Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Patho Osteo 2
Uploaded by
Veyck Thor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
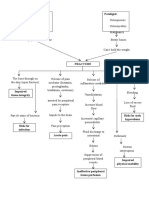
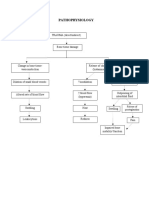
46 views1 pagePathophysiology of Osteomyelitis Risk factors Untreated abscess History of bone trauma (open fracture of long bone) Age Sex Causative agent (staphylococcus aureus) Thru blood stream Organisms grow and multiply in the area Inflammatory response Formation of purulent exudate Phagocytes generate toxic oxygen radicals and release proteolytic enzymes that destroy surrounding tissue.
Original Description:
Original Title
patho osteo 2
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPathophysiology of Osteomyelitis Risk factors Untreated abscess History of bone trauma (open fracture of long bone) Age Sex Causative agent (staphylococcus aureus) Thru blood stream Organisms grow and multiply in the area Inflammatory response Formation of purulent exudate Phagocytes generate toxic oxygen radicals and release proteolytic enzymes that destroy surrounding tissue.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views1 pagePatho Osteo 2
Uploaded by
Veyck ThorPathophysiology of Osteomyelitis Risk factors Untreated abscess History of bone trauma (open fracture of long bone) Age Sex Causative agent (staphylococcus aureus) Thru blood stream Organisms grow and multiply in the area Inflammatory response Formation of purulent exudate Phagocytes generate toxic oxygen radicals and release proteolytic enzymes that destroy surrounding tissue.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
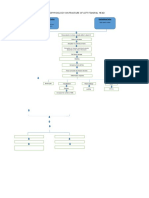
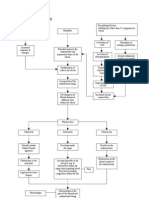
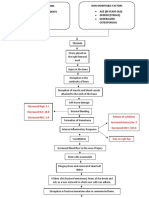
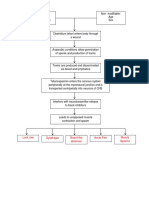
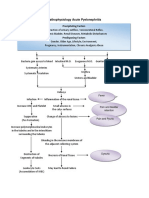
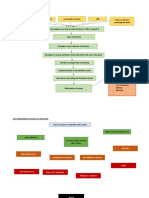
Pathophysiology of Osteomyelitis
Risk factors
Untreated abscess
History of bone trauma (open fracture of
long bone)
Age
Sex
Causative agent (Staphylococcus aureus)
Thru blood stream
Organisms grow & multiply in the area
Sudden pain on the
Inflammatory response
affected side
Tenderness
Formation of purulent exudate Heat
Swelling
Restricted movement
Phagocytes generate toxic oxygen radicals & release Tachycardia
proteolytic enzymes that destroy surrounding tissue Sudden fever
Nausea
Purulent drainage ensues spread into the bone Malaise
Increased WBC
Increased ESR
Increase intraosseous pressure
Obstruction by septic thrombus
Ischemic necrosis of bone
Process continues
New Bone separates from the surrounding
bone to form devascularized fragments
Formation of sheath of new bone – involucrum
You might also like
- Pathophy OsteomyelitisDocument1 pagePathophy OsteomyelitisCxarina RamirezNo ratings yet
- pathoPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOMYELITIS (DIAGRAM)Document1 pagepathoPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOMYELITIS (DIAGRAM)redhoney100% (5)
- Pa Tho Physiology of OsteomyelitisDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Osteomyelitismai_serpicNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Pathophysiology of Osteomyelitis DiagramDocument1 pageDokumen - Tips Pathophysiology of Osteomyelitis DiagramRodriguez, Joyce Ann G.No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology On Fracture of Left Femoral Head: Precipitating Factor Predisposing FactorDocument2 pagesPathophysiology On Fracture of Left Femoral Head: Precipitating Factor Predisposing FactorEsther Mendez CatubigNo ratings yet
- PathwayDocument1 pagePathwaykomangNo ratings yet
- Pathway FractureDocument1 pagePathway FractureNym SukerataNo ratings yet
- Narrative PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesNarrative Pathophysiologymyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of OsteomyelitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Osteomyelitissorryandreosayanisalreadytaken100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorscadayNo ratings yet
- Aureus. It Can Be Either Acute or ChronicDocument7 pagesAureus. It Can Be Either Acute or ChronicfortunelobsterNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument1 pageOsteoarthritisReshiel RubioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology PDFJenievieve MerzaNo ratings yet
- Bone Fracture Grp3Document12 pagesBone Fracture Grp3Marjian BaruaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYAndree GalloNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY MyomaDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY MyomaDevikomala50% (2)
- Osteomyelitis Definition: Infection of The Bone and Surrounding Tissues, Most Commonly Caused byDocument3 pagesOsteomyelitis Definition: Infection of The Bone and Surrounding Tissues, Most Commonly Caused byAngelie_Elvamb_8952No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseDocument1 pagePathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseLeLi CortezNo ratings yet
- A. Pathway: (Lutfi, 2007 Smeltzer, 2000: 360)Document1 pageA. Pathway: (Lutfi, 2007 Smeltzer, 2000: 360)Yosef HidayatNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis: Pembimbing: Dr. Dimas Febrianto, Sp. OT Oleh: Rheza Rizaldy (30101407301)Document20 pagesOsteomyelitis: Pembimbing: Dr. Dimas Febrianto, Sp. OT Oleh: Rheza Rizaldy (30101407301)Rheza RizaldyNo ratings yet
- PathooDocument1 pagePathooMary Louise LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Blok 17 - InfeksiDocument75 pagesBlok 17 - InfeksiNorbertus MacekaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology FractureDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology Fracturecsy123No ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY MyomaDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY MyomareapRaven0856% (9)
- Complications of FractureDocument3 pagesComplications of FractureGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Skinabscess2003Document1 pagePathophysiology Skinabscess2003яoxel яayмoи eитяeиaNo ratings yet
- Decreased HGB: 9.1 Decreased HCT: 28.8 Decreased RBC: 2.8 Release of Cytokines Increased Monocytes: 9 Decreased MCV: 103.6Document3 pagesDecreased HGB: 9.1 Decreased HCT: 28.8 Decreased RBC: 2.8 Release of Cytokines Increased Monocytes: 9 Decreased MCV: 103.6kim cortezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Spinal Cord InjuryDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Spinal Cord InjuryLouie AdorNo ratings yet
- Lock Jaw Dysphagia Board-Like Abdomen Acute Pain Muscle SpasmsDocument1 pageLock Jaw Dysphagia Board-Like Abdomen Acute Pain Muscle SpasmsheyyymeeeNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiologygoodie1988No ratings yet
- Appendicitis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageAppendicitis PathophysiologyPatricia Beatrice Dela CenaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument11 pagesRheumatoid Arthritisicecreamcone_201No ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMaDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMakyawNo ratings yet
- PathopysiologyDocument1 pagePathopysiologyLouis LazaroNo ratings yet
- Bone and Joint Infections 09Document4 pagesBone and Joint Infections 09Ali 10No ratings yet
- Patho MyomaDocument1 pagePatho MyomaJurilyne Rose TundagNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Tetanus: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Tetanus: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsPernel Jose Alam Micubo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factor Etiology Precipitating FactorDocument6 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing Factor Etiology Precipitating FactorJoanna EdenNo ratings yet
- Book Based Risk Factor Tall For Age Repeated Trauma Hereditary Exposure To RadiationDocument2 pagesBook Based Risk Factor Tall For Age Repeated Trauma Hereditary Exposure To RadiationJenievieve MerzaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of OsteomyelitisDocument4 pagesPa Tho Physiology of OsteomyelitisninasaguidNo ratings yet
- Fisioterapi Olah Raga Pertemuan 3Document84 pagesFisioterapi Olah Raga Pertemuan 3Indra IndfisNo ratings yet
- Jenis Cidera OlahragaDocument84 pagesJenis Cidera OlahragayusufNo ratings yet
- Tibia Fracture: Motor Vehicular Accident Age (61 Years Old) Sex (Male)Document1 pageTibia Fracture: Motor Vehicular Accident Age (61 Years Old) Sex (Male)Jack BangcoyoNo ratings yet
- Bones and Joints: Bone Is A Specialised Connective Tissue Which HasDocument34 pagesBones and Joints: Bone Is A Specialised Connective Tissue Which HasvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888No ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of A FractureDocument2 pagesPathogenesis of A FractureAubrey Marie GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Lo MSK 2-2Document14 pagesLo MSK 2-2FirmanHidayatNo ratings yet
- Iii. Clinical Discussion of The Disease A. Pathophysiology of Fracture I. (Book Based)Document4 pagesIii. Clinical Discussion of The Disease A. Pathophysiology of Fracture I. (Book Based)Lemuel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Bone Healing: Prepared By: Nurul Amirah Binti Mustafa 1120491Document18 pagesBone Healing: Prepared By: Nurul Amirah Binti Mustafa 1120491Aiman ArifinNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCellulitis PathophysiologyWilfredo Mata Jr.100% (8)
- FPP Sem4Document15 pagesFPP Sem4Nur NajminaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Tibial FractureDocument1 pagePa Tho Tibial FractureimusenianNo ratings yet
- Inflammation of The Bone: Inflammatory LesionsDocument17 pagesInflammation of The Bone: Inflammatory LesionsstajziehchiNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology: Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsDocument2 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology: Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsAl-Mujib TanogNo ratings yet
- Complications of FracturesDocument55 pagesComplications of FracturesMina SamirNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)No ratings yet
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)