Professional Documents
Culture Documents
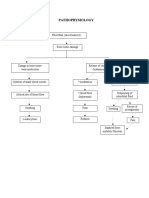
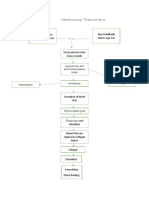
Decreased HGB: 9.1 Decreased HCT: 28.8 Decreased RBC: 2.8 Release of Cytokines Increased Monocytes: 9 Decreased MCV: 103.6
Uploaded by
kim cortezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Decreased HGB: 9.1 Decreased HCT: 28.8 Decreased RBC: 2.8 Release of Cytokines Increased Monocytes: 9 Decreased MCV: 103.6
Uploaded by
kim cortezCopyright:
Available Formats
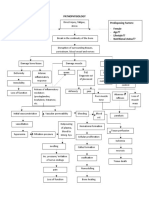
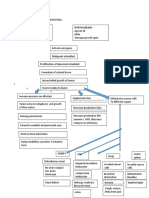
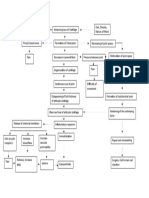
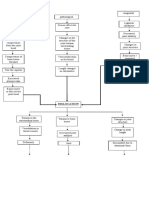
MODIFIABLE FACTORS NON-MODIFIABLE FACTORS
FALLS / ACCIDENTS AGE (89 YEARS OLD)
GENDER (FEMALE)
GENERALIZED
OSTEOPOROSIS
TRAUMA
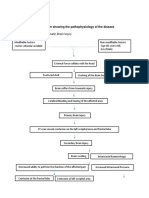
Stress placed on
the right femoral
neck
Injury in the bone
Disruption in the
continuity of bone
Disruption of muscle and blood vessels
attached to the ends of the bone
Soft tissue damage
Decreased Hgb: 9.1
Decreased Hct: 28.8 Internal bleeding
Decreased RBC: 2.8 Release of cytokines
Formation of Hematoma
Increased monocytes: 9
Intense Inflammatory Response Decreased MCV: 103.6
Vasodilation Pain on right hip
Increased blood flow to the area of injury
Mast cells accumulate
Phagocystosis and removal of dead cell
debris
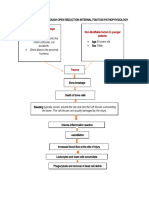
A fibrin clot (fracture hematoma) forms at the break and
acts as a new network to which new cells can adhere.
Disruption in fracture hematoma due to comminuted bone.
Fixation or proper bone alignment is
needed to facilitate bone healing
Open Reduction Internal Fixiation
Stress on the opposed of the
broken bones, which accelerated
osteoblastic activity at the break
leading to hastened normal bone
healing.
Osteoblastic activity is
immediately stimulated, both
intraosseous and periosteal from
osteoprogenitor cell
Immature new bone or callous Is
formed
Fibrin clot is soon reabsorbed and
the new bone cells are slowly
remodeled to form true bone.
Decreased pain True bone replaces callous and is
and on the slowly calcified. (Several weeks to
process of few months)
healing.
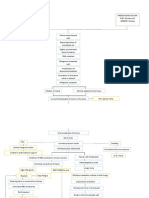
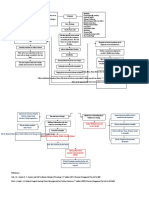
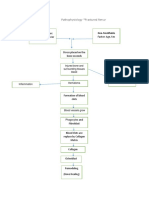
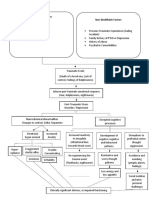
NON-MODIFIABLE FACTORS
AGE (89 YEARS OLD)
GENDER (FEMALE)
GENERALIZED
OSTEOPOROSIS
TRAUMA
Stress placed on
the right femoral
neck
Injury in the bone
Disruption in the
continuity of bone
Disruption of muscle
and blood vessels
attached to the ends
of the bone
Soft tissue damage
Release of cytokines
Decreased Hgb: 9.1 Internal bleeding Increased monocytes: 9
Decreased Hct: 28.8 Formation of Hematoma Decreased MCV: 103.6
Decreased RBC: 2.8
Intense Inflammatory Response Pain on right hip
Vasodilation
Increased blood flow to the area of injury
Mast cells accumulate
Phagocystosis and removal of dead cell
debris
You might also like
- Patho FractureDocument2 pagesPatho FracturejaninenicoleNo ratings yet
- Patho FractDocument1 pagePatho FractJordan Garcia AguilarNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY MyomaDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY MyomaDevikomala50% (2)
- Doctor Profile Format Dr. Sarika Trimbak Shinde, MSDocument3 pagesDoctor Profile Format Dr. Sarika Trimbak Shinde, MSSwapnil JaikarNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology PDFJenievieve MerzaNo ratings yet
- AHA-PALS 2010: Pediatric Chain of SurvivalDocument10 pagesAHA-PALS 2010: Pediatric Chain of SurvivalIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Complications of FractureDocument3 pagesComplications of FractureGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Fracturemyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Checklists For Heat and Cold ApplicationDocument5 pagesChecklists For Heat and Cold ApplicationJay Harold Cordero PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of OsteoarthritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of OsteoarthritisGLADYS GARCIANo ratings yet
- Iii. Clinical Discussion of The Disease A. Pathophysiology of Fracture I. (Book Based)Document4 pagesIii. Clinical Discussion of The Disease A. Pathophysiology of Fracture I. (Book Based)Lemuel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Patho MyomaDocument1 pagePatho MyomaJurilyne Rose TundagNo ratings yet
- Bone HealingDocument2 pagesBone HealingGerardLum100% (2)
- Screening, Diagnosis and Early Intervention in Autism Spectrum DisordersDocument5 pagesScreening, Diagnosis and Early Intervention in Autism Spectrum DisordersDaniele PendezaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of FractureLawrence Espinosa82% (11)
- Chapter 22Document6 pagesChapter 22Danielle ShullNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation (Ortho Ward) :: Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesCase Presentation (Ortho Ward) :: Pathophysiology of FractureAbigail BrillantesNo ratings yet
- pathoPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOMYELITIS (DIAGRAM)Document1 pagepathoPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOMYELITIS (DIAGRAM)redhoney100% (5)
- Effective CommunicationDocument19 pagesEffective Communicationkim cortezNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMaDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMakyawNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseDocument1 pagePathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseLeLi CortezNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument7 pagesArthritisGerardLum100% (1)
- Bone Fracture Grp3Document12 pagesBone Fracture Grp3Marjian BaruaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology On Fracture of Left Femoral Head: Precipitating Factor Predisposing FactorDocument2 pagesPathophysiology On Fracture of Left Femoral Head: Precipitating Factor Predisposing FactorEsther Mendez CatubigNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorscadayNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYAndree GalloNo ratings yet
- Tibia Fracture: Motor Vehicular Accident Age (61 Years Old) Sex (Male)Document1 pageTibia Fracture: Motor Vehicular Accident Age (61 Years Old) Sex (Male)Jack BangcoyoNo ratings yet
- Narrative PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesNarrative Pathophysiologymyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of FractureEunice CuñadaNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument1 pageOsteoarthritisReshiel RubioNo ratings yet
- A. Pathway: (Lutfi, 2007 Smeltzer, 2000: 360)Document1 pageA. Pathway: (Lutfi, 2007 Smeltzer, 2000: 360)Yosef HidayatNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiologygoodie1988No ratings yet
- Post Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPost Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyRizalyn QuindipanNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology FractureDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology Fracturecsy123No ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of OsteomyelitisDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Osteomyelitismai_serpicNo ratings yet
- PathwayDocument1 pagePathwaykomangNo ratings yet
- Bone Fracture PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBone Fracture Pathophysiologymyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Bone Fracture PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBone Fracture Pathophysiologynananana123No ratings yet
- Pathway FractureDocument1 pagePathway FractureNym SukerataNo ratings yet
- Disease Affects The Joint: DislocationDocument1 pageDisease Affects The Joint: DislocationVeggy LiansyahNo ratings yet
- FracturesDocument39 pagesFracturesKim Gonzales100% (5)
- Patho Osteo 2Document1 pagePatho Osteo 2Veyck ThorNo ratings yet
- Fracture Healing and BonegraftingDocument76 pagesFracture Healing and BonegraftingJio AmurNo ratings yet
- Fractures and Compartment SyndromeDocument4 pagesFractures and Compartment SyndromeTom MallinsonNo ratings yet
- Lo MSK 2-2Document14 pagesLo MSK 2-2FirmanHidayatNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of OsteomyelitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Osteomyelitissorryandreosayanisalreadytaken100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factor Etiology Precipitating FactorDocument6 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing Factor Etiology Precipitating FactorJoanna EdenNo ratings yet
- The Management of Facial Palsy and Bell's PalsyDocument60 pagesThe Management of Facial Palsy and Bell's PalsyAjayi FolamiNo ratings yet
- Pathophy OsteomyelitisDocument1 pagePathophy OsteomyelitisCxarina RamirezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Spinal Cord InjuryDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Spinal Cord InjuryLouie AdorNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Tibial FractureDocument1 pagePa Tho Tibial FractureimusenianNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Pathophysiology of Osteomyelitis DiagramDocument1 pageDokumen - Tips Pathophysiology of Osteomyelitis DiagramRodriguez, Joyce Ann G.No ratings yet
- Section of Rheumatology, Internal Medicine Department Faculty of Medicine GMU / Dr. Sardjito General HospitalDocument47 pagesSection of Rheumatology, Internal Medicine Department Faculty of Medicine GMU / Dr. Sardjito General HospitalYane Aulia YasminNo ratings yet
- Fracture Healing - Basic Science - Orthobullets PDFDocument2 pagesFracture Healing - Basic Science - Orthobullets PDFMelAcostaNo ratings yet
- Altered Neurovascular Status: FractureDocument3 pagesAltered Neurovascular Status: FractureCake ManNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis Definition: Infection of The Bone and Surrounding Tissues, Most Commonly Caused byDocument3 pagesOsteomyelitis Definition: Infection of The Bone and Surrounding Tissues, Most Commonly Caused byAngelie_Elvamb_8952No ratings yet
- Bone FractureDocument25 pagesBone FractureDaramola JuwonNo ratings yet
- Bone Healing: Prepared By: Nurul Amirah Binti Mustafa 1120491Document18 pagesBone Healing: Prepared By: Nurul Amirah Binti Mustafa 1120491Aiman ArifinNo ratings yet
- Hemartrosis PPT EnglishDocument27 pagesHemartrosis PPT EnglishAri SamadNo ratings yet
- PPPDocument3 pagesPPPJack BangcoyoNo ratings yet
- Fractures and Bone HealingDocument40 pagesFractures and Bone Healingandre kesumaNo ratings yet
- 1868-Article Text-5360-1-10-20201204Document22 pages1868-Article Text-5360-1-10-20201204kim cortezNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Social Media Exposure and Interpersonal Discussion On Intention of COVID-19 Vaccination Among NursesDocument13 pagesThe Impact of Social Media Exposure and Interpersonal Discussion On Intention of COVID-19 Vaccination Among Nurseskim cortezNo ratings yet
- Modifiable Factors Non-Modifiable FactorsDocument8 pagesModifiable Factors Non-Modifiable Factorskim cortezNo ratings yet
- Fetal AssessmentDocument57 pagesFetal Assessmentkim cortezNo ratings yet
- Mumbai Claim FormDocument5 pagesMumbai Claim FormsunsangraNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine 5th MidtermDocument13 pagesInternal Medicine 5th MidtermIashdip iashdipNo ratings yet
- Colorectal SurgeryDocument8 pagesColorectal SurgeryGeramyl Ramos AnapiNo ratings yet
- Aneurin Bevan University JCF 040-CF675 - Job Description and Person SpecificationDocument7 pagesAneurin Bevan University JCF 040-CF675 - Job Description and Person Specificationsarah.regina97No ratings yet
- Diagnosis Procedure: DRG Sri Rezeki, SP - PMDocument94 pagesDiagnosis Procedure: DRG Sri Rezeki, SP - PMNiska DarliantiNo ratings yet
- Personal Decisions Are The Leading Cause of Death PDFDocument13 pagesPersonal Decisions Are The Leading Cause of Death PDFLan HươngNo ratings yet
- Coass V-Ear TumorsDocument32 pagesCoass V-Ear TumorsErshine Villany100% (1)
- Notes On Cancer (Class XII)Document2 pagesNotes On Cancer (Class XII)Aryan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 10.daftar PustakaDocument4 pages10.daftar PustakaInka SitiNo ratings yet
- Hospital Impact Emergency DepartmentDocument20 pagesHospital Impact Emergency DepartmentydtrgnNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Complications PDFDocument21 pagesPostoperative Complications PDFDoctor's BettaNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument125 pagesIlovepdf MergedinnyNo ratings yet
- BISTOST 770 OP Manual 770 ENG OPM EUR R03Document51 pagesBISTOST 770 OP Manual 770 ENG OPM EUR R03jorge baquedanoNo ratings yet
- Hospitalisation Claim FormDocument2 pagesHospitalisation Claim Formsujay13780No ratings yet
- COVID-19 Outbreak, Its Impact On Global EconomyDocument110 pagesCOVID-19 Outbreak, Its Impact On Global EconomyramaramoinNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanHannah ChiuNo ratings yet
- Addiction Treatment Center Near Houston, TXDocument2 pagesAddiction Treatment Center Near Houston, TXSharon DikirrNo ratings yet
- Sample CollectionDocument8 pagesSample CollectionwillowmaecayabyabNo ratings yet
- JAC - 22 - 2 Mount Fuji Sign With Changes AcceptedDocument2 pagesJAC - 22 - 2 Mount Fuji Sign With Changes Acceptedipe.jacobNo ratings yet
- NovoMix 30 Patient LeafletDocument16 pagesNovoMix 30 Patient LeafletArslan KhalidNo ratings yet
- At The Doctor - Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesAt The Doctor - Multiple ChoiceGinaNo ratings yet
- ETT Vs LMADocument33 pagesETT Vs LMAitaindrianiNo ratings yet
- Great Medical Doctor CV ExampleDocument1 pageGreat Medical Doctor CV ExampleEkvan DanangNo ratings yet
- Trypanosoma MCQDocument2 pagesTrypanosoma MCQsummiya100% (2)
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument3 pagesTetralogy of FallotKamal FauzeNo ratings yet