem BondingRakib HaqueNo ratings yet
- Chemistrypresentationalifafi 140302090537 Phpapp01Document20 pagesChemistrypresentationalifafi 140302090537 Phpapp01Chris MadridNo ratings yet
- ChemChapter8 PANES PDFDocument7 pagesChemChapter8 PANES PDFTn F'dzNo ratings yet
- Module in Chemical BondingDocument36 pagesModule in Chemical BondingJaycee De LeonNo ratings yet
- Ions & Ionic Bonds (Multiple Choice) QPDocument7 pagesIons & Ionic Bonds (Multiple Choice) QPBăng Băng LêNo ratings yet
- Science-Grade-9-Handout-2-Ion Formation and LEDSDocument10 pagesScience-Grade-9-Handout-2-Ion Formation and LEDSClinton YmbongNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Inch 2101Document80 pagesCh3 Inch 2101liyou eshetuNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonds: Chemistry Mrs. CoyleDocument35 pagesIonic Bonds: Chemistry Mrs. CoyleNeen NaazNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table ReportDocument7 pagesPeriodic Table Reportangelo pascuaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry AtomicDocument13 pagesOrganic Chemistry AtomicJasmin SauraNo ratings yet
- NMR Facility Service Form: User InformationDocument2 pagesNMR Facility Service Form: User InformationJudimar DulayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - NMR SpectrosDocument13 pagesChapter 15 - NMR SpectrosHepi NuriyawanNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument33 pagesMole Concept: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryNaman AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Build An AtomDocument2 pagesBuild An Atomapi-553259322No ratings yet
- Chemistry I: Lecture Notes on Atomic StructureDocument55 pagesChemistry I: Lecture Notes on Atomic StructureHà ChiNo ratings yet
- 7 markscheme-HL-paper1Document29 pages7 markscheme-HL-paper1Onur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- ATOICV1 8 0 Electronic Spectra of Transition Metal ComplexesDocument136 pagesATOICV1 8 0 Electronic Spectra of Transition Metal ComplexesNITISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of SpectrosDocument10 pagesBasic Principles of SpectrosAlexiss Chavez-De la MoraNo ratings yet
- BMS1011 W1L1Document39 pagesBMS1011 W1L1PutterNo ratings yet
- Group Displacement Law: Z M - Z-2 M-4 2 4Document2 pagesGroup Displacement Law: Z M - Z-2 M-4 2 4Athira I PNo ratings yet
- (English) Particles and Waves - The Central Mystery of Quantum Mechanics - Chad Orzel (DownSub - Com)Document4 pages(English) Particles and Waves - The Central Mystery of Quantum Mechanics - Chad Orzel (DownSub - Com)SatAprNo ratings yet
- Bio 112 - Activity 3Document3 pagesBio 112 - Activity 3LAGMAY, Daniel Scott G.No ratings yet
- Fariz Arif Khan - Periodic TableDocument4 pagesFariz Arif Khan - Periodic TableFariz Arif KhanNo ratings yet
- Lectures UV SpectrosDocument20 pagesLectures UV SpectrosTaufi Hemyari100% (2)
- Assertion Reason Q (For D and F Block Elements)Document5 pagesAssertion Reason Q (For D and F Block Elements)kabir singhNo ratings yet
- Core 6 SPECIMEN 2018-19 PDFDocument11 pagesCore 6 SPECIMEN 2018-19 PDFHarry VincentNo ratings yet
- Photochemistry: Dr. M.A Kazi Institute of Chemistry University of Sindh JamshoroDocument22 pagesPhotochemistry: Dr. M.A Kazi Institute of Chemistry University of Sindh JamshoroPeerBuxNo ratings yet
- Vanadocene oxidation state from magnetic momentDocument6 pagesVanadocene oxidation state from magnetic momentANGIE PAOLA RODELO PANZANo ratings yet
- Espectros de RMN PDFDocument47 pagesEspectros de RMN PDFJéssicaNo ratings yet
- Bohr's Radius DerivationDocument2 pagesBohr's Radius Derivationmuputism100% (3)
- Atomic Structure GuideDocument11 pagesAtomic Structure GuideLizbeth ChiNo ratings yet
- Valence Electrons and Electron Configuration: Chemistry WorksheetDocument2 pagesValence Electrons and Electron Configuration: Chemistry Worksheetrobertkani2004No ratings yet
- Bonding and Molecular Shapes: Experiment 6Document24 pagesBonding and Molecular Shapes: Experiment 6Nonilyn GalanoNo ratings yet
- Dissociation Energy of Iodine by Absorption SpectroscopyFINALDocument12 pagesDissociation Energy of Iodine by Absorption SpectroscopyFINALwillharvey94100% (1)
- FleroniumDocument11 pagesFleroniumRiki BebiNo ratings yet
- DLL 2QDocument55 pagesDLL 2Qrenver.perezNo ratings yet
- Learning about atomic structure and the periodic tableDocument40 pagesLearning about atomic structure and the periodic tableFontanilla, Nathaniel D.No ratings yet