100% found this document useful (1 vote)
904 views2 pagesQuadratic Functions Quiz
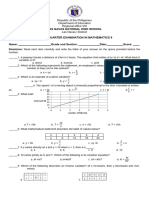
This document contains a 30-item summative test on quadratic functions. The test covers topics such as the standard form of a quadratic function, identifying quadratic functions, graphing quadratic functions, determining the equation of a quadratic function given its table of values or roots, transforming quadratic functions between standard, vertex and factored forms, identifying properties of quadratic functions like the vertex and domain and range, and how translations affect the graph of a quadratic function.
Uploaded by
MAYREEN JANERCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
904 views2 pagesQuadratic Functions Quiz
This document contains a 30-item summative test on quadratic functions. The test covers topics such as the standard form of a quadratic function, identifying quadratic functions, graphing quadratic functions, determining the equation of a quadratic function given its table of values or roots, transforming quadratic functions between standard, vertex and factored forms, identifying properties of quadratic functions like the vertex and domain and range, and how translations affect the graph of a quadratic function.
Uploaded by
MAYREEN JANERCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Summative Test in Quadratic Functions