Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Teachers Edition Teachers Edition Removed
Uploaded by
Suhaan HussainOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Teachers Edition Teachers Edition Removed
Uploaded by
Suhaan HussainCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet 6
Name: ( )
Class: Date:
Nutrition in Plants
for Chapter 7
CONNECT IT!
Complete the concept map below using keywords learnt in the chapter. Discuss with your
classmates how the concept map can be extended.
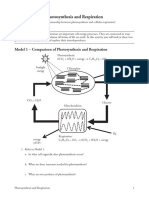
Photosynthesis
intensity
raw materials
limiting Reactions in
factors affects
concentration chloroplasts
, affects
Sunlight,
of
photosynthesis
Equation chlorophyll
dioxide + light energy + Glucose
excess glucose
converted to
for Transport
converted and
stored as
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited Worksheet 6 49
TEST IT!
Section A: Multiple-Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer, and write its letter in the brackets provided.
1. Which of the following leaf cells do not contain chloroplasts?
A Guard cells
B Palisade mesophyll cells
C Spongy mesophyll cells
D Upper epidermal cells ( )
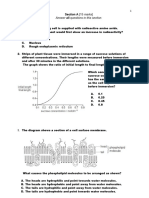
For questions 2 and 3, refer to the diagram below which shows a section from the leaf of a green plant.
2
3 vascular
4 bundle
2. Which regions contain cells with the highest and lowest number of chloroplasts?
Region with highest number of Region with lowest number of
chloroplasts chloroplasts
A 1 2
B 2 6
C 5 2
D 6 1 (
( ))
3. After a period of bright light, which regions contain the most starch?
A 1 and 6
B 2 and 4
C 2 and 5
D 3 and 5 ( )
50 Worksheet 6 © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited
4. The photo below shows part of a green plant. What is X?
A Guard cell
B Palisade mesophyll
C Spongy mesophyll
D Stoma ( )
5. How does most of the carbon dioxide enter the photosynthesising cells of a leaf?
A Diffusion through the epidermis of the leaf
B Diffusion through the phloem of the leaf
C Diffusion through the stomata of the leaf
D Diffusion through the xylem of the leaf ( )
6. The first step in the test for starch in a leaf, is to place the leaf in boiling water for about 5 minutes.
What is the rationale for this step?
A To denature all enzymes in the leaf
B To make the leaf softer so that it is easier to test for starch
C To remove air in the leaf
D To remove chlorophyll from the leaf ( )
7. Glucose, that is manufactured by green leaves during photosynthesis, may be converted into a
storage form or be transported to parts of the plant that need glucose. In what form is glucose
being stored and transported within the plant?
Storage form of glucose Transported form of glucose
A Glycogen Glucose
B Glycogen Sucrose
C Starch Glucose
D Starch Sucrose ( )
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited Worksheet 6 51
Section B: Structured Questions
Answer the following questions in the spaces provided.
1. The equation for photosynthesis is usually given as:
light energy
Water + Carbon dioxide Glucose + Oxygen
chlorophyll
Which organelle does photosynthesis occur in?
2. The graph shows the rate of photosynthesis of a plant with increasing light intensity. The temperature
was kept at 20°C.
Rate of
photosynthesis
Light intensity
(a) Mark the section of the graph where light intensity is the major limiting factor.
Label this section as X.
(b) Mark the section of the graph where a factor other than light intensity is limiting the rate of
photosynthesis. Label this section as Y.
(c) Suggest a possible limiting factor at section Y.
52 Worksheet 6 © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited
3. The graph below shows the effect of light intensity on a plant’s rate of photosynthesis at two
different temperatures. Curve A was obtained from a plant kept at lower temperature, while curve
B was obtained from a plant kept at a higher temperature.
Rate of
photosynthesis
4
B
2
A
Light intensity
(a) What factor(s) was (were) affecting the rate of photosynthesis at each of the regions, 1, 2 and 3,
on the graph? Give reasons for your answers.
(b) Suggest two factors that might have been limiting the rate of photosynthesis at region 4 on
curve B.
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited Worksheet 6 53
4. The apparatus below can be used to investigate the rate of photosynthesis.
air bubble plastic tube
graduated
capillary tube
well-lubricated
syringe
cork
dilute sodium
hydrogencarbonate
solution
water
water at room temperature
plant
boiling tube
(a) Suggest what is measured in this experiment to show that photosynthesis has occurred.
(b) Describe how this apparatus can be used to measure the effect of light intensity on the rate of
photosynthesis.
(c) State three steps that need to be taken during the experiment described in (b) to minimise
sources of errors.
54 Worksheet 6 © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited
5. A shoot of Hydrilla was placed in a boiling tube containing pond water. A bench lamp with a 60 W
bulb shining at the boiling tube, was placed 25 cm away. An oxygen probe was put into the boiling
tube, and the oxygen concentration was recorded by a data logger. The oxygen concentration was
recorded after 5 minutes and again 10 minutes later. The experiment was then repeated using the
same Hydrilla in the same boiling tube, but with the lamp placed 5 cm away from the boiling tube.
The results are given in the table below.
Distance of lamp/cm Oxygen concentration after Oxygen concentration after
5 mins/% saturation 10 mins/% saturation
25 60 65
5 64 84
(a)
(a)
oxygen sensor
interface computer
thermometer
boiling tube
light intensity sensor
beaker
pond water lamp
Hydrilla
water bath (to keep
temperature constant)
retort stand
tripod stand
25 cm
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited Worksheet 6 55
(a) Based on the results of this experiment, explain the effect of light intensity on oxygen
production.
(b) (c) (i) What process are we trying to investigate when we measure the oxygen concentration in
this experiment?
(ii) Why is the measurement of oxygen concentration considered an inaccurate measurement
of the rate of the process stated in (c)(i)?
(c) (d) State one environmental condition that would need to be kept constant during this experiment.
Describe how this condition can be kept constant.
56 Worksheet 6 © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited
6. Photosynthesis takes place mostly in the leaves of plants. The laminae of most leaves are wide
and thin, as shown in the diagram below.
(a) Name the cells in the leaf where most photosynthesis takes place.
(b) Which tissue in the leaf supplies water to the cells for photosynthesis?
(c) Explain how having a wide lamina helps a leaf to photosynthesise.
(d) Explain how having a thin lamina helps a leaf to photosynthesise.
(e) Most leaves are covered with a transparent, waterproof cuticle. How does this feature aid in
photosynthesis?
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited Worksheet 6 57
Section C: Free-Response Questions
Answer the following questions.
1. Discuss the major adaptations of the leaf for photosynthesis.
58 Worksheet 6 © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited
2.
results in a table. Plot a graph to show the rate of bubbling per minute against the temperature.
photosynthesis to a certain extent. At very high temperatures, the rate of photosynthesis will
decrease.”
Photosynthesis is an enzyme-catalysed reaction. There will be increased collision of enzyme and
substrate molecules as temperature increases. This results in more enzyme-substrate complexes
being formed, and thus, a higher rate of reaction. However, at very high temperatures, enzymes being
protein in nature, will be denatured. The substrate no longer fits into the active site, and an
enzyme-substrate complex cannot be formed. Thus, the rate of photosynthesis will decrease.
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited Worksheet 6 59
You might also like
- Photosynthesis-What's in A LeafDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis-What's in A LeafMarvellousNo ratings yet
- Water Demand All SlidesDocument23 pagesWater Demand All Slidesrajat debnathNo ratings yet
- DOPE Personality TestDocument8 pagesDOPE Personality TestMohammed Hisham100% (1)
- Macromolecules Worksheet Answer KeyDocument10 pagesMacromolecules Worksheet Answer KeyHarriet KirklandNo ratings yet
- CIE IAL BIOLOGY Topic Questions PDFDocument137 pagesCIE IAL BIOLOGY Topic Questions PDFMaisha IslamNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide to M.C.Q,Science (C.B.S.E & N.C.E.R.T) Class 10: CBSE MCQ Series, #3From EverandA Complete Guide to M.C.Q,Science (C.B.S.E & N.C.E.R.T) Class 10: CBSE MCQ Series, #3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- C0904 091814 PDFDocument54 pagesC0904 091814 PDFBuddy JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Bio Factsheet Chloroplasts - Structure and Function Number 198 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukDocument4 pagesBio Factsheet Chloroplasts - Structure and Function Number 198 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukbekoNo ratings yet
- 07 Test BankDocument18 pages07 Test BankAditya PaluriNo ratings yet
- Chloroplasts Structure and Function FactsheetDocument4 pagesChloroplasts Structure and Function Factsheettapas kundu100% (1)
- Module 3 - Transport MechanismDocument12 pagesModule 3 - Transport MechanismVynch jyd bachinichaNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Science Stage 9 - 2018 - tcm143-353968Document82 pagesScheme of Work Science Stage 9 - 2018 - tcm143-353968Arjun SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Bài tập thì Quá khứ đơn-Quá khứ tiếp diễnDocument8 pagesBài tập thì Quá khứ đơn-Quá khứ tiếp diễnÁnh Hồng100% (1)
- Acs - Ed - Ed-2010-004867 1.Document4 pagesAcs - Ed - Ed-2010-004867 1.finatikamustikasNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: B. Carbon DioxideDocument107 pagesPhotosynthesis: B. Carbon DioxideJing LiNo ratings yet
- New Alian High School & College Raru Ambore MZDDocument1 pageNew Alian High School & College Raru Ambore MZDPrince ArsalNo ratings yet
- Biology 11Th Edition Raven Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesBiology 11Th Edition Raven Test Bank Full Chapter PDFlewis.barnes1000100% (12)
- Assignment Booklet: BBYCT-137Document4 pagesAssignment Booklet: BBYCT-137Ashish YadavNo ratings yet
- Final 23 June Autumn 2020sDocument15 pagesFinal 23 June Autumn 2020sLucy grahamNo ratings yet
- Focus Batch PCB Test 25Document72 pagesFocus Batch PCB Test 25Aditya rajNo ratings yet
- CE Biology 2007 Paper 2Document17 pagesCE Biology 2007 Paper 2api-37022300% (1)
- 9 ADV - Inspire-Coverage Based Practice - Term1 - 2023Document56 pages9 ADV - Inspire-Coverage Based Practice - Term1 - 2023s618765No ratings yet
- 11 Biology Imp Ch13 2Document4 pages11 Biology Imp Ch13 2Kiran KrutanjaliNo ratings yet
- Bio150 Final Online Test Question July 2020 - ArauDocument10 pagesBio150 Final Online Test Question July 2020 - ArauNor Iftiha AzizNo ratings yet
- Test Series 2 PDFDocument44 pagesTest Series 2 PDFTani SinghNo ratings yet
- 9700 Topic QuestionsDocument137 pages9700 Topic QuestionsBrownsonNo ratings yet
- BIO Sessional-1 Nov 22Document4 pagesBIO Sessional-1 Nov 22dreamivory29No ratings yet
- School Chemistry 3 Corrosion, Redox Reaction Stoichiometry and Faraday's Law in Electrolysis CellsDocument15 pagesSchool Chemistry 3 Corrosion, Redox Reaction Stoichiometry and Faraday's Law in Electrolysis CellsAmeliana FitriyantiNo ratings yet
- Analysis Table Concept-2Document16 pagesAnalysis Table Concept-2blackwhite121201No ratings yet
- Worksheet D (Covers Practical 5) : Name Prac Partners Prac Date Due DateDocument7 pagesWorksheet D (Covers Practical 5) : Name Prac Partners Prac Date Due DateRamya PamidimukkalaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 405Document2 pagesChemistry 405Aniket SinghaNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis RcsiDocument4 pagesPHD Thesis Rcsiseewbyvff100% (2)
- 9 Science Q1 W7Document11 pages9 Science Q1 W7Mark Ivan AbrizaNo ratings yet
- CH 06Document42 pagesCH 06Divine Grace InovejasNo ratings yet
- 1.2.7 Practice - Cell Membrane Structure and Function (Practice)Document6 pages1.2.7 Practice - Cell Membrane Structure and Function (Practice)Lilith GodchildNo ratings yet
- Please Note: Assignment BookletDocument3 pagesPlease Note: Assignment BookletDasNo ratings yet
- 05 Test BankDocument17 pages05 Test Bankchloe0916767551No ratings yet
- 2019 Johor Biology K2 SET B Jawapan - Ms.enDocument16 pages2019 Johor Biology K2 SET B Jawapan - Ms.enHarshene KumaranNo ratings yet
- Bioc202 Problem SetsDocument14 pagesBioc202 Problem SetsSYZCNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Biology Key DR Sunil Model Feb 2024Document6 pagesHsslive Xi Biology Key DR Sunil Model Feb 2024abhaianil24No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis IntroductionDocument29 pagesPhotosynthesis IntroductionyashalabdullashafeeuNo ratings yet
- Biochem 323-Final 2005Document1 pageBiochem 323-Final 2005api-3763291No ratings yet
- Notes by Alakh PandeyDocument9 pagesNotes by Alakh Pandeyirfanalirind181No ratings yet
- MIC 201 - Theory Paper 1 - June 2022Document9 pagesMIC 201 - Theory Paper 1 - June 2022Lucas LuluNo ratings yet
- Acsbiomedchemau 1c00068Document6 pagesAcsbiomedchemau 1c00068mudhra143No ratings yet
- Question Paper Grade 9 10Document14 pagesQuestion Paper Grade 9 10Inspire BoosterNo ratings yet
- BCH 369 Lecture 16: Nov 1/5, 2018: How Would The Following Carbohydrate Be Classified?Document4 pagesBCH 369 Lecture 16: Nov 1/5, 2018: How Would The Following Carbohydrate Be Classified?Paul Stephen SorianoNo ratings yet
- Search PHD Thesis OnlineDocument6 pagesSearch PHD Thesis OnlineBuyEssaysOnlineForCollegeNewark100% (2)
- 1: Biological Molecules - Topic Question S: Year Series Paper NumberDocument10 pages1: Biological Molecules - Topic Question S: Year Series Paper NumberlenaNo ratings yet
- 14 Photosynthesis and Respiration-SDocument6 pages14 Photosynthesis and Respiration-SAddy MilliganNo ratings yet
- The Big Picture: Leaf StructureDocument20 pagesThe Big Picture: Leaf StructureSoumiya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Everyday Science McqsDocument5 pagesEveryday Science Mcqsnewidmvp3No ratings yet
- Practice 1 - MS Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesPractice 1 - MS Introduction To Organic ChemistryNew Generation ClubNo ratings yet
- C 1 3 2025 Topic Test MsDocument5 pagesC 1 3 2025 Topic Test MsRawanMazen SharifNo ratings yet
- Syllabus and Sample Questions For JRF: Agricultural and Ecological Research Unit (Test Code: RAE)Document6 pagesSyllabus and Sample Questions For JRF: Agricultural and Ecological Research Unit (Test Code: RAE)api-26401608No ratings yet
- Plants QuizDocument11 pagesPlants QuizMasheNo ratings yet
- CELL BIO - 101 - THEORY - June 2019Document7 pagesCELL BIO - 101 - THEORY - June 2019Lucas LuluNo ratings yet
- Elements of Ecology Canadian 1st Edition Smith Test BankDocument20 pagesElements of Ecology Canadian 1st Edition Smith Test Bankluongsophieixvqp100% (29)
- MIC 201 - Prac Paper 2 - June 2022Document6 pagesMIC 201 - Prac Paper 2 - June 2022Lucas LuluNo ratings yet
- Biology: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument16 pagesBiology: PAPER 1 Multiple Choicesiriyo7821No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 2Document10 pagesPhotosynthesis 2Ali AshrafNo ratings yet
- Bio Trial Paper SET 1Document8 pagesBio Trial Paper SET 1m-7319562No ratings yet
- Journal of Colloid and Interface ScienceDocument11 pagesJournal of Colloid and Interface ScienceNazmul AlamNo ratings yet
- Syllabus NEETDocument5 pagesSyllabus NEETSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Physics Command WordsDocument5 pagesPhysics Command WordsSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Biotec q1 Bacteria FermenterDocument1 pageBiotec q1 Bacteria FermenterSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Shape All FormulaDocument1 pageShape All FormulaSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- VocabularyDocument3 pagesVocabularySuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Daily VocabularyDocument1 pageDaily VocabularySuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- (O LEVELS) Biology Definitions Here - SGExamsDocument17 pages(O LEVELS) Biology Definitions Here - SGExamsSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactor NotesDocument2 pagesNuclear Reactor NotesSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- DRAGONDocument1 pageDRAGONSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- 4024 Y18 SP 2.inddDocument2 pages4024 Y18 SP 2.inddSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Vectors (Add Math) Unsolved PDFDocument14 pagesVectors (Add Math) Unsolved PDFSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Notes and Past PapersDocument38 pagesKinematics Notes and Past PapersSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument25 pagesUntitledSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument54 pagesNuclear PhysicsSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Physics Definitions, Laws, Principles - o LevelDocument35 pagesPhysics Definitions, Laws, Principles - o LevelSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- All Electric Circuit SymbolDocument1 pageAll Electric Circuit SymbolSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Physics Book 5054 o Level PDFDocument1,015 pagesPhysics Book 5054 o Level PDFSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- E - Mail WrittingDocument1 pageE - Mail WrittingSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Physical Method of Food PreservationDocument2 pagesPhysical Method of Food PreservationSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- O Level Math Trigonometry (Solved)Document36 pagesO Level Math Trigonometry (Solved)Suhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis 2Document1 pageHomeostasis 2Suhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Physics 16 - Thermal ProcessesDocument19 pagesPhysics 16 - Thermal ProcessesSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis 1Document1 pageHomeostasis 1Suhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes ME Task Lesson 06Document8 pagesEnergy Changes ME Task Lesson 06Suhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- After Spending Over 12 Hours On The PlaneDocument1 pageAfter Spending Over 12 Hours On The PlaneSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Food PreservationDocument2 pagesFood PreservationSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Strong Comparison For Descriptive EssayDocument1 pageStrong Comparison For Descriptive EssaySuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Physics Waves RevisionDocument13 pagesPhysics Waves RevisionSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- 1 Minute TiopicsDocument5 pages1 Minute TiopicsSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument17 pagesElectrolysisSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument3 pagesScoliosisTracy100% (1)
- AUKEY EP-T21 TWS User Manual 20190921Document1 pageAUKEY EP-T21 TWS User Manual 20190921Manuel MartínNo ratings yet
- Fifa 11+Document7 pagesFifa 11+HeiYu TongNo ratings yet
- Anti-Violence Against Women and Their Children Act of 2004 (Republic Act No. 9262)Document5 pagesAnti-Violence Against Women and Their Children Act of 2004 (Republic Act No. 9262)Tobythe BullyNo ratings yet
- Case Study PanajiDocument28 pagesCase Study PanajiKris Kiran100% (1)
- Success Strategies Fro Grad SchoolDocument18 pagesSuccess Strategies Fro Grad SchoolbiplabdekaNo ratings yet
- Lovely LungsDocument6 pagesLovely Lungsapi-285970439No ratings yet
- Body Systems TestDocument6 pagesBody Systems TestIRENE DÁVALOS SMILGNo ratings yet
- Tyler Resume Updated 3 23 17Document1 pageTyler Resume Updated 3 23 17api-285213449No ratings yet
- Selecting Employees: Publishing As Prentice Hall 1Document55 pagesSelecting Employees: Publishing As Prentice Hall 1Waisuddin KarimiNo ratings yet
- Bi No.6 Karmachari Khula SullabusDocument78 pagesBi No.6 Karmachari Khula SullabusshaimenneNo ratings yet
- The Wall Street Journal - 05.01.22Document28 pagesThe Wall Street Journal - 05.01.22TIMOTEO ROJAS CARRILLONo ratings yet
- (Susan Aldridge) The Thread of Life The Story ofDocument272 pages(Susan Aldridge) The Thread of Life The Story ofsergioNo ratings yet
- ELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: L 4: C A Delta - Star TDocument68 pagesELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: L 4: C A Delta - Star TJesús RomeroNo ratings yet
- Deltaweld 453 MilDocument40 pagesDeltaweld 453 MilHugo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- REVISED Syllabus GR 6-8 Science CambridgeDocument10 pagesREVISED Syllabus GR 6-8 Science CambridgePooja SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Roberto Conrado Guevara - Response From The Laity (Oct 2)Document29 pagesDr. Roberto Conrado Guevara - Response From The Laity (Oct 2)Joviner Yabres LactamNo ratings yet
- Don Honorio Ventura Technological State University Bacolor, PampangaDocument10 pagesDon Honorio Ventura Technological State University Bacolor, PampangaAnonymous Xwd7uWe0YUNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 7 Human Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSEDocument6 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 7 Human Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSEImran MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Science Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesScience Investigatory ProjectVhon AndreaNo ratings yet
- Air Cargo (Assignment 1)Document5 pagesAir Cargo (Assignment 1)Sara khanNo ratings yet
- Disersa GuatemalasurDocument340 pagesDisersa GuatemalasurGerson David Ortíz MoralesNo ratings yet
- Appointment RecieptDocument1 pageAppointment Recieptaqil faizanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 Reference Notes Class 10Document3 pagesLesson 14 Reference Notes Class 10Seetha Lekshmi KishoreNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka PDFDocument7 pagesDaftar Pustaka PDFaulia rahmiNo ratings yet
- SPM 7 Form 5 Chapter 2: ElectricityDocument31 pagesSPM 7 Form 5 Chapter 2: Electricitylelon81No ratings yet