Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2.ppt (Compatibility Mode)
Uploaded by
Elhussain HassanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2.ppt (Compatibility Mode)
Uploaded by
Elhussain HassanCopyright:
Available Formats
ﺑﺴﻢ اﷲ اﻟﺮﺣﻤﻦ اﻟﺮﺣﯿﻢ
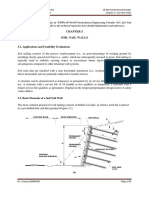
Foundation Engineering
Chapter 2
by
Prof. Adel Ahmed Dif
Structural Eng. Dept.
Faculty of Engineering
El-Mansoura University
Deep Foundations 2
n Piles
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
Pile Foundations 2
n Pile foundations are the part of a structure
used to carry and transfer the load of the
structure to the bearing ground located at
some depth below ground surface. The main
components of the foundation are the pile
cap and the piles.
n Piles are long and slender members which
transfer the load to deeper soil or rock of
high bearing capacity avoiding shallow soil of
low bearing capacity.
Pile Foundations 2
n A preliminary selection of the pile type may
usually be made from a study of the
foundation investigations. However, the
nature of the structure, type of applied loads,
and technical and economic feasibility must
be considered in the determination of pile
type, length, spacing, batters, etc.
n Piles are slender structural elements installed
in the ground to support a load or compact
the soil. They are made of several materials or
combinations of materials and are installed by
impact driving, jacking, vibrating, jetting,
drilling, grouting, or combinations of these
techniques.
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
Pile Foundations 2
Design issues
The key design issues in relation to pile foundations
include:
1. Selection of the type of pile and installation method;
2. Estimation of the pile size in order to satisfy the
requirements of an adequate margin of safety against
failure of both the supporting soil and the pile itself,
both in compression and tension;
3. Estimation of the settlement of the foundation, and
the differential settlement between adjacent
foundations;
Pile Foundations 2
4. Consideration of the effects of any lateral loading, and
the design of the piles to produce an adequate margin
of safety against failure of the soil and the pile, and
an acceptable lateral deflection;
5. Consideration of the effects of ground movements
which may occur due to external causes (such as soil
settlement and swelling), and the estimation of the
movements and forces induced in the pile by such
movements;
6. Evaluation of the performance of the pile from
appropriate pile loading tests, and the interpretation
of these tests to evaluate parameters which may be
used to predict more accurately the performance of
the pile foundation.
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
• The selection of a pile foundation type for a
structure should be based on the specific soil
conditions as well as the foundation loading
requirements and final performance criteria.
• There are numerous types of foundation piles.
A pile classification system may be based on type
of material, installation technique and
equipment used for installation.
• Foundation piles can also be classified on the
basis of their method of load transfer from the
pile to the surrounding soil mass.
PILE TYPES 2
• Piles are difficult to summarize and classify because there
are many types of piles, and new types are still being
developed.
•Concrete piles can also be classified according to the
condition under which the concrete is cast. Some concrete
piles (precast piles) are cast in a plant before driving, which
allows controlled inspection of all phases of manufacture.
Other piles are cast-in-place (CIP), a term used to
designate piles made of concrete placed into a previously
driven, enclosed container; concrete-filled corrugated shells
and closed-end pipe are examples of CIP piles. Other piles
are cast-in-situ (CIS), a term to designate concrete cast
directly against the earth; drilled piers and auger grout
piles are examples of CIS piles.
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Selection of the type of pile and installation
method :ﺃﻨﻭﺍﻉ ﺍﻟﺨﻭﺍﺯﻴﻕ
ﻜﻴﻔﻴﺔ ﻨﻘل،ﻴﻤﻜﻥ ﺘﻘﺴﻴﻡ ﺍﻟﺨﻭﺍﺯﻴﻕ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻋﺩﺓ ﺃﻨﻭﺍﻉ ﺇﻤﺎ ﺒﺎﻟﻨﺴﺒﺔ ﻟﻔﻜﺭﺓ ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫﻫﺎ
ﺃﻭ ﻟﻨﻭﻉ ﻤﺎﺩﺓ، ﻁﺭﻴﻘﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ، ﺃﻭ ﻟﻠﻐﺭﺽ ﻤﻥ ﺍﺴﺘﻌﻤﺎﻟﻬﺎ،ﺍﻟﺤﻤل ﻟﻠﺘﺭﺒﺔ
ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺯﻭﻕ ﻭﻋﻤﻭﻤﺎﹰً ﻴﻤﻜﻥ ﺃﻥ ﺘﻘﺴﻡ ﺍﻟﺨﻭﺍﺯﻴﻕ ﺒﺎﻟﻨﺴﺒﺔ ﻟﻔﻜﺭﺓ ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫﻫﺎ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻨﻭﻋﻴﻥ
:ﺃﺴﺎﺴﻴﻴﻥ
(Displacement piles) ﺨﻭﺍﺯﻴﻕ ﺍﺯﺍﺤﺔ ﺃﻭ ﺍﺨﺘﺭﺍﻕ-١
ﻭﻓﻰ ﻫﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﻨﻭﻉ ﻴﺼﻨﻊ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺯﻭﻕ ﺜﻡ ﻴﺘﻡ ﻭﻀﻌﻪ ﻓﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﺭﺒﺔ ﺇﻤﺎ ﺒﺎﻟﺩﻕ ﺃﻭ
(Large & Small ) ﺍﻟﻀﻐﻁ ﺃﻭ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻡ ﻭﻫﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﻨﻭﻉ ﻴﻤﻜﻥ ﺘﻘﺴﻴﻤﻪ ﺍﻟﻰ ﻗﺴﻤﻴﻥ
(Replacement piles) ﺨﻭﺍﺯﻴﻕ ﺘﻔﺭﻴﻎ-٢
(Non-Displacement piles)
ﻭﻓﻰ ﻫﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﻨﻭﻉ ﻻ ﻴﺘﻡ ﻋﻤل ﺃﻯ ﺇﺯﺍﺤﺔ ﻟﻠﺘﺭﺒﺔ ﻭﻋﺎﺩﺓ ﺘﺤﻔﺭ ﺍﻟﺘﺭﺒﺔ ﺜﻡ ﻴﺘﻡ
.ﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺯﻭﻕ ﺩﺍﺨل ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﺤﻔﺭﺓ
PILE TYPES 2
Displacement Piles
Piles which are driven are termed ‘Displacement Piles’
because their installation methods displace laterally the
soils through which they are introduced.
Replacement Piles
Piles that are formed by creating a borehole into which the
pile is then cast or placed, are referred to as ‘Replacement
Piles’ because existing material, usually soil, is removed as
part of the process.
There are two principal types of replacement pile. These
are bored-and-cast-in-place piles, and drilled-in tubular
(including caisson) piles.
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
A) classification of piles based on installation
technique :
These categories may be subdivided into:
1. Large Displacement :
• Preformed :driven into the ground and left in position
a) Solid : Timber/Concrete
( Precast concrete piles Non prestressed, prestressed )
b) Hollow with a closed end : Steel or concrete tubes
• Formed in-situ : closed-ended tubular driven then
.
withdrawn filling void with concrete. ( Driven cast –
in-place piles such as Franki, Raymond, Montube etc )
•The British Standard Code of Practice for Foundations
2
(BS 8004) places piles in three categories.
•Large displacement piles comprise solid-section piles or
hollow-section piles with a closed end, which are driven or
jacked into the ground and thus displace the soil. All types
of driven and cast-in-place piles come into this category.
•Small-displacement piles are also driven or jacked into the
ground but have a relatively small cross-sectional area. They
include rolled steel H- or I-sections, and pipe or box sections
driven with an open end such that the soil enters the hollow
section. Where these pile types plug with soil during driving
they become large displacement types.
•Replacement piles are formed by first removing the soil by
boring using a wide range of drilling techniques. Concrete
may be placed into an unlined or lined hole, or the lining may
be withdrawn as the concrete is placed. Preformed elements
of timber, concrete, or steel may be placed in drilled holes.
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
• Types of piles in each of these categories can be listed as
follows.
1-a- Large displacement piles (driven types)
1. Timber (round or square section, jointed or continuous).
2. Precast concrete (solid or tubular section in continuous
or jointed units).
3. Prestressed concrete (solid or tubular section).
4. Steel tube (driven with closed end).
5. Steel box (driven with closed end).
6. Fluted and tapered steel tube.
7. Jacked-down steel tube with closed end.
8. Jacked-down solid concrete cylinder.
PILE TYPES 2
1-b- Large displacement piles (driven and cast-in-place
types)
1. Steel tube driven and withdrawn after placing concrete.
2. Precast concrete shell filled with concrete.
3. Thin-walled steel shell driven by withdrawable mandrel
and then filled with concrete.
2- Small-displacement piles
1. Precast concrete (tubular section driven with open end).
2. Prestressed concrete (tubular section driven with open end).
3. Steel H-section.
4. Steel tube section (driven with open end and soil removed as
required).
5. Steel box section (driven with open end and soil removed as
required).
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
3- Replacement piles
1. Concrete placed in hole drilled by rotary auger, baling,
grabbing, airlift or reverse-circulation methods (bored
and cast-in- place).
2. Tubes placed in hole drilled as above and filled with
concrete as necessary.
3. Precast concrete units placed in drilled hole.
4. Cement mortar or concrete injected into drilled hole.
5. Steel sections placed in drilled hole.
6. Steel tube drilled down.
Composite piles
•Numerous types of piles of composite construction may be
formed by combining units in each of the above categories, or
by adopting combinations of piles in more than one category.
PILE TYPES 2
2. Small displacement :
- Screw piles
- Steel H piles
- Box piles
- Steel tube piles – open ended (Tube sections
may plug and become large displacement).
3. Non-displacement (Replacement) :
Void formed by boring or excavation then filled
with concrete. During construction the hole
may need to be supported for which there are
two main options : (Bored Piles – cased or uncased)
- steel casing
- drilling mud
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Displacement or Low-Displacement ?
Displacement piles are piles that
actually displace the material they
are driven into.
Low (Non) Displacement piles are
piles that displace very little of the
material they are driven into.
PILE TYPES 2
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
• For all pile types a further distinction is
required based on their method of
installation.
a. Driven piles:
These piles are generally pre-formed before
being driven, jacked, screwed or hammered
into the ground.
b. Bored piles:
For these piles a hole is first bored in the
ground, and the pile is then usually formed in
the hole.
PILE TYPES 2
Types of Displacement Piles
Displacement
Large Small
Hollow tube, or
Preformed Formed in-situ H-section Screw
Steel
Hollow tube Tube former
Solid Closed end withdrawn
Concrete,
or Timber Steel or Concrete void filled with
concrete
١٠
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Types of Non-displacement Piles
Bored Piles
Unsupported Supported
during during
Construction Construction
Steel Casing Drilling Mud
Void filled with
Reinforced Concrete
PILE TYPES 2
What is a Driven Pile?
A Driven Pile is a deep foundation
that is constructed by driving a
concrete, steel or timber pile to
support the anticipated loads in
competent subsurface material.
Prefabricated concrete piles are driven
using a pile driver equipped with a
hydraulic free fall hammer.
Prefabricated concrete piles are
primarily used in loose soils.
١١
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
What is a Bored Pile?
A Bored Pile is a deep foundation that
is constructed by removing the soil in
the pile location by an excavating tool
(bucket- auger – core barrel- etc..) to
correct depth.
When the drill has arrived at the
correct depth, the pile is concreted
using a tremmie pipe or pumped
through the end of the centre pipe
(CFA).
PILE TYPES 2
B) Classification of piles with respect to load
transmission :
• Piles are used to transmit foundation loads
through soil strata of low bearing capacity to
deeper soil or rock having a higher bearing
capacity. The method by which this occurs is
the basis of the simplest pile type classification.
• Three main pile types:
1. End bearing piles (point bearing piles)
2. Friction piles (cohesion piles )
3. Combination of friction and end bearing piles
١٢
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
• Piles are used under structures to transmit the
foundation load to a deeper soil stratum which
has a higher load carrying capability.
• Piles that transmit their load to the soil by
friction between the pile surface and the soil are
called friction piles. Those that transmit their
load to a particular soil stratum at the end of the
pile are called end bearing piles.
•The vast majority of piles transmit the load to the
soil by a combination of both actions ( friction and
end bearing piles ).
PILE TYPES 2
: ﺏ( ﺘﻘﺴﻴﻡ ﺍﻟﺨﻭﺍﺯﻴﻕ ﺒﺎﻟﻨﺴﺒﺔ ﻟﻁﺭﻴﻘﺔ ﻨﻘل ﺍﻷﺤﻤﺎل ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﺭﺒﺔ
ﻭﻫﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﻨﻭﻉ ﻴﻨﻘل ﺍﻟﺤﻤل ﺇﻟﻰ،End-Bearing Piles ﺨﻭﺍﺯﻴﻕ ﺍﺭﺘﻜﺎﺯ-١
.(Qb) ﺍﻟﺘﺭﺒﺔ ﺒﺎﻟﻤﻘﺎﻭﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻭﻟﺩﺓ ﻋﻨﺩ ﻨﻘﻁﺔ ﺍﺭﺘﻜﺎﺯﻩ ﺃﻭ ﻗﺎﻋﺩﺘﻪ
ﻭﻫﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﻨﻭﻉ ﻴﻨﻘل ﺍﻟﺤﻤل ﺃﺴﺎﺴﺎ،Friction piles ﺨﻭﺍﺯﻴﻕ ﺍﺤﺘﻜﺎﻙ-٢
.(Qs) ﺒﻤﻘﺎﻭﻤﺔ ﺍﻻﺤﺘﻜﺎﻙ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺴﻁﺤﻪ
ﺍﺤﺘﻜﺎﻙ/ ﺨﻭﺍﺯﻴﻕ ﺍﺭﺘﻜﺎﺯ-٣
،End-bearing-Friction Piles
ﻭﻫﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﻨﻭﻉ ﻴﻨﻘل ﺍﻟﺤﻤل ﺠﺯﺌﻴﺎ ﺒﻭﺍﺴﻁﺔ
ﺍﻻﺤﺘﻜﺎﻙ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺴﻁﺤﻪ ﻭﺠﺯﺌﻴﺎ ﺒﻤﻘﺎﻭﻤﺔ
.( Qb+Qs) ﺍﻻﺭﺘﻜﺎﺯ ﻋﻨﺩ ﻗﺎﻋﺩﺘﻪ
١٣
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
End bearing piles
Friction piles
PILE TYPES 2
END BEARING PILE FRICTION PILE
LOAD LOAD
SAND SAND
L SANDS
L L
O O
O
A A
D A
SOFT D
D CLAYS
CLAY
CLAY
ROCK SAND
١٤
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Qu End bearing - Friction pile
∆z1 RS1 Layer 1
∆z2 RS2 Layer 2
∆z3 RS3 Layer 3 Qu = RSN + RT
∆z4 RS4 Layer 4
RT
PILE TYPES 2
C) Classification of piles with respect to pile
materials :
.ﺗﺼﻨﻊ اﻟﺨﻮازﯾﻖ ﻣﻦ اﻟﺨﺮﺳﺎﻧﺔ أو اﻟﺤﺪﯾﺪ أو اﻟﺨﺸﺐ أو أﻛﺜﺮ ﻣﻦ ﻣﺎدة ﻣﻦ ھﺬه اﻟﻤﻮاد
The main types of materials used for piles are wood, steel and
concrete.
١٥
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Materials used for piles
PILE TYPES 2
Concrete Piles
١٦
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PRESTRESS Piles 2
PILE TYPES 2
١٧
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Steel Pile – H piles :
Similar to I-beam except that
cross-section is generally
heavier and the flange width
and distance from flange face
to flange face is nearly the
same.
H - Piles
PILE TYPES 2
Steel Pile – H piles :
١٨
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Steel Pipe Pile
(Tube piles)
Spin Fin Pile
PILE TYPES 2
Steel Pipe Pile
١٩
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Steel Pipe Pile
PILE TYPES 2
Steel Pipe Pile
٢٠
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Wood piles :
(Timber piles)
PILE TYPES 2
Timber
piles
Corrosion of steel H piles
٢١
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Fiber-reinforced polymer piles
Fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composite piles.
SEAPILE composite marine piles
consist of an extruded recycled
plastic material reinforced by
fiberglass bars.
SEAPILE pile sample after
axial compression test.
PILE TYPES 2
PPI manufactures
recycled plastic piles
reinforced by steel bars
PPI pile.
Trimax structural plastic
lumber material consists of
recycled plastic, fiberglass,
and selected additives Trimax pile.
٢٢
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
(FRP) piles (FRP) Fender piles
PILE TYPES 2
Composite Pile
• Concrete – H-Pile
• Pipe – H-Pile
• Pipe – concrete Pile
• Corrugated Shell –
Timber Pile
٢٣
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
PILE TYPES 2
TYPES OF BEARING PILE
DISPLACEMENT NON-DISPLACEMENT
Grout intruded Concrete intruded
TOTALLY PREFORMED DRIVEN CAST- IN-PLACE
the soil (unless deliberately isolated by
In these piles concrete is cast against
A bore is formed by A bore is formed with
A section, tubular or otherwise A tube is driven into means of a hollow - a hollow -stemmed
is driven into the ground . the ground to form centered flight auger. flight auger. Concrete
The sections is : a void. The tube is Grout is intruded is pumped through
and either displaces the stem as the auger is
or is mixed with bore extracted
spoil
A void is formed by
a membrane)
boring or excavation
Hollow Solid Concrete Steel
Partially preformed piles
Steel Concrete Concrete Steel Timber
The close-ended tube The tube is
is filled with concrete Preformed units are
and left in position grouted in place
The void is
Precast reinforced Precast prestressed
Closed - ended Open -ended
Percussion bored Rotary bored
Drilled
Tube is left in position The basic system
and filled with concrete involves driving a Small diameter
Joined by Joined using
the tube is retrievable tube and
splicing proprietary
1) of constant section forming a pile with Large diameter
system Small diameter
2) tapered or without an Straight-shafted
Underreamed
enlarged base
Classification of bearing pile types. After Weltman and Little (1977)
٢٤
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Other special pile types
• Underreamed (Belled) Shaft
• Tangent Pile Wall ( Secant Pile)
• Micro Piles
• Barrettes
PILE TYPES 2
Underreamed (Belled) Shaft
A special feature of auger bored piles which is sometimes
used to enable to exploit the bearing capacity of suitable
strata by providing an enlarged base. The soil has to be
capable of standing open unsupported to employ this
technique. Stiff and to hard clays, such as the London clay,
are ideal.
٢٥
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Underreamed (Belled) Shaft
Bottom hinge Top hinge
Under-reaming tools
PILE TYPES 2
Underreamed (Belled) Shaft
Bell pile technique is able to increase the end-bearing capacity
of the pile by enlarging its bottom sectional area.
٢٦
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Underreamed (Belled) Shaft
PILE TYPES 2
Tangent Pile or Secant Pile Wall
٢٧
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Tangent Pile or Secant Pile Wall
PILE TYPES 2
Tangent Pile Wall
ANCHORS
Un-reinforced Primary Pile
Reinforced Primary Piles ELEVATION
٢٨
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Tangent Pile Wall
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
Micro piles are relatively small diameter, usually 3 to 12 inch
diameter, high capacity deep foundation elements.
These drilled and grouted reinforced piles are typically used
for structural support where conventional deep foundation
elements cannot be installed due to project constraints such
as limited work space or where heavy machinery cannot be
used.
Micro piles are manufactured with a coupling sleeve and are
either hot dip galvanised or left untreated.
A pile shoe is fitted when the piles are installed.
The piles are installed using special machines equipped with
a light hydraulic or pneumatic ram.
٢٩
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
• A micropile is a small-diameter (typically less than
300 mm), drilled and grouted replacement pile that is
typically reinforced. A micropile is constructed by
drilling a borehole, placing reinforcement, and
grouting the hole.
• Micropiles are installed by methods that cause
minimal disturbance to adjacent structures, soil, and
the environment. They can be installed in access-
restrictive environments and in all soil types and
ground conditions. Micropiles can be installed at any
angle below the horizontal using the same type of
equipment used for ground anchor and grouting
projects.
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
٣٠
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
Fundamentals are similar to traditional pile design
♦ However, due to the small structural section,
structural design and stiffness can often control
Construction Techniques
“Drill Rig”
Micropile Materials :
- Permanent Steel Pipe
- Steel Reinforcement
- Cement Grout
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
Micropile Design Steps
♦ Internal - Structural
♦ External - Geotechnical
♦ Connection of Pile to Structure
Micropiles through existing New pile cap attached to existing
footing footing
Two Common Options for Connecting Micropiles
to an Existing Structure
٣١
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
1. Structural Design
♦ Components
– Cased length
– Uncased length
– Grout to steel bond
– Transitions between reinforcement types
– Strain compatibility
– Casing or bar splice and connection
– Footing connection
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
2- Geotechnical Design
♦ Evaluate Load Transfer Parameters
– grout to ground average bond values
– identify variations throughout profile and
across the site
– define the required minimum bond length
♦Evaluate pile spacing
– impact from group effects
٣٢
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
Figure 2- 1
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
• Micropiles are made of 50 to 80 ksi steel casing and
4,000 to 5,000 psi grout. The casing is drilled down to a
pre-determined depth or socketed into rock, then
tremie-filled with grout.
• The most popular micropile sizes, assuming allowable
steel stress of 18 ksi and 4,000 psi grout:
٣٣
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
٣٤
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
٣٥
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Micro Piles
PILE TYPES 2
Barrettes
ONE PILE ONE COLUMN Approach
(PILED COLUMN)
The pile type and capacity shall be governed by column
load characteristics :
- only pile caps connect pile to column - no large fat raft
- less excavation - less dewatering
- less temporary earth support
- less risk to the neighboring buildings
- technical uncertainties are minimal
- maximizing the potential of pile material strength
- suitable for all types of soil unlike piled raft, which is only
suitable for some soil conditions (Poulos 2001)
However, comprehensive quality control is needed.
٣٦
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
ONE PILE ONE COLUMN Approach
(PILED COLUMN)
Barrettes ( Multiform strip piles )
Barrettes are very large bored piles.
* If the correct equipment is used they
are faster to construct and less cost/ton
than conventional bored piles.
* Can the same design methods apply?
Spacing – end bearing – shaft resistance?
French Code: 15% reduction
PILE TYPES 2
Barrettes ( Multiform strip piles )
٣٧
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Barrettes
PILED COLUMNS
PILED RAFT ONE PILE ONE COLUMN
GROUND SURFACE
GROUNDWATER TABLE
SIDE SUPPORTING & DEWATERING DEPTH
R.C RAFT R.C Slab R.C Pile Cap
12 00
5000
PLAIN CONCRETE TH=200 MM
ONE PILE
350
GROUP OF PILES
PILE TYPES 2
Barrettes
Typical barrette layout for a transmission tower
Cruciform barrette for a monopole type tower
٣٨
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Barrettes
Barrette construction sequences (schematic)
PILE TYPES 2
Barrettes
Guide wall for
a cruciform barrette
Reinforcement being
installed in the trench
٣٩
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Barrettes
It concerns a type of drilled and cast-in-place pile, the
distinctive characters of which are the shape and way of
drilling. Grab-bucket or Hydrofraise type drilling tools
are used. The size of these tools determines that of the
piles. The simplest piles are made with one stroke of a
standard size grab-bucket (or Hydrofraise cutting
drums). The sizes are :
• width : 0.52, 0.62, 0.82, 1.02, 1.22, 1.52 m
• length : 1.80, 2.20, 2.70, 3.0 m
The methods of calculation and
measurement are the same as those for
drilled and cast-in-place circular piles.
PILE TYPES 2
٤٠
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
SAN STEFANO COMPLEX
PILE TYPES 2
Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Y6 Y7
MECHANICAL FLOOR MECHANICAL FLOOR
FLOOR 29 FLOOR 29
FLOOR 28 FLOOR 28
FLOOR 27
FLOOR 26
FLOOR 25
RESIDENTIAL FLOOR
FLOOR
FLOOR
27
26
25
FLOOR 24 FLOOR 24
FLOOR 23 FLOOR 23
FLOOR 22 FLOOR 22
FLOOR 21 FLOOR 21
FLOOR 20 FLOOR 20
FLOOR 19 FLOOR 19
FLOOR 18 FLOOR 18
FLOOR 17 FLOOR 17
FLOOR 16 FLOOR 16
FLOOR 15 FLOOR 15
FLOOR 14 FLOOR 14
FLOOR 13 FLOOR 13
FLOOR 12 FLOOR 12
FLOOR 11 HOTEL FLOOR 11
FLOOR 10 FLOOR 10
FLOOR 09 FLOOR 09
FLOOR 08 FLOOR 08
FLOOR 07 FLOOR 07
FLOOR 06 FLOOR 06
FLOOR 05 FLOOR 05
FLOOR 04 FLOOR 04
FLOOR 03 FLOOR 03
FLOOR 02 FLOOR 02
FLOOR 01
GROUND FLOOR
HOTEL FLOOR 01
GROUND FLOOR
UPPE R UPP ER
GROUND FLOOR GROUND FLOOR
GROUND FLOOR
LOWER
LOWER
BASEMENT 1 BASEMENT 1
BASEMENT 2 BASEMENT 2
BASEMENT 3 BASEMENT 3
Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Y6 Y7
SAN STEFANO COMPLEX
NUMBER OF FLOORS = 36 TOTAL LOAD = 826,000 TON
32 ABOVE GROUND SURFACE + 4 BELOW GROUND SURFACE
٤١
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
SAN STEFANO COMPLEX
SAN STEFANO COMPLEX (Deep Foundation Summary) 2
Type Shape Capacity (t) No. Length
(m)
Comp. Tens.
Pile D=1.20m 650 110 360 20
Pile D=1.50m 900 160 36 20
Barrette (1.0X2.80m) 1450 250 31 20
Barrette (1.20X2.80m) 1670 300 38 20
Barrette (1.50X2.80m) 2000 340 128 20
Barrette (1.20X4.0m) 2300 400 44 20
T – Barrette (1.20m) 3000 500 6 20
T – Barrette (1.20m) 3000 500 2 20
T – Barrette (1.50m) 4000 575 12 22
٤٢
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
SAUDI EMBASSY -
TOP OF PARAPET 181.8
LIFT MACHINE RM. 178.0
CAIRO
PLANT RM.-II 175.0
PLANT RM.-I 171.4
18th FLOOR
AMBASSADOR'S SUITE 167.8
17th FLOOR - DEPUTY AMBASSADOR 164.2
16th FLOOR - ECONOMIC AFFAIRS 160.6
COMMUNICATIONS
15th FLOOR - ADMIN./FINANCIAL AFFAIRS 157.0
ROOF LEVEL (T.O.S.) +156.60 BUILDING ADMIN.
14th FLOOR - ADMIN./FINANCIAL AFFAIRS 153.4
TERRACE FLOOR (T.O.S.) +153.20
13th FLOOR - ARAB LEAUGE DELEGATION 149.8
14th FLOOR (T.O.S.) +149.80
(TYPE-A, UPPER LVL.)
12th FLOOR - MILITARY ATTACHE 146.20
13th FLOOR (T.O.S.) +146.40
(TYPE-A, LOWER LVL.)
12th FLOOR (T.O.S.) +143.00 11th FLOOR - MILITARY ATTACHE 142.6
11th FLOOR (T.O.S.) +139.60 10th FLOOR - NATIONAL GUARDS 139.0
10th FLOOR (T.O.S.) +136.20 9th FLOOR - EDUCATIONAL ATTACHE 135.4
9th FLOOR (T.O.S.) +132.80 8th FLOOR - EDUCATION ATTACHE 131.8
8th FLOOR (T.O.S.) +129.40 7th FLOOR - HEALTH ATTACHE 128.2
7th FLOOR (T.O.S.) +126.00
6th FLOOR - COMMERCIAL ATTACHE 124.6
6th FLOOR (T.O.S.) +122.60
5th FLOOR - SAUDI RECRUITMENT OFFICE 121.0
5th FLOOR (T.O.S.) +119.20
4th FLOOR - SAUDI NEWS AGENCY 117.4
INFORMATION AFFAIRS
4th FLOOR (T.O.S.) +115.80
STEP TRANSFER DECK 113.8
3RD FLOOR (T.O.S.) +112.00 3RD FLOOR 112.0
2ND FLOOR 108.200
2ND FLOOR (T.O.S.) +108.20
1ST FLOOR 104.400
1ST FLOOR (T.O.S.) +104.40
GROUND FLOOR (T.O.S.)+100.60
GROUND FLOOR (T.O.S.) +100.60
BASEMENT FLOOR (T.O.S.)+97.00
BASEMENT FLOOR (T.O.S.) +97.00
NUMBER OF FLOORS = 23 TOTAL LOAD = 141,000 TON
20 ABOVE GROUND SURFACE + 1 BELOW GROUND SURFACE
PILE TYPES 2
SAUDI EMBASSY - CAIRO
A B C D E F G H I J K
MATCH LINE
67500
7500 6900 6100 5500 5500 5500 7500 5500 7500 7500 2500
2750 2750 2750
7 1000
7
800
2500
2500
310
DB1 DB3 DB2 DB1 50
1015
P3
8 8
270
270
100
100
100
235
P1 P2 P2
200 P5 200
P5 P3
200
P5
3500
3500
9 1200 250
250 1600
50
9
1155
1155
1155
100 P3 P3 P3
1000
1000
750
300
425
425
425
25
25
25
25
10 P1 B1
P5
B1 P3 B1 P3
10
4500
4500
450 6100 450
B1 DB4
F OR CONTINUATION REFER TO DWG. NO. S -S-G-01 -11
1400
1400
1250
1075 50
11 11
600
100
100
100
100
100
100
P1 B1 P1 B1
B1 P3
1625
P3 P2 P4
DB4
4500
4500
3275
100 50 100
750 50
DB4
12 DB4
12
32000
32000
DB4
100
100
P1 P2 B1 P2 P3 P2
P1 P2 P2
DB4
4500
4500
1075
1625
50
700
13 B1
13
100
100
100
100
100
600
P1 B1 P1 B1 P4 P3
1400
1400
P3 P2
250
450 DB4 450
4500
4500
2625
1200 250
250 1600
13 B1
13
375
375
B1 B1 B1 50 50 100 100
1050
1050
P1
1150
1150
P3
P5
P3 P3 P3 P3
4500
4500
650
B1 200 50 50
1195
925
300
14 14
500
250 P2
100
100
50
P2
860
1015
P1 P3
P5
2500
2500
DB4
P5 B1 P3
15 15
MATCH LINE
1000 2250
7500 6900 6100 5500 5500 5500 7500 5500 7500 7500 2500
67500
A B C D E F G H I J K
٤٣
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
SAUDI EMBASSY (Deep Foundation Summary)
Type Shape Capacity (t) No. Grout Length
Length (m)
Comp. Tens.
Pile D=0.60m 95 24 3 11
Pile D=0.80m 160 89 3 11
Pile D=0.80m 290 34 9 22
Pile D=1.0m 450 18 9 22
Pile D=1.20m 580 22 9 22
Barrette (0.80X2.80m) 1150 17 10 22
T - Barrette (1.0X2.80m) 3300 2 18 30
PILE TYPES 2
NILE CITY
NUMBER OF FLOORS = 34 TOTAL LOAD = 518,500 TON
30 ABOVE GROUND SURFACE + 4 BELOW GROUND SURFACE
٤٤
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
005
8.10
010
8.10
1.1800
3.5670
015
8.10
020
8.10
025
8.10
030
8.10
035
8.10
040
NILE CITY
8.10
045
8.10
050
8.10
055
8.10
060
8.10
DIAPHRAGM WALL
065
8.10
070
8.10
075
8.10
080
8.10
085
8.10
090
8.10
095
8.10
100
8.10
105
8.10
110
8.10
115
8.10
120
8.10
125
X=329049.3350
Y=3327980.9000
1.1800
M
3.68
3.68
0.33
2.26
X=329091.0020
8.10
8.10
4.1000
Y=3328153.6120 INNER WALL
4.42
4.42
4.42
4.42
4.42
4.42
0.983
1.3 1.3 1.6 1.6 1.6 1.6 1.3 1.3
1.8 1.8
1.8 1.8
0.40
0.40
1.3 1.3
1.3 1.3
1.8 0.9
1.8 0.9
1.600
1.600
L L
3.11
2.35 2.86
4.05 2.86
8.10
8.10
1.400 T T T T 1.400 T
4.05 4.05
4.05
4.05
4.05
4.05
1.600
4.0500
3.28 1.075 1.075 1.600 0.975 0.975 5.60
0.975
0.975
0.975
0.975
0.600
T T
0.600
K K
2.79
1.72
1.72
1.72
1.72
4.05
4.05
2.79
4.05
2.80 2.80 2.80 2.80
3.65 3.65 3.65 3.65
8.10
8.10
0.50
T T T
4.73
3.52 1.47 3.52
1.33
4.0500
0.39 2.41
2.41
4.67 4.87 4.87
4.67 3.74
1.07
2.50
2.50
1.07
0.39
J
2.58
J
1.43
1.43
1.43
2.58
1.43
1.33 1.47 1.47 1.33 1.47 1.33
2.58
2.50
2.50
3.9600
3.10
4.05
4.05
4.05
4.05
4.05 2.82
5.3825
8.10
8.10
T T T T T T T
2.23 4.05
4.05
0.30 4.05
4.05
3.60
4.0500
4.05
4.05
3.655
6.24 4.87 4.72 3.55 4.73 4.05 4.05 3.52 4.48 5.12
L
4.05
R WAL
1.7 1.7
1.7 1.7
0.7
0.7
T T T
0.975
0.975
I
0.7
I
0.7
4.05
3.7260
L
INNE
0.7
GM WAL
1.12 1.075 0.7 4.05 1.02
1.7 1.7
8.10
8.10
L
T T T T T T T
R WAL
4.05
HRA
4.05
4.05
1.60 2.40
1.60 2.40
2.40 1.60
2.40 1.60
INNE
2.50
2.50
2.40
2.40
DIAP
1.7 1.7
1.7 1.7
0.7
0.7
T
L
H
0.7
0.7
H
M WAL
2.40
2.40
2.50
2.50
0.36 0.7 0.7
8.10
8.10
HRAG
1.7 1.7
81
2.25 2.25 2.25
4.
2.25
4.
1.60 1.60 1.60 1.30 1.60 1.30
81
4.05
4.05 2.34
DIAP
2.523
2.35
03
2.35
29
3.99 1.83
0.71
8
2.523
V
0.
2.339
0.35
4.05
1.175
1.175
1.175
1.175
1.175
1.175
1.175
1.175
1.30
1.30
0.36
0.64
T
50
0.64
T
.225
G T
1.
G
1.625
1.625
1.625
1.50
1.50
1.625
1.625
1.625
1.
3.52
4.0500
1.40
50
3.5250
43
2.10 2.10 3.90
1.
T T
4.20
50
4.20
1.82
8.10
8.10
1.
T T
2.49 1.50
2.49 1.50
T
1. 50
3.90
1.
0.89
4.05
4.05
07
4.05
8
2.
T
4.05
2.57
2.07
4.
1.
4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 1.625 4.05 4.40
1.38
1.37
1.625 3.00 1.50 1.50
58
58
0.
4.
T T T T T T T T T
45
F
2.66
F
20
T
3.09
2.60 T
4.05
2.66
4.05
4.05
4.
3.09
3.00 0.15 2.85
4.05 4.05 4.05 2.85 3.00 1.951.05 3.00 4.05 4.20 4.05 2.25 0.75 4.05 3.47
3.32
3.75
1.
0
1.
3.30
1.77
3.00 3.00
29
29
8.10
8.10
02 1.
20
1.
0
3.
T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T
0.60
4.58
4.
4.58
75
77
4.
4.
2.17 2.13 2.13 2.17
40
20
4.05
4.05
4.05
4.05
0.15
2.93
T T
20
1.
4.07
0
1.29
29
2.
20
4.20
4.
93
00
4.
4.
1.40
0
T T T T T T 1.05 T T T
20
40
E E
81
1.
0
0.
4.05
1.95
0.
72
T T
20
81
4.20
1.
1.61
4.
4.
4.81
1.
20
72
8.10
8.10
T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T 0.50
1.
0
4.58
4.58
29
29
60
4.05
4.05
4.05
1.
00
4.20
1.
1.5734 5.55 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05
0.
Y=3328185.6190
T T T T T
X=329018.9070
T T T T T T
60
D
2.50
D
4.05
4.05
4.05
70
68
2.25 3.00 0.15 3.00
0.42
3.00
1.
2.10
4.05 2.40 2.40
1.
1.80 3.14 3.30 4.05 4.05 1.95 3.00 0.15 3.00 2.25 0.75 3.30 3.82
1.60
1.05
1.
0.
1.70
8.10
8.10
2.10
68
42
10
T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T
5
2.
T T
0.
2.10
65
50
27
4.05
4.05
1.
2.
1.50
0.30
65
1.50
4.05 1.17
2.2293
4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05 4.05
2.03
0.
0.
2.27
0.23
18
0.
77
T T T T T T T T
10
1.50
18
T
2.24
2.25
2.50
C
2.67
2.67
2.
0.
C
2.87
2.10
4.05
4.05
4.05
4.05
1.
10
50
0.08 T
2.
0.15 0.15 4.05 T T
1.50
T T T T T
2.
T T 3.27 2.10
0.87
10
1.50
8.10
8.10
1.50
20
0.
T T T T 2.83 1.34 2.64 2.64 2.83 T T T T
43
87
4.
0.18
1.42 2.90
4.
3.
T T
4.05
4.05
20
T T T T T T
2.77
3.43
1.34 T
3.10
2.77
2.77
18
2.49
T T 2.05 2.15 1.75 2.45
0.
1.42
2.45 1.75 2.15 2.05 5.08
0.75
0.75
0.89
T T T T T
1.47
1.47
T T T
1.78
1.78
2.41
B 1.05 1.27 B
3.00
3.00
2.90
3.00
3.00
3.00
3.00
3.53
3.53
3.69
3.42 2.41 1.37 2.96 T T 3.06 2.99 1.37 2.43 3.42 4.39
INNER WALL X=328963.5530
8.10
8.10
1.22
2.95 0.42 2.28 1.22 2.28 0.42 2.95 Y=3328023.5810
1.36
4.70
4.40
4.40
4.40
4.40
4.40
4.40
16
1.36
2.6207
9.
1.1728
6.48
DIAPHRAGM WALL
7.20
A A
00
40
4.
8.
X
00
8.40
4.
4.
00
4.
W
00
1.92
83
4.
6.75
6.75
U
03
40
1.91
6.48
1
9.16
8.
8.
40
03
090
03
03
9
4
Q
2
03
7.20
6
P
06
1
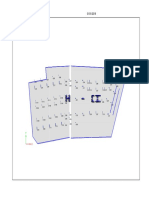
PILE LAYOUT
N
4.
06
1 : 200
83
S
3
03
03
3
O
7
06
2
03
8
PILE TYPES 2
NILE CITY (Deep Foundation Summary)
Type Shape Capacity (t) No. Length
(m)
Comp. Tens.
Pile D=1.20m 700 100 240 20
Pile D=1.0m 500 60 189 20
Barrette (1.0X2.80m) 1600 24 27
Barrette (1.20X2.80m) 2000 30 27
Barrette (1.50X2.80m) 2600 36 27
T – Barrette (1.20m) 4000 16 27
٤٥
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Burj Khalifa, Dubai
- World’s tallest building (828m)
- Founded on a piled raft
- Tower foundation –196 No. 1.5m bored piles, 45-50m long
- Raft 3.7m thick
- Podium foundation -750 No. 0.9m bored piles, 30m long
- A total of over 900 piles
- Piles constructed using polymer
PILE TYPES 2
Burj Khalifa, Dubai
٤٦
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
PILE TYPES 2
Burj Khalifa, Dubai
PILE TYPES 2
Trench cutters capable of excavating
barrettes down to 120m
below ground level. The
Reverse Circulation Drilling
method can be used to build
piles over 3m in diameter to
depths of more than 100m.
International Commerce Centre,
Hong Kong
٤٧
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
THANK YOU 2
Pile Foundations
by
Prof. Adel Ahmed Dif
Structural Eng. Dept.
Faculty of Engineering, El-Mansoura University
٤٨
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
You might also like
- Chapter 4 (Compatibility Mode)Document50 pagesChapter 4 (Compatibility Mode)Elhussain HassanNo ratings yet
- Offshore Lifting CalculationsDocument12 pagesOffshore Lifting Calculationspandi muthuppandiNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering-I Design of Shall PDFDocument44 pagesFoundation Engineering-I Design of Shall PDFAhmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Piles and Caissons PDFDocument30 pagesPiles and Caissons PDFMahmood MuftiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Piling: Icon LegendDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Piling: Icon LegendVijayNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Foundations: November 2016Document42 pagesSeismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Foundations: November 2016Rraffrizal ChandsNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations - D02Document3 pagesPile Foundations - D02Ashis MingalaNo ratings yet
- What Is Pile Foundation? Its Types, Uses, DesignDocument12 pagesWhat Is Pile Foundation? Its Types, Uses, DesigngattaiahNo ratings yet
- Group Members: 1. Sachittra Ranasinghe 2. Mohamed Siyath 3. Sahl Buhary 4. Mohamed Juhry 5. Mohamed HiyasDocument38 pagesGroup Members: 1. Sachittra Ranasinghe 2. Mohamed Siyath 3. Sahl Buhary 4. Mohamed Juhry 5. Mohamed Hiyasmominul hoqueNo ratings yet
- Study of Design and Construction Methods of Bored PilesDocument38 pagesStudy of Design and Construction Methods of Bored PilesAlphaNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering: Introduction/ Definition Lesson 1Document16 pagesFoundation Engineering: Introduction/ Definition Lesson 1Julz PDNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Pra Tice: Pile FoundationDocument81 pagesCivil Engineering Pra Tice: Pile Foundationyasir_mushtaq786No ratings yet
- IS2911 (Part1sec2) 2005draft PDFDocument35 pagesIS2911 (Part1sec2) 2005draft PDFkanagarajodishaNo ratings yet
- E Brochure Technique 210 BoredPiles InteractiveDocument5 pagesE Brochure Technique 210 BoredPiles Interactiveamirulardhian1996No ratings yet
- Piletype LamDocument5 pagesPiletype LamfieeeeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2aDocument10 pagesLecture 2a20pwciv5477No ratings yet
- Stability Analysis of 18 M Deep Excavation Using Micro PilesDocument4 pagesStability Analysis of 18 M Deep Excavation Using Micro PilesMiljan TrivicNo ratings yet
- Reserch Paper Final FormatDocument14 pagesReserch Paper Final FormatLaxmi KaleNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Cast-In-situ Pile Foundation.Document5 pagesFactors Affecting Cast-In-situ Pile Foundation.Gaurav Dhang100% (1)
- Pile Foundations - D03Document3 pagesPile Foundations - D03Ashis MingalaNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design ApproachDocument3 pagesFoundation Design ApproachYuvrajJainNo ratings yet
- Prefabricated Structures - Exam, Viva, Interview Questions With Solution For Civil EngineeringDocument15 pagesPrefabricated Structures - Exam, Viva, Interview Questions With Solution For Civil Engineeringनोलराज पौडेलNo ratings yet
- Triangle), and Practical Examples Are Provided in Section 9.4 ofDocument2 pagesTriangle), and Practical Examples Are Provided in Section 9.4 oflenanaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Other TypesDocument4 pages6 - Other TypespeterNo ratings yet
- Form Two Foundation NotesDocument6 pagesForm Two Foundation NotesTEMNo ratings yet
- Report BQDocument27 pagesReport BQAiman HakimNo ratings yet
- Sample Method Statement For Foundation WorksDocument28 pagesSample Method Statement For Foundation Workskatherine100% (5)
- Introduction To Design of Foundation LabDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Design of Foundation LabAmith Unnimadhavan UNo ratings yet
- Building Technology Assignment: Question and AnswerDocument6 pagesBuilding Technology Assignment: Question and AnswerBorel JasonNo ratings yet
- Pad FoundationDocument4 pagesPad Foundationnuraina aqilahNo ratings yet
- 4 Commentary On Standard Practice For Design and Conbstruction of Concrete Silos and Stacking Tubes For Storing Granular Materials ACI 313-97Document20 pages4 Commentary On Standard Practice For Design and Conbstruction of Concrete Silos and Stacking Tubes For Storing Granular Materials ACI 313-97Nikki Marlo CruzNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design IsOCD 19902Document38 pagesFoundation Design IsOCD 19902Abdulkadir DinçerNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument21 pagesMini Projectlawrence100% (1)
- Prefabricated BuildingsDocument8 pagesPrefabricated BuildingsJudelle GumallaoiNo ratings yet
- IS 2911 Part 1 Sec 2 Single PageDocument1 pageIS 2911 Part 1 Sec 2 Single Pagesmit_ghoseNo ratings yet
- Advanced Foundation Design-Notes - CBRDocument30 pagesAdvanced Foundation Design-Notes - CBRChannabasavaraj WollurNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2011 Dda2132 CHP 3 Substructure Foundation A PDFDocument25 pagesLecture Notes 2011 Dda2132 CHP 3 Substructure Foundation A PDFvinothiniNo ratings yet
- Construction Engineering Full ReportDocument11 pagesConstruction Engineering Full ReportNoor Liyana MismanNo ratings yet
- Is.2911.1.2.2010 Part2Document6 pagesIs.2911.1.2.2010 Part2Dixit JariwalaNo ratings yet
- Space XDocument17 pagesSpace Xertc13m220101No ratings yet
- For Construction Technology and Management: Instructor: Amsalu ADocument200 pagesFor Construction Technology and Management: Instructor: Amsalu AtazebNo ratings yet
- FDN Engg Chapter 7Document39 pagesFDN Engg Chapter 7Jelminda AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 FoundationDocument7 pagesChapter 9 FoundationPrescila QuietaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document27 pagesLecture 1Umar JavedNo ratings yet
- Course Material WEEK 6Document24 pagesCourse Material WEEK 6Nicole FrancisNo ratings yet
- A Study of Pile Foundation To Enhance Soil Bearing Capacity For The StructureDocument12 pagesA Study of Pile Foundation To Enhance Soil Bearing Capacity For The StructurearjunNo ratings yet
- Design Procedures For A Building Foundation (Step by Step)Document2 pagesDesign Procedures For A Building Foundation (Step by Step)Parikshit JoshiNo ratings yet
- Arbt5 ReviewerDocument3 pagesArbt5 ReviewerBrenna de RamosNo ratings yet
- Types of Piles According To Method of InstallationDocument13 pagesTypes of Piles According To Method of InstallationShara PalosNo ratings yet
- Basement ABCM 7th SemDocument42 pagesBasement ABCM 7th SemrenukaNo ratings yet
- Seminar 26Document20 pagesSeminar 26Rupesh KhandekarNo ratings yet
- 150 IndDocument13 pages150 Ind2022486166No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Foundation EngineeringDocument6 pages1 Introduction To Foundation EngineeringJhan SeenNo ratings yet
- Types of Foundation and Site InvestigationDocument60 pagesTypes of Foundation and Site InvestigationDr. V. VigneshNo ratings yet
- Building DesignDocument10 pagesBuilding DesignJozel IluminNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design - Day 1-Day 2Document86 pagesFoundation Design - Day 1-Day 2ochukoikogho0% (1)
- IS 2911 Part 1 Sec2 2010Document26 pagesIS 2911 Part 1 Sec2 2010Maheswara VarmaNo ratings yet
- Curs 9-10-11 12 (Compatibility Mode)Document75 pagesCurs 9-10-11 12 (Compatibility Mode)Ammar QafishehNo ratings yet
- CH - 2Document8 pagesCH - 2habtamu abateNo ratings yet
- Soil Investigation and Foundation DesignFrom EverandSoil Investigation and Foundation DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- T.THABET DeepFoundations017Document45 pagesT.THABET DeepFoundations017Elhussain HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3ADocument69 pagesChapter 3AElhussain HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6A PPT (Compatibility Mode)Document47 pagesChapter 6A PPT (Compatibility Mode)Elhussain HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 SoilNailWalls 05042015Document25 pagesChapter5 SoilNailWalls 05042015Elhussain HassanNo ratings yet
- 8 BeeDocument162 pages8 BeeElhussain HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.ppt (Compatibility Mode)Document44 pagesChapter 1.ppt (Compatibility Mode)Elhussain HassanNo ratings yet
- Jeddah Foundation Co. JF Technical Office Check On Pile Design 1Document1 pageJeddah Foundation Co. JF Technical Office Check On Pile Design 1Elhussain HassanNo ratings yet
- Project Columns PlanDocument1 pageProject Columns PlanElhussain HassanNo ratings yet
- Name: Stage: 1: Jeddah Foundation Co. Design Sheet PilesDocument1 pageName: Stage: 1: Jeddah Foundation Co. Design Sheet PilesElhussain HassanNo ratings yet
- Jubail 3A - IWP: Marine Works Jubail 3A - IWP: Marine Works: Document Submittal Document SubmittalDocument1 pageJubail 3A - IWP: Marine Works Jubail 3A - IWP: Marine Works: Document Submittal Document SubmittalElhussain HassanNo ratings yet
- Method Statement Bored PileDocument9 pagesMethod Statement Bored PileShuvro ChakravortyNo ratings yet
- Geo5 Output: Onshore Trench Shoring Works - Project: Jubail 3A - IWP: Marine WorksDocument1 pageGeo5 Output: Onshore Trench Shoring Works - Project: Jubail 3A - IWP: Marine WorksElhussain HassanNo ratings yet
- Method Statementfor PileDocument16 pagesMethod Statementfor PileAkhilesh Dwivedi100% (1)
- Project Business Risk RegisterDocument9 pagesProject Business Risk RegisterElhussain Hassan100% (2)
- Chemical EngineeringDocument3 pagesChemical EngineeringWendell Kim LlanetaNo ratings yet
- 2001 ME Thesis PapersDocument53 pages2001 ME Thesis Papersazd1973No ratings yet
- Physical & Chemical PropertiesDocument10 pagesPhysical & Chemical PropertiesJohnree A. Evangelista100% (1)
- Flexiroc T20 R: Atlas Copco Surface Drill RigsDocument4 pagesFlexiroc T20 R: Atlas Copco Surface Drill RigsalmirNo ratings yet
- MGD 2621 P Medical Greyscale Display: Installation & User ManualDocument27 pagesMGD 2621 P Medical Greyscale Display: Installation & User ManualJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Receiver Feedline Dipole Antenna: 1. Monopole Antenna Concept Monopole AntennaDocument17 pagesReceiver Feedline Dipole Antenna: 1. Monopole Antenna Concept Monopole Antennaنورول نضيره رشديNo ratings yet
- Regulatory Documentation PDFDocument21 pagesRegulatory Documentation PDFJohn Mark BordeosNo ratings yet
- Website Design Contest-6!9!2023Document1 pageWebsite Design Contest-6!9!2023maha sowmeNo ratings yet
- 7 1988Document62 pages7 1988Broomie Ajem100% (1)
- 1662 SMC Ds tcm228-701431635Document12 pages1662 SMC Ds tcm228-701431635cersanedNo ratings yet
- SK1SI50 - /4 Bre5 - IEC71: Date Name Drawn SystemDocument1 pageSK1SI50 - /4 Bre5 - IEC71: Date Name Drawn SystemHugo AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Lifting Lug Calculation - Concrete BucketDocument3 pagesLifting Lug Calculation - Concrete Bucketali akbarNo ratings yet
- 2019 - Chapter 31F Marine Oil Terminals 7Document1 page2019 - Chapter 31F Marine Oil Terminals 7sidhappy86No ratings yet
- BSS Student Portal User ManualDocument13 pagesBSS Student Portal User ManualMaheshNo ratings yet
- CADA QP-Ktunotes - in PDFDocument3 pagesCADA QP-Ktunotes - in PDFsachinNo ratings yet
- DNV Rules For Woodenships 1970Document146 pagesDNV Rules For Woodenships 1970Manuel Cares FuentesNo ratings yet
- 5 Heating SystemsDocument29 pages5 Heating Systemsventus13No ratings yet
- Installation Guide: Connecting Workstations Problem SolvingDocument2 pagesInstallation Guide: Connecting Workstations Problem Solvingjuan_mxNo ratings yet
- Abb Contactor A45!40!00 24 Vac 60 HZDocument4 pagesAbb Contactor A45!40!00 24 Vac 60 HZRodriguez JohannNo ratings yet
- Alignment Report (Kolar-Chikkaballapura)Document38 pagesAlignment Report (Kolar-Chikkaballapura)Kiran R Gowda100% (2)
- Scope CC 2559Document183 pagesScope CC 2559HOD Scitpl [Sands]No ratings yet
- CLSM SpecDocument24 pagesCLSM SpecgullipalliNo ratings yet
- TigerPMS CM63Document19 pagesTigerPMS CM63Mohamed BahaaNo ratings yet
- Jinma 284 ManualDocument35 pagesJinma 284 ManualJuan Garcia100% (1)
- Testo 622 Data SheetDocument2 pagesTesto 622 Data SheetMochammad Zaki NasrullohNo ratings yet
- Doosan DBC130 Mechanical Repair ManualDocument157 pagesDoosan DBC130 Mechanical Repair ManualDarryl Hardt80% (5)
- Atlas Copco Tech Tip - Resetting Service TimersDocument9 pagesAtlas Copco Tech Tip - Resetting Service TimersEnio0% (1)
- Comparing The Mechanical Properties of Cyanate Ester Modified Epoxy /glass LaminatesDocument7 pagesComparing The Mechanical Properties of Cyanate Ester Modified Epoxy /glass LaminatesAndrew NallayanNo ratings yet
- Storage Tanks Piping and LayoutDocument18 pagesStorage Tanks Piping and LayoutAmir RazmiNo ratings yet
- CrO3 Alternatives in Decorative and Functional PlatingDocument22 pagesCrO3 Alternatives in Decorative and Functional PlatingLukeNo ratings yet