Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nutrition and Weight Management
Uploaded by
Farmisa Mannan100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
20 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Nutrition-and-Weight-management
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
20 views2 pagesNutrition and Weight Management
Uploaded by
Farmisa MannanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
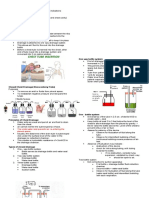
Nutrition and Weight management Obesity -when overweight is the result of excessive
body fat rather than enhanced muscle or skeletal
Enzymes -complex protein produced by living cells
tissue.
that acts as catalyst to speed the rate of chemical
reaction. OBESITY- defined as excess fat accumulation under the skin
o -facilitate chemical changes. and around the organs in the body.
Catalyst -a chemical or compound that speeds up
Subcutaneous fat – fat accumulated in the lower
the chemical reaction but is not change in the
body (the pear shape).
process.
Visceral fat – fat in the abdominal area (the apple
Hormone -internally secreted substances from the
shape)
endocrine glands that carried in the blood to another
*abdominal fat correlates more with health risks
organ or tissue on which they act to stimulate
such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
functional activity or secretion.
*in women, it also correlates with breast cancer risk
Leptin - an appetite –suppressing hormone involved
and gallbladder disease.
in maintenance of body composition.
o -help maintain normal weight. Factors that Influence Food Intake
Ghrelin -a hormone released from the
stomach that signal the brain (hypothalamus) it’s 1. Lifestyle Behaviors
time to eat. o eating pattern
Coenzymes - many enzymes requires partners to o eating breakfast
assist in completing their work. These coenzymes o the length of time spend chewing food
partners are often vitamins, especially B-complex
Cofactors -increase the rate of reaction required for 2. Human Physiology- numerous hormones and
enzyme to function. neuoropeptides that stimulate or inhibit food intake
o -various minerals that participate in enzyme
3. Macronutrients Energy Composition
reactions.
Substrate -the specific organic substance on which a Obesity and Health--weight-related health problems can be
particular enzyme acts to produce a new metabolic divided into four categories:
product.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)- high energy 1. Metabolic
Phosphate compound, are major energy source for type 2 diabetes
carrying out body functions. Dyslipidemia (elevated blood lipids, high
Phosphocreatinine (PCr) – another type of high cholesterol)
Energy compound present in muscle cells and can be
quickly broken down to released enough energy to 2. Degenerative- osteoarthritis and joint problems and
make more ATP. pulmonary diseases
TRANSFORMATION OF ENERGY 3. Neoplastic-any forms of cancer (endometrial breast, colon,
prostate, and ovarian)
1. Chemical energy – food is a good example of stored
chemical energy 4. Anatomic individuals- exceeding a healthy weight have a
2. Electrical energy – use for transmitting nerve greater risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and
impulses and carrying out brain activity obstructive sleep apnea
3. Mechanical energy – muscle contractions
How to Achieve Weight Loss
4. Thermal energy – regulation of body temperature
Metabolism - is a term that is used to describe all 1. Diet therapy-consume highly nutritious food vegetable,
chemical reactions involve in maintaining the living high fiber grains, heart-healthy protein such as sea food and
state of the cells and organism. low fat dairy.
2 types of Metabolic Reaction
Catabolism -the breakdown of molecules into 2. Behavior change method or Behavior modification
smaller unit. regardless of which type of eating pattern for weight loss,
Anabolism –builds simple molecules into small true behavior change is a must.
complex one. Weight control: Behavior modification technique
SOURCES OF STORED ENERGY
Glycogen - only 12-36 hour reserve of glycogen exist
in liver and muscle and is quickly depleted.
Adipose (fat) tissue - fat stores are generally the
largest resource of stored energy.
Muscle mass - energy stores in the form of muscle
protein. ENERGY BALANCE:
Body weight is maintained when calories eaten
equal the number of calories the body expends or
burns.
Overweight-a person weights more according to
standard of height and weight.
the way food is absorbed. The pouch is only about the size of
a walnut.
Vertical sleeve gastrectomy (VSG). This newer
procedure involves removing much of the stomach
in a vertical fashion, allowing only a tubular sleeve-
shaped stomach which empties into the duodenum.
Because so much stomach is removed, there is less
ghrelin which reduces hunger more than banded
gastroplasty.
Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenum switch
(BPD-DS). Sometimes this surgery is done 6-18
3. Physical activity staying physically active to build and
months after a sleeve surgery, as a “staged
preserve muscle, in tandem with a healthier diet, are the
approach” to weight loss surgery. It involves
ingredients for weight loss and healthy weight maintenance.
rerouting the sleeve from much of the small
BENEFITS OF EXERCISE intestine and diverting bile and gastric juices to
change digestion and absorption.
Improved health
Stronger muscles Underweight-extreme underweight is associated with serious
Better flexibility health problems in all age group.
Improved posture General causes of Malnutrition
Improved heart
Better appetite Poor food intake
Feeling more relax Increase in energy requirements
Better social life Poor utilization of available nutrients
Improved quality of life
Interventions
Reduced risk of disease and ill-health
Eat frequently (five or six small meals per day) to
avoid feeling full.
Eat food that are dense in nutrients and calories
(e.g., nuts, seeds, dried fruit, egg, avocado, yogurt).
Limit heavy amounts of sugar or unhealthy fats.
Add healthy fat to food in cooking such as olive or
canola oil or mayonnaise. Butter, whole milk, and
cheese have higher amounts of saturated fats and
may need to be used with a little more discretion in
those with cholesterol concerns.
Pack foods to eat when away from home so there
are no gaps in eating if a restaurant is not
convenient.
Check out high-calorie snack recipes to make at
4. Weight Loss Drugs home such as milk shakes and puddings and dense
foods such as a homemade peanut butter granola
xenical (1990) reduces the body’s ability to absorb bar.
fats from foods Consider supplement drinks to boost calories as
fenfluramine, Meridia needed.
5. Surgery Encourage parents of underweight children to
provide support, but not threaten, bribe, or
- Adjustable gastric band (AGB). A small bracelet-like band is forcefeed their child, as their child will engage in the
placed around the top of the stomach to restrict the size of opposite behavior and back away from the food.
the opening from the throat to the stomach, thereby Fully investigate the root cause of the underweight
reducing food intake. The size of the opening can be status.
controlled via a balloon inside the band. Consult a doctor or dietitian for a full evaluation and
treatment plan.
Adjustable gastric band (AGB). A small bracelet-like band is
placed around the top of the stomach to restrict the size of
the opening from the throat to the stomach, thereby
reducing food intake. The size of the opening can be
controlled via a balloon inside the band.
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). Food intake is limited as
surgeuons create a small pouch for the stomach. This pouch
is then connected to a different part of the intestine
(bypassing the stomach and duodenum), thereby changing
You might also like
- TRANSFORMATION OF ENERGY (Nutri)Document5 pagesTRANSFORMATION OF ENERGY (Nutri)mroxandeeNo ratings yet
- Weight ManagementDocument3 pagesWeight ManagementTimol, Sophea B.No ratings yet
- Module 9 Weight ManagementDocument28 pagesModule 9 Weight ManagementHas SimNo ratings yet
- THE Process of DigestionDocument39 pagesTHE Process of DigestionskaiiNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Metab N EndocrineDocument148 pagesNCM 103 Metab N EndocrinernrmmanphdNo ratings yet
- Module 1 6 Lec Nutrition and Diet Therapy Prelim ReviewerDocument7 pagesModule 1 6 Lec Nutrition and Diet Therapy Prelim Reviewerjoyce.feir03No ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy AssDocument2 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy AssMary Angeline DabuNo ratings yet
- Basic NutritionDocument46 pagesBasic NutritionRahul Humpal100% (2)
- Nutrition: A. E B - Energy Is Derived or Obtained From Foods ConsumedDocument11 pagesNutrition: A. E B - Energy Is Derived or Obtained From Foods Consumeddlneisha6167% (6)
- Ncm105 Nutrition and DietDocument13 pagesNcm105 Nutrition and DietRizald CordovaNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Lec: Nutriton and Diet Therapy Project On Therapeutic DietsDocument15 pagesNCM 105 Lec: Nutriton and Diet Therapy Project On Therapeutic DietsVinz OñoNo ratings yet
- Pe&h Q1 NotesDocument10 pagesPe&h Q1 NotesGrinesteinNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Prelim Notes Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument21 pagesNCM 105 Prelim Notes Nutrition and Diet Therapys.labita.sherynejoelNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance and Body CompositionDocument3 pagesEnergy Balance and Body CompositionYcell LatidoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument64 pagesNutrition and Diet TherapyAnn Myriel BuctuanNo ratings yet
- Powepoint Mark 1Document40 pagesPowepoint Mark 1XanderNo ratings yet
- Nutritional and Dietary Lecture ReviewerDocument4 pagesNutritional and Dietary Lecture ReviewerJohn Mikelangelo V. AndonNo ratings yet
- Nutrition & Diet Therapy Digestion, Absorption, MetabolismDocument13 pagesNutrition & Diet Therapy Digestion, Absorption, MetabolismMary Queenie Tulin100% (1)
- Kin 163 - Review Exam 3Document3 pagesKin 163 - Review Exam 3bookworm100313No ratings yet
- IronMagazine CompleteBodyBuilding PDFDocument95 pagesIronMagazine CompleteBodyBuilding PDFTheoNo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument40 pagesNUTRITIONShene Claire VigillaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument24 pagesNutrition and Diet TherapyKimberly Marie BayangNo ratings yet
- Basic Nutrition (Teresita)Document12 pagesBasic Nutrition (Teresita)Veloria AbegailNo ratings yet
- Finale NCM 105 Week 2-Lesson 1-3: Hydrolysis - Chemical Breakdown, Adding ofDocument3 pagesFinale NCM 105 Week 2-Lesson 1-3: Hydrolysis - Chemical Breakdown, Adding ofAnna SantosNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument8 pagesDigestive System NotesDale Gil JuliaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Energy RequirementDocument40 pagesFactors Affecting Energy RequirementKaviish AnandanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER I BASIC CONCEPT NUTRITION AND DIET THERAPY Questions01Document30 pagesCHAPTER I BASIC CONCEPT NUTRITION AND DIET THERAPY Questions01Jeeyan DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To Nutrition NutritionDocument7 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To Nutrition NutritionMajo Ramirez MataverdeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Key TermsDocument3 pagesChapter 12 Key TermsAlthea MangasarNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Part 2Document25 pagesNutrition Part 2vanNo ratings yet
- االتغذيه كاملهDocument13 pages االتغذيه كاملهreadsa722No ratings yet
- Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument51 pagesBasic Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Lecture 1 IntroductionBethrice Melegrito100% (1)
- Digestive SystemDocument29 pagesDigestive SystemcayananjefffrancisNo ratings yet
- OBESITY BASICSDocument10 pagesOBESITY BASICSgraceNo ratings yet
- P108.module 7.hunger, Eating, & HealthDocument18 pagesP108.module 7.hunger, Eating, & HealthMiles Rommel G. RitosNo ratings yet
- Physical Education 1 NotesDocument3 pagesPhysical Education 1 Notesbalbutin.marycarmelNo ratings yet
- Obesity PDFDocument7 pagesObesity PDFRoderick RichardNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Food Intake: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran USUDocument17 pagesRegulation of Food Intake: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran USURhena Fitria KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Physical Education 1 HandoutsDocument3 pagesPhysical Education 1 HandoutsGrace Hope SinilongNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition TrifoldDocument4 pagesAnimal Nutrition TrifoldLogan GarfieldNo ratings yet
- NDT LecDocument13 pagesNDT LecAia RecaidoNo ratings yet
- Physiologic Value of FoodDocument2 pagesPhysiologic Value of FoodCrisheila Sarah Piedad0% (1)
- Nutrition Quiz NotesDocument8 pagesNutrition Quiz NotesThomas AssisNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance and ObesityDocument6 pagesEnergy Balance and Obesityalihussein100% (4)
- Handout NRG201Document13 pagesHandout NRG201Kyle DoloritosNo ratings yet
- Obesity & Weight ManagementDocument44 pagesObesity & Weight Managementonline masterNo ratings yet
- Principles of Training: Overload CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Training: Overload CarbohydratesJesseca JosafatNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids and ProteinsDocument82 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids and Proteinskalyani.shindeNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy Summary of BookDocument17 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy Summary of BookMabes100% (2)
- The Six Stages of NutritionDocument4 pagesThe Six Stages of Nutritioncaptaincupcakes95No ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy GuideDocument29 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy GuideLouie Pangilinan LanajaNo ratings yet
- Sports Nutrition Concept MapDocument1 pageSports Nutrition Concept Mapcharmaine caratingNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument14 pagesNutrition and Diet TherapyJOVEMEA LIRAYNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument3 pagesNutritionAramella VaronaNo ratings yet
- OBESITY OriginalDocument33 pagesOBESITY OriginalJenny ChhadwaNo ratings yet
- Digestion, Nutrients, and Human Body CompositionDocument10 pagesDigestion, Nutrients, and Human Body CompositionLeordean VeronicaNo ratings yet
- Sports Health DisciplinesDocument15 pagesSports Health Disciplinesjade brionesNo ratings yet
- Consider Four Basic Food GroupsDocument3 pagesConsider Four Basic Food GroupsPrecious ViterboNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics Nutrition in Sports: Newton's LawDocument6 pagesBiomechanics Nutrition in Sports: Newton's LawMarco ZasoNo ratings yet
- Plant Based Nutrition for Endurance Athletes: The New Science of Exploiting Organic and Raw FoodsFrom EverandPlant Based Nutrition for Endurance Athletes: The New Science of Exploiting Organic and Raw FoodsNo ratings yet
- Neurologic System - Lec 1Document6 pagesNeurologic System - Lec 1Farmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- YasinDocument3 pagesYasinFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- ShizopreniaDocument5 pagesShizopreniaFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- This Phase Occurs When The Community Organization Has Already Been Established and The Community Members Are Already Actively Participating in Community Wide UndertakingsDocument2 pagesThis Phase Occurs When The Community Organization Has Already Been Established and The Community Members Are Already Actively Participating in Community Wide UndertakingsFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- What Were The Ideas Embedded in My Dance When I Started To Create My PieceDocument5 pagesWhat Were The Ideas Embedded in My Dance When I Started To Create My PieceFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Community DiagnosisDocument6 pagesCommunity DiagnosisFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Hema Nclex Q'SDocument6 pagesHema Nclex Q'SFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- ElsieDocument4 pagesElsieFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- CHN Week 3 Sy 2022Document29 pagesCHN Week 3 Sy 2022Farmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Demography: Sources of Demographic DataDocument8 pagesDemography: Sources of Demographic DataSHERMINA HASANNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 CHNDocument5 pagesLecture 1 CHNFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Book For NurdrDocument34 pagesBook For NurdrFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- 10 11 Planning Community Health InterventionDocument3 pages10 11 Planning Community Health InterventionFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- 1 - Hema Lec FinalsDocument8 pages1 - Hema Lec FinalsFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and Evaluating Community Health ProgramsDocument1 pageMonitoring and Evaluating Community Health ProgramsFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- 2 - School Health NursingDocument2 pages2 - School Health NursingFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- 3 RolesDocument2 pages3 RolesFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument2 pagesFetal CirculationFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- 3 Physical AssessmentDocument19 pages3 Physical AssessmentFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- 4 Pulmo Exercises TreatmentDocument6 pages4 Pulmo Exercises TreatmentFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- ABBREVIATION LIST FOR MEDICAL RECORD DOCUMENTATIONDocument11 pagesABBREVIATION LIST FOR MEDICAL RECORD DOCUMENTATIONHyoyeon KimNo ratings yet
- Module EardropsDocument4 pagesModule EardropsFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Human SexualityDocument4 pagesHuman SexualityFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- 5 Chest Tube ThoracostomyDocument6 pages5 Chest Tube ThoracostomyFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Published Vers Ns ArticleDocument7 pagesPublished Vers Ns ArticleFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- ABBREVIATION LIST FOR MEDICAL RECORD DOCUMENTATIONDocument11 pagesABBREVIATION LIST FOR MEDICAL RECORD DOCUMENTATIONHyoyeon KimNo ratings yet
- Themes in Philo of ManDocument3 pagesThemes in Philo of ManFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Man's Search For Meaning (Philosophy)Document5 pagesMan's Search For Meaning (Philosophy)Ma Yumi Angelica Tan75% (4)
- Medication ErrorsDocument8 pagesMedication ErrorsFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- CHN 104j Course Outline Indiv Fam S2Document4 pagesCHN 104j Course Outline Indiv Fam S2Farmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Ch4 - Questions 6th EditionDocument13 pagesCh4 - Questions 6th EditionWala Abu GharbiehNo ratings yet
- Ccle Mid002Document23 pagesCcle Mid002Frankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Excipients ListDocument10 pagesExcipients ListDilla Wulan NingrumNo ratings yet
- It Is Easy To Be Hard, But It Is Hard To Be Smart.Document18 pagesIt Is Easy To Be Hard, But It Is Hard To Be Smart.Anthony DinicolantonioNo ratings yet
- You are what you eat: How Indian diets and lifestyles are making people unhealthyDocument16 pagesYou are what you eat: How Indian diets and lifestyles are making people unhealthyShashank Kamshetty100% (1)
- Assessing The Impact of Sugary Beverage Consumption On Public Health in Ghana: Trends, Challenges, and Policy ImplicationsDocument16 pagesAssessing The Impact of Sugary Beverage Consumption On Public Health in Ghana: Trends, Challenges, and Policy ImplicationsJosephine NarteyNo ratings yet
- + +Over+40+Ab+Solution+PDF eBook,+Shaun+HadsallDocument65 pages+ +Over+40+Ab+Solution+PDF eBook,+Shaun+HadsallSherif Abdel Hamid Fakhry100% (2)
- Diet Choices-1Document9 pagesDiet Choices-1mahmoud raedNo ratings yet
- Case dm2Document6 pagesCase dm2Timothy HallNo ratings yet
- 14 Deadlift Tips and TricksDocument4 pages14 Deadlift Tips and TricksSovietPrimeNo ratings yet
- HA-RLE-WS # 10 Assessing Nutritional StatusDocument4 pagesHA-RLE-WS # 10 Assessing Nutritional StatusJULIE ANNE CORTEZNo ratings yet
- PE 3 Modules StudentsDocument96 pagesPE 3 Modules StudentsRosemarie R. Reyes50% (2)
- Taylor 5563 Scale 5563 ManualDocument2 pagesTaylor 5563 Scale 5563 ManualNick Visutsithiwong0% (1)
- Add Maths Project Pictures SPMDocument4 pagesAdd Maths Project Pictures SPMdanushvar maheswaranNo ratings yet
- FC Orth (SA) Intermediate Past Papers - 2012 Sept 28-3-2015Document2 pagesFC Orth (SA) Intermediate Past Papers - 2012 Sept 28-3-2015Uhuebor DavidNo ratings yet
- Intermediary MetabolismDocument91 pagesIntermediary MetabolismConrad Monterola100% (1)
- Adol ch2 PDFDocument11 pagesAdol ch2 PDFSari Yuli AndariniNo ratings yet
- Statistics Study ProposalDocument5 pagesStatistics Study ProposalEuliya MohamadNo ratings yet
- Vegetarian or Non-Vegetarian?Document3 pagesVegetarian or Non-Vegetarian?nandini_goel1408No ratings yet
- Comparison of Health-Related Quality of Life of Elderly With Hypertension Living in Long-Term Facility vs. CommunityDocument82 pagesComparison of Health-Related Quality of Life of Elderly With Hypertension Living in Long-Term Facility vs. CommunityEllah ChristineNo ratings yet
- Alan Aragon Macro and Calorie Calculator Template 6Document8 pagesAlan Aragon Macro and Calorie Calculator Template 6tatiNo ratings yet
- Self Blood Sugar MonitoringDocument8 pagesSelf Blood Sugar MonitoringAniruddh Varadarajan100% (1)
- L3 Anatomy and Physiology Learner Workbook 1A Mar12Document84 pagesL3 Anatomy and Physiology Learner Workbook 1A Mar12markNo ratings yet
- NEW MI40 7-Day PrimerDocument15 pagesNEW MI40 7-Day PrimerHakimAlioua67% (6)
- Cardiac Rehabilitation and Exercise Therapy in Pediatric and Adult PatientsDocument24 pagesCardiac Rehabilitation and Exercise Therapy in Pediatric and Adult PatientsebookNo ratings yet
- HTTP Healthmedicinet Com II 2013 12 PDFDocument336 pagesHTTP Healthmedicinet Com II 2013 12 PDFtuni santeNo ratings yet
- Cesarean Delivery Pre OpDocument17 pagesCesarean Delivery Pre OpAncuta CalimentNo ratings yet
- Calorie Needs by Age, Gender and ActivityDocument2 pagesCalorie Needs by Age, Gender and ActivityИндийскаяДевушкаNo ratings yet
- DnlodDocument43 pagesDnlod312887No ratings yet
- Sprint Relay Exchanges and Speed Development TechniquesDocument52 pagesSprint Relay Exchanges and Speed Development TechniquesDemetrio Frattarelli100% (1)