Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 7 Human Anatomy
Uploaded by
Angelica CruzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 7 Human Anatomy
Uploaded by
Angelica CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Anatomy Lecture 7: Nervous System o Stimulate activity of intestines
o Contract bladder
o Functions of the Nervous System
o Gfdjbhsabd
o Receiving sensory input
o Sympathetic nerves
o Integrating information
o Dilate pupils
o Controlling muscles and glands
o Inhibit salivation
o Maintaining homeostasis
o Increase heartbeat
o Establishing and maintaining mental
o Relax airways
activity.
o Division of Nervous System o Inhibit activity of stomach
o Central Nervous System o Inhibit gallbladder
Motor input o Inhibit activity of intestines
Brain o Secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine
Spinal Cord o Relax bladder
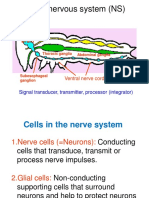
o Peripheral Nervous System o Cells of the nervous system
More on sensory input o Neurons
Nerves to face o Cell body
Ganglia o Dendrite
Nerves to upper limb o Axon
Nerves to lower limb Multipolar neuron has
o Organization of the Nervous system many dendrites and an
axon
Bipolar neuron has a
dendrite and an axon
Pseudo-unipolar neuron
appears to have an axon
and no dendrites.
o Glial cells
o Sympathetic and Parasympathetic o Astrocytes (CNS)
o Parasympathetic o Ependymal cells ( CNS)
o Constrict pupils o Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
o Stimulate saliva o Microglial cells (CNS)
o Slow heartbeat o Satellite cells (PNS)
o Constrict airways o Schwann cells (PNS)
o Stimulate activity of stomach o Parts of a cell
o Stimulate gallbladder o Myelin Sheath
o Unmyelinated neuron (top)
o Myelinated neuron (bottom)
Organization of the Nervous Tissue:
You might also like
- Animal Nervous SYS: Chapter 15: 407-420Document65 pagesAnimal Nervous SYS: Chapter 15: 407-420Cameron KlugNo ratings yet
- Muna 62Document4 pagesMuna 62nhuvdNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemanneNo ratings yet
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.From EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.No ratings yet
- Nervous System Part 1Document4 pagesNervous System Part 1Cyrill Denise CastañedaNo ratings yet
- #4 Nervous-SystemDocument19 pages#4 Nervous-SystemLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Pearson Nervous System ReviewerDocument8 pagesPearson Nervous System ReviewerViaBNo ratings yet
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- 49 Neural Regulation in Animals-2018 PDFDocument61 pages49 Neural Regulation in Animals-2018 PDFlaw0516No ratings yet
- Final Exam MaterialDocument258 pagesFinal Exam MaterialYousef Ahmad2No ratings yet
- Functional Classification of The Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesFunctional Classification of The Peripheral Nervous SystemLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Week 10 MS Responses To Altered Perception Neurological Dysfunctions IntroductionDocument8 pagesWeek 10 MS Responses To Altered Perception Neurological Dysfunctions IntroductionMICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- First Eaxam SlidesDocument49 pagesFirst Eaxam SlidesYousef Ahmad2No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - THE BASES OF HUMAN BEHAVIOURDocument28 pagesChapter 3 - THE BASES OF HUMAN BEHAVIOURchithu thomasNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Reference NotesDocument18 pagesUnit 2 - Reference NotesRia JainNo ratings yet
- ENTO415 NervesDocument26 pagesENTO415 NervesGiovana Mamani HuayhuaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PDFDocument91 pagesNervous System PDFGayathri SNo ratings yet
- Pharma 2Document12 pagesPharma 2MARIEMIL FOLLOSONo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesThe Nervous SystemROSEMARIE ONG100% (1)
- Med Surg NotesDocument64 pagesMed Surg NotesRAYMUND IAN ABALOS100% (2)
- Day 1 - 2-Brain and Spine - Basic Spine Anatomy 4ADocument5 pagesDay 1 - 2-Brain and Spine - Basic Spine Anatomy 4AAla'a Emerald AguamNo ratings yet
- Insect Nervous System (NS) : BrainDocument26 pagesInsect Nervous System (NS) : BrainAnju AnjiNo ratings yet
- Sistem NervosumDocument35 pagesSistem NervosumRaniyah Az-zahraNo ratings yet
- NEUROGLIAL ("White Matter") AstrocytesDocument12 pagesNEUROGLIAL ("White Matter") AstrocytesGabrielle MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart For Nervous System (Class 10 ICSE)Document3 pagesFlow Chart For Nervous System (Class 10 ICSE)Sagnik100% (2)
- The Nervous System First PartDocument15 pagesThe Nervous System First PartNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Nervous System NotesDocument6 pagesNervous System NotesHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- Medicine 1 Neuro Lectures 2023 PDFDocument84 pagesMedicine 1 Neuro Lectures 2023 PDFnesinhle AunthiaNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafDocument31 pagesKonsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafdiandraNo ratings yet
- BiopsyDocument69 pagesBiopsyErioluwa OyewoNo ratings yet
- NEUROANATOMY IntroductionDocument10 pagesNEUROANATOMY IntroductionIshant SinghNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemJustGellaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Biological PerspectiveDocument39 pagesChapter 2 The Biological PerspectiveSULDAANUL CAASHIQIINNo ratings yet
- NervousDocument50 pagesNervousnona wayne dela peñaNo ratings yet
- NervousDocument128 pagesNervousNaveen KumarJangirNo ratings yet
- Cohen - B7.5 - MSK - Central - and - Peripheral - Nervous - System - Histology - 19-20Document80 pagesCohen - B7.5 - MSK - Central - and - Peripheral - Nervous - System - Histology - 19-20Monica Hitomi MekaruNo ratings yet
- 3 Chap 2 Nervous System UnifiedDocument71 pages3 Chap 2 Nervous System Unifiedralphfarah53No ratings yet
- Neural Control and CoordinationDocument16 pagesNeural Control and Coordinationadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Biopsychology NotesDocument5 pagesBiopsychology NotesPatricia100% (1)
- 8 - Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument23 pages8 - Autonomic Nervous SystemibhaslauraNo ratings yet
- 7 Control & CoordinationDocument38 pages7 Control & CoordinationSaifAkhtarNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy - Nervous TissueDocument73 pagesAnaPhy - Nervous TissuesoraruNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction & General Features of Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesLecture 1 Introduction & General Features of Nervous Systemdaw022No ratings yet
- Sheniblog SSLC Biology - RAJESH ENG 2Document12 pagesSheniblog SSLC Biology - RAJESH ENG 2dfathima300No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy: The Nervous System: Neural TissueDocument49 pagesHuman Anatomy: The Nervous System: Neural TissueLeilaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing PinoyDocument67 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Pinoyalfred31191% (23)
- Nervous Systems: BiologyDocument73 pagesNervous Systems: BiologyLê NgânNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Review Notes 30pgsDocument32 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Review Notes 30pgsNormala Macabuntal SaripadaNo ratings yet
- 03 Nervous System BDocument41 pages03 Nervous System BBalew KassieNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesHistology of The Peripheral Nervous SystemREMAN ALINGASANo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemCally ChanNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing 64 PagsDocument64 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing 64 Pagstanya nNo ratings yet
- Assessing Neurologic System - FinalDocument66 pagesAssessing Neurologic System - FinalAngelo EstanislaoNo ratings yet
- Tipo de Glândulas:: Sistema NervosoDocument7 pagesTipo de Glândulas:: Sistema NervosoInês NovaisNo ratings yet
- Zoology LectureDocument4 pagesZoology LectureAngelica CruzNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Levels of Organization - Cells and TissuesDocument26 pagesUnit 3 Levels of Organization - Cells and TissuesAngelica CruzNo ratings yet
- THESIS Super FINAL 1Document46 pagesTHESIS Super FINAL 1Angelica CruzNo ratings yet
- Nub Imrad FormatDocument5 pagesNub Imrad FormatAngelica CruzNo ratings yet
- Ana Kidnap EditedDocument2 pagesAna Kidnap EditedAngelica CruzNo ratings yet
- Uncovering The Lived Experiences of Filipino Drug Recoverees Towards Occupational Participation and Justice Through An Interpretative Phenomenological AnalysisDocument14 pagesUncovering The Lived Experiences of Filipino Drug Recoverees Towards Occupational Participation and Justice Through An Interpretative Phenomenological AnalysisAngelica CruzNo ratings yet
- LE 8 The Sensory SystemDocument3 pagesLE 8 The Sensory SystemAngelica CruzNo ratings yet
- Ana - ReviewerDocument5 pagesAna - ReviewerAngelica CruzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Human AnatomyDocument4 pagesLecture 9 Human AnatomyAngelica CruzNo ratings yet
- AIIMS PG Entrance May 2004 Solved Question Paper With KeyDocument15 pagesAIIMS PG Entrance May 2004 Solved Question Paper With KeySAIFNo ratings yet
- Medicine High YieldDocument213 pagesMedicine High Yield5jqr2r7z2hNo ratings yet
- MEDT 19 (Lec)Document17 pagesMEDT 19 (Lec)Erick PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Urine Analyzer IEEEDocument6 pagesUrine Analyzer IEEESamin ZarifNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentilationDocument19 pagesMechanical VentilationDoha EbedNo ratings yet
- Vlaar2021 Article TransfusionStrategiesInBleedinDocument25 pagesVlaar2021 Article TransfusionStrategiesInBleedinRaul DoctoNo ratings yet
- Grassi, Et Al. Lercanidipine Update. J of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapy 2017Document11 pagesGrassi, Et Al. Lercanidipine Update. J of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapy 2017Ruth RachmawatyNo ratings yet
- Machanical Ventilator Nursing Care PalnDocument13 pagesMachanical Ventilator Nursing Care PalnAnnie Priscilla100% (1)
- Cardiac Catheterization and Coronary AngiographyDocument5 pagesCardiac Catheterization and Coronary Angiographyedem100% (1)
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning (Cop)Document35 pagesCarbon Monoxide Poisoning (Cop)malak amerNo ratings yet
- Analytical ExpositionDocument3 pagesAnalytical ExpositionratiNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Hemolytic AnemiaDocument4 pagesAutoimmune Hemolytic AnemiaSamuel WibowoNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease Knowledge QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesHeart Disease Knowledge QuestionnaireFerdy LainsamputtyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology, Monitoring, and Therapy of Shock With Organ FailureDocument11 pagesPathophysiology, Monitoring, and Therapy of Shock With Organ FailureAli SedawiNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT OF THORAX, LUNGS, Heart Neck Vessels, Breast, Lymphatic, Peripheral Vascular SystemDocument33 pagesASSESSMENT OF THORAX, LUNGS, Heart Neck Vessels, Breast, Lymphatic, Peripheral Vascular Systemandramercadejas730No ratings yet
- AHA JNC 8 GuidelineDocument12 pagesAHA JNC 8 GuidelineFamidur RsNo ratings yet
- MTHISTO100 Lesson 2 Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesMTHISTO100 Lesson 2 Respiratory SystemJaeri HuangNo ratings yet
- Dr. Diyal Das NewDocument2 pagesDr. Diyal Das NewSaleem AliNo ratings yet
- B Pharmacy Human Anatomy Lecture 1 - Part ADocument5 pagesB Pharmacy Human Anatomy Lecture 1 - Part AAngela SamarNo ratings yet
- Paclitaxel-Induced Pneumonitis in PatientsDocument5 pagesPaclitaxel-Induced Pneumonitis in PatientsAndiie ResminNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument63 pagesCommunity Acquired PneumoniaLet BorlagdanNo ratings yet
- Notes: Student Book 1Document115 pagesNotes: Student Book 1Farah AwadNo ratings yet
- April 2021 - Pediatric Emergency CareDocument128 pagesApril 2021 - Pediatric Emergency CareEdison Junior Juarez LaricoNo ratings yet
- Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy For Ischemic Stroke Chest 2012Document36 pagesAntithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy For Ischemic Stroke Chest 2012dinaNo ratings yet
- Inhalation Anaesthetic AgentsDocument9 pagesInhalation Anaesthetic Agentsapi-142637023No ratings yet
- Test Bank Clinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease Mid PartDocument24 pagesTest Bank Clinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease Mid Partweekup035No ratings yet
- Cholinergic drugs-BPTDocument39 pagesCholinergic drugs-BPTHUZAIFA YAMAANNo ratings yet
- Spirometry in PracticeDocument24 pagesSpirometry in Practiceuser_at_scribd100% (1)
- Cataract Case PresentationDocument7 pagesCataract Case PresentationShahbaz AAnsariNo ratings yet
- ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation)Document22 pagesECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation)dhivya singhNo ratings yet