Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study On TB
Uploaded by
Melvin D. Ramos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views27 pagesThis document provides information on the drug isoniazid, including its indications, contraindications, mechanism of action, side effects, and the nursing responsibilities for its administration. It indicates that isoniazid is used to prevent and treat tuberculosis by interfering with lipid and nucleic acid synthesis in actively growing mycobacterium tuberculosis cells. Potential side effects include CNS effects, hepatitis, peripheral neuritis, and hypersensitivity reactions. Nurses are responsible for educating patients, monitoring for effectiveness and side effects like hepatitis and visual changes, and ensuring proper dosage administration and supplementation with vitamin B6.
Original Description:
Original Title
Drug Study on TB
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on the drug isoniazid, including its indications, contraindications, mechanism of action, side effects, and the nursing responsibilities for its administration. It indicates that isoniazid is used to prevent and treat tuberculosis by interfering with lipid and nucleic acid synthesis in actively growing mycobacterium tuberculosis cells. Potential side effects include CNS effects, hepatitis, peripheral neuritis, and hypersensitivity reactions. Nurses are responsible for educating patients, monitoring for effectiveness and side effects like hepatitis and visual changes, and ensuring proper dosage administration and supplementation with vitamin B6.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views27 pagesDrug Study On TB
Uploaded by
Melvin D. RamosThis document provides information on the drug isoniazid, including its indications, contraindications, mechanism of action, side effects, and the nursing responsibilities for its administration. It indicates that isoniazid is used to prevent and treat tuberculosis by interfering with lipid and nucleic acid synthesis in actively growing mycobacterium tuberculosis cells. Potential side effects include CNS effects, hepatitis, peripheral neuritis, and hypersensitivity reactions. Nurses are responsible for educating patients, monitoring for effectiveness and side effects like hepatitis and visual changes, and ensuring proper dosage administration and supplementation with vitamin B6.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
STUDENT NAME: KRISHELLE ANNE TEOFILO ROTATION: 3RD ROTATION AREA: VCHO
YR. LEVEL AND SEC: BSN 2 B DATE: March 22,2021 CLINICAL INSTRUCTOR: CLAUDINE ALMACHAR
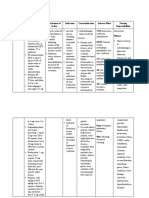
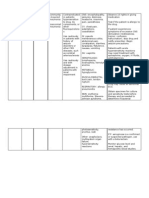
NAME OF DRUG INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
ACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: To prevent tuberculosis Acute hepatic disease Interferes with lipid and CNS: Clumsiness, 1. Nurse needs to give
Isoniazid Isoniazid-related liver nucleic acid synthesis in confusion, dizziness, knowledge to the
As an adjunct to treat damage actively growing encephalopathy, client on how to take
Brand name: active tuberculosis Fatal hepatitis tubercule bacilli cells. It fatigue, fever, it and tell the
Isotamine Risk of developing also disrupts bacterial hallucinations, possible risks and
Actively growing hepatitis cell wall synthesis and neurotoxicity, benefits of taking
Classification: tubercle bacilli Cautiously in elderly may intefere with paresthesia, peripheral the drug.
Antibiotics Chronic non-isoniazid- mycolic acid synthesis neuritis, psychosis, 2. Monitor for
related liver disease in mycobacterial cells. seizures, weakness therapeutic
Dosage: Chronic alcoholism CV: Vasculitis effectiveness:
Injection: 100mg/mL EENT: Optic neuritis Evident within the
Seizure disorders
Oral solution: ENDO: Gynecomastia, first 2–3 wk of
CNS depression Hyperglycemia therapy. Over 90%
50mg/5Ml
Tablets: 50 mg, Hypersensitivity to GI: Abdominal pain, of patients receiving
100mg, 300 mg isoniazid anorexia, elevated liver optimal therapy
function test results, have negative
Frequency: epigastric distress, sputum by the sixth
Tablet: OD Once a hepatitis, nausea, month.
day pancreatitis, vomiting 3. Perform appropriate
IV/IM: as needed GU: Glycosuria susceptibility tests
HEME: before initiation of
Route: Agranulocytosis, therapy and
IV Aplastic anemia, periodically
IM eosinophilia, hemolytic thereafter to detect
Oral anemia, sideroblastic possible bacterial
anemia, resistance.
thrombocytopenia 4. Lab tests: Monitor
MS: Arthralgia, joint hepatic function
stiffness periodically.
SKIN: jaundice, Isoniazid hepatitis
pruritus, rash, Steven (sometimes fatal)
Johnson syndrome usually develops
OTHER: Anaphylaxis, during the first 3–6
hypocalcemia, mo of treatment, but
hypophosphatemia, may occur at any
injection-site irritation, time during therapy;
lupus-like symptoms, much more frequent
lymphadenopathy in patients 35 y or
older, especially in
those who ingest
alcohol daily.
5. Monitor for visual
disturbance. An eye
examination may be
warranted.
6. Note: Inactivation of
the drug is
genetically
determined. Slow
inactivation leads to
high plasma drug
levels and increased
risk of toxicity.
7. Isoniazid-induced
pyridoxine (vitamin
B6) depletion causes
neurotoxic effects. B
6 supplementation
(10–50 mg) usually
accompanies
isoniazid use.
8. Peripheral neuritis,
the most common
toxic effect, is
usually preceded by
paresthesia of feet
and hands
(numbness, tingling,
burning). Patients
particularly
susceptible include
alcoholics and
patients with liver
disease,
malnourished
patients, diabetics,
slow inactivators,
pregnant women,
and older adults.
9. Monitor BP during
the period of dosage
adjustment. Some
experience
orthostatic
hypotension;
therefore, caution
against rapid
positional changes.
10. Monitor diabetics
for loss of glycemic
control.
11. Check weight at
least twice weekly
under standard
conditions.
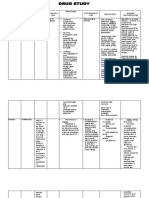
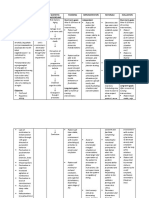
NAME OF DRUG INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
ACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: As adjunct to treat Concurrent use of Inhibits bacterial and CNS: headache, 1. Administer on an
Rifampicin tuberculosis caused by nonnucleoside reverse mycobacterial RNA drowsiness, fatigue, empty stomach, 1
all strains of transcriptase inhibitors synthesis by binding to dizziness, inability to hr before or 2 hr
Brand name: Mycobacterium or protease inhibitors DNA-dependent RNA concentrate, mental after meals.
Rifadin, Rifadin IV, tuberculosis by patients with HIV polymerase, thereby confusion, generalized 2. Administer in a
Rimactane, Rofact Hypersensitivity blocking RNA numbness, muscle single daily dose.
Prevention of disease Acute hepatic disease transcription. Exhibits weakness, visual 3. Consult
Classification: caused by Haemophilus Lactation dose-dependent disturbances pharmacists for
Antimycobacterial, influenzae type B in bactericidal or Dermatologic: Rash, rifampin
Atitubercular close contacts bacteriostatic action. It pruritus, urtic aria, suspension for
is highly effective flushing, reddish patients unable to
Dosage: Treatment for against rapidly dividing discoloration of body swallow capsules.
Adults: 600mg every tuberculosis and bacilli in extracellular fluids - tears, saliva, 4. Prepare patient for
12 hr for 2 days Neisseria meningitidis cavitary lesions, such as urine, sweat, sputum. the reddish-orange
Infants and children: bacteria but have no those found in GI: heartburn, distress, coloring of body
10 mg/kg Maximum: symptoms of disease, nasopharynx. anorexia, vomiting gas, fluids (urine,
600 mg daily mycobacteriu m avium cramps, diarrhea, sweat, sputum,
Infants under age 1 complex, leprosy, and hepatitis, pancreatitis. tears, feces,
month: 5 mg/kg Legionnaires disease GU: hemoglobinuria, saliva); soft
Frequency: hematuria, renal contact lenses may
Adults: 600mg every To eliminate insufficiency, acute be permanently
12 hr for 2 days meningococci from renal failure, menstrual stained; advise
Infants and children: nasopharynx of disturbances patients not to
10 mg/kg every 12 hr asymptomatic carriers Hematologic: wear them during
for 2 days of Neisseria eosinophilia, therapy.
Infants under age 1 meningitidis thrombocytopenia, 5. Warning: arrange
month: 5 mg/kg every transient leukopenia, for follow-up visits
12 hr for 2 days hemolytic anemia, for liver and renal
decreased Hgb, function tests,
Route: hemolysis CBC, and
Oral suspension RESP: Shortness of ophthalmic
Capsules breath, wheezing examination.
IV infusion MS: Arthralgia,
extremity pain, muscle
weakness, myalgia
EENT: Conjunctivitis,
Discolored saliva,
tears, sputum, mouth
and tongue soreness,
periorbital edema
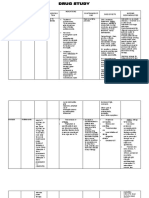
NAME OF DRUG INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
ACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: As adjunct to treat Hypersensitivity Ethambutol is CNS: Burning 1. Should be taken
Ethambutol tuberculosis and Inability to report bacteriostatic against sensation or weakness with food
hydrochloride atypical mycobacterial changes in vision actively growing TB in arms and legs, 2. Advice patient to
infections caused by Optic neuritis bacilli. It works by confusion, take medication
Brand name: Mycobacterium Retrobulbar neuritis obstructing the disorientation, exactly as directed
Etibi, Myambutol tuberculosis People with diabetic formation of cell wall. dizziness, fever, if a dose is missed
retinopathy Mycolic acids attach to headache, malaise, take as soon as
Classification: To prevent tuberculosis Clouding of the lens of the 5'-hydroxyl groups paresthesia, peripheral possible Perform
Antitubercular the eye called of D-arabinose residues neuritis C&S prior to and
cataracts, sudden of arabinogalactan and EENT: Blurred vision, periodically
Dosage: blindness and pain form mycolyl- decreased visual acuity, throughout
Adults and upon moving the eye arabinogalactan- eye pain, optic neuritis, therapy.
adolescents who peptidoglycan complex red-green color 3. Perform
Decreased kidney
haven’t received function
in the cell wall. It blindness ophthalmoscopic
previous disrupts GI: Abdominal pain, examination prior
antituberculotic arabinogalactan anorexia, hepatic to and at monthly
therapy: 15mg/kg synthesis by inhibiting dysfunction, nausea, intervals during
Adults and the enzyme arabinosyl vomiting therapy. Test eyes
adolescents who have transferase. Disruption HEME: Leukopenia, separately as well
previous of the arabinogalactan neutropenia, thrombo- as together.
antituberculotic synthesis inhibits the cytopenia MS: 4. Note: Ocular
therapy: 25 mg/kg; formation of this Arthralgia, gouty toxicity generally
after 60 days, complex and leads to arthritis, joint pain appears within 1–7
decreased to 15mg/kg increased permeability RESP: Pulmonary mo after start of
of the cell wall. infiltrates therapy. Symptoms
Frequency: SKIN: Dermatitis, usually disappear
Daily May suppress bacterial erythema multiforme, within several
complication by pruritus, rash Other: weeks to months
Route: interfering with RNA Anaphylaxis, after drug is
Oral synthesis in susceptible hypersensitivity discontinued,
bacteria that are actively syndrome (rash or depending on
dividing exfoliative dermatitis, degree of ocular
eosinophilia, and one of damage.
the following: hepatitis, 5. Monitor I&O ratio
pneumonitis, nephritis, in patients with
myocarditis, renal impairment.
pericarditis), Report oliguria or
lymphadenopathy any significant
changes in ratio or
in laboratory
reports of kidney
function. Systemic
accumulation with
toxicity can result
from delayed drug
excretion.
6. Lab tests: Perform
liver and kidney
function tests,
CBC, and serum
uric acid levels at
regular intervals
throughout therapy
7. Teach patient to
recognize possible
adverse reactions
to ethambutol. •
Advise patient to
take drug with
food if he
experiences
adverse GI
reactions.
8. Instruct patient to
take a missed dose
as soon as he
remembers, unless
it’s nearly time for
the next dose, but
not to double dose.
9. Explain that
ethambutol therapy
may last months or
years and that
compliance is
essential.
10. Advise patient to
notify prescriber if
no improvement
occurs within 3
weeks of starting
ethambutol
therapy; if
bothersome or
severe adverse
reactions occur; if
his vision changes;
or if a rash, fever,
or joint pain
(possible
hypersensitivity)
develops.
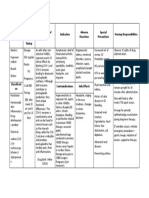
NAME OF DRUG INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
ACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: As adjunct to treat Acute gout Inhibits growth of CNS: Burning or pain 1. Review liver
Pyrazinamide tuberculosis, along with hypersensitivity to Mycobacterium in arms and legs, function test
other antitubercular pyrazinamide or its tuberculosis by clumsiness, confusion, results before and
Brand name: drugs. components decreasing pH level; depression, mental or every 2 to 4 weeks
Tebrazid Severe hepatic exhibits bactericidal or mood changes, during therapy.
damage bacteriostatic action, paresthesia, 2. Be aware that drug
Classification: depending on blood unsteadiness can affect the
Antitubecular pyrazinamide level CV: Orthostatic accuracy of certain
hypotension urine ketone strip
Dosage: EENT: Blurred vision, test results.
50 to 70 mg/kg eye pain, increased 3. Because drug is
salivation, metallic metabolized by
Frequency: taste, optic neuritis, liver, monitor
2 or 3 times a week stomatitis, vision loss patient for
ENDO: Goiter, evidence of
Route: hypoglycemia, hypo- hepatotoxicity,
Oral thyroidism such as darkened
GI: Anorexia, hepatitis, urine, fever,
nausea, vomiting jaundice, malaise,
SKIN: Jaundice, rash nausea, severe pain
HEME: Porphyria in feet or toes, and
MS: Arthralgia, gout, vomiting.
myalgia 4. Instruct patient to
SKIN: Acne, take a missed dose
photosensitivity, as soon as he
pruritus, rash, urticaria remembers unless
it’s nearly time for
the next dose.
Caution him not to
double the dose.
5. Encourage patient
to notify prescriber
if no improvement
occurs within 3
weeks; if
bothersome or
severe adverse
reactions occur; if
his vision changes;
or if he has
burning,
numbness, pain, or
tingling in his
hands and feet.
NAME OF DRUG INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
ACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: To manage, or as Concurrent aliskiren Inhibits CNS: dizziness, fatigue, 1. If hypotension
Candesartan adjunct in managing, therapy vasoconstrictive action headache. occurs after a dose
hypertension Diabetes of angiotensin II by CV: chest pain, of candesartan,
Brand name: Renal impairment blocking angiotensin II peripheral edema place the patient in a
Altacand To treat heart failure in GRF less than 60 receptor on the surface EENT: pharyngitis, supine position and
patients with an ejection ml/min of vascular smooth rhinitis, sinusitis treat appropriately.
Classification: fraction of 40% or less Hypersensitivity to muscle and other tissue GI: abdominal pain, 2. Most of the drug's
Antihypertensive and NYHA class II–IV candesartan or its cells. diarrhea, nausea, antihypertensive
to reduce the risk of components vomiting effects occur within
Dosage: death from Patients who are Selectively blocks GU: albuminuria 2 weeks. Maximal
Adults. Initial: 16 mg cardiovascular causes volume or salt binding of angiotensin Musculoskeletal: effect may take 4 to
Maintenance: 8 to and reduce depleted; may cause (AT) II to AT1 receptor arthralgia, back pain. 6 weeks. Diuretic
32 mg daily or 4 to 16 hospitalizations for symptoms of sites in many tissues, Respiratory: coughing, may be added if BP
mg every 12 hr. heart failure hypotension including vascular bronchitis, URI. isn’t controlled by
smooth muscle and Other: Angioedema drug alone.
Children younger than
Frequency: adrenal glands. This 3. Carefully monitor
age 1
Initial: Daily inhibits elderly patients and
Maintenance: 8 to vasoconstrictive and those with renal
32 mg daily or 4 to 16 aldosterone-secreting disease for
mg every 12 hr. effects of AT II, which therapeutic response
reduces blood pressure. and adverse
Route: reactions.
Oral 4. Inform female
patient of
childbearing
potential of the
consequences of
exposure to drug
during pregnancy
and to notify the
prescriber
immediately if
pregnancy is
suspected.
5. Advise
breastfeeding
patients of the risk
of adverse effects on
the infant and the
need to stop either
breastfeeding or
drug. Instruct
patients to store
drug at room
temperature in
tightly sealed
containers.
6. Inform the patient to
report all adverse
reactions without
delay.
7. Tell the patient that
the drug may be
taken without regard
to meals.
8. If patient has known
or suspected
hypovolemia and/or
salt depletion such
as may occur with
prolonged diuretic
therapy, dietary salt
restriction, dialysis,
diarrhea or
vomiting, expect to
provide treatment,
such as I.V. normal
saline solution, as
prescribed, to
correct it before
starting candesartan.
9. Continue to monitor
blood pressure
throughout
candesartan therapy,
especially after a
dosage increase.
10. Monitor patient
closely during major
surgery and
anesthesia because
candesartan
increases risk of
hypotension by
blocking
renin-angiotensin
system.
11. Watch for elevated
BUN and serum
creatinine levels,
especially if patient
has heart failure or
impaired renal
function; drug may
cause acute renal
failure. Report
significant or
persistent increases
immediately.
12. If blood pressure
isn’t controlled with
candesartan alone,
expect to give a
diuretic, such as
hydrochlorothiazide,
as prescribed.
NAME OF DRUG INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
ACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: To manage • Hypersensitivity to the Blocks binding of CNS: Dizziness, 1. In some patients,
Losartan Potassium hypertension drugs and its contents angiotensin II to fatigue, headache, losartan is more
• Diabetic patients receptor sites in many insomnia, malaise effective when
Brand name: To treat nephropathy in • Impaired renal or tissues, including CV: Hypotension given in two
Cozaar patients with type 2 hepatic function vascular smooth muscle EENT: Nasal divided doses daily;
diabetes and • Patients undergoing and adrenal glands. congestion it may be used with
Classification: hypertension aliskiren therapy Angiotensin II is a GI: Diarrhea, other
Antihypertensive potent vasoconstrictor indigestion, nausea, antihypertensives.
To reduce stroke risk in that also stimulates the vomiting 2. Know that patients
Dosage: patients with adrenal cortex to secrete HEME: of African descent
Adults: 50 mg Dosage hypertension and left aldosterone. The Thrombocytopenia MS: with hypertension
Children age 6 and ventricular hypertrophy inhibiting effects of Back pain, leg pain, and left ventricular
over: 0.7 mg/kg angiotensin II reduce muscle spasms hypertrophy may
blood pressure. RESP: Cough, upper not benefit from
Frequency: Inhibits vasoconst respiratory tract losartan to reduce
OD rictive and aldosteron e- infection stroke risk.
secreting action of SKIN: Erythroderma 3. Monitor blood
Route: angiotensi nII by Other: Angioedema, pressure and renal
Oral blocking angiotensi n II hyperkalemia, function studies to
receptor on the surface hyponatremia evaluate drug
of vascular smooth effectiveness.
muscle and other tissue 4. Periodically
cells. monitor patient’s
serum potassium
level, as
appropriate, to
detect
hyperkalemia.
5. Monitor patient for
muscle pain; rarely,
rhabdomyolysis
develops in patients
taking other
angiotensin II
receptor blockers.
NAME OF DRUG INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
ACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: To manage • Concurrent Blocks angiotensin II CNS: Asthenia, 1. Give telmisartan
Telmisartan hypertension, alone or aliskiren therapy from binding to receptor dizziness, cautiously to
with other • Diabetes or renal sites in many tissues, fatigue, headache, patients with
Brand name: antihypertensives impairment including vascular syncope, weakness dehydration or
Micardis • GFR less than 60 smooth muscle and CV: Atrial fibrillation, hyponatremia.
To reduce risk of MI, ml/min adrenal glands. This bradycardia, chest pain, 2. Expect prescriber
Classification: stroke, or death from • Hypersensitivity to action inhibits the congestive heart failure, to add a diuretic to
Antihypertensive cardiovascular causes telmisartan or its vasoconstrictive and hypertension, regimen if
in patients at high risk components aldosterone-secreting hypotension, patient’s blood
Dosage: who are unable to take • Biliary obstruction effects of angiotensin II, MI, orthostatic pressure isn’t well
Adults: 40 mg ACE inhibitors disorders which reduces blood hypotension, controlled by
Adults age 55 and • Renal and hepatic pressure. peripheral edema telmisartan.
over: 80 mg insufficiency EENT: Pharyngitis, 3. Check patient’s
sinusitis blood pressure
Frequency: ENDO: Hypoglycemia regularly. Be
OD (in diabetics) prepared to treat
GI: Abdominal pain, symptomatic
Route: diarrhea, hypotension by
Oral elevated liver enzyme placing patient in
levels, supine position
indigestion, nausea, and giving normal
vomiting saline solution, as
GU: Acute renal failure, ordered.
erectile 4. Monitor BUN and
dysfunction, serum creatinine
renal dysfunction, UTI levels and urine
HEME: Anemia, output in patients
eosinophilia, with impaired
thrombocytopenia renal function
MS: Back pain, leg or because they’re at
muscle cramps, myalgia, increased risk for
tendon pain, tendinitis, oliguria,
tenosynovitis progressive
RESP: ACE cough, azotemia, and
upper possibly acute
respiratory tract renal failure.
infection 5. Monitor liver
SKIN: Diaphoresis, function test
erythema, rash, results, as
urticaria appropriate, and
Other: Anaphylaxis, assess for evidence
angioedema, elevated of drug toxicity in
uric patients with
acid level, flulike severe hepatic
symptoms disease because
they’re at
increased risk for
toxicity from
increased drug
accumulation.
6. Avoid using
telmisartan in
pregnant women
during second and
third trimesters
because drug can
increase the risk of
fetal harm. patient
teaching
7. Advise patient to
avoid hazardous
activities until
telmisartan’s CNS
effects are known.
8. Instruct patient to
change position
slowly to minimize
effects of
orthostatic
hypotension.
9. Urge patient to
immediately notify
prescriber about
diarrhea, dizziness,
severe nausea, or
vomiting.
10. Instruct patient to
consult prescriber
before taking any
new drug.
11. Advise patient to
drink adequate
amounts of fluid
during hot weather
and when
exercising.
12. Advise female
patients of
childbearing age to
notify presciber
immediately about
known or
suspected
pregnancy.
NAME OF DRUG INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
ACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: To control blood • Chronic intestinal Inhibits action of alpha- CV: Edema 1. Be aware that
Acarbose glucose level in patients disease amylase and GI: Abdominal acarbose isn’t
with type 2 (non– • Cirrhosis alphaglucoside distention and pain, recommended for
Brand name: insulin-dependent) • Colonic ulceration, enzymes. Normally, diarrhea, flatulence, patients with
Precose diabetes mellitus when conditions that may alphaamylase fulminant hepatitis, significant renal
the level can’t be deteriorate because of hydrolyzes complex hepatotoxicity, ileus, dysfunction and a
Classification: controlled by diet alone increased gas starches to intestinal wall gas-filled serum creatinine
Antidiabetics formation in intestines oligosaccharides in the cysts, jaundice level above 2 mg/dl.
Management of type 2 • Diabetic ketoacidosis, small intestine and HEME: 2. If patient is
Dosage: diabetes in conjunction digestive or alpha-glucoside Thrombocytopenia receiving acarbose
25mg/tablet with dietary therapy; absorption disorders hydrolyzes SKIN: Erythema, and a sulfonylurea
may be used with • History of bowel oligosaccharides, exanthema, rash, or insulin to
Frequency: insulin or other obstruction, trisaccharides, and urticaria enhance glucose
TID Thrice a Day hypoglycemic agents. • Hypersensitivity to disaccharides to glucose control, check blood
acarbose and other glucose level often,
Route: • Inflammatory bowel monosaccharides in the as appropriate.
Oral disease brush border of the 3. Store drug in sealed
small intestine. In container in cool
diabetic patients, environment.
acarbose inhibits these 4. Expect to decrease
actions and delays dosage to control GI
glucose absorption, upset.
reducing blood glucose 5. Monitor
level after meals. glycosylated
hemoglobin level as
ordered every
3 months for first
year to evaluate
glucose control and
patient compliance.
6. Monitor hematocrit
and serum AST
level every
3 months during
first year of therapy
and periodically
thereafter, as
ordered, because
acarbose may
decrease hematocrit
and increase serum
AST level. patient
teaching
7. Explain importance
of self-monitoring
glucose level during
acarbose therapy.
8. Teach patient to
recognize
hypoglycemia and
hyperglycemia.
9. Warn patient that
noncompliance with
treatment can
increase risk of
diabetic
complications,
including
neuropathy,
retinopathy, and
renal insufficiency.
10. Explain that
temporary insulin
therapy may be
needed if fever,
trauma, infection,
illness, surgery, or
other stress alters
blood glucose
control.
11. Warn patient not to
take other drugs
within 2 hours of
acarbose unless
specifically
instructed by
prescriber.
12. Tell him to consult
prescriber before
taking OTC drugs
during acarbose
therapy.
13. Advise patient who
also takes another
antidiabetic to carry
glucose with him at
all times in case
hypoglycemia
occurs.
NAME OF DRUG INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
ACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: To reduce blood • Hypersensitivity to May promote storage of CNS: Headache 1. Give metformin
Metformin glucose level in type 2 metformin or its excess glucose as EENT: Metallic taste tablets with food,
Hydrochloride diabetes mellitus components glycogen in the liver, ENDO: Hypoglycemia which decreases and
• Impaired renal which reduces glucose GI: Abdominal slightly delays
Brand name: As adjunct to insulin function, metabolic production. Metformin distention, anorexia, absorption, thus
Fortamet therapy in type 2 acidosis also may improve constipation, diarrhea, reducing risk of
Gen-Metformin diabetes mellitus • Use of iodinated glucose use by skeletal flatulence, indigestion, adverse GI
Glucophage contrast media within muscle and adipose nausea, vomiting reactions.
Glucophage XR preceding 48 hours tissue by increasing HEME: Aplastic 2. Give E.R. tablets
Glumetza glucose transport across anemia, megaloblastic with evening meal;
Glycon cell membranes. This anemia, don’t break or crush
NovoMetformin drug also may increase thrombocytopenia them.
Riomet the number of insulin SKIN: Photosensitivity, 3. Expect prescriber to
receptors on cell rash alter dosage if
Classification: membranes and make Other: Lactic acidosis, patient has a
Antidiabetics them more sensitive to weight loss condition that
insulin. In addition, decreases or delays
Dosage: metformin modestly gastric emptying,
500 to 1000 mg decreases blood such as diarrhea,
triglyceride and total gastroparesis, GI
Frequency: cholesterol levels. obstruction, ileus, or
Once a Day- night vomiting.
4. Expect to assess
Route: BUN and serum
Oral creatinine level
before and during
longterm therapy in
those at increased
risk for lactic
acidosis.
5. Monitor patient’s
hepatic function, as
ordered, because
impaired hepatic
function may
significantly reduce
the liver’s ability to
clear lactate,
predisposing the
patient to lactic
acidosis.
6. Monitor patient’s
blood glucose level
to evaluate drug
effectiveness.
7. Assess for
hyperglycemia and
the need for insulin
during times of
increased stress,
such as infection
and surgery.
8. Withhold drug, as
ordered, if patient
becomes dehydrated
or develops
hypoxemia or sepsis
because these
conditions increase
the risk of lactic
acidosis.
9. Iodinated contrast
media used in
radiographic studies
increases risk of
renal failure and
lactic acidosis
during metformin
therapy. Expect to
withhold drug for
48 hours before and
after testing.
10. Be aware that
women should not
breastfeed while
taking metformin
because nursing
infants may develop
hypoglycemia.
11. Instruct patient to
take metformin
tablet at breakfast if
taking drug once a
day, or at breakfast
and dinner if taking
drug twice a day.
Instruct him to take
E.R. tablets once
daily with evening
meal and to
swallow them
whole without
crushing or
chewing.
12. Direct patient to
take drug exactly as
prescribed and not
to change the
dosage or frequency
unless instructed.
13. Emphasize
importance of
following
prescribed diet,
exercising regularly,
controlling weight,
and checking blood
glucose level.
14. Teach patient how
to measure blood
glucose level and
recognize
hyperglycemia and
hypoglycemia. Urge
him to notify
prescriber of
abnormal blood
glucose level.
15. Caution patient to
avoid alcohol,
which can increase
the risk of
hypoglycemia.
NAME OF DRUG INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
ACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: Adjunct to diet and • Patients hypersensitive Slows inactivation of CNS: headache 1. Monitor patients for
Alogliptin exercise to improve to drug or its incretin, which EENT: naso- signs and symptoms
glycemic control in components increases blood pharyngiti s of HF (shortness of
Brand name: adults with type 2 • Type 1 diabetes concentration of Metabolic: breath, orthopnea,
Nesina diabetes. mellitus or incretin and reduces hypoglycemia tiredness, weakness,
ketoacidosis. fasting or postprandial Respiratory: URI fatigue, weight gain,
Classification: • liver disease or injury glucose in patients with peripheral or
Antidiabetics • history of pancreatitis type 2 diabetes. abdominal edema).
• Gallstones Drug may need to
Dosage: • History of alcoholism, be discontinued and
25 mg/tab renal disease, or other antidiabetics
history of angioedema may be needed.
• History of HF or renal 2. Assess renal
Frequency: disease function at baseline
Once a day and periodically
during treatment.
Route: 3. Monitor patient for
Oral hypersensitivity
reactions, including
Steven- Johnson
syndrome (rare).
Stop the drug
immediately if
hypersensitivity is
suspected.
4. Monitor patient for
signs and symptoms
(rare) of acute
pancreatitis (severe
abdominal pain that
may radiate to the
back with or
without vomiting).
5. Assess LFTs before
treatment. If liver
injury (rare) is
suspected during
treatment (fatigue,
anorexia, abdominal
discomfort, dark
urine, jaundice),
obtain LFTs. if
elevated LFT values
are present, persist
or worsen, withhold
drug and determine
probable cause.
Restart drug only if
cause isn’t
alogliptin- related.
6. Monitor blood
glucose level if
patient is receiving
concurrent
antidiabetics
medications; adjust
dosages of these
medications if
needed.
7. May cause joint
pain that can be
severe and
disabling. Report
severe and
persistent joint pain
to prescriber, drug
may need to be
discontinued.
8. Instruct patient to
immediately report
signs and symptoms
of HF. Patient
shouldn’t stop drug
without first
discussing with
prescriber.
9. Instruct patient to
monitor blood
glucose level
carefully.
NAME OF DRUG INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
ACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: As an adjunct to diet • History of medullary Tanzeum (albiglutide) GI: Pancreatitis Upper 1. Advise patient to
Albiglutide and exercise to thyroid carcinoma is an agonist of the respiratory tract read the Patient
improve glycemic • Multiple Endocrine albumin-based infection, Diarrhea, Medication Guide
Brand name: control in adults with • Neoplasia syndrome glucagon-like peptide Nausea, Delayed before starting
Tanzeum type 2 diabetes type (GLP)-1 fusion protein. gastric emptying, albiglutide and with
mellitus. • Hypersensitivity It augments glucose- dyspepsia, reflux each Rx refill.
Classification: reaction to albiglutide depende nt insulin GU: Renal impairment 2. Instruct patient on
Antidiabetics or any of the product secretion and slows ENDO: Thyroid cell use of Tanzeum
components gastric emptying tumors, hypoglycemia pen and to take
Dosage: • Renal impairment Others: albiglutide as
30mg/single-use Pen • Severe hypersensitivity directed. Pen should
50 mg/single-use Pen gastrointestinal reactions, Injection site never be shared
disease reaction between patients,
Duration of • Lactation even if needle is
administration: changed.
7 minutes 3. Inform patient that
nausea is the most
Frequency: common side effect,
Once weekly but usually
decreases over time.
Route: 4. Explain to patient
Parenteral that this medication
administration - controls
Subcutaneous hyperglycemia but
Injection does not cure
diabetes. Therapy is
long-term.
5. Review signs of
hypoglycemia and
hyperglycemia with
patient. If
hypoglycemia
occurs, advise
patient to take a
glass of orange
juice or 2–3 tsp of
sugar, honey, or
corn syrup
dissolved in water
and notify health
care professional.
6. Encourage patient
to follow prescribed
diet, medication,
and exercise
regimen to prevent
hypoglycemic or
hyperglycemic
episodes.
7. Instruct patient in
proper testing of
serum glucose and
ketones.
8. Advise patient to
tell health care
professional what
medications they
are taking and to
avoid taking new
Rx, OTC, vitamins,
or herbal products
without consulting
health care
professional.
9. Advise patient to
discontinue
albiglutide and
notify health care
professional
immediately if signs
of pancreatitis
(nausea, vomiting,
abdominal pain)
occur.
10. Advise patient to
carry a form of
sugar and
identification
describing disease
process and
medication regimen
at all times.
11. Advise patient to
inform health care
professional of
medication regimen
before treatment or
surgery.
12. Inform patient of
risk of benign and
malignant thyroid
C-cell tumors.
Advise patient to
notify health care
professional if
symptoms of
thyroid tumors
occur.
13. If pregnancy is
planned, consider
stopping albiglutide
at least 1 month
before a planned
pregnancy
14. Emphasize the
importance of
routine follow-up
exams.
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to Myasthenia Gravis (Updated), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Myasthenia Gravis (Updated), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDocument10 pagesDrug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- StreptomycinDocument1 pageStreptomycinDemilyn Fat100% (2)
- Myasthenia Gravis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMyasthenia Gravis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Anti-InfectiveDocument8 pagesDrug Study: Anti-InfectiveTri ShaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyIsha Catimbang GenerilloNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative Colitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandUlcerative Colitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Nursing responsibilities for common drugsDocument8 pagesNursing responsibilities for common drugsEden Marie FranciscoNo ratings yet
- PTB DrugsDocument4 pagesPTB DrugsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: CnsDocument4 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: CnsRoxy TofyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationDocument2 pagesNursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationOmar IzzoNo ratings yet
- TelmisartanDocument2 pagesTelmisartanRea LynNo ratings yet
- Student Drug Study Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesStudent Drug Study Mefenamic AcidJEWEL DEEN VILLARMENTE OQUIANANo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument60 pagesDrug StudyKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyLyka PerezNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication /contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument10 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication /contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJohnmark PascuaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ParacetamolDocument4 pagesDrug Study - ParacetamolMary Grace VillegasNo ratings yet
- Allopurinol (Drug Study)Document2 pagesAllopurinol (Drug Study)Daisy PalisocNo ratings yet
- Brand and Generic Name Action Uses/ Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument12 pagesBrand and Generic Name Action Uses/ Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationBiggs JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Methylergometrine Maleate Bupivacaine HydrochlorideDocument3 pagesDexamethasone Methylergometrine Maleate Bupivacaine HydrochlorideOmyl-Khayr M. SulogNo ratings yet
- TELMISARTANDocument8 pagesTELMISARTANCidny CalimagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CisplatinDocument3 pagesDrug Study - CisplatinDanielle Aglusolos50% (2)
- Drug Study PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesDrug Study Prednisoloneunnamed personNo ratings yet
- Nursing responsibilities for mefenamic acidDocument4 pagesNursing responsibilities for mefenamic acidStephen VillegasNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument14 pagesDischarge PlanAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahNo ratings yet
- MefenamicDocument3 pagesMefenamicassilamorNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyJessica Pacris MaramagNo ratings yet
- Dosage and effects of ampicillinDocument1 pageDosage and effects of ampicillinkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy TuberculosisDocument10 pagesDrugStudy TuberculosisJohn Roger VillegasNo ratings yet
- Drug therapeutic recordDocument2 pagesDrug therapeutic recordjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationNicole CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument2 pagesAspirinBARRISTERFLOWERSEAURCHIN6No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Other AntibioticDocument2 pagesOther AntibioticPrince Mark BadilloNo ratings yet
- Naprex Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNaprex Drug StudyAngelica shane NavarroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyLorelyn FabrigarasNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsPRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Drug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, VecuroniumDocument12 pagesDrug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, Vecuroniumpaupaulala100% (4)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledALYSSA MARIE MATANo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sespsis - Drug StudyDocument6 pagesNeonatal Sespsis - Drug StudyAlvincent D. BinwagNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudySavannah KhrisNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OrthoDocument12 pagesDrug Study OrthoSienaNo ratings yet
- Name and Classification of DrugDocument3 pagesName and Classification of DrugAnicas, Ralph Joshua V.No ratings yet
- ShitDocument15 pagesShitEden Marie FranciscoNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsmelody_loki1464No ratings yet
- Clindamycin and Balsalazide Drug SheetDocument5 pagesClindamycin and Balsalazide Drug SheetLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- CNS: Headache,: Aureus and Staphyl Ococcus EpidermisDocument9 pagesCNS: Headache,: Aureus and Staphyl Ococcus EpidermisKristal Cyril PolzNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy FluconazoleCasilaoDocument4 pagesDrugStudy FluconazoleCasilaoArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- CNS: Headache,: Aureus and Staphyl Ococcus EpidermisDocument9 pagesCNS: Headache,: Aureus and Staphyl Ococcus EpidermisKristal Cyril PolzNo ratings yet
- CNS: Headache,: Aureus and Staphyl Ococcus EpidermisDocument9 pagesCNS: Headache,: Aureus and Staphyl Ococcus EpidermisKristal Cyril PolzNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin nursing responsibilitiesDocument3 pagesGentamicin nursing responsibilitiesjoanamariedguanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingDocument3 pagesDrugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingHazel Palomares100% (1)
- Name of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument13 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitieskev mondaNo ratings yet
- Naproxen Sodium Drug StudyDocument1 pageNaproxen Sodium Drug StudyKarl Lourenz Deysolong100% (1)
- Levofloxac in (Levox)Document2 pagesLevofloxac in (Levox)jbespirituNo ratings yet
- NOVIDA, ALEYA CRYSTINE G. BSN 3BDocument4 pagesNOVIDA, ALEYA CRYSTINE G. BSN 3BMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Laminectomy Procedure ExplainedDocument27 pagesLaminectomy Procedure ExplainedMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for a Patient with DementiaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan for a Patient with DementiaMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Background Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short-Term Goals: Independent: Short-Term GoalsDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Background Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short-Term Goals: Independent: Short-Term GoalsMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ischemic StokeDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ischemic StokeMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On FatigueDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan On FatigueMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Seretide Accuhaler and VentolinDocument7 pagesSeretide Accuhaler and VentolinMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On FatigueDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan On FatigueMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Certain DrugsDocument10 pagesDrug Study On Certain DrugsMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for a Patient with DementiaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan for a Patient with DementiaMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- How Self-Awareness and Personal Growth Can Help Overcome LimitsDocument3 pagesHow Self-Awareness and Personal Growth Can Help Overcome LimitsMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On HFDocument13 pagesDrug Study On HFMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ischemic StokeDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ischemic StokeMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Self-AwarenessDocument1 pageThe Importance of Self-AwarenessMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication: C - Clarification S - SilenceDocument1 pageTherapeutic Communication: C - Clarification S - SilenceMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- How Self-Awareness and Personal Growth Can Help Overcome LimitsDocument3 pagesHow Self-Awareness and Personal Growth Can Help Overcome LimitsMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- The Foundation of Self-AwarenessDocument2 pagesThe Foundation of Self-AwarenessMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic RelationshipsDocument1 pageTherapeutic RelationshipsMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Go Fast, or Slow Down?Document23 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Go Fast, or Slow Down?Mikhael OiraNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry MSCDocument29 pagesStereochemistry MSCBapu Thorat50% (2)
- Meralco Bill 330370940102 04142023Document2 pagesMeralco Bill 330370940102 04142023Jha CruzNo ratings yet
- Experimental Monitoring of The Humber Bridge UsingDocument7 pagesExperimental Monitoring of The Humber Bridge Using정주호No ratings yet
- 2008 Infosys Model QuestionsDocument23 pages2008 Infosys Model Questionsapi-3824713No ratings yet
- Air release plug and lifting lug details for 15 MVA 66/11.55 kV transformer radiatorDocument1 pageAir release plug and lifting lug details for 15 MVA 66/11.55 kV transformer radiatorshravan Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- SPC英文版教材Document83 pagesSPC英文版教材bing cai100% (2)
- Practice Quiz M1 (Ungraded) - MergedDocument22 pagesPractice Quiz M1 (Ungraded) - MergedAbdullah Abdullah100% (1)
- Deskripsi (Caffein)Document4 pagesDeskripsi (Caffein)jibefahlaNo ratings yet
- 9709 s15 QP 12Document4 pages9709 s15 QP 12Abrar JahinNo ratings yet
- Hearing Aid InformationDocument22 pagesHearing Aid InformationDeepakRodeyNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations CookbookDocument2 pagesDifferential Equations CookbookAugustinZNo ratings yet
- Welcome Students!: Week 8 (3 Quarter)Document28 pagesWelcome Students!: Week 8 (3 Quarter)Erika Lloren Luyun-GaliaNo ratings yet
- A Review: HPLC Method Development and Validation: November 2015Document7 pagesA Review: HPLC Method Development and Validation: November 2015R Abdillah AkbarNo ratings yet
- Category D Fluid ServiceDocument2 pagesCategory D Fluid Serviceaslam.ambNo ratings yet
- Electronic V-MAC IV Vehicle Mgmt. and Control With Co-Pilot Display Operator ManualDocument133 pagesElectronic V-MAC IV Vehicle Mgmt. and Control With Co-Pilot Display Operator Manualsanach0412No ratings yet
- Encapsulation and Inheritance in Object-Orlented Programming LanguagesDocument8 pagesEncapsulation and Inheritance in Object-Orlented Programming Languageszsolt kormanyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Food and Beverage IndustryDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Food and Beverage IndustryRhyza BehaveNo ratings yet
- Bio Sem2 EssayDocument2 pagesBio Sem2 EssayEileen WongNo ratings yet
- 3M CatalogueDocument32 pages3M Cataloguefandi.azs37No ratings yet
- 5020-Article Text-10917-1-10-20220808Document9 pages5020-Article Text-10917-1-10-20220808indah rumah4No ratings yet
- Mañanita Songs Mañanita SongsDocument2 pagesMañanita Songs Mañanita SongsSanchez Bayan100% (1)
- Cell Structure ActivityDocument4 pagesCell Structure ActivitysharksiedNo ratings yet
- Adding True Bypass To A Vintage Big MuffDocument8 pagesAdding True Bypass To A Vintage Big MuffOliver SuttonNo ratings yet
- Rajagiri Public School Unit Test PhysicsDocument3 pagesRajagiri Public School Unit Test PhysicsNITHINKJOSEPHNo ratings yet
- New Patient Needing Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT)Document9 pagesNew Patient Needing Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT)sergey_1972No ratings yet
- NTPC Training ReportDocument83 pagesNTPC Training ReportAbhishek Mittal100% (2)
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractramyaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsAira Jane Irarum78% (18)