Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A4 Summary Sheet
A4 Summary Sheet
Uploaded by
Lisa BruntonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A4 Summary Sheet
A4 Summary Sheet
Uploaded by
Lisa BruntonCopyright:
Available Formats
Systems broken down by hyaluronidase insulin but cells are insulin resistant
Integumentary system Fibres- Collagen, reticular, elastic Homeostasis: The maintenance of relatively constant conditions
Consists of epidermis, hair follicle, hairs, sebaceous glands, Marfan syndrome within physiologically tolerate limits
sweat glands, nails, sensory receptors, dermis, hypodermis. Hereditary disease defect in fibrillin, less fibrillin so more GF Hyperglycemia: Increase in blood glucose level
Main functions: thermoregulation, blood reservoir, protection, Connective tissue cell types: Fibroblasts, adipocytes (these are Hypoglycemia: stimulate alpha cells in our pancreas to secrete
cutaneous sensations, excretion, absorption, synthesis of two most common). Others include: macrophages, plasma cells, glucagon, which acts on liver and skeletal cells to increase
vitamin D mast cells, leucocytes breakdown of the storage of glucose
Muscular system Classification of connective tissue: Embryonic (Mesenchyme and Insulin: Produced by B cells of pancreas
Consists of skeletal muscle (axial and appendicular), tendons mucous) and mature (connective (Loose (areolar, adipose, Glucagon: Produced by alpha cells of pancrea, stimulates the
(bone to muscle) and aponeuroses (muscle to muscle). reticular), or dense (dense regular, dense irregular, elastic)), fluid breakdown of glycogen to increase blood sugar level
Main functions include providing skeletal movements, controlling (blood and lymph) and supporting (cartilage and bone)
entrances to digestive and respiratory system, producing heat, Cell signalling
protect soft tissue Nervous tissue Reception - transduction - response
Skeletal system 3 major functions: sensory, integrative, motor Intracellular receptors: Least common, primary messenger is
Includes bones, cartilage, red bone marrow(red blood cell Multipolar neurons: most common in CNS. all motor neurons are hydrophobic and or small, so can enter cell, eg testosterone,
production), yellow bone marrow (fat store and stem cells), this class. oestrogen
ligaments Bipolar neurons: 2 distinct processes (1 dendritic and one axon). Membrane bound / cell surface receptors: Primary messenger is
Main functions- support soft tissues, assist in movement, mineral Rare and small (30nm) in special sense organs. generally hydrophilic or large, most common method of
homeostasis, blood cell production, triglyceride storage. Unipolar neurons: Dendrites and axons are continuous with the signalling, eg GPCRs, receptor tyrosine kinase, ligand gated ion
Nervous system cell body off to the side. Most sensory neurons are this channel
Includes: central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), brain, Anaxonic neuron: Rare and function poorly understood, anatomy Ligand gated ion channel: Binding of ligand stimulates a change,
spinal cord, special senses (all of PNS except optic nerve which cannot distinguish dendrites from axons, found in brain and channel opens or closes
is CNS. Includes sensory input to the brain relating to sight, special sense organs. Signal transduction pathway: Signals relay from receptors to
hearing, smell, taste and equilibrium), PNS (links CNS to other Neuroglia: Support neurons in both CNS and PNS. Includes target. Eg phosphorylation cascade
systems and senses organs). astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, IV ependymal cells in cAMP: Is a second messner, in GPCR. Adenylyl cyclase is
PNS is divided into somatic nervous system, autonomic nervous CNS. PNS ones include neuroglia, satellite cells activated and converts ATP to cAMP.
system, and enteric nervous system.
Main function: direct immediate responses to stimuli, usually by Organelles DNA
coordinating the activities of other organ systems Cytoplasm: everything inside the plasma membrane including Transcription: Initiation- promoter commonly including a TATA
Endocrine system the organelles but not the nucleus. Cytosol is the liquid portion of box, evernal transcription factors recognize the TATA box and
Includes pineal gland, thyroid gland, hypothalamus/pituitary it bind to the DNA before RNA polymerase II can bind in the
gland, thymus, adrenal glands, kidneys, pancreas, gonads Endomembrane system: Regulates protein traffic and performs correct position and orientation. Elongation- RNA nucleotides
(ovaries and testes). metabolic functions. Endomembrane system and plasma added to 3’ end of growing transcript. Hydrogen bonds form, and
Main function- direct long term changes in other organ systems membrane work together to label and ship molecules. Includes then it forms a phosphodiester bond, which is a lot stronger.
Lymphatic system nucleus, smooth and rough ER, golgi, lysosomes. Termination- after transcription of the polyadenylation signal,
Includes lymphatic vessels, lymphatic fluid, B cells and T cells, Plasma membrane: Double layer of phospholipids with nuclear enzymes release pre-mRNA and the RNA polymerase
lymph nodes including tonsils, spleen, thymus, lymphatic ducts. embedded proteins. Contains integral proteins. Functions dissociates from the DNA
Main function: defend against infection and disease, returns include transport, enzymatic activity, signal transduction, cell to mRNA processing: capping, tailing, splicing
tissue fluid to bloodstream cell signalling, intercellular joining. Alternative splicing: When different combinations of exons are
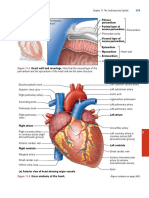
Cardiovascular system Nucleus: Largest organelle, includes nuclear envelope, nuclear joined together, resulting in the production of multiple forms of
Includes heart, blood vessels, arteries, capillaries, veins, blood pores, nucleolus, mRNA, rRNA, and it houses and protects DNA mRNA from single preMRNA.
Main function- transports cells and dissolved materials, including Nucleosome: 2 x groups of 8 histones Translation: Initiation- start codon is AUG. Elongation- codon
nutrients, wastes and gases. Ribosomes: Protein production, consists of 2 subunits recognition, peptide bond formation, translocation. Termination-
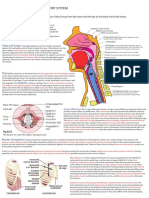
Respiratory system Endoplasmic reticulum: An extensive network of tubes and reaches a stop codon polypeptide chain release
Includes nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, pharynx, larynx, tubules stretching out from the nuclear membrane. Rough ER Signal peptide: At N terminus of protein, about 20 aas. Makes
trachea, bronchi, lungs. has ribosomes, and helps with the production of secreted, ribosome take it to the rough ER
Main functions include- delivers air to site where gas exchange membrane and organelle proteins. Smooth ER lacks ribosomes
occurs between the air and circulating blood, produces sound and stores proteins and enzymes, synthesises lipids, and stores Cell cycle
Digestive system calcium ions Checkpoints: G1, S, G2, M
Includes- oral cavity, salivary glands, pharynx, stomach, small Golgi apparatus: 3-20 flattened membranous sacs called Mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and
intestine, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, large intestine, rectum, cisternae, stacked on top of one another, they modify, sort and cytokinesis
anus package and transport proteins received from the rough ER, Meiosis: Meiosis I, prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I,
Main function- process food and absorb nutrients Formation of secretory vesicles, transport vesicles. Telophase I, Meiosis II, prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II,
Urinary system Lysosomes: Membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that many Telophase II
Includes- kidneys (EPO hormone), ureters, urinary bladder, eukaryotic cells use to digest macromolecules. Highly acidic Large scale alterations: Chromosomal rearrangements in mitosis
urethra. inside, for destroying compounds, like to destroy immune or where it shouldn't happen
Main functions- eliminates excess water, salts and wastes pathogen cells Small scale modifications: a mutation occurring in either a single
Reproductive system Mitochondria: For cellular respiration, not part of the nucleotide, or nucleotide pair insertions or deletions
Includes- testes, epididymis, ductus deferens, seminal glands, endomembrane system. Types of mutation effects: Silent, mussense, nonsense,
prostate gland, urethra, penis, scrotum, ovaries, uterine tubes, Cytoskeleton: Consists of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, frameshift
uterus, vagina, mammary glands and microtubules MPF: Maturation promoting factor, when the cyclic and Cdk are
together it allows mitosis to commence, because it is able to
Epithelial tissue Path of secreted protein: mRNA is made in the nucleus and pjosrpulation other proteins
Covers body surfaces, forms glands, forms selective barriers, leaves out the nuclear pores. Ribosome in cytosol starts, Proto Oncogenes: Genes that normally stimulate cell production
secretory and protective functions reached SRP, Ribosome goes to rough ER to finish translation, Tumour suppressor genes: Genes that keep proliferation in
Junctions: protein folds in lumen on rough ER, then it goes to the golgi check
Tight, adherens, desmosome, gap, hemidesmosome junctions apparatus to be shipped away to the membrane to be secreted
Basement membrane Embryology
Consists of basal lamina (secreted by epithelial cells containing Cellular respiration: Consists of glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, Three primary germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
collagen, laminin, proteoglycans, glycoproteins and reticular citric acid cycle and electron transport chain (including Cleavage: Rapid cell division after fertilisation
lamina (secreted by underlying connective tissue fibroblasts, chemiosmosis) Implantation: Blastocysts implants to endometrium
contains fibrous proteins such as fibronectin and collagen. Blood Glycolysis: Glucose turns into 2 pyruvates and 2 waters. 2 ATP Development of the trophoblast and bilaminar embryonic disk:
vessels below basement membrane net produced (2 used and 4 made). 2NAD turns into 2NADH. Trophoblast develops into 2 layers after about 8 days after
Malignant melanoma Occurs in cytosol, anaerobic. fertilisation. Trophoblast gives rise to placenta
ABCD warning signs: asymmetry, border irregularity, colour, Phosphofructokinase: Rate limiting for glycolysis. Inhibited by Gastrulation: Formation of 3 disc layers from 2
diameter >6mm citrate and ATP. It catalyses an early step in glycolysis. This Embryonic folding: Embryo folds into tube
Mesothelium feedback regulation adjusts the rate of respiration as the cells Stem cells: Includes totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent,
Forms the epithelial layer of serous membrane (peritoneum, catabolic and anabolic demands change nullipotent
pleura, pericardium) Pyruvate oxidation: Forms acetyl CoA. Occurs in mitochondrial
Endothelium matrix, aerobic. Produces no ATP, but produces 2 NADH per Proteins
Lines the cardiovascular and lymphatic systems (heart, blood glucose (1 per pyruvate enables the 2-Carbon acetyl group to What do proteins do?: Transport, structural, hormone signalling,
vessels, lymphatic vessel linings. Lines the inside of the heart enter the citric acid cycle immunologica, contractile, storage, toxins
and blood and lymphatic vessels. Citric acid cycle: Occurs in mitochondrial matrix, results in 2 ATP, Primary structure: Entire sequence of aas in a protein
Present at sites of filtration, or diffusion 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 4CO2 per glucose molecule Secondary structure: localised folding of the polypeptide into
Glands Oxidative phosphorylation: Electron transport chain. Occurs at antiparallel or parallel b sheets or right hand alpha helices
Can be endocrine, exocrine or single cell glands proteins within the inner membrane, aerobic. NADH and FADH2 Tertiary structure: Opposite charred R groups attract
are oxidised to donate 1 oe 2 electrons. Electrons transfer from Quaternary structure: Some proteins only. Driven by ionic
Connective tissue protein to protein along the chain in a series of redox reactions, interactions
Binds support and strengthen other body tissues, A major giving up a small amount of energy at each transfer which
transport system of the body, and a major site of stored energy. enables H+ ions to be pumped into the intermembrane space.
CT = ECM + Cells Includes chemiosmosis, which is H+ ions being pumped into the
ECM = the material located between widely spaced cells, ECM = intermembrane space. Produces 26-28 ATP
GS + fibres Substrate phosphorylation: ATP generated by direct transfer
Ground substance = Composed of a mixture of water, proteins (from a substrate) of a phosphate group to ADP. glycolysis and
and sugars. GS = H2O + Proteins + polysaccharides citric acid cycle make ATP via substrate phosphorylation.
GAG (sugar) - Long, unbranched polysaccharides. Trap water,
making GS more jelly like. Can be sulfted or non sulfated. Diabetes
Sulfated ones include dermatan sulphate (skin, tendons, blood Type 1 diabetes: Body does not produce insulin, affects 5-10%
vessels, heart valves), heparin sulphate, keratan sulphate (bone, of diabetics, usually though autoimmune or environmental
cartilage, cornea), chondroitin sulphate (cartilage, bone, skin, factors
blood vessels). Non sulfated includes hyaluronic acid, which is Type 2 diabetes: Affects over 90% of diabetics, body produced
You might also like
- Grade 10 Biology NotesDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Biology Noteskatwal0986% (21)
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Reviewermashup100% (14)
- RT Skills ChecklistDocument3 pagesRT Skills ChecklistMond SantosNo ratings yet
- BBMS1001 NotesDocument41 pagesBBMS1001 NotesHelen WanNo ratings yet
- AP 18 Endocrine OverviewDocument19 pagesAP 18 Endocrine OverviewMARICRIS NEBIARNo ratings yet
- Science 1-3-1Document46 pagesScience 1-3-1Cesareann A RamosNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function: Endoplasmic Reticulum ERDocument2 pagesCell Structure & Function: Endoplasmic Reticulum ERLiling CassiopeiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Nervous System OutlinesDocument45 pages1 Nervous System OutlinesTestingAccNo ratings yet
- 2nd Semester MidtermsDocument45 pages2nd Semester Midtermsguillesjhobel0701No ratings yet
- Biochemistry CHAPTER 1Document10 pagesBiochemistry CHAPTER 1Joyce ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Physiology2Document63 pagesIntroduction To Physiology2Hasan NouriNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument6 pagesEndocrineshiela marieNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous SystemJessica Febrina WuisanNo ratings yet
- 420-510chapter 1 (3) An Introduction To CellsDocument6 pages420-510chapter 1 (3) An Introduction To Cellstomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy: Ex. Sweat, Salivary, MucusDocument12 pagesHuman Anatomy: Ex. Sweat, Salivary, MucusLeslie CuevasNo ratings yet
- Genexglob ManualDocument23 pagesGenexglob ManualSurendran KrishnanNo ratings yet
- 1st Week (2) - OrganellesDocument38 pages1st Week (2) - OrganellesyazicigaamzeNo ratings yet
- ReviewDocument6 pagesReviewAlbisladys Castellanos PujolsNo ratings yet
- ScieDocument3 pagesSciellubitpauloNo ratings yet
- Physiology02 Cell PhysiologyDocument63 pagesPhysiology02 Cell PhysiologysmpoojasubashNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab ReviewerDocument6 pagesAnaphy Lab ReviewerJhom Andrei ApolinarNo ratings yet
- Endo 1 2005Document53 pagesEndo 1 2005api-3698357No ratings yet
- Cell Strucure & Functions - Part - 1Document23 pagesCell Strucure & Functions - Part - 1Sree Harini SNo ratings yet
- IB Bio Notes MasterDocument45 pagesIB Bio Notes MasterE. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma Chapter 6 SummaryDocument6 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma Chapter 6 SummaryDana PorterNo ratings yet
- Body PhysiologyDocument88 pagesBody PhysiologyThe KittyNo ratings yet
- 11 THDocument8 pages11 THHarleen Kaur MehtaNo ratings yet
- 1-Histology of Nerve Tissue The Nervous System Part 1Document33 pages1-Histology of Nerve Tissue The Nervous System Part 1Ahmad MsalmahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Principles of Systemic PhysiologyDocument16 pagesLecture 1: Principles of Systemic PhysiologySeanGuntvedtNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument13 pagesCell Structure and FunctionNatalie KwokNo ratings yet
- Cell Body Perikaryon Soma: Neural PlasticityDocument29 pagesCell Body Perikaryon Soma: Neural PlasticitymaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Study 2Document20 pagesFinal Exam Study 2carlaponce010100No ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY 4 - Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesHISTOLOGY 4 - Endocrine SystemGauri SulekhaNo ratings yet
- PRINTED Endocrine System HandoutsDocument6 pagesPRINTED Endocrine System HandoutsKate GutierrezNo ratings yet
- The Nervous and The Endocrine SystemsDocument9 pagesThe Nervous and The Endocrine SystemsluciaarecesdiazNo ratings yet
- Organization of Brain & Synaptic Transmission: Santosh DevDocument32 pagesOrganization of Brain & Synaptic Transmission: Santosh DevdevdsantoshNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument20 pagesCell PhysiologySerra ÇevikkanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesEndocrine SystemRonald A. OganiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Lecture 3Document49 pagesCell Lecture 3gracechirangoNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Nervous Control in Plants and AnimalsDocument8 pagesChemical and Nervous Control in Plants and AnimalsSophia BandojaNo ratings yet
- 1 CytologyDocument86 pages1 CytologyRathana Nguon100% (1)
- 1 Cns HistoDocument54 pages1 Cns HistoNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- Functions of Different Organ SystemsDocument4 pagesFunctions of Different Organ Systemsleeannhernandez0414No ratings yet
- The Neuron 2024Document47 pagesThe Neuron 2024Zablon OtienoNo ratings yet
- CH 1: Evolution, The Themes of Biology, and Scientific InquiryDocument27 pagesCH 1: Evolution, The Themes of Biology, and Scientific InquiryZackNo ratings yet
- FINALEXAM Human AnatomyDocument8 pagesFINALEXAM Human AnatomyAlieya MustafaNo ratings yet
- Review of The Endocrine System: Dr. Amiruddin Eso, M.Kes Department of Physiology Medical Faculty Halu Oleo UniversityDocument75 pagesReview of The Endocrine System: Dr. Amiruddin Eso, M.Kes Department of Physiology Medical Faculty Halu Oleo UniversityWidodo MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Homeostasis Is Constancy/balance of The Internal EnvironmentDocument42 pagesHomeostasis: Homeostasis Is Constancy/balance of The Internal EnvironmentKristin ElderNo ratings yet
- Classification of Connective or Supporting TissuesDocument9 pagesClassification of Connective or Supporting Tissuesferdinand padillaNo ratings yet
- L3 Neurons and GliaDocument4 pagesL3 Neurons and GliamoshlingmomoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Free RadicalsDocument37 pagesCell Structure & Free RadicalsSAMANTHA WHITTAKERNo ratings yet
- NOTES ReportingsDocument16 pagesNOTES Reportings2240739No ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1 Study GuideDocument3 pagesBiology Unit 1 Study GuideJohans MascardoNo ratings yet
- BCH 202 CellNotes-1Document8 pagesBCH 202 CellNotes-1timilehinfalemuNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument3 pagesHistologyKeith DevonNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 Cell Structures and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesWEEK 3 Cell Structures and PhysiologyMarjorie Lyka LingatNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Normal HistologyDocument10 pagesVeterinary Normal HistologyIshtar Katherine ChanNo ratings yet
- Anat Physio Basics 2008Document108 pagesAnat Physio Basics 2008Chandan AhireNo ratings yet
- Final Review Renal SystemDocument30 pagesFinal Review Renal SystemCarolyne CharvozNo ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- Mind Diet Adherence and Cognitive PerformandeDocument13 pagesMind Diet Adherence and Cognitive PerformandeSaionara FranciscoNo ratings yet
- The World Market For Cardiovascular DiagnosticsDocument200 pagesThe World Market For Cardiovascular Diagnosticsjessiliang9100% (1)
- Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument10 pagesAltered Tissue PerfusionLaurence ZernaNo ratings yet
- Excretory-SystemDocument90 pagesExcretory-SystemArchitaNo ratings yet
- T Wave / T TalasDocument14 pagesT Wave / T TalasLidianaBeka0% (1)
- GP MCQ 2Document4 pagesGP MCQ 2Marta MoreiraNo ratings yet
- 100 Cases in Pulmonary MedicineDocument404 pages100 Cases in Pulmonary MedicineTas AktherNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Notes (Chris Andersen, ICUPrimaryPrep - Com)Document14 pagesRespiratory Notes (Chris Andersen, ICUPrimaryPrep - Com)PkernNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Haemorrhage (APH) : DR Nitin TiwariDocument49 pagesAntepartum Haemorrhage (APH) : DR Nitin TiwariPravin SasaneNo ratings yet
- MCQ6Document8 pagesMCQ6Alaa JaibatNo ratings yet
- Serdang Protocol ObgynDocument152 pagesSerdang Protocol ObgynNadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Analysis of ECG Signals by Dynamic Mode DecompositionDocument12 pagesAnalysis of ECG Signals by Dynamic Mode Decompositionmadhumita mishraNo ratings yet
- 18Th June 2019 Plab 1 Mock Test Plab ResourcesDocument30 pages18Th June 2019 Plab 1 Mock Test Plab Resourceskhashayar HajjafariNo ratings yet
- The Kidney and Its DisordersDocument71 pagesThe Kidney and Its Disordersreuben kwotaNo ratings yet
- Imaging of Vascular MalformationsDocument16 pagesImaging of Vascular MalformationsHector Hernandez-SoriaNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Adult Patient With Syncope in The Emergency DepartmentDocument26 pagesApproach To The Adult Patient With Syncope in The Emergency DepartmentVinicius DumontNo ratings yet
- BURN August 2022Document51 pagesBURN August 2022SHAYNE MERYLL CHANNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Six-Minute Walk TestDocument5 pagesGuidelines For The Six-Minute Walk TestHuang HasjimNo ratings yet
- Clinical Methods Update, by Dr. AbiloDocument283 pagesClinical Methods Update, by Dr. AbiloROBUSTNo ratings yet
- Apixaban Eliquis MonographDocument14 pagesApixaban Eliquis MonographTran Minh NgocNo ratings yet
- Cavaliere 2016Document3 pagesCavaliere 2016Huệ MinhNo ratings yet
- Acromegaly and Gigantism: South Afr J Anaesth AnalgDocument5 pagesAcromegaly and Gigantism: South Afr J Anaesth AnalgatarNo ratings yet
- Movement Disorder: Mrs. Keerthana.B Assistant Professor MSN, PSG ConDocument69 pagesMovement Disorder: Mrs. Keerthana.B Assistant Professor MSN, PSG ConKeerthana BNo ratings yet
- Student'S Name: Kim Christian P. Pagobo Subject: Science 120: Anatomy and Physciology Instructor: Mrs. Roma Grace DizonDocument9 pagesStudent'S Name: Kim Christian P. Pagobo Subject: Science 120: Anatomy and Physciology Instructor: Mrs. Roma Grace Dizonkim christianNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology For Nurses: The Islamic UniversityDocument118 pagesPharmacology For Nurses: The Islamic UniversityRojina AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Printable Pages - MariebDocument6 pagesCardiovascular System - Printable Pages - MariebChristal Rae Tac-anNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic GastritisDocument17 pagesAcute and Chronic GastritisIndah Nur PratiwiNo ratings yet
- 84-Article Text-538-1-10-20201115Document54 pages84-Article Text-538-1-10-20201115Rubilin NitishaNo ratings yet
- PIHDocument18 pagesPIHArtyom GranovskiyNo ratings yet