Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name: Oàn V Hào Student ID: 31201028653 Class: HRM-DH46ISB-01
Uploaded by
Nguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Oàn V Hào Student ID: 31201028653 Class: HRM-DH46ISB-01
Uploaded by
Nguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcCopyright:
Available Formats
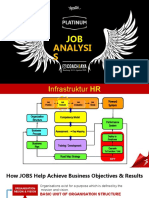
Job Analysis refers to the process of getting detailed information ab Name: o à n V Hà o
out jobs. It is important for organizations to understand and match jo Definition Student ID: 31201028653
b requirements and people to achieve high-quality performance Class: HRM-DH46ISB-01
As previously discussed, job analysis
Work Redesign
and job design are interrelated
In human resource planning, managers analyze an organizatio n’s
human resource needs in a dynamic environment and develop a Human Resource Planning
ctivities that enable a firm to adapt to change
Human resource selection identifies the most qualified applicants for employment Selection
Almost every employee hired by an organization will require training Training and Development
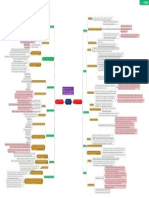
The Importance of Job Analysis
Performance appraisal deals with getting information about how well each employee is performi
ng in order to reward those who are effective, improve the performance of those who are ineffect Performance Appraisal
ive, or provide a written justification for why the poor performer should be disciplined.
Career planning entails matching an individual’s skills and aspirations Definition: The process of analyzing the tasks necessary for the production of a product or se
Career Planning
with opportunities that are or may become available in the organization rvice, prior to allocating and assigning these tasks to a particular job category or person
The process of job evaluation involves assessing the relative dollar value An output is the product of a work unit and
Job Evaluation
of each job to the organization to set up internally equitable pay structures this is often an identifiable object
Managers must have detailed information about all the jobs i An output can also be a service
Analyzing Work Outputs
n their work group to understand the work-flow process
Merely identifying an output or set of outputs is not sufficient.
Managers need to understand the job requirements The Importance of Job An Once these outputs have been identified, it is necessary to spe
to make intelligent hiring decisions alysis to Line Managers cify standards for the quantity or quality of these outputs.
A manager is responsible for ensuring that each i The work processes are the activities that members o
ndividual is performing satisfactorily (or better) f a work unit engage in to produce a given output
A job description is a list of the tasks, duties, Every process consists of operating procedures that specify how things
and responsibilities (TDRs) that a job entails should be done at each stage of the development of the product
Nature of Information Job Analysis
A job specification is a list of the knowledge, skills, These procedures include all the tasks that must be performed i
abilities, and other characteristics (KSAOs) that an n the production of the output
individual must have to perform the job
Job Analysis Information The use of teams can also be seen in the field of medicine, where team-based ca
The process of job analysis entails obtaining re is increasingly becoming the norm. Rather than a single one-on-one.
information from people familiar with the job
Kinds of errors are less likely to happen when people are working face-to-face i
In general, it will be useful to go to the job incumbent to get the m n teams relative to when the hand-off is a depersonalized electronic exchange f
Sources of Job Analysis Information
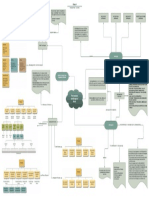
ost accurate information about what is actually done on the job Work-Flow Analysis Analyzing Working Process rom one functional unit to another
Job incumbents are also useful when one is trying to assess the informal s Teams are not a panacea. For teams to be effective, it is essential that the level of t
ocial network that exists within the formal organizational structure ask interdependence matches the level of outcome interdependence
Where and how a worker gets information needed to perform the job Information Input Movement that creates no value
The reasoning, decision making, planning, and information-p Three kinds of waste The overburdening of specific people or machines
Mental Processes
rocessing activities that are involved in performing the job
Inconsistent production that creates excessive inventories
The physical activities, tools, and devices used by the worker to perform the job Work Outputs
Position Analysis Questionnaire (PAQ) Lean production refers to processes emphasizing m
The relationships with other people required in performing the job Relationships With Other Persons anufacturing goods with a minimum amount of time,
The physical and social contexts where the work is performed Job Context Organizations often work hard to minimize materials, money - and most important - people
overstaffing via lean production techniques
The activities, conditions, and characteristics other than th Job Analysis Methods Although lean design is great for employers, it is not al
Other Characteristic
ose previously described that are relevant to the job ways great for workers
Served as a vehicle for helping the new public employment system link To identify the inputs used in the development of the work uni t’s product
the demand for skills and the supply of skills in the U.S. workforce These inputs can be broken down into the raw materials, e
The Occupational Information Network (O*NET) quipment, and human skills needed to perform the tasks
Technological changes in the nature of work, global competition, and a
shift from stable, fixed manufacturing jobs to a more flexible, dynamic, Raw materials consist of the materials that wil
service-based economy were quickly making the system obsolete The Analysis Work-Flow Analysis and l be converted into the work uni t’s product
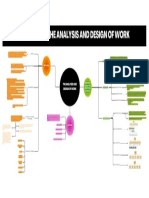
Jobs tend to change and evolve over time and Design of Work Organization Structure
Equipment refers to the technology and machinery necessary t
Dynamic Elements of Job Analysis Analyzing Work Inputs
Although there are numerous sources for error in the job analysis process, most i o transform the raw materials into the product
naccuracy is likely to result from job descriptions simply being outdated The final input in the work-flow process is the human
skills and efforts necessary to perform the tasks
Job design is the process of defining how work will be perf
The human skills consist of the workers available to the company
ormed and the tasks that will be required in a given job
Definition In terms of human skills, work should be delegated to the lowest-cost em
Job redesign refers to changing the tasks or t
ployee who can do the work well, and in some cases this principle is viola
he way work is performed in an existing job
ted when too much emphasis is placed on reducing headcount
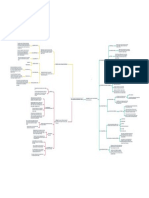
The mechanistic approach has roots in classical industrial engineering
Definition: Organization structure refers to the relatively stable and formal network of ve
Identifying the simplest way to structure work that maximizes efficiency rtical and horizontal interconnections among jobs that constitute the organization
t-
Scientific management was one of the earliest and bes Centralization refers to the degree to which decision-making authority resides at the top o
known statements of the mechanistic approach f the organizational chart as opposed to being distributed throughout lower levels
Dimensions of Structure
Be maximized by taking a scientific approach to the process of designing jobs Departmentalization refers to the degree to which work units are grouped based on
Mechanistic Approach functional similarity or similarity of work flow
The scientific management approach was built upon in later years, resulting in a mec
hanistic approach that calls for jobs to be designed so that they are very simple There are an infinite number of ways to combine centralization Functional structure
Organization Structure Structural Configurations and departmentalization, two common configurations of organi
Designing jobs in this way, the organization reduces its need for high-ability Divisional structure
zation structure tend to emerge in organizations
individuals and thus becomes less dependent on individual workers
The type of organization structure also has implications for t
Many jobs structured this way are performed in developing countries where there is a large
he design of jobs
supply of low-skilled labor and relatively lax legal guidelines regarding safety standards
Jobs in functional structures need to be narrow and highly specialized
Job design has roots in organizational psychology and management literature and, i
n many ways, emerged as a reaction to mechanistic approaches to job design The choice of structure also has implications for people who would
It focuses on the job characteristics that affect psychological meaning and motivational potential, and assume the jobs created in functional versus divisional structures
Job Design
it views attitudinal variables (such as satisfaction) as the most important outcomes of job design Structure and Nature of Jobs Taller structures also have implications for organizational c
A model of how job design affects employee reactions is the Job Characteristics Model ulture in terms of ethics and accountability
Motivational Approach In the next two sections, we cover specific approaches f
Skill Variety is the extent to which the job requires
or analyzing and designing jobs
a variety of skills to carry out the tasks
Skill Variety and Task Identity Although all of these approaches are viable, each focuses on a single, is
Task Identity is the degree to which a job requires complet
olated job
ing a “w hol e” piece of work from beginning to end
Job design interventions emphasizing the motivational approach t
end to focus on increasing the meaningfulness of jobs
The biological approach to job design comes primarily from the sciences of biomechanics,
work physiology, and occupational medicine, and it is usually referred to as ergonomics
Ergonomics is concerned with examining the interface between individual s’ p
Biological Approach
hysiological characteristics and the physical work environment
The biological approach has been applied in redesigning e
quipment used in jobs that are physically demanding.
The perceptual – motor approach to job design ha
s roots in human-factors literature
Perceptual-Motor Approach
Similar to the mechanistic approach, this approach
generally decreases the jo b’s cognitive demands
You might also like
- Professional Experience Context StatementDocument3 pagesProfessional Experience Context Statementapi-512442435No ratings yet
- HRD Flow Chart AssessmentDocument4 pagesHRD Flow Chart AssessmentSatya Eswarao100% (1)
- A Separate Peace Teacher GuideDocument44 pagesA Separate Peace Teacher GuideSwagat Sukumar Sahoo100% (3)
- MYP: Language Acquisition GuideDocument45 pagesMYP: Language Acquisition GuideCIS Admin100% (3)
- Job Characteristics ModelDocument14 pagesJob Characteristics ModelAnivesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Brain Based Learning Teaching The Way... Z LibraryDocument241 pagesBrain Based Learning Teaching The Way... Z LibraryJOANNA REAN SAGUIRELNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper InstructionsDocument2 pagesReflection Paper InstructionsRose Celine DiazNo ratings yet
- Bùi Ngọc Minh Hương - 31211021957 - CHAPTER 4Document1 pageBùi Ngọc Minh Hương - 31211021957 - CHAPTER 4Huong Bui Ngoc MinhNo ratings yet
- Job Design and Job AnalysisDocument27 pagesJob Design and Job AnalysistinalaurenaNo ratings yet
- Io Psych Chap2Document3 pagesIo Psych Chap2Gela FabianiaNo ratings yet
- SHRM Group-1Document45 pagesSHRM Group-1xyrieltolentinoNo ratings yet
- JobanalysisDocument25 pagesJobanalysismihir.chauhan1No ratings yet
- Job Analysis: MBA 120: Personnel and Employee RelationsDocument28 pagesJob Analysis: MBA 120: Personnel and Employee RelationsSyrah Mae ColomaNo ratings yet
- MBA HR - Compensation Management Notes & Ebook - Second Year Sem 4Document333 pagesMBA HR - Compensation Management Notes & Ebook - Second Year Sem 4Syam SandeepNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Unit 7Document7 pagesPaper 1 Unit 7Ruchi MishraNo ratings yet
- Computation of CompensationDocument22 pagesComputation of Compensationabdulrauf032119No ratings yet
- Humres ReviewerDocument6 pagesHumres ReviewerIrene LadesmaNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document1 pageChap 4Nhứt Phú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- W2.Reading 01 - Designing and Analyzing JobsDocument27 pagesW2.Reading 01 - Designing and Analyzing JobsuyenNo ratings yet
- HRM MagbooDocument2 pagesHRM MagbooEsmilla JasonNo ratings yet
- The Analysis and Design of WorkDocument1 pageThe Analysis and Design of WorkPhương NgânNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis Learning 28100Document3 pagesJob Analysis Learning 28100MAVERICK BROADCASTNo ratings yet
- Presentation By: Yoan Elisa G - 3303017030 Birgitta Alun S - 3303017041 Fanny Marcia - 3303017054Document28 pagesPresentation By: Yoan Elisa G - 3303017030 Birgitta Alun S - 3303017041 Fanny Marcia - 3303017054Yan GunawnNo ratings yet
- KTC Related To JOB: Prepared by Ansumalini PandaDocument19 pagesKTC Related To JOB: Prepared by Ansumalini PandaRojalin NathNo ratings yet
- HR Procurement: 2.1 Human Resource PlanningDocument114 pagesHR Procurement: 2.1 Human Resource PlanningSmithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Job Evaluation and Work-Flow AnalysisDocument5 pagesChapter 6 Job Evaluation and Work-Flow AnalysisJenefer Diano100% (1)
- Job Analysis: Dr. Richa DasDocument18 pagesJob Analysis: Dr. Richa DasRicha DasNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis and DesignDocument44 pagesJob Analysis and DesignParkbyun HanaNo ratings yet
- Analyze Work & Design Lecture 3Document39 pagesAnalyze Work & Design Lecture 3Shahzad AliNo ratings yet
- IOP - Module 2Document24 pagesIOP - Module 2Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis 2020Document23 pagesJob Analysis 2020Kave MathiNo ratings yet
- Job AnalysisDocument20 pagesJob AnalysisKalyan MurmuNo ratings yet
- Work Flow AnalysisDocument16 pagesWork Flow Analysisanjali_parekh37No ratings yet
- Job Analysis & Talent Management Rev 3Document25 pagesJob Analysis & Talent Management Rev 3Glorya Monalisa NapituNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis TuteDocument32 pagesJob Analysis TuteSithara AlwisNo ratings yet
- 11 GP - Job AnalysisDocument20 pages11 GP - Job Analysisdea larasintaNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis - JD & JSDocument20 pagesJob Analysis - JD & JSAbderrahim HAMDAOUINo ratings yet
- 07.31 IOP Refresher Course Notes-RevisedDocument4 pages07.31 IOP Refresher Course Notes-RevisedJesusa Angelika IlustreNo ratings yet
- 2 - Job AnalysisDocument4 pages2 - Job AnalysisPhia CustodioNo ratings yet
- Job ShopDocument331 pagesJob ShopGYANA RANJAN SAHOONo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 I O PsychDocument4 pagesChapter 2 I O Psychchristineruthfare03No ratings yet
- HRM PresentationDocument39 pagesHRM PresentationMd Fahim Muntasir HeavenNo ratings yet
- Purpose of Job Analysis: Job Description Job Specificatio NDocument11 pagesPurpose of Job Analysis: Job Description Job Specificatio NDEEPALI ANANDNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis & Job DesignDocument19 pagesJob Analysis & Job DesignwardhantpeNo ratings yet
- Hres MidtermDocument8 pagesHres MidtermYOSHIKI SHIMIZUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Recruitment and Selection: Job AnalysisDocument2 pagesChapter 2: Recruitment and Selection: Job AnalysistivaashiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument50 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource ManagementSALIL DHIMANNo ratings yet
- Job AnalysisDocument30 pagesJob AnalysisNetsu JenNo ratings yet
- Chap 006Document68 pagesChap 006Fariz Imran Mohd ShaariNo ratings yet
- RS ModuleDocument11 pagesRS ModuleSomething NewNo ratings yet
- Paper:: 01, Human Resource Management 07, Job AnalysisDocument17 pagesPaper:: 01, Human Resource Management 07, Job AnalysisprabodhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 & 4: Human Resource Planning and Job AnalysisDocument20 pagesChapter 3 & 4: Human Resource Planning and Job AnalysisDuaNo ratings yet
- JOB AnalysisDocument8 pagesJOB Analysisjohnrovietbauat41No ratings yet
- Brendah Oduori OutDocument1 pageBrendah Oduori OutWilliams Grant MaxwelNo ratings yet
- Kisii University Main CampusDocument1 pageKisii University Main CampusWilliams Grant MaxwelNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Job AnalyisisDocument36 pagesUnit - 3 Job AnalyisisuttranisinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 (Slide) - Analyzing Work and Designing JobsDocument36 pagesUnit 2 (Slide) - Analyzing Work and Designing JobsLongNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis Heneman ChapterDocument56 pagesJob Analysis Heneman ChapterZahra AlhalwachiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2-MCQ of PHRMDocument11 pagesUNIT 2-MCQ of PHRMNeil NakadeNo ratings yet
- Role & Job Analysis Session 5-6Document42 pagesRole & Job Analysis Session 5-6Yaramala Sai Venkata Rami ReddyNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis, Design, Specification Description and EvaluationDocument68 pagesJob Analysis, Design, Specification Description and Evaluationkenawy.mubarakNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis - Job Description and Job SpecificationDocument19 pagesJob Analysis - Job Description and Job SpecificationnirakhanNo ratings yet
- Ch04 Peacock EtalDocument26 pagesCh04 Peacock EtalTowkirNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document23 pagesPresentation 3Shuvo DattaNo ratings yet
- Group-Presentation Reengineering Group-1Document64 pagesGroup-Presentation Reengineering Group-1Nguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Group 1 HRM01 Assignment JD JSDocument24 pagesGroup 1 HRM01 Assignment JD JSNguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Group 1 HRM01 Assignment 1 Group JD&JS Slides EvaluationDocument33 pagesGroup 1 HRM01 Assignment 1 Group JD&JS Slides EvaluationNguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Group 1 HRM01 Assignment Job Advertisement RevisedDocument31 pagesGroup 1 HRM01 Assignment Job Advertisement RevisedNguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Name: Oàn V Hào Student ID: 31201028653 Class: HRM-DH46ISB-01Document1 pageName: Oàn V Hào Student ID: 31201028653 Class: HRM-DH46ISB-01Nguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Name: Oàn V Hào Student ID: 31201028653 Class: HRM-DH46ISB-01Document1 pageName: Oàn V Hào Student ID: 31201028653 Class: HRM-DH46ISB-01Nguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Trial Essay Questions V3 DoneDocument5 pagesTrial Essay Questions V3 DoneNguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 - AnsDocument3 pagesChap 5 - AnsNguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Sales Unit 20,000 5,000 Selling Price 15 100Document3 pagesSales Unit 20,000 5,000 Selling Price 15 100Nguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- 30 Quick Wins RebrandDocument11 pages30 Quick Wins Rebrandshivangi guptaNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Aug 22-23Document4 pagesScience 6 Aug 22-23Chelsea SerranoNo ratings yet
- What Are The Expected Tasks You Have Successfully AccomplishedDocument1 pageWhat Are The Expected Tasks You Have Successfully AccomplishedImmortality Realm67% (18)
- Rlong IspDocument1 pageRlong Ispapi-214448028No ratings yet
- Imposter Phenomenon 1Document24 pagesImposter Phenomenon 1گل میوہNo ratings yet
- New BIT Structure For 081 AboveDocument17 pagesNew BIT Structure For 081 Aboveعلي برادةNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan: Learning Outcome Topic Week No. Learnig ActivitiesDocument2 pagesLearning Plan: Learning Outcome Topic Week No. Learnig ActivitiesJereek EspirituNo ratings yet
- REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE FTF LearningDocument6 pagesREVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE FTF LearningHuolynehb TiagoNo ratings yet
- Cur DevDocument23 pagesCur DevKa JoannehNo ratings yet
- Approaches To School CurriculumDocument28 pagesApproaches To School CurriculumChristyNo ratings yet
- Q1W4MAPEH9 Oct10-14,2022Document6 pagesQ1W4MAPEH9 Oct10-14,2022beanila barnacheaNo ratings yet
- Piaget's Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentDocument12 pagesPiaget's Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentAlif Syaiful AdamNo ratings yet
- 20140926090933bill Buckler Learning Process ModelDocument11 pages20140926090933bill Buckler Learning Process ModelrajeeneNo ratings yet
- Ib Psych Command TermsDocument2 pagesIb Psych Command Termsloveis102050% (2)
- Bulls Eye Document - Yes I CanDocument2 pagesBulls Eye Document - Yes I CanmiculapostolNo ratings yet
- Brocklehurst Stephanie Edvt12015 at 1 1Document45 pagesBrocklehurst Stephanie Edvt12015 at 1 1api-366587339No ratings yet
- MY Significant ExperiencesDocument8 pagesMY Significant ExperiencesJennelyn DuranNo ratings yet
- Summery: The Future of Higher Education:: How Technology Will Shape LearningDocument3 pagesSummery: The Future of Higher Education:: How Technology Will Shape LearningAnonymous eubbii2No ratings yet
- The Cleveland Scale For Activities of DaDocument14 pagesThe Cleveland Scale For Activities of DaJesena SalveNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - GALERA, TrinaDocument1 pageActivity 1 - GALERA, Trinatrina mari cassandra GALERANo ratings yet
- Assignment Neural NetworksDocument7 pagesAssignment Neural NetworksSagar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Malfunctions of CommunicationDocument9 pagesMalfunctions of CommunicationJitu NovomeNo ratings yet
- MetaphorDocument205 pagesMetaphoramani mahiNo ratings yet
- Study File 7Document19 pagesStudy File 7Leones JessiejuneNo ratings yet
- Aiml 5 Units NotesDocument134 pagesAiml 5 Units NotesAnand KedhariNo ratings yet