Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adlay National High School Daily Lesson Log: Quadratic Equations
Uploaded by
Marie Grace Ollave0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesThis document contains a daily lesson log for a 9th grade mathematics class covering quadratic equations. On Monday, students will define real numbers and identify the nature of roots of quadratic equations. On Tuesday, students will recall skills in adding and multiplying rational numbers, and find the sum and product of roots of quadratic equations. The lesson will review previous concepts, present new material through examples and practice problems, and develop mastery through formative assessment involving real-life applications of quadratic equations.
Original Description:
Original Title
MATH 9- JUly 22-27,2018
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a daily lesson log for a 9th grade mathematics class covering quadratic equations. On Monday, students will define real numbers and identify the nature of roots of quadratic equations. On Tuesday, students will recall skills in adding and multiplying rational numbers, and find the sum and product of roots of quadratic equations. The lesson will review previous concepts, present new material through examples and practice problems, and develop mastery through formative assessment involving real-life applications of quadratic equations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesAdlay National High School Daily Lesson Log: Quadratic Equations
Uploaded by
Marie Grace OllaveThis document contains a daily lesson log for a 9th grade mathematics class covering quadratic equations. On Monday, students will define real numbers and identify the nature of roots of quadratic equations. On Tuesday, students will recall skills in adding and multiplying rational numbers, and find the sum and product of roots of quadratic equations. The lesson will review previous concepts, present new material through examples and practice problems, and develop mastery through formative assessment involving real-life applications of quadratic equations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
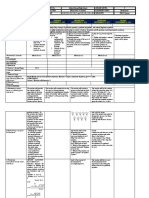
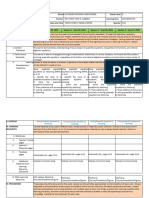
SCHOOL Adlay National High School GRADE LEVEL 9
DAILY LESSON LOG TEACHER Marie Grace O. Aparre LEARNING AREA Mathematics
TIME 7:30- 8:30 -(8:30-9:30), (9:45-10:45) QUARTER FIRST Quarter
MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY
JULY 22, 2019 JULY 23, 2019 JULY 24, 2019 JULY 25, 2019 JULY 26, 2019
I.OBJECTIVES
A.Content Standards The learner demonstrates understanding of key concepts of quadratic equations, quadratic inequalities, and rational algebraic equations.
B.Performance Standards The learner is able to investigate thoroughly mathematical relationships in various situations, formulate real-life problems involving quadratic
equations, quadratic inequalities, and rational algebraic equations and solve them using a variety of strategies.
C.Learning In this lesson, you are expected In this lesson, you are expected
Competencies/Objectives to: to:
1. Define real numbers, rational 1. Recall the basic skills in
and irrational numbers. adding and multiplying rational
2. Identify the nature of the numbers.
roots of the quadratic equation. 2. Find the sum and product of
roots of quadratic equations.
3. apply the understanding of
the sum and product of roots of
quadratic equation to real-life
applications
Write the LC Code for each M9AL-Ic-1 M9AL-Ic-1
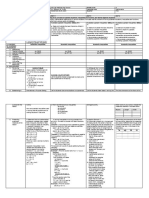
II.CONTENT
III.LEARNING RESOURCES
A.References
1.Teacher’s Guides/Pages
2.Learner’s Materials Pages
3.Textbook Pages
4.Additional Materials from BEAM Second Year, Module 4 BEAM Second Year, Module 4
Learning Resources (LR) portal (TG) (TG)
2. EASE Module Second Year 2. EASE Module Second Year
Quadratic Quadratic
Equations, Module 3 Chapter 2 Equations, Module 3 Chapter 2
Quadratic Equations pp.53-59 Quadratic Equations pp.53-59
(LM) (LM)
3. Advanced Algebra, 3. Advanced Algebra,
Trigonometry, and Statistics IV. Trigonometry, and Statistics IV.
2003. pp. 103-104* 2003. pp. 103-104*
4. Integrated Mathematics III. 4. Integrated Mathematics III.
2001. pp. 116-119* 2001. pp. 116-119*
B.Other Learning Resources
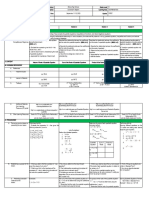
IV.PROCEDURES
A.Reviewing previous lesson or The teacher will let the students The teacher will let the students
presenting the new lesson realize that given the values of perform mathematical tasks to
a, b, and c, the value of activate their prior
b² – 4ac can be obtained. Then, mathematical
will ask them to perform knowledge and skills then let
Activity 4. In this activity, the them connect these to their new
students lesson, sum and
will write the quadratic equation product of roots of quadratic
given the values of a, b, and c equations. Emphasize to the
and solve this using students this important
any of the methods presented in question: “How do the sum and
the previous lessons. Let them product of roots of quadratic
explain how they equation facilitate in
came up with the roots of each understanding the required
equation. conditions of real-life
situations?”
B.Establishing a purpose for the Immediately after the students Start the lesson by asking the
lesson do Activity 4, ask them to students to add and multiply
perform Activity 5. rational numbers.
Tell them to write their answers These are the basic skills that
for Activities 3 and 4 in the students need to learn about the
table provided. Let the relationships among
students describe the roots of the values of a, b, and c in a
the quadratic equation and quadratic equation ax2 +bx + c
relate these to the value of = 0 and its roots.
its discriminant. The students
should realize at this stage that
the value of the
discriminant of a quadratic
equation can be used to describe
its roots.
C.Presenting examples/instances of Ask them to perform Activity
the new lesson 1. Let them explain how they
arrived at their answers and
how they applied the different
mathematics concepts or
principles in performing each
operation.
D.Discussing new concepts and Provide the students with
practicing new skills #1 opportunities to enhance their
skill in finding the
roots of quadratic equations by
doing Activity 2. Let them use
the different methods
of solving quadratic equations
which were already presented
in the previous lessons.
Finding the solutions of a
quadratic equation facilitates in
determining the
relationships among its roots
and its terms. Once the roots
are known, the students
can then relate these to the
terms of the quadratic equation.
E.Discussing new concepts and
practicing new skills #2
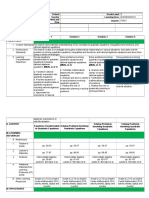
F.Developing mastery Develop students’ In Activity 3 of this lesson, the
(Leads to formative assessment) understanding of the nature of students will be asked to
roots of quadratic equations determine the values
through a real-life situation of a, b, and c of quadratic
involving a quadratic equation. equations written in standard
Ask the students to solve form and their respective roots.
the problems given in Activity Let the students find the sum
6. This activity provides the and product of these roots and
students with an relate the results to the values
opportunity to realize that the of a, b, and c. At this point, the
occurrence of a particular event students should realize that the
may not always be sum and the product of roots of
possible for a given condition. a quadratic equation are equal
For example, a ball cannot to a
reach a height of 160 ft. + b and a/c , respectively. The
following the initial conditions students should also learn that
of the problem. Hence, s = 160 the quadratic equation can be
is not a realistic value determined given its roots or
of s in the equation s = 100t – the sum and product of its
16t². roots.
G.Finding practical/applications of
concepts and skills in daily living
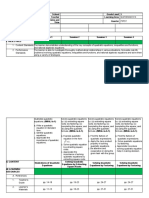
H. Making generalizations and Give the students opportunities Present to the students a real-
abstractions about the lesson to demonstrate their life illustration of the
understanding of the relationships among the
nature of roots of quadratic roots and the terms of a
equations by doing a practical quadratic equation. Let them
task. Let them perform perform Activity 4. In this
Activity 10. You can ask the activity, the students should
students to work individually or realize that the dimensions of
in groups. In this activity, the garden represent the roots
the students will be asked to of the quadratic equation.
solve a particular real-life Hence, the sum of the roots
problem involving the represents one-half of the
discriminant of quadratic perimeter of the garden and the
equations and then cite similar product of the roots represents
or other situations where its area.
this mathematics concept is
applied.
I.Evaluating Learning The teacher will give 5 item
quiz to the students.
J.Additional activities for
application or remediation
V.REMARKS
VI.REFLECTION
A.No. of learners who earned 80% of
the formative assessment
B.No. of learners who require
additional activities to remediation
C.Did the remedial lessons work?No.
of learners who have caught up with
the lesson
D.No. of learner’s who continue to
require remediation
E.Which of my teaching strategies
worked well? why did these work?
F.What difficulties did I encounter
which my principal or supervisor
can help me solve?
G.What innovation or localized
material did I use/discover which I
wish to sharewith other teachers?
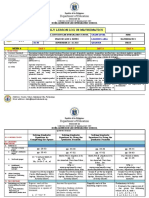
Prepared by: Checked by: Noted by:
MARIE GRACE O. APARRE MYRACELL P. BUENAFLOR VICTORINO S. NIMES, P-1
Subject Teacher Academic Coordinator School Head
You might also like
- MATH 9 - Sept 18finalDocument5 pagesMATH 9 - Sept 18finalMarie Grace OllaveNo ratings yet
- MATH 9 - Sept 12Document6 pagesMATH 9 - Sept 12Marie Grace OllaveNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations in Multiple WaysDocument3 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations in Multiple WaysSHERYL JOY GALVEZNo ratings yet
- I. ObjectivesDocument12 pagesI. ObjectivesKemberly GamaNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document5 pagesWeek 3Jefferson TorresNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 math lesson on quadratic equationsDocument12 pagesGrade 9 math lesson on quadratic equationsAngelo Morcilla Tiquio100% (1)
- Grade 9 Math DLLDocument9 pagesGrade 9 Math DLLjohnson gappiNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 3-LC 3,4,5Document10 pagesDLL-WK 3-LC 3,4,5Alejandro Jr. RicardoNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 3-LC 3,4,5 - 011351Document10 pagesDLL-WK 3-LC 3,4,5 - 011351Ainee Grace DolleteNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document6 pagesWeek 5Jefferson TorresNo ratings yet
- DLL IN MATH 9 JuneDocument9 pagesDLL IN MATH 9 JuneDIOSDADO MARIMON, IINo ratings yet
- GM - DLL Week 3Document5 pagesGM - DLL Week 3Nimrod CabreraNo ratings yet
- Sept. 11-15Document4 pagesSept. 11-15anna bernadette anchetaNo ratings yet
- DLL August 5Document13 pagesDLL August 5dearlyNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math Solves Quadratic EquationsDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Math Solves Quadratic EquationsJayson CatabayNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 3-LC 3,4,5Document12 pagesDLL-WK 3-LC 3,4,5Nemcris Mae OpleNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument8 pagesI. Objectives: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayBabyjane HumildeNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations Daily Lesson LogDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equations Daily Lesson LogMay Ann C. Payot100% (1)
- DLL-WK 3-LC 3,4,5Document12 pagesDLL-WK 3-LC 3,4,5Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Mathematics Lesson on Solving Quadratic InequalitiesDocument13 pagesGrade 9 Mathematics Lesson on Solving Quadratic InequalitiesRey Mark ColladoNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 1-LC 1Document12 pagesDLL-WK 1-LC 1Rebecca PabilloNo ratings yet
- (M9AL-Ij-1) (M9AL-Ij-1) (M9AL-Ii-j-2) : I. ObjectivesDocument8 pages(M9AL-Ij-1) (M9AL-Ij-1) (M9AL-Ii-j-2) : I. ObjectivesAlma Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 5-LC 7,8,9Document13 pagesDLL-WK 5-LC 7,8,9Jessebel AndresNo ratings yet
- Grades 9 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level 9 Teacher Learning Area MATHEMATICS Teaching Dates and Time Quarter FIRSTDocument13 pagesGrades 9 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level 9 Teacher Learning Area MATHEMATICS Teaching Dates and Time Quarter FIRSTBenying GiananNo ratings yet
- DLL WK 5 LC 789Document13 pagesDLL WK 5 LC 789JOHN MARK ORQUITANo ratings yet
- Grade 9 math quadratic equationsDocument12 pagesGrade 9 math quadratic equationsroy raluto67% (3)
- DLPDocument10 pagesDLPFlorita LagramaNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 1-LC 1Document12 pagesDLL-WK 1-LC 1Farrah QuiyanNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Quadratic Equations LessonDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Quadratic Equations LessonianNo ratings yet
- MATH 10 DLL WEEK 5 Jul. 1-4, 2019Document4 pagesMATH 10 DLL WEEK 5 Jul. 1-4, 2019Fatima YZ100% (1)
- The Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of... : B. Other Learning Resources Iv. ProceduresDocument3 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of... : B. Other Learning Resources Iv. ProceduresIan Kristian MulayNo ratings yet
- Math 9 DLL-WK 4Document9 pagesMath 9 DLL-WK 4Leny Enguio BelsondaNo ratings yet
- DLL9 2ndQuarterWeek4Document3 pagesDLL9 2ndQuarterWeek4Ramon CasildoNo ratings yet
- MATH G9 - DLL Aug. 27-31, 2018Document2 pagesMATH G9 - DLL Aug. 27-31, 2018mpar04100% (1)
- Grade 9 Math Lesson on Solving Quadratic EquationsDocument12 pagesGrade 9 Math Lesson on Solving Quadratic EquationsBenying GiananNo ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON LOG OF M9AL-Ia-b-1 (Day Four)Document4 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG OF M9AL-Ia-b-1 (Day Four)julito iliganNo ratings yet
- DLL-Math 9 Quarter 1week 4 SY 2023-2024Document8 pagesDLL-Math 9 Quarter 1week 4 SY 2023-2024rhea diadulaNo ratings yet
- Sept. 25-29Document4 pagesSept. 25-29anna bernadette anchetaNo ratings yet
- Sept. 18-22Document4 pagesSept. 18-22anna bernadette anchetaNo ratings yet
- Gumaca Math Lesson on Quadratic EquationsDocument2 pagesGumaca Math Lesson on Quadratic Equationsmpar04No ratings yet
- DLL-WK 1-LC 1Document10 pagesDLL-WK 1-LC 1Alejandro Jr. RicardoNo ratings yet
- DLL in PRECALCULUS - Jesus M. Del Rosario - Sept 11 15 2023Document9 pagesDLL in PRECALCULUS - Jesus M. Del Rosario - Sept 11 15 2023mike guiamNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of... : B. Other Learning Resources Iv. ProceduresDocument3 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of... : B. Other Learning Resources Iv. ProceduresIan Kristian MulayNo ratings yet
- DLLMath 9 W1 Q 1Document12 pagesDLLMath 9 W1 Q 1Dan DanNo ratings yet
- Mr. Renato S. de Las Alas JR - Mr. Neo B. Villareal August October 3120-Octoseptember 233, 2020september 20 - 30, 2021Document3 pagesMr. Renato S. de Las Alas JR - Mr. Neo B. Villareal August October 3120-Octoseptember 233, 2020september 20 - 30, 2021Neo VillarealNo ratings yet
- Relationships Between Coefficients and Roots of a Quadratic EquationDocument66 pagesRelationships Between Coefficients and Roots of a Quadratic EquationIvan Jay Buere100% (1)
- Grade 9 Mathematics DLLDocument10 pagesGrade 9 Mathematics DLLjohnson gappiNo ratings yet
- DLL-1st Week 4Document13 pagesDLL-1st Week 4Frances Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- Mansasa National High School Math Lesson LogDocument4 pagesMansasa National High School Math Lesson Logpbaranas16No ratings yet
- GRADES 9 Math Lesson on Quadratic InequalitiesDocument11 pagesGRADES 9 Math Lesson on Quadratic InequalitiesBernaliza CaserNo ratings yet
- Sept 23-29 Factoring Quadratic EquationDocument9 pagesSept 23-29 Factoring Quadratic EquationShieny Mae Ortega AlberioNo ratings yet
- DLL-jan 9-13, 2023Document11 pagesDLL-jan 9-13, 2023Florita LagramaNo ratings yet
- DLL InequalitiesDocument10 pagesDLL InequalitiesTRISTAN RYAN TINGSONNo ratings yet
- DLL Gen Math Week 2Document8 pagesDLL Gen Math Week 2edcel bagsicNo ratings yet
- DLL WK 3 LC 345Document7 pagesDLL WK 3 LC 345Absy BunsayNo ratings yet
- Cot 101323Document7 pagesCot 101323Michelle ValorosoNo ratings yet
- Grades 1 to 12 Math LessonsDocument3 pagesGrades 1 to 12 Math LessonsAlona Jane Wafa Divino75% (8)
- Grades 9 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level 9 Teacher Learning Area MATHEMATICS Teaching Dates and Time Quarter FIRSTDocument13 pagesGrades 9 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level 9 Teacher Learning Area MATHEMATICS Teaching Dates and Time Quarter FIRSTIsabel0% (1)
- I-Day 27Document2 pagesI-Day 27Jean Marie Ga LacsonNo ratings yet
- Stages of Intimate RelationshipsDocument4 pagesStages of Intimate RelationshipsKrystalline ParkNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document20 pagesPresentation 1nikitakhanduja1304No ratings yet
- Act 1&2 and SAQ No - LawDocument4 pagesAct 1&2 and SAQ No - LawBududut BurnikNo ratings yet
- S06 - 1 THC560 DD311Document128 pagesS06 - 1 THC560 DD311Canchari Pariona Jhon AngelNo ratings yet
- TNG UPDATE InstructionsDocument10 pagesTNG UPDATE InstructionsDiogo Alexandre Crivelari CrivelNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Evaporative CoolerDocument12 pagesProject Report On Evaporative Coolersourabh singh tomerNo ratings yet
- PAPERBOARD QUALITYDocument8 pagesPAPERBOARD QUALITYaurelia carinaNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 Application FormDocument13 pagesAppendix 1 Application FormSharifahrodiah SemaunNo ratings yet
- Class Opening Preparations Status ReportDocument3 pagesClass Opening Preparations Status ReportMaria Theresa Buscato86% (7)
- Multivariate Analysis Homework QuestionsDocument2 pagesMultivariate Analysis Homework Questions歐怡君No ratings yet
- Tuberculin Skin Test: Facilitator GuideDocument31 pagesTuberculin Skin Test: Facilitator GuideTiwi NaloleNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Gen EconDocument10 pagesWeek 4 Gen EconGenner RazNo ratings yet
- Dyna 2000 LiteDocument2 pagesDyna 2000 LiteRNKNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF WATER SAMPLEDocument5 pagesCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF WATER SAMPLEAiron Fuentes EresNo ratings yet
- Tirfor: Lifting and Pulling Machines With Unlimited Wire RopeDocument26 pagesTirfor: Lifting and Pulling Machines With Unlimited Wire RopeGreg ArabazNo ratings yet
- European Business in China Position Paper 2017 2018 (English Version)Document408 pagesEuropean Business in China Position Paper 2017 2018 (English Version)Prasanth RajuNo ratings yet
- Business Analysis FoundationsDocument39 pagesBusiness Analysis FoundationsPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The CurriculumDocument119 pagesBuilding and Enhancing New Literacies Across The CurriculumLowela Kasandra100% (3)
- DLL Grade7 First 1solutions ConcentrationDocument5 pagesDLL Grade7 First 1solutions ConcentrationJaneth de JuanNo ratings yet
- Medicinal PlantDocument13 pagesMedicinal PlantNeelum iqbalNo ratings yet
- Best Home Oxygen Concentrators-Lowest Prices & Fast Shipping (Oxygen Machines) - 2021 - YuwellDocument1 pageBest Home Oxygen Concentrators-Lowest Prices & Fast Shipping (Oxygen Machines) - 2021 - YuwellPelayanan ResusitasiNo ratings yet
- 96 Amazing Social Media Statistics and FactsDocument19 pages96 Amazing Social Media Statistics and FactsKatie O'BrienNo ratings yet
- Kennedy 1945 Bibliography of Indonesian Peoples and CulturesDocument12 pagesKennedy 1945 Bibliography of Indonesian Peoples and CulturesJennifer Williams NourseNo ratings yet
- Load Frequency Control of Hydro and Nuclear Power System by PI & GA ControllerDocument6 pagesLoad Frequency Control of Hydro and Nuclear Power System by PI & GA Controllerijsret100% (1)
- Administracion Una Perspectiva Global Y Empresarial Resumen Por CapitulosDocument7 pagesAdministracion Una Perspectiva Global Y Empresarial Resumen Por Capitulosafmqqaepfaqbah100% (1)
- Answer Questions Only: Chemical Engineering DeptDocument2 pagesAnswer Questions Only: Chemical Engineering DepthusseinNo ratings yet
- MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDSDocument39 pagesMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDSAbdul Musavir100% (1)
- 5 Guys Nutrition InfoDocument1 page5 Guys Nutrition InfoJody Ike LinerNo ratings yet
- 8.4 Example: Swiss Market Index (SMI) : 188 8 Models of VolatilityDocument3 pages8.4 Example: Swiss Market Index (SMI) : 188 8 Models of VolatilityNickesh ShahNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Liturgy of The Catholic ChurchDocument27 pagesAn Introduction To Liturgy of The Catholic ChurchElsha DamoloNo ratings yet