100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views7 pagesGranular Sub Base Layer
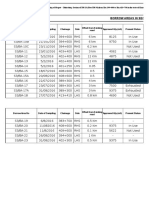
Granular sub-base (GSB) consists of compacting well-graded material between a road's sub-grade and wet mix macadam base layer. It acts as an intermediate drainage layer. GSB uses materials like sand, gravel, crushed stone or slag and must meet grading and permeability standards. Quality tests evaluate properties like sieve analysis, moisture content and compaction density to ensure the GSB effectively drains water away from the sub-grade. GSB construction involves dumping, spreading, watering and compacting the material in layers not exceeding 250mm thickness to at least 98% density.
Uploaded by
Pathankot MandiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views7 pagesGranular Sub Base Layer
Granular sub-base (GSB) consists of compacting well-graded material between a road's sub-grade and wet mix macadam base layer. It acts as an intermediate drainage layer. GSB uses materials like sand, gravel, crushed stone or slag and must meet grading and permeability standards. Quality tests evaluate properties like sieve analysis, moisture content and compaction density to ensure the GSB effectively drains water away from the sub-grade. GSB construction involves dumping, spreading, watering and compacting the material in layers not exceeding 250mm thickness to at least 98% density.
Uploaded by
Pathankot MandiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Granular Sub-base (GSB)
- Grading Requirements
- Quality Tests and Frequency
- GSB Construction Operation